Introduction
A blockchain is a series of time-stamped immutable data usually managed by a group of computers in most cases not owned by single entities. The individual blocks of data are bound and secured using cryptographic principles. Thus, a blockchain has no central authority and operates more like a democratized system. The blockchain system is an immutable ledger; therefore, the information is open for every individual on the platform to view. Every individual is therefore accountable for their actions within the blockchain network. There are no transaction costs involved in blockchain transactions apart from the infrastructure cost. Blockchain is the simplest way of passing away from two points though ingenious. First, the deal is safe and fully automated. Once a transaction is initiated, a block gets created (Crosby, Pattanayak, Verma, & Kalyanaraman, 2016). Then, the block gets verified by other networks of computers, probably in millions or thousands. Once the block gets verified, it’s added into a chain, usually stored across the web. Thus, a single record with a unique history gets created.
The world of business is currently diversifying, and every company is trying to cut on expenses that increase the operation cost overall. Blockchain ensures that individuals get paid for the services and goods they offer without hidden charges. Blockchain cuts the fee-processing middleman and eliminates the necessity for a match-making platform. The transaction in the blockchain is free as businesses can charge in minuscule amounts for their services. Taking, for instance, a video streaming platform can charge 1/100 of a cent if a customer or user wants to view a section of the videos. Traditional businesses rely on monthly or annual subscriptions to provide their services. For instance, a person who would only be interested in a section of Forbes Magazine will not pay for the entire magazine.
Bitcoin uses such a model for monetary transactions, but the method can find usage in many other ways. For instance, a public transport payment system like train or tram buses. Travelers will buy tickets through the web or a mobile application and pay through credit card. The credit card companies will take cuts to affect the transaction. However, with blockchain, the bus company will save on costs when the credit company processes the deal. The entire ticketing will, therefore, get moved to the blockchain. In such cases, the parties in the transaction are the transport company and the passenger. The ticket in the scenario is the block that gets added to the ticket blockchain. Transactions on the blockchain are unique and get verified independently. The tickets will also get checked separately. The last ticket on the blockchain also indicates a record for all transactions done. The entire blockchain process, therefore, will replace any processor models that charge for a purchase committed.
Businesses like recorded music sales are bound to profit as the artists would no longer rely on the various music companies and distribution platforms like Amazon, Apple, and Spotify. The musicians will get the full benefit from their works. For music cases, the downloaded music can be encoded within the chain and archived the music purchased in a cloud in blockchain technology. The amounts charged are minimal; hence there will be no need to subscribe to the various streaming websites and platforms (Daniel, 2017). Other services like eBooks are likely to fit in the blockchain system perfectly. Amazon is cutting with the current systems, and the credit companies are equally earning from the sales. With blockchain, books would get circulated in an encoded form. All successful transactions will eventually get channeled to the author and not royalties.
The financial world may be the biggest beneficiary of blockchain technology. The technology is set to revolutionize how stock exchange gets managed, insurance contracts, and loans bundled. Blockchain is set to eliminate bank account and other services primarily offered by the banking sector (Daniel, 2017). Elimination of such transactions may render most banks bankrupt, forcing most institutions to change their system of operations. The banking institutions may be turned into financial advisers while the stockbrokers are unlikely to earn any commission as the buy and sell spread in the stock market will disappear.
Previous approaches
The conventional methods of payment have for many years denied businesses the potential of getting maximum profits. The banks and credit card companies charge a massive sum of money to effect transactions within different platforms. Blockchain may be a new technology though it has received praise and backlash in the mainstream sector. The technology of blockchain is believed to be the most significant innovation in finance. In the Renaissance period, merchants had a problem with their bookkeeping; therefore, double-entry bookkeeping emerged. The double-entry was so helpful that it led to the formation of corporations by different investors and entrepreneurs, thereby giving rise to modern-day capitalism.
The double-entry ledgers still needed verification from a third party who could be trusted to ascertain that the information was correct. Others believe blockchain technology is similar to the 1970s TCP/IP, a networking protocol that allowed the computer to communicate and swap data. A protocol that formed the backbone for the invention of the internet. Five hundred years after the Renaissance, blockchain added a new entry of ledger which verifiable cryptographically and is much safer and transparent to the standards set by the global financial systems.
Current approaches
Major financial institutions are currently researching to create a proof of concept and further hunt for talent in blockchain technology. The number of individuals learning or interested in acquiring skills in blockchain has trebled, and the number is set to increase in the coming days. The wave of blockchain is taking over the finance sector and other industries like energy, health, and food technology, which are seen initiating pilot projects and joining groups trying to figure out how blockchain operates. SWIFT, a multinational organization that processes international payments, recently embarked on a pilot project in which the results are to be validated by some twenty-two banks. TUI Group, which is known as a world leader in tourism, currently uses blockchain to track the contracts issued internally. Airbus is also projecting to use blockchain to monitor the complex parts involved in making a jet plane.
Blockchain technology gets more useful when monitoring the movement of goods since all transactions need to go through the ledger. The system keeps a copy of the transactions, therefore, providing instant access when required. A good example would be Maersk, the shipping company that has started a test for monitoring shipment and coordinate with the customs officials in the different countries of operation.
State agencies are also getting a form like the Colombia central bank, which joined one of the consortia operating globally. The Russian government also announced plans to commence building a quantum computing and blockchain research hub to enable members of its citizen to acquire knowledge in the new form of technology slowly taking over markets. In collaboration with the Bank of Japan, European Central Bank has launched a blockchain research project (Ølnes, Ubacht, & Janssen, 2017). Blockchain gets praised, and most analysts believe the technology has the potential of disrupting several industries just like the internet did two decades ago. However, few distributed applications are in the mass market, and some large companies continuously shy away from the technology. Moreover, some companies that initiate pilot projects do not move to the next step after showcasing (Nam, Dutt, Chathoth, & Khan, 2019). Perhaps the leading companies in technology have not pushed the technology into the mainstream and popularized it.
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrencies are by far the most popular form of blockchain technology and in the recent days there have been various debates as cryptocurrency’s popularity gets higher. Digital currencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin have become popular and even major businesses are beginning to accept cryptocurrency as payment. Close to 6,700 cryptocurrencies are available globally resulting to a market cap of almost $1.6 billion with Bitcoin enjoying the bigger share (Kasar, 2021). The security details of blockchain makes cryptocurrencies secure as each has its irrefutable unique identifier attached to a single owner. Cryptocurrencies are getting accepted more in business world with a striking example being Tesla, the electric vehicle, announcing to be accepting Bitcoin as form of payment.
The Pillars of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is considered to operate based on three principles.
Decentralization
Before the invention of BitTorrent and Bitcoin, most services seemed to get centralized. Data would get stored in one platform or entity, and to get the desired information, one must interact with the data owner to receive feedback. A good example would be the banking system. The banks store our money, and the only way one can effect payment to a different party is to go through the bank. Thus, the traditional server model describes the centralized system.
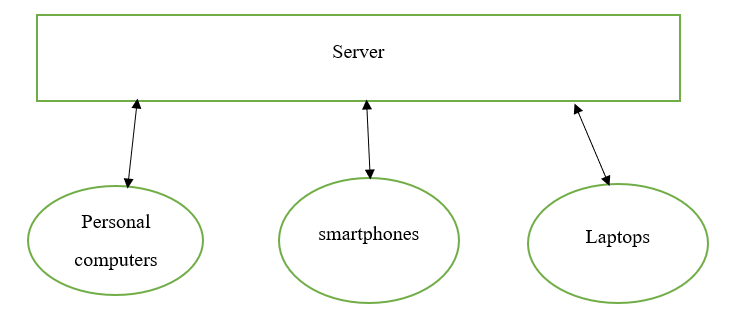
When a person with a laptop or smartphone wants to navigate the web, they will send a query to the server, who will get back with the relevant information. The centralized systems for many years have served the digital platform appropriately though several shortcomings experienced. First, the data in a centralized system are in one spot, making such data vulnerable to successful hacking. Secondly, in the event of the software upgrade, the whole system would be stopped, which may lead to losses in business. System shutdowns would mean nobody can access the information they have like when Gmail or Yahoo serves to get shut; individuals will not have access to their emails. Finally, a decentralized system gives the users the freedom to interact with their peers without necessarily going through a third party. For instance, the principle behind Bitcoin is that the developers needed a way where individuals have full control of their money. One may send them to anyone they desire without communicating with the bank.
Transparency
The concept of transparency in the blockchain is often misunderstood. Some analysts would say the technology provides privacy, as some say it is transparent. In the blockchain, a person’s identity gets hidden through complex cryptography and is only presented using the public address (Pilkington, 2016). For example, checking on a person’s transaction history would not give “Joe sent 10 BTC”; instead, one will see “1MG1thsFLkBzzz9vpFY3mvqqT2TbyCt7Bzj sent 10 BTC.” Thus, the person’s identity would be secure though all the transactions would still be visible through their public address. Such a level of financial transparency has not been witnessed with any technology before. Every individual, therefore, is accountable for the transactions they make, making it easier for financial institutions to monitor suspicious dealings.
In cryptocurrency, for instance, once an individual knows the public address of the companies or persons, all that is required is to load it on an explorer, and all the transactions they have engaged in will show (Crosby, Pattanayak, Verma, & Kalyanaraman, 2016). The system will force corporations and companies to be honest in their dealings. Though companies may not fully transact using cryptocurrencies, they may need to hide some books, perhaps to evade taxation. Further integration of the supply chain in blockchain technology would force most, if not all to transact faithfully.
Immutability
The pillar of immutability in blockchain implies that if something gets into the blockchain, tampering would be difficult, and that would be valuable for financial institutions. Embezzlement cases will reduce significantly, and individuals will not fiddle with a company’s accounts. Blockchain operates using a cryptographic hash function. Hashing means having an input string of any desired length though the output will be of a fixed period (Giungato, Tarabella, & Tricase, 2017).
| Input | HASH |
| Hello | 45T6737563HD8RTI48H9HFB988YH0H7N |
| Welcome to Bitcoin | P8I9ING9JIC849IJUCH8I897998783908782 |
In the above example, one would notice that the resultant output will have a fixed number of bits’ length, whether big or small input. The concept of hash becomes useful while dealing with extensive data and transactions. Remembering the input may sometimes get unnecessary due to its length, so the hash can help keep track of the sale.
Maintaining Blockchain Network and Nodes
The blockchain gets maintained by the peer-to-peer network, a collection of nodes interconnected to each other (Pilkington, 2016). The nodes are single computers taking in different inputs to perform a particular function and later output. Blockchain partitions the whole workload among the participants, and their no central server as several decentralized peers.
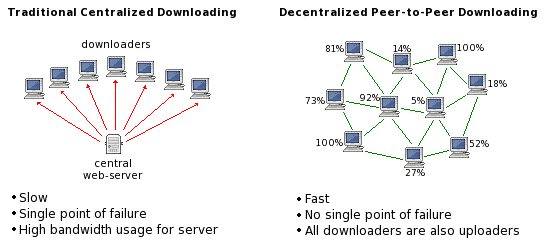
The peer-to-peer network is appropriate for file sharing. The client-server model at times gets slow and depends on the stability of the server. You may still have more peers to download from with a decentralized network, even if one peer goes out of the network (Pilkington, 2016). The system in peer to peer is not prone to censorship hence preferred by most individuals.
Conclusion
The technology of blockchain is set to revolutionize how transactions are going to get conducted in the future. Currently, there are high demands for blockchain developers. The technology cuts out brokerage and intermediaries in operations and further reduces the possibility of fraud and embezzlement in state agencies and business organizations. Transactions done online are in most instances connected to identity verification, making transactions tamperproof. The technology of blockchain will give internet users the possibility of creating value by authenticating their digital information. The different arguments against blockchain-based technologies are warranted, however, the popularity and acceptability of the technology is likely to push governments and other stakeholders into accepting it as a legitimate form of payment and probably legislate and have regulations in place.
References
Crosby, M., Pattanayak, P., Verma, S., & Kalyanaraman, V. (2016). Blockchain technology: Beyond bitcoin. Applied Innovation, 2(6-10), 71.
Daniel, R. (2017). Understanding Blockchain: Explore the Full-Circle Effect Blockchain Technology Has on the World and Our Future Generations (Books on Bitcoin, Cryptocurrency, Internet Money, Invest Ethereum, FinTech). Createspace Independent Publishing Platform.
Giungato, P., Rana, R., Tarabella, A., & Tricase, C. (2017). Current trends in the sustainability of bitcoins and related blockchain technology. Sustainability, 9(12), 2214.
Kasar, N. D. (2021). Review on Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Management (No. 5312). EasyChair.
Nam, K., Dutt, C. S., Chathoth, P., & Khan, M. S. (2019). Blockchain technology for smart city and smart tourism: latest trends and challenges. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 1-15.
Ølnes, S., Ubacht, J., & Janssen, M. (2017). Blockchain in government: Benefits and implications of distributed ledger technology for information sharing.
Pilkington, M. (2016). 11 Blockchain technology: principles and applications. Research handbook on digital transformations, 225.
 write
write