Executive Summary
During the past years, Ryanair’s continuous growth and strategies have successfully made the Company one of the largest low-cost airlines in Europe. On the other hand, Ryanair is experiencing a significant disruption: the COVID-19 pandemic. The outbreak of coronavirus across the globe has created a significant wave of uncertainty set to have a significant influence in the airline sector. With most of its revenues coming from passenger bookings, the Irish Company is currently experiencing a sequence of decisions that require to be considered to ensure survival amid the pandemic. The scope of this study is to offer several firm strategies to help it to adapt to the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic. In this regard, as a lengthy tactical; analysis is carried out, with the outcomes serving as a knowledge base for a situation planning analysis. The situations developed are to present the airline’s problems in different scenarios, and it is on these problems that the tactical recommendations are based on. The overview of the Company is focused on its corporate framework and governance, its mission and vision, and its competitors and business model. The tactical analysis consists of several separate analyses to examine the macro-environment, its competitive state, its leading industry indicators, and the sector it operates in.
For the Irish Company, the major decisions that require to be made are concerning: the number of hedging activities Ryanair has to take, the routes in which the Company has to decrease or increase the number of flights, the ideal number of regions, supply of available resources and aircraft orders in the effort of ensuring an effective risk-cost balance. The outcomes achieved are situation-specific, with every situation having an ideal mix of the aspects mentioned earlier.
Investment Analysis
Ryanair has been in the news for good reasons. The Company has built its reputation as among the leading carriers in the EU with various advancements and intensifying offering of its low-priced services. The move has brought an advantage to the Company regarding increasing the number of clients on its routes. Additionally, it is progressively focusing on effectively controlling costs which have helped Ryanair gain a competitive advantage over its rivals. Despite continued financial strain due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Ryanair has cut losses versus the 2nd and 3rd fiscal quarters in the last financial year. The rough road to the turnaround is expected to continue. The firm’s shares represent compelling value for long-term investors relative to the expectations of returns and cash flow on invested capital. The Company’s premium has fallen on difficult times because of increased spending on autonomous technologies and a substantial decrease in the number of customers because of the current pandemic. On the other hand, intelligent route selection has increased its revenue with an eight percent increase in the international volume of its clients in the recent past. Over the past decade, some competitors have copied our strategies making the market share retreat to 30% from a peak of 40% in 2010. This was driven by Ryanair’s management failure to develop new strategies for gaining a competitive edge.
Ryanair’s narrow financial moat assessment is driven by the strength and international recognition of its services. The strength of services enables premium pricing that leads to solid margins and healthy financial benefits. Low-priced services are meant to increase demand. Unlike its closest competitors, Ryanair concentrates on the policy of one-way tickets, where it targets travelers and business people who usually use other means of transport like vehicles and trains. Based on the demands of specific flights and the planned time for departure, the corporation plans suitable ticket packages to meet the requirements of clients. It sells about seventy percent of seats per the minimum available for the route at interest, meaning it aims at pursuing the “more sales for increased returns” tactic by a rise of occupied seats. Additionally, the Company targets short-haul routes to help it increase its day-to-day average round trip. Other strategies include reduction of operating costs, using charge competitive airports to decrease costs of operations, and renting 3rd party contractors to operate on its behalf in terms of handling guests and booking.
Company Overview
The Airline sector has remained a rapidly growing industry. It facilitates travel and leisure, international investment, world trade, and economic growth, and it is thus essential for globalization taking place in other sectors. Ryanair was launched in 1985 by the Ryan family as a scheduled carrier operating between Ireland and the United Kingdom. It was purposed to be an alternative to a state monopoly airline, Aer Lingus. Ryanair experienced an increase in the number of clients. However, it faced a loss amounting to approximately IR £20 m at the close of 1990. The loss made the management of the Company develop strategies of surviving in the sector. As a result, they restyled the corporation to a low-fare airline, making it the first low-fare carrier in Euro grounded on the Southwest Airline’s model. Michael O’Leary and Tony Ryan were selected to be board members of the airline. The restyled model now brought benefits for Ryanair. In the equity analysis project at hand, I will examine interesting insights on Ryanair’s problems, risks and progress it has experienced, its completion, and future tactics for progress and succession.
“Top-Down” Analysis
The flight sector remains a rapid and developing sector. It facilitates leisure and travel, global investment, international trade, and economic development and is therefore essential to the globalization taking place in many other sectors. Ryanair is not going to release a mission affirmation or formal eyesight. On the other hand, their standard direction is to continue being the most significant low-priced innovator in the European airline sector and carry more than 50 million passengers per year before the COVID-19 pandemic (Rodríguez-García et al., 2020). Effecting this vision is a function of several techniques such as flying to additional destinations, normalization on one type of airplane, non-union operations, quick gate turnarounds, and value chain that offers significant personal savings for the airline. Strategy is a collaborative and integrated group of activities and commitments made to gain a competitive advantage and exploit main competencies. The long-term positioning and purpose of the airline purpose are to tightly turn itself as Europe’s leading low-fares Company through the widened offering of services and continued advancements.
Macroeconomic Environment
Socio-Cultural Environment
The rising traveling lifestyles will have a significant impact on the business enterprise for Ryanair. For instance, business travels, family travels, and educational vacations. People opt to use budget airlines for short-haul travels since it is not just cheap, but it will also save your time, particularly when traveling for business purposes (Harvey & Turnbull, 2020). Terrorist issues made passengers use other means of transport such as ferry and train services since they were considered safer than flights. The airline sector has not just been troublesome, but it has also negatively affected a financial aspect, particularly for budget airlines. People come up with poor opinions and thoughts as far as budget airlines are concerned. Such labeling has posed a critical concern for companies like Ryanair. The restriction on the flight, luggage cancellation and delays, and the general inefficiency have put pressure on the Company’s management and the passengers. Ryanair,
Technological Environment
The Company uses Boeing 737 planes to lower aircraft maintenance costs. It replaced its fleet of old airplanes with new environmental-friendly planes on top of lowering the average fleet period to 2.4 years. Ryanair uses a program of winglet modification on its fleet to provide better performance for its aircraft. The new planes produce 45% fewer noise emissions, 45% lower petrol melt away, and 50% fewer emissions. As a result, it is significant for the Company to invest in promising technology and keep it up-to-date in the mission of gaining a competitive advantage.
Environmental Factor
Every country worldwide is concerned about global warming and the effect of the emission of harmful gases to the atmosphere. Research has revealed that the airline sector is responsible for 2.6 percent of the emission of harmful gases. Airline companies are aiming at coming up with strategies of lessening noise pollution. It is essential to put in mind that the environment is among the most significant matter to airlines. On top of that, it might result in an economic effect credited to heavy sanctions and penalties. Besides, the political effect would be considerably planned to a great petitioning by environmentalists.
Legal Environment
Getting illegal subsidies from global airports is a crime in Europe. As a result, the legal mean of getting such necessary crossing point subsidies will be the ability to continue being competitive. The allegation of deceptive articles on airlines will result in legal action too. Legal actions of this kind would be monetarily damaging to budget air travel. As mentioned earlier, environmental breaches and concerns of stipulated emission charges might result in legal action too.
Overview of Key Megatrends Affecting Ryanair
Ryanair has been in the recent past been affected by client pressure for improved and new service and an urgent requirement for an advanced brand image. On top of that, it has been impacted by fines for going against the labor laws in France and financial warnings due to the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result, the Company needs to quickly change its tactics in the wake of new business conditions, that is, a challenging market in Europe, fluctuation of currency, and increased costs of fuel and competition to determine how it will continue being successful as one of the leading airlines in Europe (Ivan et al., 2020). Diversifying its distribution, advancing its corporate website, tapping into online platforms, and revamping client service denotes a brilliant, even though delayed instead, move by the Company in what is challenging and a competitive business environment. If implemented correctly, these modifications could be profitable to Ryanair and attract a large clientele base, including those traveling for business purposes.
Several profit warnings have been released by the Irish firm in the recent past. It all started when Ryanair warned its shareholders that its target in terms of financial performance might not be achieved at the end of the day. The announcement was followed by another review of the prediction some months later. Concerns originated from the fact that the airline company was downgrading its annual profit expectations from €570 million to something close to €520, brought about by increased competition of price not just from schedule operators but also from budget rivals and to a lower demand plus a weaker pound resulting to both two percent decrease in fares and a fall in annual bookings. The statements affected the airline sector greatly, with several speculations being brought forward on what is ailing the sector and what needs to be done to save it from the unsatisfactory financial prospects. The financial go-slow of an airline company such as Ryanair brings about more queries if the firm is losing its desirability among clients and whether overcapacity has been over speeded, weakening its competitive advantage in due course.
The Irish Company was also affected by the announcement of the French government that saw Ryanair being penalized €9 million after being breaching the labor laws of the country for employing French citizens using the labor contracts of Ireland on among its bases. The ruling increased the financial costs for the Company on top of undermining its reputation both as an employer and as a brand. The main distribution of the Irish firm, its website, together with its dubious client service, has also been one of the most significant areas to be focused on, has continued to be criticized sharply for a long time. On the other hand, change is inevitable for the firm. Ryanair has decided to improve its website via a significant renovation after receiving many complaints from the clients, thus making it easier for the users to make a booking at the end of the day. It also requires changing its strategy as far as distribution is concerned. The Irish Company is considering working with travel agents on online platforms, which it have faith that will pave the way for a good tap into the business category. The no-frills firm aims at focusing on allocated seating too, an effort it hopes will attract more customers and diversify its clientele base, but simultaneously copying what Easy Jet, its closest competitor, has already been doing. As shocking as it appears, the Company seems prepared not just to experiment but also maybe to control the business model it is interested in. This is a method that is not necessarily aligned to the loathsome style of business of its current leadership, which seems to favor the continuous involvement of Ryanair in undesirable public relations. Although the airline is threatened by a decrease in its operations following the COVID-19 pandemic, it is changing its business model in the mission of achieving its 110 million targets of clients by 2025.
On the other hand, the strength of the Irish firm does not have to be underestimated. Ryanair is still one of the leading budget airlines in the European market and has continued to maintain its lowest cost per client in Europe compared to competitors like Easy Jet (Morlloti et al., 2020). On top of that, the Company is among the best companies in the region as far absorbing increases in costs is concerned but simultaneously effecting aggressive wars on pricing. The suppleness with which Ryanair can achieve deseasonalization and ground fleet also helps it save costs when not getting significant outcomes and simultaneously providing a better pricing framework. Significantly, nonetheless, a leader in the market has to continuously court clients, improve and innovate service in the mission of retaining the leadership in due course. Failure to take such efforts threatens both financial stability and its brand. The inability to do so does not just become a very expensive but also an irreversible mistake.
Industry Analysis and Competitive Positioning
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2019, the airline sector has been significantly affected due to the decrease in the number of passengers because of lockdown, among other factors. On the other hand, firms in this sector, such as Ryanair, are coming up with strategies to increase the clientele base and improve economic conditions to overcome the pandemic issues ultimately. In the recent past, the European market has been experiencing a slowdown in growth since the outbreak of coronavirus (Dube et al., 2021). The concept of improving economic conditions has been around for years, but it has not been realized since the beginning of 2020. In other words, the airline sector is experiencing a crisis amidst the international COVID-19 pandemic with a significant decline in the number of passengers. A loss of revenue is expected to hit the industry for an unknown number of years. As a result, companies are looking forward to assistance from the government to prevent the companies in this sector from collapsing.
In such hard times, it is vitally significant that the involved parties are holistic and agile at managing risk, including accounting risk in line with direct economic risks. Driven by Markets Authority and European Securities plus other international regulators, there is a dire requirement to concentrate on transparency in market disclosures and financial reporting. Airline companies require to properly evaluate how market volatility, economic uncertainties, travel bans, and fleet groundings may impact accounting conclusions (Haines, 2021). Such contemplations might include revision of overhaul cost, maintenance cost, re-evaluation of prevailing operating leases, re-evaluation of regular consumption of fuel and amounts of fuel hedged, the effect of prolonging of expiry dates of loyalty points, review of future salary expectations in overall liabilities, and change in methods of depreciation. Changes in travel patterns by cautious clients and contraction of economic activity might avert a return to pre-crisis demand levels even as containment and lockdown measures are loosened in many regions. Research has revealed that commercial air travel will be slow as far as recovery is concerned. As of September last year, the number of commercial flights remained below 40 percent of the number of flights worldwide before the outbreak of COVID-19, as shown in figure 2. It is essential to consider that the captured information includes some business jet flights, charter flights, cargo flights, and commercial passenger flights; it does not include drones, military flights, government flights, ambulance flights, helicopter flights, gliders, and private flights.
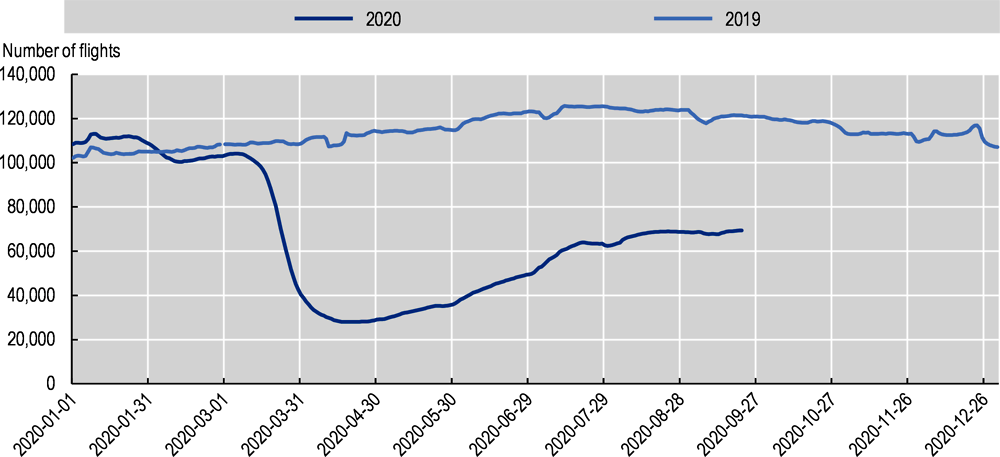
Figure 2: (Commercial air traffic, world) Number of flights tracked daily by Flightradar24, 2020 v. 2019
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Power of Suppliers
Traditionally, Boeing has been the leading supplier for Ryanair. However, unconfirmed reports have shown that the Company is planning to switch to Comac’s planned C919 aircraft. The jet manufacturer from China is attracting the interest of the Irish Company because of the many seats it has in its planes and an increased level of effectiveness that is linked to consumption of fuel. This fact portrays the increasing bargaining power of suppliers of the Company towards Boeing, its leading supplier. However, the switching costs of suppliers for the Company are extremely high since there is no sufficient supply of highly experienced and qualified pilots.
Power of Clients
The power of clients can be discussed as a benefit that comes with exerting pressure on the sellers to improve quality or reduce prices. The clients of Ryanair enjoy a high bargaining power since switching to another company is not complex and is not linked with extra expenses. On the other hand, it is essential to mind that clients in the airline sector enjoy a higher bargaining power; it is not only for Ryanair. This fact is attributable to the idea that most airline companies are forced to reduce prices due to antagonistic competitors.
Threat of Substitutes
A substitute can be referred to as a service or a product of another sector with a similar value for the client. The threat of a substitute is a significant factor in the level of profitability in the sector. There are no significant substitutes for high-speed traveling except high-speed trains that are not entirely developed and do not cover most regions in the world. Nonetheless, substitute services for Ryanair in specific and airline sectors, in general, include car rental companies, coach transport, sea transports, and railway networks (Akbar et al., 2020). However, typically ferry, bus, or train tickets are more expensive than the air tickets of Ryanair because of the Company’s selected strategy that depends on low prices to gain a competitive edge.
The threat of New Entrants
The threat mentioned above is associated with the magnitude of ease of entering into the sector and competing with present market players. The threat of new entrants is not high for the Company because of the significant barriers to entry linked with entering the airline industry that incorporates access to distribution channels, capital needs, and economies of scale, among other factors.
Fundamental and technical valuations
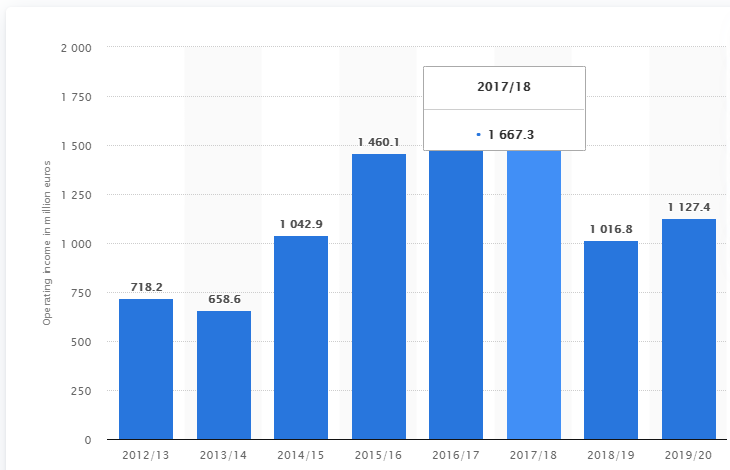
Figure 3: Operating income of Ryanair from 2013 to 2020
The following table summarizes Ryanair’s performance over the last four quarters:
| Quarter Ending | Gross Profit | Revenue | Margin |
| 31/3/2020 | 67.3M | 1.199 B | 5.6% |
| 30/06/2020 | -11.2M | 125.2 B | -8.9% |
| 30/9/2020 | 237.3M | 1.051B | 22.6% |
| 31/12/2020 | -138.5M | 341.2M | -40.6% |
Figure 4: Ryanair’s Performance in 2020
Ryanair’s latest twelve months gross profit margin is 5.7%. Ryanair’s gross profit margin for fiscal years ending March 2016 to 2020 averaged 32.6%. Ryanair’s operated at the median gross profit margin of 33.4% from fiscal years ending March 2016 to 2020.
News and Investment Risks
On 17th September, 2001, Ryanair reported abnormal returns, which were part of six companies outside the United States. The stocks of the Irish firm also experienced downturns. In the following five days of trading, the Company reported an upward trend as far as its returns were concerned, but there was no clear explanation of the behavior. The cumulated abnormal profits for the time past 24th September indicated that the general market reaction mostly showed negative results for the following six weeks after the shock. The overview of the abnormal profits following the 11th September attacks in the United States provided some insights into the possible differencing aspects and the market’s reaction. The attacks made airline companies implement new security standards for airlines and airports across the globe. Most airline companies and airports started hiring additional security personnel. Companies in the European market include Ryanair, also started to increase their standards in terms of security. Major airports in the world introduced new baggage security policies, aircrafts started to be accompanied by additional sky marshals, and suppliers came up with new cockpit doors to keep off the hijackers. All the above measures increased cost for airlines, which is why the coming to an end was being experienced with companies outside the United States immediately after the 9/11 attack. So far, the assessment of the stock performance of airline companies has not been the same since the 9/11 attacks in the United States. A regression analysis has been carried out in the efforts of explaining the abnormal profits that were experienced after the terror attacks.
Profits in the airline sector have been declining due to the overcapacity in the European market. And irrespective of some issues, the scenario will become favorable to the Irish Companies. Ryanair has been facing typical issues in the airline sector. Due to the prevailing airline overcapacity in the European market, air tickets are going down, and higher operating costs are harming its returns. At the same time, other events like delays in the supply of planes will impact the corporation over the medium period. However, the general issues being faced by the Company create a long-term investment prospect. Other investment risks facing the Irish firm include the long-term opportunity, the effect of increasing prices of oil, and bankruptcies, and overcapacity in the European market. However, Ryanair is placed in a favorable position to take advantage of the issues mentioned above. Bankruptcies in other European companies are helping in lessening the overcapacity while Ryanair is still making profits. Additionally, the firm’s total debt is low, and prudent oil hedging of the corporation is eliminating exposure to volatile oil prices. As a result, the Irish Company is an exciting prospect for investors. The assessment is rational, while Ryanair looks self-assured to develop thanks to its organizational advantages.
In summing up, the Company sells various items ranging from priority boarding of clients to on-board sales of foods and beverages. The commonality of the services offered by the Irish Company is that they are harmonizing as far as essential air transport is concerned. It is, however, essential to put in mind that clients can enjoy the services of the Company without necessarily paying for food and beverages or priority boarding. Ryanair is planning to increase the number of its flights to eight percent of pre-pandemic levels in the next three months as the management of the Company is criticizing the government of the United Kingdom for giving warnings on booking abroad summer holidays in 2021. The management has said that it is confident that Britons would be visiting beaches in Europe and that the Company would have a profitable period thanks to the European and the United Kingdom’s rapid, albeit politically troubled, vaccination programs. Ryanair has said that it would fly almost half of the number of flights it runs before the COVID-19 outbreak in 2019. Its hopefulness for a quick return of global travel differentiated with the cautious view of the United Kingdom’s government. Its closest competitors, such as Easy Jet, have also reported summer bookings after most governments worldwide lifted bans on international travel. The Irish airline has also reported that it will be launching twenty-six new routes from Birmingham, Liverpool, Edinburg, and Stansted. The Company has for a long time asserted that resuming flying brings a low-risk change of coronavirus. On the other hand, the management of the Company has announced that it will maintain its policy on the wearing of face masks until next year unless the governments aligned to the European market relax the measures on COVID-19 transmission.
Bibliography
Akbar, Y.H. and Kisilowski, M., 2020. To bargain or not to bargain: Airlines, legitimacy and nonmarket strategy in a COVID-19 world. Journal of air transport management, 88, p.101867.
Dube, K., Nhamo, G. and Chikodzi, D., 2021. COVID-19 pandemic and prospects for recovery of the global aviation industry. Journal of Air Transport Management, 92, p.102022.
Haines, A., 2021. Ryanair to appeal EU court’s decision on French and Swedish state aid. International Tax Review.
Harvey, G. and Turnbull, P., 2020. Ricardo flies Ryanair: Strategic human resource management and competitive advantage in a Single European Aviation Market. Human Resource Management Journal, 30(4), pp.553-565.
Ivan, D.I.A.S., Panno, G., Martellotta, A. and Allis, T., 2021. LOW-COST AIRLINES BRANDING DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC. Marketing & Tourism Review, 6(1).
Morlotti, C., Birolini, S., Cattaneo, M. and Redondi, R., 2020. Introducing connecting flights in LCCs’ business model: Ryanair’s network strategy. Journal of Air Transport Management, 87, p.101849.
Rodríguez-García, M., Orero-Blat, M. and Palacios-Marqués, D., 2020. Challenges in the Business Model of Low-Cost Airlines: Ryanair Case Study. International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems (IJEIS), 16(3), pp.64-77.
 write
write