Executive Summary
Data communication and computer networks are the essential part of our day-to-day life. It is invaded all aspects of our life, i.e., entertainment, business, education and research, space mission, PC revolution, and telecommunication. This paper discusses data communication and computer networks, their importance in the current technological world, and how they are related. It will also provide some managerial and practical implications and recommendations for businesses that use these technologies. In addition, it will explain the different types of networks and the various technologies used to connect them. Finally, it will conclude with a summary of the paper’s contents.
Introduction
Data communication and computer networks are two of the most critical technologies in the current world. Data communication is used to transmit data from one point to another, while computer networks are used to connect computers and other devices. The two have become increasingly intertwined in recent years as the Internet has grown in popularity and businesses have adopted new methods of data transmission (Forouzan, 2007).
Today computer is available in many offices and homes, so there is a need to share data and programs among various computers. With the advancement of data communication facilities, the communication between computers has increased, and thus it has extended the power of computers beyond the computer room. A user sitting in one place can communicate with computers of any remote site through a communication channel (Forouzan, 2007). This lesson aims to introduce you to the various aspects of computer networks and data communication and discuss how the technology/trend is related to data communication and computer networks, managerial and practical implications.
Data Communication
Data communication is the process of sending data from one point to another. It can be used to transmit information over both wired and wireless networks. Examples of data communication technologies include email, instant messaging, file transfer protocols, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP).
Components of data communication
The term “data communication” refers to transferring information between two devices using a medium such as a cable, wire, air, or vacuum. Devices that exchange data must be connected to a communication system, which may consist of other hardware and software components.
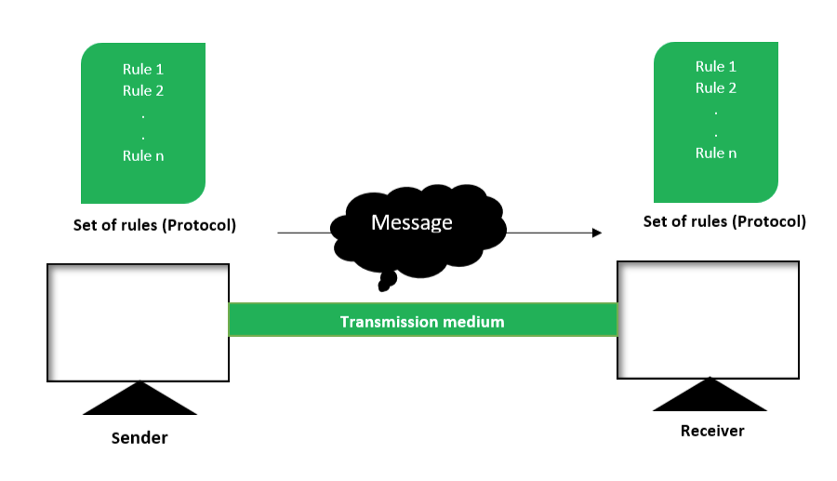
Message: This is the data communication system’s greatest strength. A message is any data or information that needs to be transmitted. You can send a message in the form of a text file, an audio file, a video file, etc.
Sender: For a message to be conveyed from its origin to its intended recipient, someone must be the source. The sender functions as a source in a data transmission system. Simply put, it is a data transmission device. Numerous gadgets exist that could be used for this function.
Receiver: The recipient is where the sender’s message has eventually arrived. It is a communication receiver. Receivers might be anything from a computer or phone to a mobile device or even a workstation.
Transmission Medium: The transmission medium serves as a link between the sender and the receiver throughout the data transmission process. The transmission channel is the path information takes as it moves from source to receiver. A transmission medium, or “medium,” can be guided (with wires) or unguided (without wires), such as twisted pair cable, fiber optic cable, radio waves, microwaves, etc.
Set of rules (Protocol): Designers of communication systems have created numerous rules to control data communications; these rules can be considered agreements between the devices involved. This is the very definition of a protocol. In its simplest form, the protocol is a collection of guidelines for how information should be transmitted. A standard protocol between linked devices is necessary for them to exchange data. Therefore, the protocol is required for data transmission.
Transmission of an email is a common data communication mechanism. To send and receive an email, both the sender and the recipient must have access to the Internet via a wireless connection; the sender is referred to as the sender, the data being sent is the message, and the recipient is the one to whom the message is being sent.
This table summarizes the key distinctions:
| Computer Network | Data Communication |
| Computer Network is best known for transferring data and information across geographies. | We may share information and coordinate efforts among disparate nodes through Data Communication. |
| It is a subset of Data Communication. | A computer network is one type of channel used for transmitting data. |
Trends and Issues in Information Technology
The global dissemination of scientific information faces both new possibilities and problems presented by the development of information technology. The trend toward cheaper and more powerful computing, networking, and data storage seen in recent years is set to continue for the foreseeable future, putting previously unattainable resources within reach of even modest-sized users. The scope of technology influencing the collection, curation, analysis, transmission, and dissemination of scientific data is growing as innovations in satellites, sensors, robotics, and fiber-optic and wireless communications are implemented. (Arsenault, 2017).
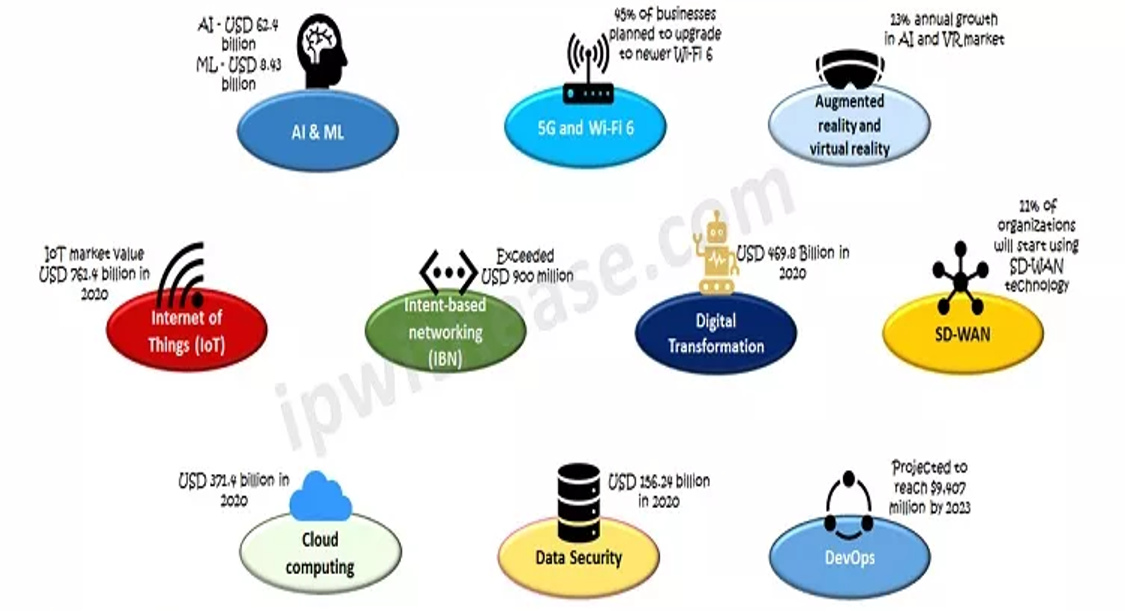
Networking technology has evolved significantly over the years as demands on Ethernet and Wi-FI have tremendously increased. Apart from supporting a range of devices, Local area networks require to manage traffic getting generated from many other sources such as live streaming video, Network attached storage (NAS), Voice over IP (VoIP), virtualization, Cloud and IoT devices and services have generated demand for additional bandwidth.
Computer Networks
Computer networks are networks of computers and other devices connected. They are used to share resources, such as files and printers, and provide Internet access. Networks can be categorized into two broad categories: local area networks (LANs) & wide area networks (WANs). LANs connect computers in a small area, such as an office or a home, while WANs connect computers across more considerable distances (Laudon & Laudon, 2021).
Types of Networks
A network consists of a set of nodes connected by media. Communication channels are how data is transmitted between the various nodes. A local area network (LAN), a metropolitan area network (MAN), and a vast area network (WAN) are the three main categories of computer networks. There are three main types of networks: local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs).
A network, in this context, refers to a system in which several users can share data and other resources among a group of computers and their attached peripherals across an established communication channel.
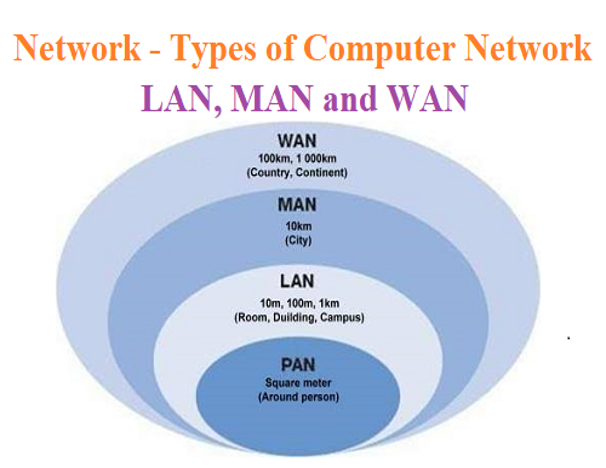
Types of networks with their advantages and disadvantages.
- Local Area Networks (LANs): These networks connect computers in small areas, such as offices or homes. They are usually fast and reliable but may be more expensive to set up and maintain.
- Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs): These networks use wireless signals to connect computers in a small area. They are generally less expensive to set up and maintain than LANs but may be less reliable.
- Wide Area Networks (WANs) connect computers across considerable distances. They are typically slower and less reliable than LANs but are more cost-effective.
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs): These networks connect computers in a large metropolitan area, such as a city or a town. They are typically more expensive to set up and maintain than LANs or WANs but can provide higher speeds and excellent reliability.
Network Technologies
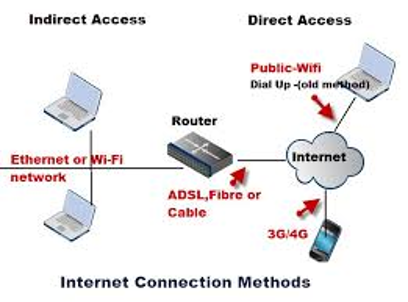
Several different technologies are used to link computers and other devices to a network. The most common technologies are:
- Ethernet: This is the most common type of wired connection. It uses cables to connect computers and other devices to a network.
- Wi-Fi: This wireless connection uses radio waves to connect computers and other devices to a network.
- Bluetooth: Computers and other devices close to each other can be connected via radio waves in this short-range wireless connection.
- Fibre Optic: This is a high-speed connection that uses glass or plastic cables to connect computers and other devices to a network.
Managerial and Practical Implications
Data communication and computer networks have several implications for businesses. They can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase security. They can also be used to improve customer service and increase customer loyalty. Additionally, businesses can use these technologies to gain competitive advantages over their rivals (Mahanta et. al 2013)
The paper concludes each section with a summary of the most critical management considerations that arose throughout that section’s discussion. We extrapolate ramifications for the administration of networks and information systems and the management of the entire organization.
There are three main takeaways for managers to consider in light of this discussion. The advent of networks and the Internet has drastically altered traditional practices. The ease with which information may be transferred between places and accessed by people both inside and outside the company has a far-reaching impact on business practices, the marketplace, and our daily lives. Those businesses and people who are open to change and seek out ways to apply networks and the Internet to improve their work will succeed, while those who resist it will lag behind.
Second, the current networking landscape is driven by standards. When a company uses standard technology, combining devices from various manufacturers is simple. Using standardized technology also facilitates the transition from one technological generation to the next, as most manufacturers build their wares to be compatible with a wide range of specifications. As a result of having fewer technologies to learn and support, the cost of networking is reduced when only a handful of standard technologies are used rather than a wide variety of vendor-specific proprietary technologies. Your organization is likely overspending on its networks if it does not use a small subset of industry-standard networking technology (such as Windows, Linux, or 802.11n wireless LANs) (NetMBA, 2021).
Third, the requirement for data storage and server expansion will grow in tandem with the demand for network services and network capacity. When we figure out how to properly archive the mountain of data we produce, we will be able to tap into hitherto untapped consumer niches. In the present day, Google operates about 500,000 server sites.
How to Optimize Your Local Area Network A bottleneck is a point in a local area network where data flow is restricted, resulting in a decrease in throughput. The bottleneck is typically located in the Network itself, either in the server or the circuit. To boost server performance, you can either upgrade the server’s central processing unit (CPU), memory, network interface card (NIC), and speed and several hard disks or purchase more servers and distribute the applications across them. Using faster technology (100Base-T instead of 10Base-T) and splitting the network into many LANs might increase circuit capacity. In general, LAN performance can be enhanced by reducing demand on the LAN through measures such as relocating files off the LAN, employing disk caching on client computers, and rearranging users’ daily habits (Laudon & Laudon, 2021).
Recommendations
Businesses should be aware of the implications of using data communication and computer networks. They should ensure that their networks are secure and that their data is transmitted securely. Additionally, businesses should ensure that their networks are reliable and that their data is transmitted reliably. Finally, businesses should ensure that their networks are cost-effective and utilize the latest technologies.
Conclusion
Data communication and computer networks are the essential part of our day-to-day life. It is invaded all aspects of our life, i.e., entertainment, business, education and research, space mission, PC revolution, and telecommunication. Security/Encapsulation, e.g., ATM, Faster Problem solving, e.g., Distributed databases, e.g., World Wide Web Collaborative Security through redundancy, e.g., space programs Encryption Codes processing, e.g., Games in a multi-user environment are the major applications (Singhal, 2017).
Data communication and computer networks are two of the most critical technologies in the current world. They are used to transmit data from one point to another, connect computers and other devices, and provide Internet access. Different networks and technologies are used to connect these devices, and businesses can use them to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase security. Finally, businesses should be aware of the implications of using these technologies and ensure that their networks are secure, reliable, and cost-effective.
Reference
Arsenault, A. H. (2017). The datafication of media: Big data and the media industries. International Journal of Media & Cultural Politics, 13(1-2), 7-24.
Forouzan, B. A. (2007). Data communications and networking. Huge Media.
Laudon, K. C., & Laudon, J. P. (2021). Management Information Systems (15th ed.). Pearson.
Mahanta, D., Ahmed, M., & Bora, U. J. (2013). A study of bandwidth management in computer networks. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 2(2), 69-73.
NetMBA. (2021). Network Topologies. Retrieved April 6, 2021, from https://www.netmba.com/networking/topologies/
Singhal, A. (2017). Network Technologies and Protocols. Retrieved April 6, 2021, from https://www.tutorialspoint.com/network_technologies_and_protocols/network_technologies_and_protocols_overview.
 write
write