Introduction
The Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) has been under increased criticism due to its inefficient services. The major problem at DMV is the long wait times, which average 75 minutes that customers must endure before they are fully serviced. The problem has been noted, and implementing changes at DMV can address the inefficiencies. To improve customer experiences and streamline operations, DMV can introduce several strategies. However, after considering and studying the strategies, the DMV has settled for providing one-stop kiosks at the DMV where people can register online but get assistance from staff when needed to reduce wait times, eliminate the need for multiple visits, and improve overall efficiency. This implementation plan outlines the steps we will take to ensure the success of this strategy.
Resources
Implementing a one-stop processing system for all DMV registrations through kiosks would require several financial, human, and other resources. Financial resources would be needed to purchase and install the necessary kiosks at all DMV locations. The kiosks must have the hardware and software to support online registration and payments. Additionally, funding would be required to train DMV staff to assist customers using the kiosks and hire additional staff if necessary. The DMV will have ten kiosks to cater for ten customers at a go. Human resources would also be required to maintain and update the kiosks, troubleshoot technical issues, and assist customers with questions or problems (Demilliere, 2014). Furthermore, other resources such as office space, utilities, and internet connectivity would also be needed to support the kiosks and staff.
The table below shows the resources required to implement the strategy of setting up computerized kiosks. The resources have been denoted in monetary value for easy visualization. However, the data in the table could be more accurate, but it estimates how much resources it would cost the DMV to set up and run the kiosks.
| Resource | Cost |
| Kiosk computer hardware and software (Jess, 2021) | $150,000 |
| Internet connectivity and maintenance (Anders, 2022) | $50,000 initial + $25,000 annually |
| Staff training and hiring (Payscale, 2023) | $200,000 |
| Marketing and Promotion | $50,000 |
| Maintenance and upgrades (Jess, 2021) | $75,000 annually |
| Total | $525,000 initial + $100,000 annually |
Table 1: Resources Required for DMV online kiosks
Stakeholder Support
The process of installing the DMV kiosks will take time and will need various stakeholder approvals. Different stakeholders have different impacts or are differently impacted by the DMV. The impact that the DMV will have on each stakeholder or the impact that the stakeholder will have on the DMV determines their criticality on the strategy implementation. The stakeholders are identified below based on their criticality in the DMV.
DMV Management and Staff
They are responsible for operating and maintaining the kiosks. Their effectiveness directly translates to DMV effectiveness. The staff working at the DMV will thus play a crucial role in successfully implementing the strategy. They must be trained to use the kiosks and assist customers needing help. It is essential to obtain their support to ensure that they are motivated and committed to the initiative’s success.
However, people only sometimes accept change. The staff at DMV are probably now used to the old working methods and may prefer to continue working in that manner since it already works (Rehman et al., 2021). To gain their support, however, they would be actively involved in the planning and decision-making and ensure they are adequately trained and supported throughout the implementation. That way, they would feel part of the change and even give suggestions as the implementation continues.
Customers
The customers’ complaints are the driving force behind the implementation of the strategy by the DMV. They are a key stakeholder in the DMV since their satisfaction and convenience are at the heart of the strategy. Thus, the customers need to support the implementation for it to be a success. To rally customer support, the implementation team would need to communicate the benefits of the new proposed system to the customers earlier. The implementation team should show that the strategy would reduce wait time, which the customers have always complained about.
Government Officials and Legislators
As the DMV is a government agency, obtaining support from relevant government officials is essential to ensure that necessary resources and funding are allocated to implement the one-stop processing strategy. The officials responsible for overseeing the DMV and its operations, such as the Director of the DMV or the Secretary of Transportation, would be critical stakeholders to gain support. Just like with the customers, the officials need to be informed by the implementation team of the system’s benefits and how it would rectify the issue at DMV. Once the officials understand it is a worthwhile strategy, they should support it and provide resources for the implementation.
IT Support Team
The IT team will be the major implementation team. They will be responsible for installing and maintaining the kiosks, ensuring they function correctly, and troubleshooting any technical issues. Their support is essential to ensure the kiosks operate smoothly and avoid significant technical problems. They should thus be assured of resource availability and commitment to the project.
Generally, to gain support from these stakeholders, it is essential to clearly communicate the strategy’s benefits (Joubert, 2021). For example, government officials may be more likely to support the initiative if it is framed as a cost-saving measure that will reduce wait times and improve customer satisfaction. It is also useful to conduct a pilot test of the kiosks to demonstrate their effectiveness to the DMV staff, customers, and IT support team. Finally, it is essential to listen to feedback and address stakeholders’ concerns to ensure their continued support for the initiative.
Implementation Plan
| Milestone | Date | Deliverable | Responsible |
| Conduct needs assessment | 4/1/2023 | Needs assessment report | Project team |
| Develop implementation plan | 4/15/2023 | Implementation plan | Project team |
| Secure funding | 5/1/2023 | Funding secured | Project manager |
| Procure equipment and software | 5/15/2023 | Equipment and software procured | Procurement team |
| Install and test equipment and software | 6/1/2023 | Equipment and software installed and tested | IT team |
| Develop training materials | 6/15/2023 | Training materials developed | Training team |
| Train staff and volunteers | 7/1/2023 | Staff and volunteers trained | Training team |
| Launch kiosks | 7/15/2023 | Kiosks operational | IT team |
| Monitor and evaluate the implementation | Ongoing | Monitoring and evaluation report | Project team |
Table 2: Project Implementation Plan
The critical tasks that must be completed include conducting a needs assessment to determine the specific needs of the DMV customers, developing an implementation plan to ensure that the project is completed within budget and on time, securing funding to cover the costs of equipment and software, procuring the necessary equipment and software, installing and testing the equipment and software, developing training materials, training staff and volunteers, launching the kiosks, and monitoring and evaluating the implementation to ensure that it is meeting the needs of the customers. Each task is critical to the project’s success and must be completed thoroughly and carefully.
Project Plan
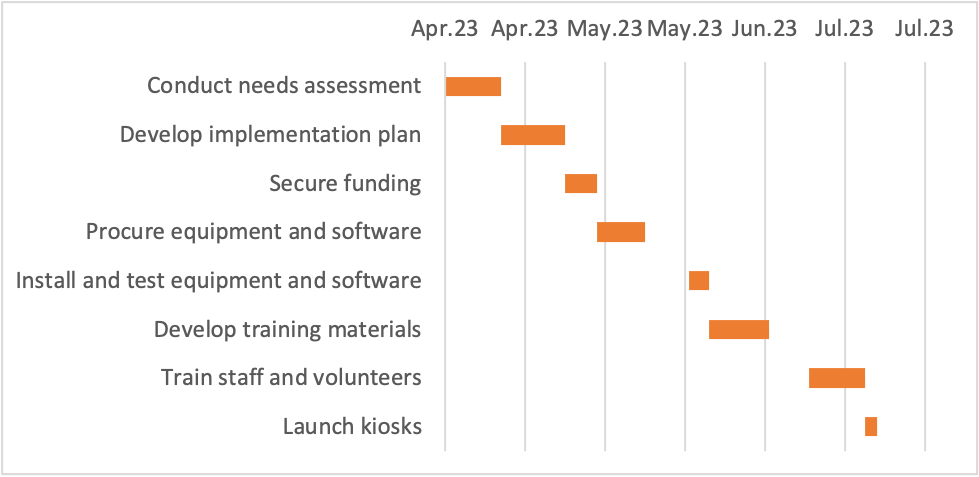
The Gantt chart above illustrates the steps that will be followed to complete the project. It is assumed that each project task will begin after the previous task has been completed for simplicity and traceability of the tasks (Neumeyer, 2022). From the Gantt chart, the project will begin on April 2023 and end in July of the same year.
Overcoming Risks/ Barriers/ Challenges
Several key issues or challenges could derail the successful implementation of the strategy to enable one-stop processing for all registrations at the DMV. These include resistance to change, lack of buy-in from key stakeholders, inadequate resources, and technological barriers. Firstly, there may be resistance to change from staff who are used to the traditional way of processing registrations (Rehman et al., 2021). It is important to communicate the new system’s benefits to them and provide training and support to ensure a smooth transition.
Secondly, gaining buy-in from key stakeholders such as government officials and regulatory bodies is crucial to the strategy’s success. It may be necessary to provide data and evidence to demonstrate the new system’s benefits and engage in ongoing communication to address concerns and maintain support.
Thirdly, implementing a one-stop processing system will require adequate resources such as staff, technology, and physical space. Conducting a thorough resource analysis and allocating resources appropriately is important to ensure the system can operate effectively. Finally, technological barriers such as insufficient bandwidth or outdated systems could hinder the implementation of the strategy. It is important to thoroughly assess the current technology infrastructure and invest in necessary upgrades and maintenance.
To mitigate these risks and ensure the change is successful and sustained, engaging in ongoing communication with all stakeholders is important, as monitoring progress and making adjustments as needed (Joubert, 2021). Providing training and support to staff and investing in adequate resources will also help ensure a successful implementation. Regular monitoring and evaluation will also be necessary to identify and address any issues arising and sustain the new system over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) has identified the need to implement strategies that improve customer experiences and streamline operations. After careful consideration, the DMV has chosen to implement a one-stop processing system for all DMV registrations through kiosks. This strategy aims to reduce wait times, eliminate the need for multiple visits, and improve overall efficiency. The implementation of this strategy would require several resources such as financial, human, and other resources. The stakeholders critical to the success of this strategy include DMV management and staff, customers, government officials and legislators, and the IT support team. To gain support from these stakeholders, it is essential to communicate the strategy’s benefits. Overall, implementing the one-stop processing system through kiosks would be a worthwhile strategy for the DMV, and it has the potential to improve customer experiences and streamline operations significantly.
References
Anders, D. (2022, October 26). What is the average internet bill? Allconnect. Retrieved March 23, 2023, from https://www.allconnect.com/blog/cost-of-high-speed-internet#:~:text=The%20average%20internet%20bill%20in,or%20more%20for%20select%20plans.
Demilliere, A. (2014). The Role of Human Resources in Project Management. https://ideas.repec.org/a/rdc/journl/v5y2014i1p36-40.html#:~:text=Human%20Resources%20in%20Project%20Management%20focus%20on%20Project%20Team%20recruitment,to%20team%20building%20and%20motivation.
DMV Clerk Hourly Pay. (2023). PayScale. Retrieved March 22, 2023, from https://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=DMV_Clerk/Hourly_Rate
Dresang, D. (2012). Case study. In The public administration workbook (pp. 97–99) (7th ed.) Boston, MA: Pearson.
Jess, J. (2021). How Much Do Computers Cost? We Love Prof – Superprof Blog. Retrieved March 22, 2023, from https://www.superprof.com/blog/cost-of-computers/
Joubert, S. (2021, August 6). The Critical Role of Communication in Project Management. Northeastern University Graduate Programs. https://www.northeastern.edu/graduate/blog/communication-in-project-management/
Neumeyer, A. (2022). Finish-to-finish dependency explained by example. Tactical Project Manager. https://www.tacticalprojectmanager.com/finish-to-finish-dependency/
Rehman, N. A., Mahmood, A., Ibtasam, M., Murtaza, S., Iqbal, N., & Molnár, E. (2021). The Psychology of Resistance to Change: The Antidotal Effect of Organizational Justice, Support and Leader-Member Exchange. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.678952
 write
write