Introduction
Successful product and service delivery in today’s global marketplace requires careful management of increasingly intricate supply chains. The current end-to-end operations, including sourcing, distribution, shipping, warehousing, sales, and customer support in the supply chain, have shifted to coordination characterized by numerous divisions inside a company and external partners. With such an environment, issues might occur that reduce a supply chain’s efficiency owing to the system’s complexity. This project investigates methods of reevaluating and enhancing supply chain performance by applying suitable tools and procedures.
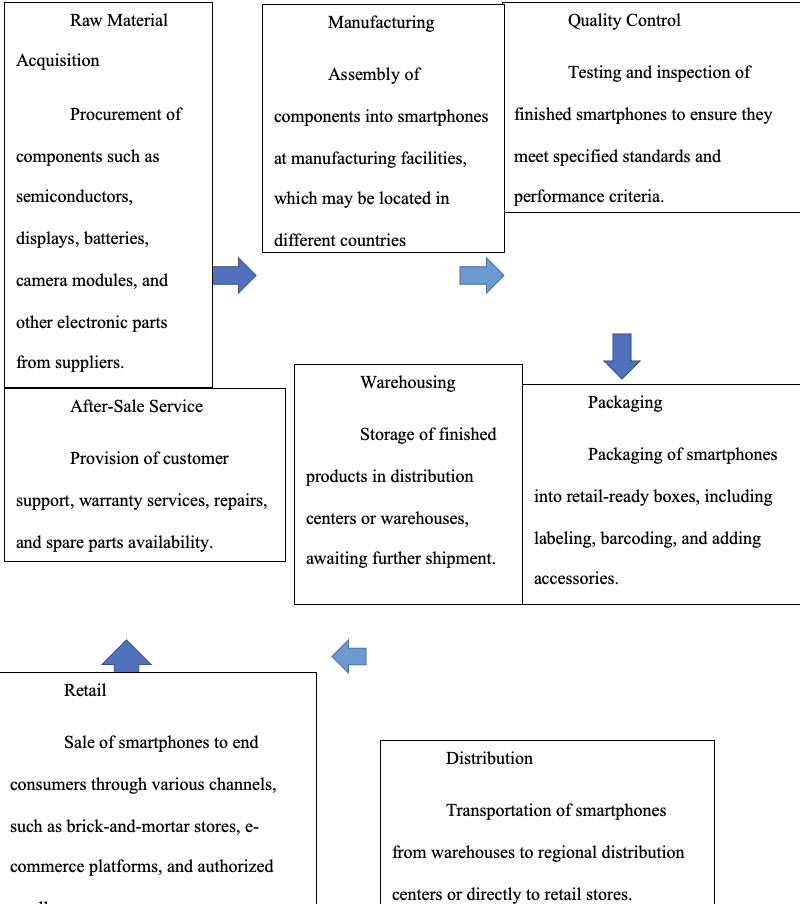
A Flow Diagram
A smartphone manufacturer is one of the kinds of businesses with a convoluted supply chain. The following diagram depicts a multinational smartphone manufacturer’s manufacturing, warehousing, and shipping processes.
Methods Analysis
Forecasting and planning for future demand are the company’s primary tactics. Predicting client demand properly allows businesses to maximize stock on hand while minimizing waste (Suflani et al., 2023). In addition, the organization can foresee market trends, client preferences, and seasonality using cutting-edge forecasting methodologies and demand planning tools, allowing for improved production and distribution decisions. Lean Manufacturing and Just-in-Time (JIT) are both essential business strategies. Adopting this method will significantly enhance the company’s supply chain efficiency. The organization may save money, shorten lead times, and increase responsiveness by cutting unnecessary steps and aligning production with demand. Kanban, Kaizen, and 5S are just a few examples of lean methods that may be implemented across the supply chain to increase efficiency and productivity.
The last and most crucial tactic is establishing cooperative ties with other organizations. A successful supply chain requires solid connections with outside parties such as suppliers, distributors, and logistics providers. Effective communication channels, real-time information sharing, and trust building are all ways to improve coordination, shorten lead times, and lessen hazards, as noted by Malecki et al. (2021). Electronic data interchange (EDI) and other cloud-based collaboration tools make it easy for supply chain partners to share and collaborate on data in real-time.
Analysis of Resolving Partner’s Problem
Pooled connections with partners are advocated to resolve the partner’s problem efficiently. The organization will be able to fix issues with communication and coordination in the supply chain by adopting this method. To put this plan into action,
The following steps provide a path to implement the plan:
- First, establish a cooperative system by forming relationships with crucial supply chain participants. The above calls for building confidence, harmonizing objectives, and outlining specific tasks for everybody involved.h
- Establish Communication Channels: If a company its business partner is to be able to share data in real-time, the company needs to use collaborative technologies like electronic data interchange (EDI) or cloud-based platforms. Improved decision-making and preemptive problem-solving result from increased transparency into stock, demand, and order statuses.
- Third, create open communication channels by encouraging frequent and open channels of contact with partners to encourage transparency, speedy problem-solving, and strategic alignment. Improve supply chain collaboration and efficiency with the support of regular meetings, collaborative planning, and feedback loops.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the success of the collaborative partnership and then use those metrics to drive continuous improvement. Tracking performance indicators like on-time shipments, lead times, and customer satisfaction may help zero in on problem areas. Participate in collaborative problem-solving and ongoing quality-improvement activities to achieve process excellence and higher supply-chain effectiveness.
Complex Supply Chain Challenges and Strategies
The complex smartphone supply chain is susceptible to several challenges. Among these is the volatility of demand. It is worth noting that fluctuating consumer demand and evolving market trends require agility in production and distribution planning. Companies must remain responsive and adaptable to ensure the timely delivery of products (Seetharam,2020). Global sourcing poses another significant challenge as managing suppliers from different regions add complexity to the process, necessitating quality assurance, on-time delivery, and regulatory compliance. Effective communication and collaboration across global supplier networks are crucial for maintaining a smooth supply chain operation. Product lifecycle management is also critical, involving coordination to introduce new models, phase out older ones, and manage component obsolescence. Staying ahead in the rapidly advancing technology landscape and seamlessly transitioning between products is essential for remaining competitive in the market.
Another challenge lies in inventory optimization, striking a delicate balance to avoid stockouts while minimizing excess inventory carrying costs. Accurate forecasting and efficient inventory management practices are crucial to promptly meeting customer demand and reducing financial burdens (Darvazeh et al., 2020). Furthermore, supply chain visibility plays a vital role. Real-time insights into product location, status, and condition throughout the supply chain are essential for better tracking, monitoring, and proactive problem-solving. This heightened visibility enables improved customer service and ensures efficient supply chain operations. Companies can navigate the challenges and maintain a successful and efficient smartphone supply chain by effectively addressing the volatility of demand, managing global sourcing, practicing astute product lifecycle management, optimizing inventory levels, and enhancing supply chain visibility.
Strategies to Address the Challenges
Demand-Driven Planning:
Entail a method of planning production and distribution that relies on accurate predictions of future consumer demand, data analytics, and knowledge of current and potential markets.
Supplier Relationship Management
It involves forming solid bonds with suppliers, encouraging cooperation, and applying supplier performance measures.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Production
Using lean manufacturing techniques to cut production lead times and stockpile just what is needed. An example is utilizing cross-functional teams, demand-driven replenishment models, and inventory management software to achieve optimal inventory levels while reducing stockouts.
Inventory Optimization.
Implementing track-and-trace technology, Internet of Things sensors, and supply chain analytics to monitor inventory, quality, and regulatory compliance in real-time constitutes e. Supply Chain Visibility and Traceability.
Conclusion
Supply chains for high-tech products are notoriously complicated, and the example of a smartphone’s supply chain illustrates this point. Challenges may be met, operations can be streamlined, and smartphones can reach customers quickly and reliably if smartphone manufacturers use best practices, including demand-driven planning, supplier relationship management, just-in-time production, inventory optimization, and supply chain visibility. To maximize supply chain efficiency and keep up with the ever-changing demands of the smartphone market, it is critical to evaluate existing methods and develop new ones regularly.
References
Darvazeh, S. S., Vanani, I. R., & Musolu, F. M. (2020). Big data analytics and its applications in supply chain management. In New Trends in the Use of Artificial Intelligence for the Industry 4.0 (p. 175). London, UK: IntechOpen.
Malecki, K. M., Keating, J. A., & Safdar, N. (2021). Crisis communication and public perception of COVID-19 risk in the era of social media. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 72(4), 697-702.
Seetharaman, P. (2020). Business models shift: Impact of Covid-19. International Journal of Information Management, 54, 102173.
Suflani, S., Khaeruman, K., & Jawahir, M. M. (2023). INVENTORY MANAGEMENT ANALYSIS USING THE MATERIAL REQUIREMENT PLANNING (MRP) METHOD IN THE OPTIMIZATION OF HANDICRAFT RAW MATERIALS. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Literature, 2(3), 359-368.
 write
write