Background
Tesla is an American automotive company focusing on the manufacturing of electric vehicles. Tesla has its beginnings in 2003 and has a focus on powering the global transition to building sustainable energy (Tesla, 2024). The company also has a focus on energy innovation to power its electric vehicles. Tesla is also in the business of developing batteries for home use and commercial applications. According to Liu (2022), environmental concerns are leading many car companies towards electric power, but rapid development means that many start-ups are still looking for a stable footing. As such, the success of Tesla brings fresh breath to the table. Many gaps in the electric field include hardware technology development, especially long-lasting batteries. These challenges bring about quality issues. In this report, we shall analyse Tesla’s successes and failures regarding the delivery of quality products and services. A key area of focus is the analysis of the use of Just in Time (JIT) and Total Quality Management (TQM) at Tesla. The analysis shows that Tesla is constantly ahead of its competitors through constant innovation of existing quality processes and strategic partnerships. There are some quality issues in the paintwork, body panels, and battery packs which require urgent attention. However, the biggest issue is the delay in delivery times, which costs the company millions annually.
In conclusion, the use of various quality control processes can assist an organisation to attain higher standards in its manufacturing processes. The use of JIT and TQM at Tesla can allow the company to exceed its customer expectations and offers advances in management. In the future, Tesla should consider integrating other mass market quality control strategies and strategies to deal with fair competition when government incentives for renewable energy are eliminated.
Introduction
Tesla initially began by offering high-end electric vehicles to high-income individuals. The company’s main focus was on high-performance and energy-efficient vehicles with an appealing, sleek design. Vehicle manufacturing is a highly capital-intensive industry. As such, Tesla requires high physical capital and equipment to operate and grow (Larcker & Tayan, 2011, p.1). Through innovative approaches, Tesla has utilised the available resources to meet customer expectations. The company chose to use a direct sales model, which was against the norm in the traditional car sales business (Gupta & Maurya, 2017, p.3). Moreover, focusing on the high-end market means that the company could focus on manufacturing a compelling car with limited resources. This is an advantageous strategy as the company needed to gain adequate experience in mass market production as well as economies of scale.
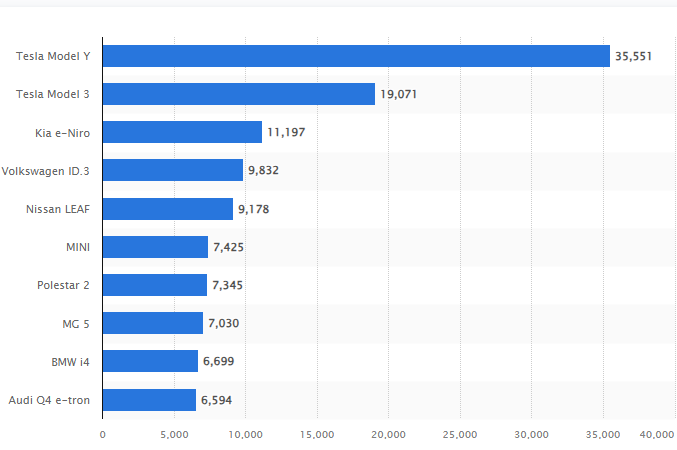
Figure 1: UK electric vehicle car sales 2022 (Carlier, 2023).
From the strategy, Tesla focuses on technology-driven vehicle experiences and the environmental protection. These elements have been an important selling point for Tesla products (Liu, 2022, p. 829). Other major revenue streams for the company include subscriptions to additional car features and a supercharging network. These offerings have been a driving force in the company’s growth and market dominance. Tesla has a high dominance in the UK, with the company having the best two-selling electric vehicles as of 2022, as shown in Figure 1.
Tesla has a hierarchical management structure. This structure is essential for defining clear boundaries, especially in manufacturing. The management structure includes the upper, middle, and lower-level staff (Sudhakaran & Uygun, 2020, p.5). This management structure is integral to enabling the company to have adequate managerial control amid expansion.
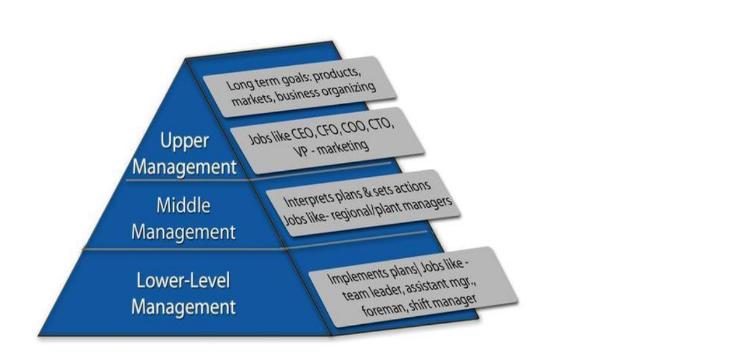
Figure 2: Tesla organisational chart (Sudhakaran & Uygun, 2020, p.5)
The management and business application model at Tesla has various pros and cons. Through a SWOT analysis in Figure 3, we can find out the main internal and external factors affecting the organisation. One of the main factors that stands out is the government support for the company. For example, in 2002, the US Department of Energy funded research on batteries to improve efficiency and quality (Liu, 2022, p. 830). President Obama’s administration also invested over $2 billion in electric vehicle development and home charging stations (Liu, 2022, p. 830). Through these opportunities, Tesla has taken advantage of various opportunities to gain a market-leading status.
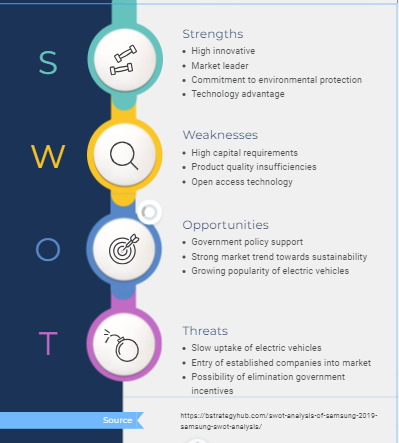
Figure 3: Tesla SWOT analysis
Tesla has developed innovative manufacturing processes to maintain a competitive advantage. One of the recent updates to its production line is the use of an “unboxing method.” This is an approach where the organisation produces large sub-parts of the cars and later joins the parts to create the whole (Shirouzu, 2023). Through the process, the company is able to cut costs by moulding large parts in a single piece rather than having multiple small parts. The know-how is an essential step in the company serving the mass market. We shall further analyse the manufacturing processes to determine their quality.
Aim and 3 or 4 objectives of the report, not the company
Problem Identification
Tesla is a relatively new player in the automotive industry compared to traditional car companies such as Toyota and Ford. In its position, Tesla has been able to disrupt the car industry. Tesla is a disruptor through its ability to bring electric vehicles to the mass market (Korsten, 2022). In this way, the company is spearheading the electrification of mobility in the world. In its ability to bring electric vehicles to the mass market, Tesla is sustaining innovation in the mobility industry in several ways. In the process, the company also defines quality control processes.
However, Tesla has a difficult production process, leading to delays in the delivery of products that have cost the organisation heavily. Tesla has several quality issues that could be improved in its growth process. Some of the quality issues include paint quality issues and varying gaps in the panels of the cars (Page, 2023). These quality issues have been attributed to ramping production, leading to less time for thorough quality checks. There are also issues with the battery packs being unable to deliver the desired customer range (Li, 2023). However, the battery pack issue is an industry-wide challenge.
Hard (Quantitative) Objective
- Determining some of the key performance indicators (KPIs) that Tesla can use to reduce customer delivery delays and improve customer satisfaction.
- Determining the monetary effect of the quality issues on the company, especially the loss of customer satisfaction and production time.
Soft (Qualitative) Objective
- Determine the advantages of using TQM and JIT to achieve customer and employee satisfaction.
Analyse the problems via a fishbone diagram
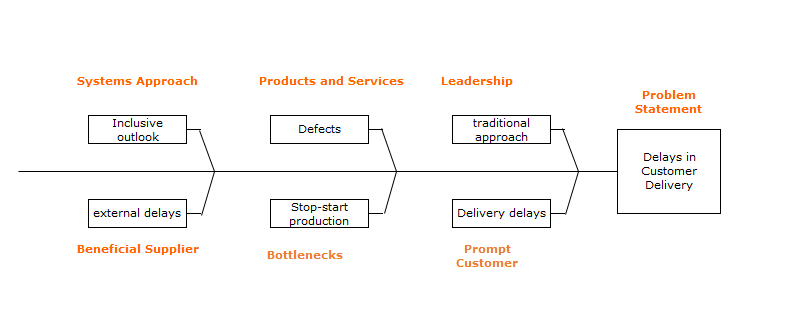
Figure 4: Fishbone Diagram of Tesla Production Issues
Total Quality Management (TQM)
The TQM approach has eight principles. They include leadership, customer-focused organisation, people involvement, process approach, systems approach, continual improvement, factual approach to decision-making, and mutually beneficial supplier relationship (Mohammed et al., 2013). We shall analyse each of the principles and apply them to Tesla to determine its effect on the overall quality of the products and services.
Tesla TQM Weaknesses
Leadership
The leadership of an organisation gives unity of purpose. The leadership highly influences the internal environment through a clear definition of the future. The internal environment also means that employees clearly understand the organisational needs and objectives (Mohammed et al., 2013). Khan (2021, p.1) finds that Tesla’s leadership is highly traditional and has a highly structured observation strategy. Arikkok (2017, p.5) notes that the traditional approaches to leadership put a lot of pressure on employees and, at times, can cause blame on the employees. In this way, they can affect the quality of output.
Products and Services and Systems Approach
For quality products and services, the organisation must consistently improve its processes to have a solid output. There is a need for consistent improvement in quality processes. Process improvement is a strength at Tesla, and it aligns with the traditional improvement principle. According to Schulz (2023), Tesla is a role model in increasing productivity. In this respect, Tesla has improved its production by 40% and created an innovative process line to meet its targets (Schulz, 2023). Through the new assembly line approach, Tesla can reduce the manufacturing time of its models by 25% (Fox, 2023). Tesla is highly innovative and this value assists the company to constantly evolve. This is in line with the systems approach of TQM, where the organisation recognises the need to systematically improve its processes. Lack of a systems approach can lead to weak points in the production line, which reflects in the overall quality of the product.
Mutually Beneficial Supplier
Finally, the mutually beneficial supplier relationship is an essential aspect of the organisation’s strategic win-win relationships with its suppliers. In the founding years, Tesla used this strategy to partner with Lotus to get new cars that Tesla would convert to electric energy (Xia, 2022, p.36). This partnership and collaboration model has been vital to Tesla’s growth. However, moving forward the company is focusing on in-house production to avert disadvantages of partnerships and collaborations. For example, the 2020 chip shortages had a severe effect on legacy car makers (Curiel & Perkins, 2022, p.519). However, Tesla was minimally affected as it had already invested in the in-house production of chips (Curiel & Perkins, 2022, p.519). Despite this adjustment, Tesla still sources most of its raw materials externally. This means that the company has to contend with supplier delays, which affects its production cycle.
Tesla TQM Strengths
The customer-focused organisation has its prime principle on the persons that are buying the product. The customers justify the end product through satisfaction (Misztal, 2010, p.126). In this way, the company has to ensure the customers see the value of their money in the product they purchase. According to Long et al. (2019, p.185), Tesla has a positive customer perception as more innovative, stylish, and environmentally beneficial. This is despite the quality issues that some customers experience.
People from various levels offer their efforts to the profitability of an organisation. As such, employees should be trained, committed and responsive to complete all the tasks well. According to Tesla (2024b), the organisation has employees’ freedom to discuss internal and external issues to promote integrity. Moreover, the organisation has a focus on teamwork skills and readiness to learn. In this way, the organisation has a solid employee base.
A factual approach to decision-making assists an organisation in making quality decisions. Based on the information collected on the data, an organisation is in a better position to progress. Tesla, through its cars, has many sensors that capture data on their customers and surroundings (Harris, 2022, p.42). This large data allows the company to access quality information to make decisions on its products and understand its customers.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
Just-in-time (JIT) production approach is a target oriented approach. According to Al-Zweeni & Al-Musawi (2019), JIT aims to reduce costs through the production of quantities and qualities required at a particular time. In this way, JIT has a focus on eliminating activities that do not add value, having zero inventory and defects, minimal stops and bottlenecks, and prompt delivery of products and services. This case study will focus on stops and bottlenecks and prompt product and service delivery.
Tesla has a reliance on the JIT production system. For example, in the third quarter of 2023, Tesla produced about 430,000 vehicles and delivered about 435,000 (Kolodny, 2023). This is an indication of the production in line with the customer orders. However, Tesla needs to improve its timely delivery. For example, in 2021, Tesla had a compounded issue of delayed delivery of cars that stretched into months (Kolodny, 2021). This is indicative of a struggle in the manufacturing process within the factory to meet the customer demand as is. The lack of prompt product delivery hurts profitability due to missed revenue.
Various stops and bottlenecks are affecting the production of Teslas. One of the key bottlenecks has been the battery production. Battery production has been cited as the real cause of many of the delays in vehicle delivery (Ferris, 2018). The stop-start process in the production line due to this battery issue also affects revenue and leads to increased production costs, which are also external factors relating to logistics. For example, violence over the Red Sea halted production of Tesla cars in Europe for about two weeks in 2024 (Sweeney, 2024). This violence means that raw materials cannot reach their destination in the desired time.
Key Performance Indicators
Key performance indicators (KPIs) identify the significant quantifiable objectives that identify the performance of an organisation. Through KPIs, stakeholders can make informed decisions (Ganesan & Paturi, 2009, p.1). There is a need for organisation for efficient and effective use of KPIs (Velimirovic et al., 2011, p.63). In the production of cars, Tesla has been keen on some essential KPIs. The two most important are the profit margin per vehicle and the return on investment. However, these KPIs have been hiding some other facts. For example, using the profit margin per vehicle, Tesla has one of the highest in its class, approximately 28.5%, in 2022 (Statista Research Department, 2023). However, Tesla had a backlog of about 72,000 orders (Wang, 2024, p.438). This backlog is a critical issue of concern. As such, the key focus areas should be the consideration of delivery time variance and on-time delivery.
Monetary Effect of the Quality Issues
One of the critical effects of Tesla’s production issues is the customer consideration of options. According to Brennan (2022), customers must consider the expense of purchasing a Tesla car in addition to the waiting period or delay in delivery. One of the critical issues is a 12-month delay in delivery, which means purchase prices are affected by inflation, leading to customers having to part with more for the same car. In this way, rivals that have near zero delivery times are quickly tempting Tesla potential buyers.
The production bottlenecks and delays in delivery have deep financial implications. For example, in 2017, Tesla had a $671 million loss attributed to delays in delivery of its Model 3 (Durbin, 2017). In 2019, Tesla recorded a £545 million loss in the first quarter due to production delays (Autocar, 2019) or bottlenecks in its production line, leading to stop-start manufacturing and eventual customer delivery delays. In 2023, Tesla profits sagged and share prices plunged by more than 3% after the announcement of difficulties in producing its much-awaited Cyber Truck (Waters, 2023). Consequently, Tesla had a 44% decline in its third quarter revenue of 2023, followed by a 37% drop in its share earnings (Waters, 2023).
Investigation
Delivery Time Variance and On-Time Delivery
The delivery issue at Tesla is a significant factor. On its website, the company does not have official targets or delivery expectations for customers. Tesla only states that availability depends on various factors (Tesla, 2024c). This statement needs to inspire confidence of vehicle delivery.
The delivery time variance is the difference betweentween the actual and promthe ised delivery times. On-time delivery is the performance indicator of the rate of on-time deliveries. However, these KPIs cannot be considered in isolation. They should be sustained through holistic consideration of the manufacturing planning, execution cycles, and other associated systems (Karim et al., 2010, p.2374). The modern business environment is making key shifts, especially in the manufacturing industry. Karim et al. (2010, p. 2378) identify global manufacturing as moving towards fewer inventories, fewer vendor locations, increasing product variety, and focusing on just-in-time manufacturing. In this aspect, many manufacturing organisations need help in making realistic delivery times.
Realising the importance of delivery times as a key performance indicator for Tesla, the company has to reconsider the integration of some common processes. This is an aspect that requires the consideration of the systems approach thinking under TQM. Tesla has fragmentations in its holistic view of self. This fragmentation creates stop-start circuits for production processes, leading to delays.
There is a need to recognise that Tesla’s success to deliver on time is dependent on its ability to coordinate a network of suppliers. These network relationships are an external factor. This is an issue resulting from lack of a beneficial mutual supplier. Developing collaborations and partnerships with the suppliers is an essential part of success. According to Osei and Asante-Darko (2022), developing supply chain collaboration is vital to ensure independent firms work towards a cohesive and singularly competitive network to improve performance. This aspect creates the realisation of the complexity of a supply chain network, especially on a global stage.
The leadership is an integral part of the organisation. The Tesla organisational chart indicates the hierarchical structure of leadership at the organisation. The top-to-bottom leadership levels have a traditional approach to management and leadership. This aspect creates an impediment to being able to address the complexity of the current business environment. While the organisation has an innovative and forward-thinking attitude, there is a need to consider other leadership approaches that can yield better results, especially when integrating supply chain factors.
Advantages of using TQM and JIT for Tesla
The use of TQM offers various advantages for Tesla to consider. The use of TQM includes the role of a quality control manager or personnel (Kumar & Sahil, 2015, p.749). The personnel addresses quality issues before reaching the consumer. As such, there is less rejection from the customer, leading to less waste. There is alignment of intrinsic worker motivation to achieving the company goals which increases the morale of the employees. Finally, there is an overall improvement in the company’s reputation.
The use of JIT is advantageous. JIT assists to reduce costs resulting from overproduction since production is based on orders. In this way, the use of JIT eliminates wastes in the production process (Kumar & Sahil, 2015, p.749). There is also a focus on delivery according to customer demands and needs, which assists in focusing on customer satisfaction.
Tesla has the opportunity to have gains from combining the use of TQM and JIT. Both TQM and JIT aim at reducing wastes and increasing product quality. The aim of the company in the industry is to be a market leader. As such, the company can gain from optimal utilisation of labour and other company resources to achieve the aim. Additionally, JIT will assist the organisation to have a better cost structure and eliminate unwanted processes in the production system. Maximum customer satisfaction through quality products and on-time service delivery is attainable.
Conclusions
Therefore, Tesla has made remarkable steps to lead the competition despite its relatively new status in the car manufacturing space. Tesla has been a disruptor through its electric vehicle for mass market. This technology has championed the manufacturer to attain high-profit margins and build a strong reputation globally. However, production processes need to be improved for the company to transition and dominate its market space. Many Tesla customers have a long delivery time that extends to almost one year. To sustain its market position, it is necessary to address the core issue of leadership, product and service quality, consider the systems approach, develop a mutually beneficial supplier network similar to its early engagement with Lotus, and eliminate production bottlenecks to improve delivery times. In an effort to ramp up production to deal with customer delays, there have been some quality issues with product which includes low paint quality and poor panel fitting. Through a study on the organisation, focusing on the profit margin per car is a worthwhile key performance indicator. However, Tesla is performing well on this indicator and should consider a focus on on-time delivery and delivery time variance as key performance indicators. The monetary effects of the delays and quality issues at Tesla are leading to loss of millions of dollars in revenue and profit.
Moreover, shareholders are losing on the share price. However, integrating TQM and JIT quality management approaches to manufacturing can inclusively and almost conclusively assist Tesla in turning around its delivery time challenges. In the process, the company can build a robust and reputable brand for a strong future.
Recommendations
The analysis shows that there are various recommendations for Tesla. To begin with, there is a need to consider the integration of business processes. This integration has a focus on improving on the on-time delivery performance at Tesla. The standard processes include the manufacturing planning, control, and execution processes under a make-to-order approach. In this way, a database can support various functional approaches to assist Tesla have an adequate forecast on the number of vehicles and the time frame for production. The integration of the process can include some critical triggers. These triggers, which can be seen as events, are the occurrences which trigger the process. A significant event can be receiving an order. The function can describe various transformations that should take place to lead to the final stage.
There is a need for pathways that indicate the various connections to assist the organisation with a whole systems approach and oversight. The manufacturing process is cross-functional. There are multiple functional areas to consider, and each function includes various tasks. The sequential and non-sequential areas should be considered. Each factor affecting the areas should be analysed and addressed to ensure all processes are supported and, in turn, support each other.
The supply chain requires a collaborative outlook. This collaboration should consider strategic partnerships and, where need be, in-house production. The chip shortage affecting many manufacturers affected Tesla less due to in-house production. This strategy can be considered for battery packs, an essential component that leads to production delays. Bhardwaj et al. (2020) note that companies should have multiple battery partnerships in key production zones. This strategy can assist the company in dealing with an expensive and crucial manufacturing component.
Another strategy for battery packs is to use “off-the-shelf” packs. These are battery packs that have no specifications and are widely compatible solutions. However, this strategy can affect the design and performance of the product. While it can assist in improving delivery times, this can negatively affect customer satisfaction levels.
There is a need to consider the integration of a horizontal management approach. This approach can assist the organisation in reducing its communication period. In turn, the organisation have improved the customer delivery time. One of the strategies is to consider the promotion of intrapreneurs and servant leadership. The intrapreneur is the skill of supporting internal entrepreneurship to assist in solving challenges as they arise. This aspect requires employee freedom and delegation of duties to promote employee spirit to solve challenges. A servant leadership approach can also assist in creating and incorporating the necessary structures to support the employees to take responsibility.
Finally, there is a need to have a purposeful integration of the TQM and JIT approaches to the manufacturing process. Combining the approaches offers a hybrid solution to deliver quality products and services. In this way, the organisation can work to eliminate mistakes in the production line and improve product and service quality. This aspect can assist the organisation to improve on its customer satisfaction. Moreover, the company can focus better on different processes that affect its production. These processes can be considered part of the whole from a systems approach perspective.
In future, there is a need to consider collaboration with other manufacturers to increase the ability to deliver on time. Through a joint venture, Tesla can tap into production strategies and market from established manufacturers. In turn, Tesla can assist in offering innovation strategies. Also, joint ventures can lead to the rebadging of ready vehicles to assist car companies in delivering on their market needs. Moreover, governments may eliminate many of the current subsidies on renewable energy which may eliminate the competitive advantages that Tesla holds. There is a need to consider early strategies to cement its position and avoid negative implications in the future.
References
Al-Zweeni, M., Al-Musawi, A. N. (2019). Just-in-Time Production. DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.18506.93121
Arikkok, M. (2017). Total Quality Management. DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.15304.72969
Autocar. (28 May, 2019). Tesla blames production delays for significant financial losses. https://www.autocar.co.uk/car-news/business/tesla-blames-production-delays-significant-financial-losses
Bhardwaj, S., Pandey, R., Sharma, S., Sejal, S., Iyer, G., Sharma, S., Ranjith, P. V., Kulkarni, S. (2020). Problems Faced by Automobile Industries: Case Study on Tesla. International Journal of Tourism & Hospitality in Asia Pacific, 3(2):78-88. DOI:10.32535/ijthap.v3i2.825
Brennan, H. (28 Apr, 2022). Rising prices and long delays — is it still worth spending big on a Tesla in 2022? Telegraph. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/money/consumer-affairs/inflation-tesla-electric-car-rising-prices-long-delays-expensive-2022/
Carlier, M. (2023). UK: best-selling battery-electric car model 2022. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1410504/uk-best-selling-battery-electric-car-model/
Curiel, J., Perkins, R. K. (2022). Using Systems Theory to Analyse Management Styles, Market, and Product Competition Between Tesla and Legacy Carmakers. International Journal of Innovative Business Strategies, 8(1). https://infonomics-society.org/wp-content/uploads/Using-Systems-Theory-to-Analyze-Management-Styles-Market-and-Product-Competition.pdf
Durbin, D. (2017). Tesla swings to US$671M loss on Model 3 delays. https://www.ctvnews.ca/mobile/autos/tesla-swings-to-us-671m-loss-on-model-3-delays-1.3659353?cache=yesclipId10406200text/html;charset=utf-80404/7.234744
Ferris, R. (18 Apr, 2018). Tesla battery production is the real bottleneck, not Model 3 production, analyst says. CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2018/04/18/tesla-battery-production-is-the-real-bottleneck-not-model-3-production.html
Fox, E. (2023). Tesla Assembly Time May Be Reduced By 25% With New Models. https://www.tesla-mag.com/en/tesla-assembly-time-may-be-reduced-by-25-with-new-models/
Ganesan, E., Paturi, R., (2009). “Key Performance Indicators Framework. AMCIS 2009 Proceedings. 736. http://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2009/736
Gupta, M., Maurya, N. (2017). Tesla’s Direct-to-Consumer Retail Model. https://www.iebrain.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Tesla-direct-Retail.pdf
Harris, M. (2022). Every Tesla is providing reams of sensitive data about its driver’s life. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=9915627
Khan, R. (2021). A critical analysis of Elon Musk’s leadership in Tesla Motors. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research. DOI:10.1007/s40497-021-00284-z
Karim, A., Samaranayake, P., Smith, A. J. R., Halgamuge, S. (2010). An on-time delivery improvement model for manufacturing organisations. International Journal of Production Research, 48(8):2373–2394. DOI:10.1080/00207540802642245
Kolodny, L. (2 Oct, 2023). Tesla reported 435,059 deliveries for the third quarter and production of 430,488 vehicles. CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2023/10/02/tesla-tsla-q3-2023-vehicle-delivery-and-production-numbers.html
Kolodny, L. (18 Aug, 2021). Tesla buyers are confounded by delivery delays stretching for months. CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2021/08/18/months-long-delivery-delays-confound-would-be-tesla-owners.html
Korsten, S. (2022). How Tesla can win: a disruptive strategy lens. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-tesla-can-win-disruptive-strategy-lens-seb-korsten/
Kumar, M., Sahil, S. (2015). Analysis of TQM and Implementation of JIT in Manufacturing Industry: A Review. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology, 4(4). https://www.ijert.org/research/analysis-of-tqm-and-implementation-of-jit-in-manufacturing-industry-a-review-IJERTV4IS040457.pdf
Larcker, D. F., Tayan, B. (2011). Tesla Motors: The Evolution of Governance from Inception to IPO. Rock Center for Corporate Governance at Stanford University Closer Look Series: Topics, Issues and Controversies in Corporate Governance No. CGRP-15. https://ssrn.com/abstract=1845715 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1845715
Li, M. (2023). Analyse the Underlying Problems of Tesla Electric Cars and Other Similar Electric Cars. Advances in Economics Management and Political Sciences, 31(1):200–205. DOI:10.54254/2754-1169/31/20231542
Liu, J. (2022). Research on the Tesla’s Business Model Analysis. Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research. DOI: 10.2991/978-94-6463-098-5_94
Long, Z., Axsen, J., Miller, I., Kormos, C. (2019). What does Tesla mean to car buyers? Exploring the role of automotive brand in perceptions of battery electric vehicles. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 129: 185-204. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0965856419300060
Mohammed, A. S. A., Tibek, S. R., Endot, I. (2013). The Principles of Total Quality Management System in World Islamic Call Society. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 102. DOI:10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.10.747
Misztal, A. (2010). Eight quality management principles – practical context. In book: Some problems and methods of ergonomics and quality management. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259479704_Eight_quality_management_principles_-_practical_context
Osei, V., Asante-Darko, D. (2022). Collaboration Within the Supply Chain. The Palgrave Handbook of Supply Chain Management. https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-3-030-89822-9_56-1#:~:text=A%20collaborative%20approach%20to%20supply,et%20al.%2C%202015).
Page, F. (2021). Elon Musk blames production ramp-up for Tesla quality issues. https://www.autocar.co.uk/car-news/new-cars/elon-musk-blames-production-ramp-tesla-quality-issues
Schulz, T. (2023). Tesla as a Role Model: How Companies Can Increase Their Productivity. https://www.silicon.eu/tesla-as-a-role-model-how-companies-can-increase-their-productivity-9301.html
Statista Research Department. (2023). Tesla’s gross margin from FY 2021 to FY 2022, by key segment. https://www.statista.com/statistics/783477/gross-margin-by-segment-of-tesla/
Sweeney, M. (12 Jan, 2024). Tesla pauses German production after Red Sea shipping attacks. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2024/jan/12/tesla-pauses-german-production-because-of-red-sea-shipping-attacks
Shirouzu, N. (2023). Tesla reinvents carmaking with quiet breakthrough. https://www.reuters.com/technology/gigacasting-20-tesla-reinvents-carmaking-with-quiet-breakthrough-2023-09-14/
Sudhakaran, P., Uygun, H. (2020). Tesla Inc Managment Report. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353104682_Tesla_Inc_Managment_Report
Tesla. (2024). Elon Musk. https://www.tesla.com/elon-musk
Tesla. (2024b). People and Culture. https://www.tesla.com/impact/people
Tesla. (2024c). Support – Delivery Day. https://www.tesla.com/support/delivery-day
Velimirovic, D., Velimirovic, M., Rade, S. (2011). Role and importance of key performance indicators measurement. Serbian Journal of Management, 6(1). DOI:10.5937/sjm1101063V
Wang, S. (2024). Study of the Transition in Tesla’s Pricing Strategy and the Challenges to Profit Margin: An Exploration of Dynamic Equilibrium. Highlights in Business Economics and Management, 24:436-441. DOI:10.54097/3cantc35
Waters, R. (19 Oct, 2023). Tesla profits fall after price cuts and plant shutdowns. Financial Times. https://www.ft.com/content/f1727de5-b3b0-439d-953f-c86d151b78af
Xia, X. (2022). SCM PMA Supply Chain Models—A Case Study of Tesla Motors. International Journal of Frontiers in Engineering Technology, 4(4): 33–40. DOI: 10.25236/IJFET.2022.040405
 write
write