Over the last four decades, there has been an increase in interest in performance management due to modifications to organizations with increased competition, workforce flexibility, and tying achievement to rewards. Performance management is becoming more popular among employers and management, and it has trickled down to shopfloor employees. The increased use of performance monitoring in enterprises can be ascribed to various issues, notably the desire for organizations to remain profitable, retain efficient staff, and improve profitability. Effective performance management offers an organized approach for employees to get feedback and coaching, allowing them to enhance their abilities and expertise and, as a result, contribute to better company results. Regardless of the potential advantages, performance management has drawbacks.
Consequently, businesses must critically examine the approach’s advantages and disadvantages and seek to implement it in a reasonable, open, and prospective-focused manner. This study assesses performance management, why more organizations use it, and the Human Resource Theory’s relationship to performance management. Furthermore, the paper will critically examine the advantages and disadvantages of performance management.
Overview Of Performance Management And HR
Today, the administration of performance mechanisms is an increasingly important focus in company operations. Essentially every human resource management (HRM) provides to performance management, instruction, and performance evaluation are of greater significance. The early years of HR and performance development for management may be traced directly to the early 1900s, throughout the industrial revolution. The industrial welfare movement advocated for employers’ efforts to improve working conditions in their respective industries. The revolution’s major goal was to ensure a higher standard of existence for employees, which impacted them psychologically. The primary objective of performance leadership is to enhance worker efficiency, motivation, and work satisfaction, eventually leading to better results for the organization. The cornerstone of a good HR system is performance management. According to Tweedie et al. (2019, p.77), most HRM literature focuses on the link between performance administration and appraisal. Integrating commercial and individual performance towards pre-defined business objectives to maximize the contribution from staff is thus a key component of strategic HR operations. Effective human resource management strategies rely on a solid grasp of human relations and the social and psychological aspects that impact employee conduct and job effectiveness. Performance administration is important for attaining HRM goals because it enables a structured procedure for reviewing and enhancing worker performance.
Theoretical Framework
The scientific approach analyses labour and discovers the most effective technique to do every task. The classical viewpoint, often known as scientific administration, emphasizes effectiveness, logic, and an organizational approach to work organization. According to scientific theory, workers are driven by financial considerations, and management organizes and directs the work process (McAuley et al., 2014). Edwin Locke developed the goal-setting theory in the year 1968. According to this concept, an employee’s specific goals are vital in encouraging him to perform well. Employees continue to work toward their objectives. If these goals are not met, they either enhance their performance or adjust the objectives to make them more achievable. The performance management framework’s objectives will be met if the performance improves. According to goal-setting theory, feedback is vital to the target-setting process (Lunenburg, 2011, p.4). Workers require periodic updates on how they are attaining their objectives to stay engaged and make any required improvements to their performances. Goal commitment is also emphasized in the philosophy. Employees dedicated to their goals are more likely to be driven to attain them. Employee commitment can be increased by integrating their input into setting objectives, offering resources and encouragement to assist them in achieving their goals and tying them to prizes and additional rewards. The relevance of communication in goal-setting is also emphasized by goal-setting theory. Employees require regular feedback on their performance in order to comprehend how they are making progress towards their objectives. Goal setting, for example, is frequently used to enhance patient outcomes in healthcare. Healthcare providers may create precise goals for their customers’ exercise routines, eating habits, and medication adherence while offering periodic updates on their progress toward these goals. The method can assist patients in remaining motivated and devoted to their therapy, resulting in improved health outcomes.
Performance Appraisal
Human resources perform a significant role in employee appraisals, thereby, are an essential part of organizational performance administration. The human resources department is critical in designing and implementing performance appraisals. The HR department is a go-between for the heads of function and evaluating authority and the employee. The HR team is in charge of designing the complete appraisal procedure. The HR team must understand the duties given to each employee to build and design a framework in which their real accomplishments may be graded concerning their primary responsibility areas. The performance appraisal criterion must be extremely straightforward and succinct. Employees should be well trained so that individuals can handle the whole performance appraisal procedure graciously and sportingly. Human resources are responsible for training and counselling managers and employees on their evaluation and appraisal process. It entails instructing managers on the most effective approaches to provide criticism and conduct employee performance reviews, enlightening employees on their potential and guiding them on creating desired outcomes and targets. Human resources are responsible for dealing with flaws that emerge during the performance review process.HR can help businesses improve worker engagement, economic viability, and staff retention by developing clear goals for performance, offering training and help to staff members and managers, and tracking performance appraisal information.
Strengths Of Performance Management
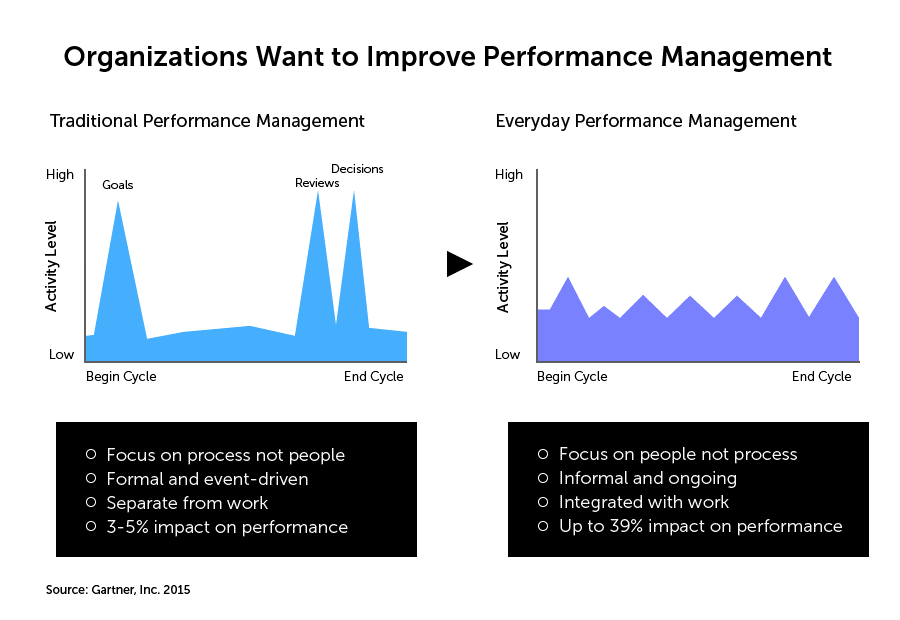
Managers can constantly discuss employees’ performance with them and offer comments on their fields of strength and need for development attributable to performance management. Between managers and staff members, such may assist in fostering confidence and improving connections, which can raise employee retention and involvement. Employees can benefit from performance management by identifying areas for growth and developing talents and abilities essential for accomplishment in their present and potential roles. Performance management may help people succeed professionally by offering regular guidance and feedback that can boost employee happiness and recruitment. For example, according to Sutton (2018), Adobe, a software developer headquartered in the United States, has established a system for managing employee performance that emphasizes continuous feedback and progress. Every year, performance evaluations have been replaced by frequent check-ins between leaders and staff members to discuss efficiency, goals, and career progress. Employee actions should be coordinated with the company’s overarching aims and objectives, partly due to performance management. Performance management assists in establishing a sense of shared direction and purpose among employees, boosting motivation and efficiency. Firms have fostered an environment of confidence and dedication by emphasizing regular communication and instruction and giving chances for individual growth and advancement. Therefore efficient feedback has aided the organization in attracting and retaining top employees and its performance in a highly competitive marketplace.
Managers can use performance management to interact with staff members regarding their work habits on an ongoing schedule and provide comments on their areas of expertise and room for growth. Mentoring can aid in developing confidence and strengthening connections between management and staff members, improving employee involvement and retention. Management can use performance information from management to make educated choices about allocating resources and long-term planning. Managers can uncover patterns and areas for enhancement regarding making decisions and allocating assets by recording and evaluating performance information. Regarding disagreement and legal difficulty, performance management establishes a standardized mechanism for tracking performance among staff members, which can give legal recourse. Businesses can show that they are taking sufficient steps to oversee staff efficiency and ensure compliance with laws and regulations by preserving assessments of achievement and recommendations. For instance, Amazon has proven able to establish confidence and deepen connections between executives and staff members by giving employees chances for career advancement and development and boosting their performance via regular coaching and evaluation (Bao et al., 2016, p.145). Management performance has aided the business’s image as a top employer and in attracting and retaining top people in an extremely competitive business.
Critiques of Performance Management
Performance management’s weakness in the setting of the neoliberal management system that customizes the job relation is that it might foster a focus on one’s accomplishments and competitiveness rather than collaboration and communal problem-solving. The results can lead to a hyper-individualistic environment in which employees are encouraged to prioritize their objectives and performance measurements over those of the firm or the wider community. Working conditions of performance management in a neoliberal framework can also add to workers’ perceptions of job instability and extreme poverty. Companies can leverage metrics for performance to argue for layoffs, reorganization, and exporting by stressing human accomplishments and results without considering broader financial, political, and social issues that may be influencing the firm or the industry. For instance, when performing as an individual is the main basis for progression and awards, it can foster an environment of prejudice and bias in which people who fit the company’s cultural and even demographic pattern are more inclined to thrive. In contrast, people who fail to succeed may be sidelined or removed.
Another criticism levelled regarding performance management is that it is discretionary and prejudiced. Performance appraisals are frequently based on managers’ and supervisors’ judgments and impressions, which can be affected by personal prejudices such as sexual orientation, colour, and temperament. A leader, for example, may offer a higher grade to a worker who is identical to themselves or they like, regardless of whether their performance does not deserve it. It thus can result in unfair and erroneous assessment, which may discourage personnel and erode a performance management system’s trustworthiness. The gender pay disparity at Google is one real-world illustration of the criticism against discretionary and biased performance oversight. The US Department of Labor sued Google in 2017 for claiming gender bias in wage and recruiting practices ( Levin, 2017). The lawsuit asserted that Google had an enduring issue of remitting female employees lower salaries than the male staff for comparable work and that Google’s performance appraisal system was “subject to bias.”
Management of performance increases workplace demands and, in many cases, a short-term perspective. Performance management can be demoralizing and foster a fear-based culture. Employees can feel agitated and concerned about attaining their objectives for performance, particularly if those targets are unreasonable or do not fit with their talents and abilities. Therefore, the performance management concept can result in fatigue, separation, and employee turnover, which can be expensive for the company’s shareholders. Furthermore, employees could feel hesitant to take threats and try something novel out of fear of missing resulting in an unfavourable performance assessment. Performance oversight may additionally contribute to an atmosphere of dread and unpredictability, especially when employees believe their careers or lives are in jeopardy due to their performance evaluations. Anxiety might result in a perpetual state of worry and tension, which can be discouraging while leading to employee burnout and turnover.
According to Foucault, performance management can be regarded as a concentration on managerial control and monitoring – disciplinary gaze. The power to discipline is an authority employing observing, measuring, and classifying persons to regulate and regulate their conduct. The regulatory gaze of managerial performance is frequently coupled with a sense of supervision and punishment, in which workers’ performance is continually observed and assessed. The result can foster an anxious and fearful culture in which employees believe they are continuously under investigation and face retribution and disciplinary proceedings if they fail to fulfil their assigned expectations. Performance management’s administrative gaze contributes to the integration of disciplinary power, in which workers start to regulate and regulate their conduct based on their performance measurements and reviews. Therefore, it can lead to a mentality of independence and monitoring, in which workers become their monitoring, continuously seeking to achieve their supervisor’s performance requirements leading to tensions.
Conclusion
Performance management is an organizational technique firms use to increase productivity among staff members, improve the quality of their goods and services, and fulfil corporate goals. Businesses can create objectives and deadlines, evaluate achievement, provide comments, and discover areas for development by adopting performance management processes. It also helps improve communication between managers and employees, as well as the identification and development of talent inside the firm. In addition, appraisal systems can foster an encouraging work environment and encourage staff members to give their all. However, there are certain constraints to performance management. One of the major complaints is that the emphasis on one’s accomplishments might foster a competitive culture that hinders working together as a team. Despite its drawbacks, performance management can help companies improve worker efficiency while reaching business goals. Therefore, it is critical for businesses to carefully organize and carry out performance management systems to ensure that they are efficient and compatible with the values and objectives of the business.
References
Bao, S., Damon, S.M., Landman, B.A. and Gokhale, A., (2016, March). Performance management of high-performance computing for medical image processing in Amazon Web Services. In Medical Imaging 2016: PACS and Imaging Informatics: Next Generation and Innovations (Vol. 9789, pp. 143–150). SPIE.
Boxall P F (2007). ‘The goals of HRM’, in (eds) Boxall P, Purcell J and Wright P, Oxford Handbook of Human Resource Management, Oxford, Oxford University Press, pp 48-67
Franco-Santos, M., Stull, D. and Bourne, M., 2021. Performance management and wellbeing at the workplace. In Handbook on management and employment practices (pp. 1-22). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Levin, S. (2017, April 7). Google was accused of “extreme” gender pay discrimination by the US labour department. Retrieved from http://www.theguardian.com/technology/2017/apr/07/google-pay-disparities-women-labor-department-lawsuit
Lunenburg, F.C., 2011. Goal-setting theory of motivation. International Journal of Management, business, and Administration, 15(1), pp.1-6.
McAuley, J., Duberley, J. and Johnson, P., 2014. Organization Theory, Challenges and Perspectives, második kiadás.
Sutton, R. I (2018, May 11).Why Adobe killed off the annual performance review – CMIRetrieved from https://www.managers.org.uk/knowledge-and-insights/case-study/why-adobe-killed-off-the-annual-performance-review/
Tweedie, D., Wild, D., Rhodes, C. & Martinov‐Bennie, N. (2019). How does performance management affect workers? Beyond human resource management and its critique. International Journal of Management Reviews, 21(1), 76–96.
Appendices
 write
write