Abstract
This paper analyzes Shi’s Tasty Cookies, a small business that produces and sells cookies. The analysis examines the business’s operations, performance, and future improvement strategies. Reviewing the company’s contribution margin, full and variable costing, special orders, internal rate of return, cash budget, and material and labor variance are all included in the analysis. According to the research, specialty cookies have the biggest contribution margin, full costing is more accurate than variable costing for inventories, taking special orders can be advantageous, new equipment should be declined, and the company should prioritize growing sales and reducing costs.
The Impact of Special Orders on Small Business Performance: An Analysis of Shi’s Tasty Cookies.
This essay analyses Shi’s Tasty Cookies, a small company that bakes and sells cookies. The research looks at the business’s operations and performance as well as potential improvement plans. The report will examine the company’s strengths and problems to offer options for improvement. The research examines the contribution margin of the business, full and variable costing, special orders, internal rate of return, cash budget, and material and labor variance.
Part 1 Contribution Margin/Breakeven
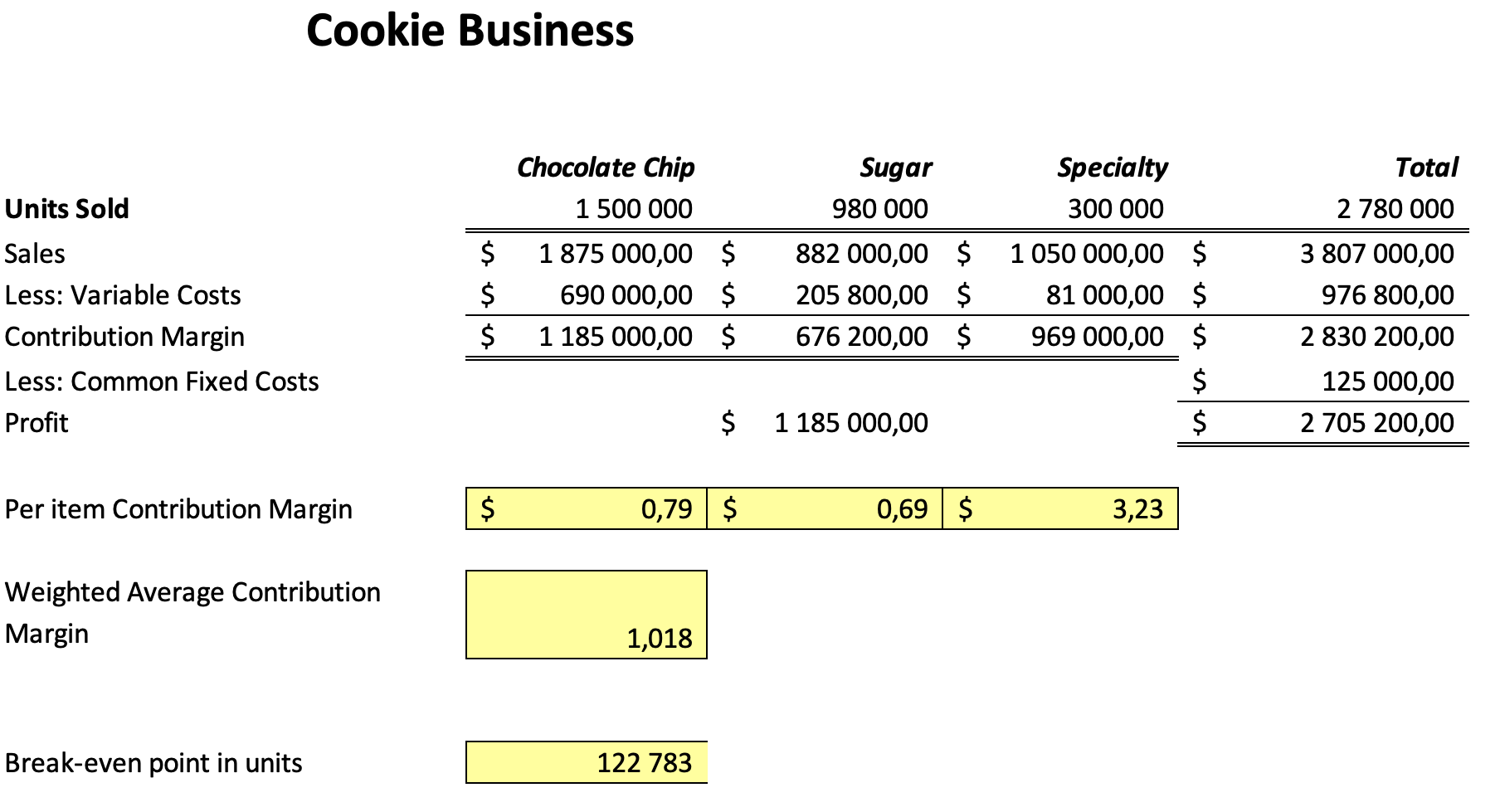
Based on my calculations, the Specialty cookie has the greatest CM of 3.23, followed by the Chocolate Chip cookie with a CM of 0.69 and the Sugar cookie with a CM of 0.69. This suggests that the specialty cookie is the most profitable of the three varieties of cookies that Shi’s Tasty Cookies sells. The Specialty cookie’s greater CM is brought on because it costs more than the other two kinds of cookies. According to this analysis, Shi’s Tasty Cookies should concentrate its efforts on increasing Specialty cookie sales to increase its earnings.
Part 2 Full and Variable Costing
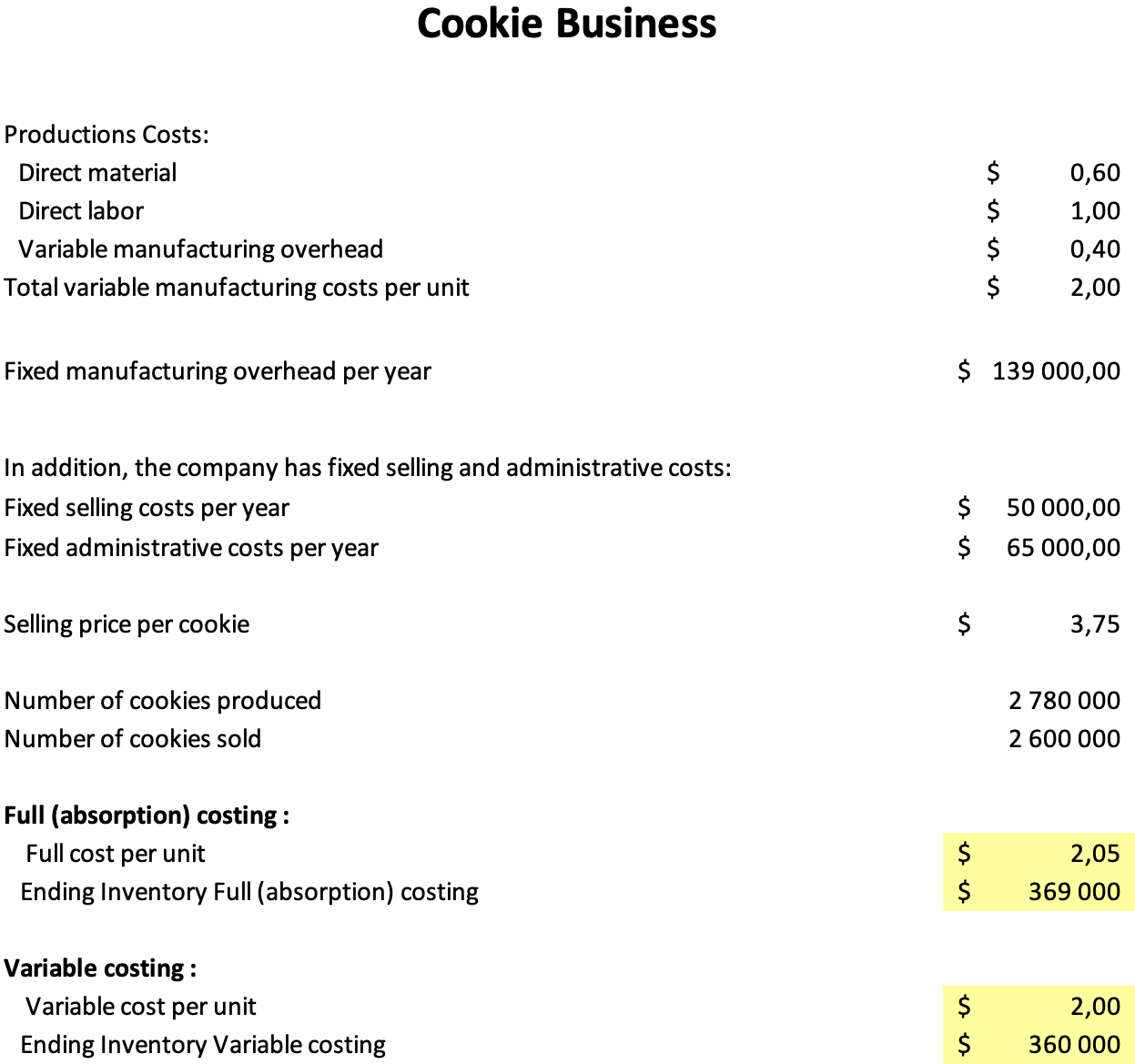
According to the findings, full or absorption costing is more valuable than variable costing when ending inventory. This is because only the variable costs related to creating a product are included in the price of goods sold with variable costing; in contrast, complete costing comprises both the fixed and variable expenses associated with producing a product. Full costing is better for managers since it provides a more accurate picture of the true cost of producing a product. Full costing also enables managers to make better choices on price and manufacturing by allowing them to determine each product’s profitability accurately.
Part 3 Special Order
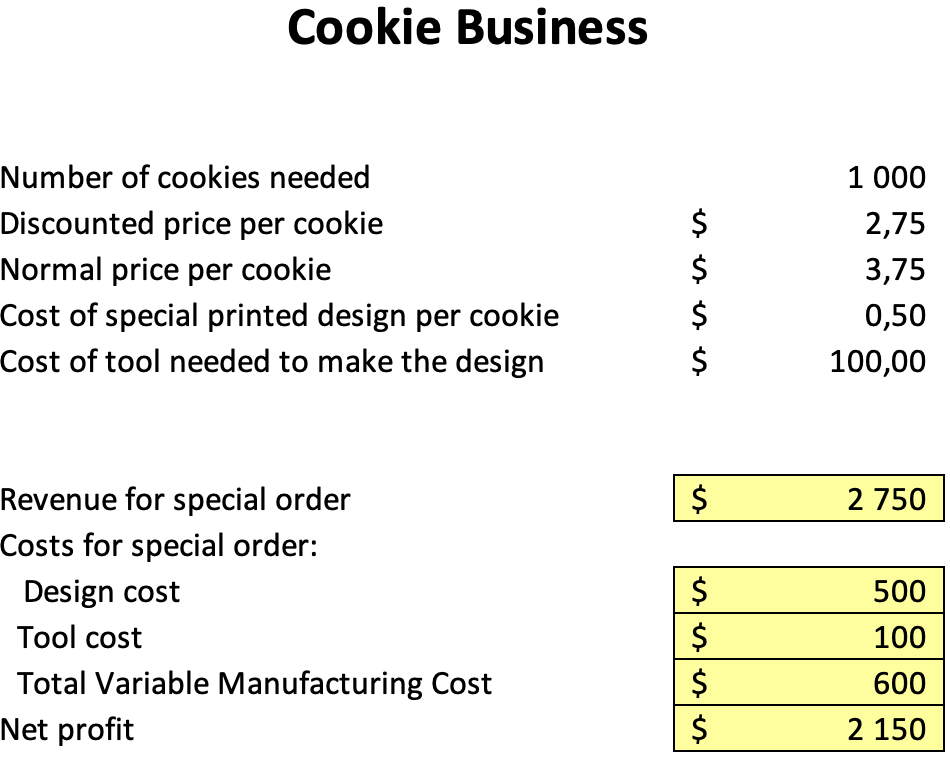
It is evident from the findings that accepting the particular order would result in a net gain of $2,150 for the cookie company. Since business has been sluggish lately, this specific order may generate much-needed revenue and profit. There are a few qualitative elements that should be taken into account to decide whether to accept the unique order or not.
The consumer is one of the most crucial elements. Is the client dependable and ready to make timely payments? It is crucial to judge their reliability because this can be a one-time client. An indicator that a customer is a good one and that the firm should accept their order is if they are prepared to pay more than the advertised price.
The risk associated with the particular order is a further crucial consideration to take into account. Is the customer requesting a large number of cookies that would take a lot of time and materials to make? If so, can the company handle the increased workload? It can be smart to turn down the order if the company is already stretched too thin and the particular order would consume too many of its resources. Finally, the company must consider how the special order will affect its current clientele. It might not be worth it if the special order uses resources and time from the regular clients.
Part 4 Internal Rate of Return
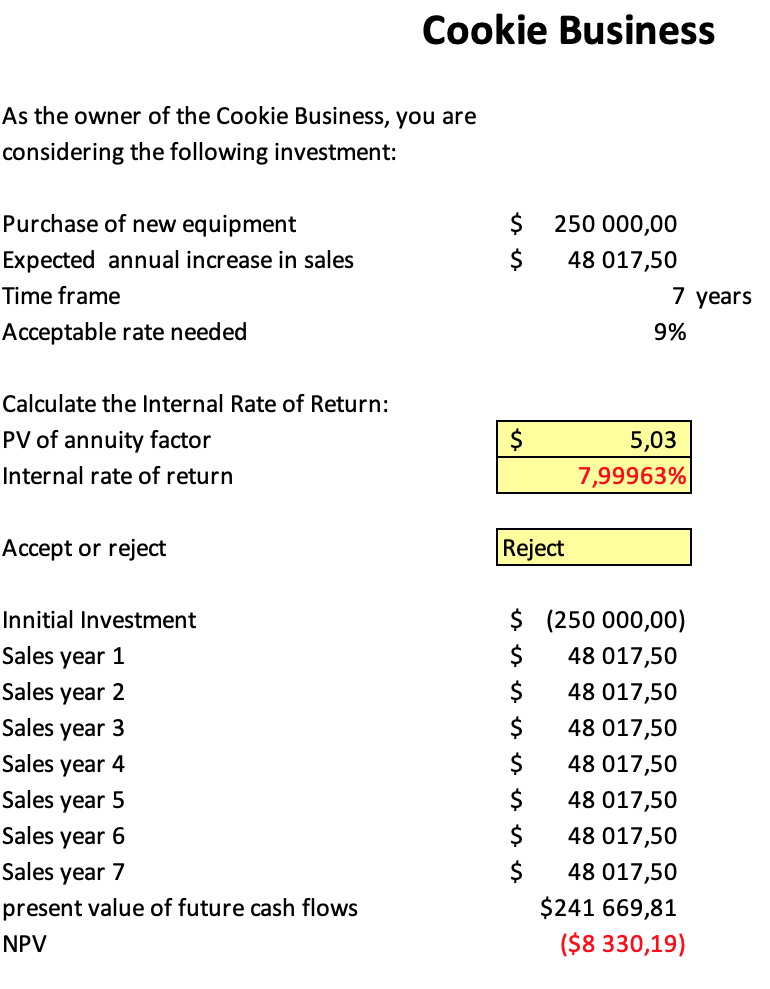
The new equipment’s calculated internal rate of return (IRR), which is 7.99963% lower than the statutory rate of return of 10%, should be rejected by the cookie company. This indicates that the potential profit from buying new equipment needs to be increased to justify the expense. Furthermore, the new equipment does not provide enough value to justify its acquisition, as shown by the $5.03 present value of the annuity component.
There are a number of ethical questions this sort of transaction raises. The fact that one of the partners is tied to the business that supplies the equipment creates the first potential conflict of interest. This might impact decision-making and result in machinery procurement, which may not be the optimal investment for the cookie business. Furthermore, the company to sell the equipment was chosen out of nepotism, which could cause the cookie company to pay more for the equipment than it would have otherwise. Lastly, the lack of transparency in the decision-making process could cause a gulf in trust between the partners and raise additional ethical questions.
Part 5 Cash Budget
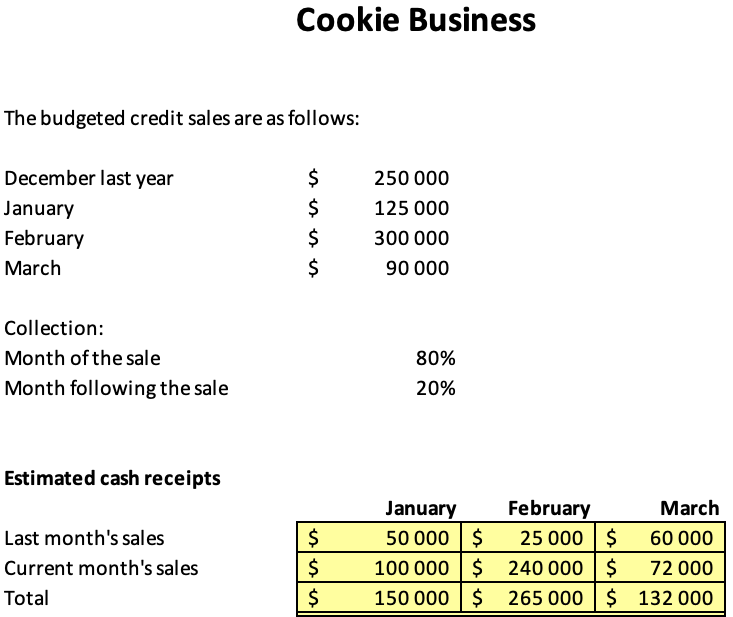
The figures above make it quite evident that the business requires more than $150,000 per month in expenses. The business needs to generate more revenue from its sales to cover its monthly costs. The company may need to investigate alternative revenue streams, such as loans, investments, or grants, to address this problem. The business should also grow sales to earn more revenue and cut costs. The company should also seek ways to cut expenses, such as locating more affordable suppliers or renegotiating current contracts. Finally, the business could consider raising pricing to improve its cash flow.
Part 6 Material and Labor Variance
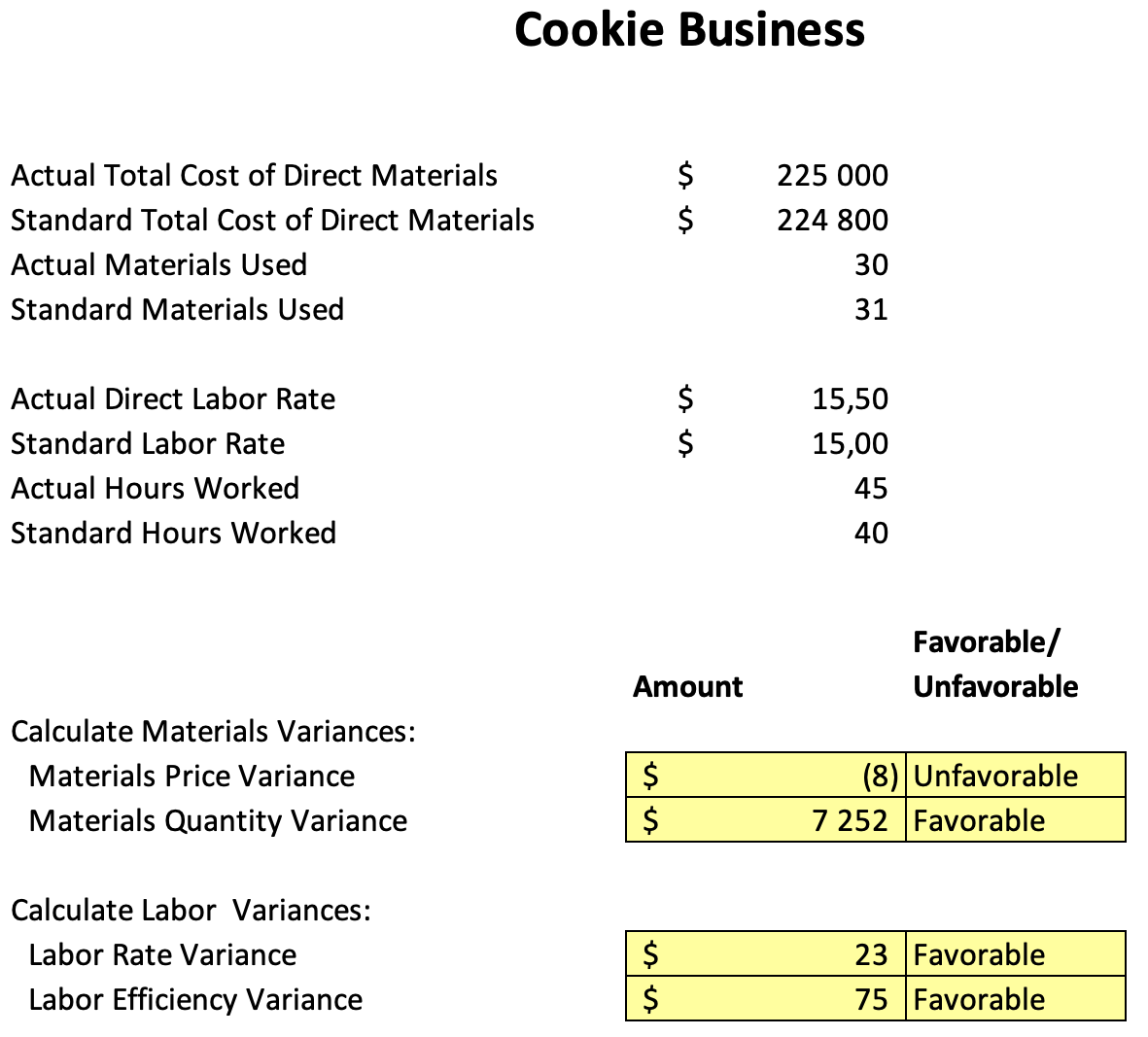
The materials price variation shows that the actual price of the materials was more expensive than the expected price of the materials. This might be the result of several things, including increased market prices, increased demand for the commodities, or the failure of the company to negotiate the lowest price for the materials. The business should consider haggling with suppliers for lower pricing or acquiring supplies from various sources to reduce this variance.
According to the materials quantity variance, the company used fewer materials than anticipated. This results from more effective material management or more productive production methods. The business should consider developing better inventory management procedures and ensuring that the appropriate quantity of materials is being ordered to reduce this discrepancy.
The Labor Rate Variance shows that the business spent less on labor than anticipated. This can result from reduced market wages or better labor force bargaining. The company should consider paying its workforce more and negotiating higher compensation to minimize this salary disparity.
The labor efficiency variance shows that the company produced more work than anticipated. This can result from better labor management or more effective production methods. The business should consider developing improved labor management rules and practices and ensuring that their production processes are efficient to reduce this variance.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The analysis of Shi’s Tasty Cookies indicates that specialty cookies have the highest contribution margin, full costing is more accurate than variable costing for inventory, accepting special orders can be advantageous, new equipment should be rejected, and the company should concentrate on growing sales and reducing costs. The company should consider additional revenue sources like loans, investments, or grants to boost sales. The company should also focus on finding more reasonable suppliers and renegotiating existing contracts to reduce costs. To lower its material and labor variations, the company should also endeavor to improve its labor management policies and production procedures.
References
Gutiérrez, M. (2021). Data, data flows, and model specifications for linking multi-level contribution margin accounting with multi-level fixed-charge problems. Data in Brief, 35, 106931.
Yalcin, S. (2019). Strategic Cost Management Process. Interdisciplinary Public Finance, Business and Economics Studies Volume II, 191.
 write
write