Introduction
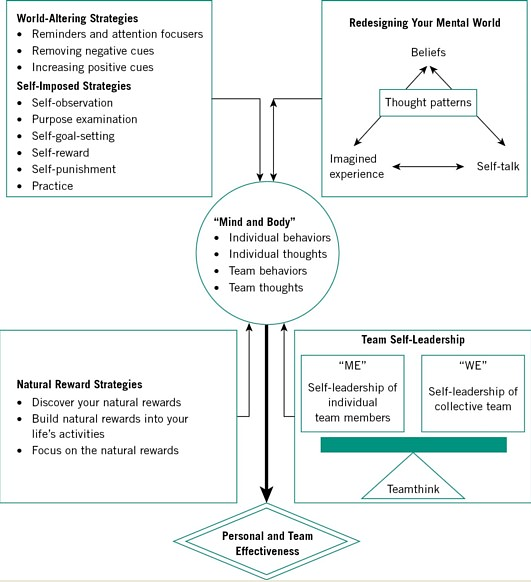
Successful leaders come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and no two leaders are same, just as no two situations or workplaces are alike. While it is correct to state that servant leadership is the most effective management style, this does not explain how a manager can be productive in any way. As a result, the personal leadership framework is put into action. Multiple elements in self-leadership interact to produce a comprehensive model by constructing a self-leadership plan to develop more efficient ways of working and living amid the turmoil of today’s society (Daud, 2020). The ultimate focus of self-leadership is on an individual’s actions, ideas, and sentiments, and how these are applied in their personal accomplishment. Natural reward methods, team self-leadership, world-changing strategies, self-imposed strategies, a reformed mental environment, the “mind and body,” and personal and team effectiveness all work together to affect efficiency through the use of numerous beneficial tactics. Leaders break old behaviors and create more productive and rewarding lifestyles by adding to each strategy.
Leaders are not born; they are developed (Daud, 2020). If a person has the desire and the determination, he or she can become an excellent leader. Good leaders emerge from a never-ending cycle of education, self-study, training, and experience. Simply said, leadership is the process by which a person persuades others to achieve a goal and directs the organization in the right direction that makes it more coherent and cohesive (Harari et.al, 2021). As a result, the framework’s areas of natural reward strategies, team self-leadership, world altering strategies, self-imposed strategies, a redesigned mental world, the “mind and body,” and personal and team effectiveness are used to evaluate primary leadership. I believe that with these leadership concepts one can become a very effective and influential leader.
Mind and Body
Individual behaviors, thoughts, team behaviors, and team opinions are all part of the mind and body. Leaders must recognize the importance of their own behaviors and attitudes in influencing the proper management of a business. Personal effectiveness entails cultivating a healthy conviction in one’s own strengths and worth as a person, as well as a fundamental and reasonably consistent sense of fulfillment in life (Jensen, Beaulieu & Neck, 2018). Personal effectiveness is not the same for everyone, but there are some common characteristics that may be identified in most scenarios. Each self-leadership method has the potential to influence an individual’s personal efficacy based on how they choose to manage a situation mentally and physically. As a result, the leader’s and a team’s thoughts and actions are useful for making good decisions and directing a group of individuals.
For a person to become a leader, one must first comprehend who they are, what they know, and what they can do. The followers, on the other hand, are the ones deciding whether the leader is successful. As a result, leaders must possess specific attributes that allow others to see them as good leaders (Harari et.al, 2021). Leader conduct refers to the characteristics and behaviors that make someone effective as a leader. Leaders use their behaviors to lead, coordinate, and influence the work of their teams. Although there are many innate characteristics that enhance leadership behavior, there are tactics and behaviors that leaders can work on to improve their performance and become more successful (Hanna et.al, 2021). My personal attributes, skills, and abilities, based on mind and body, are honesty, confidence, integrity, open communication, and the capacity to address team concerns.
Recognizing Personal Mental World
A leader must build a thought pattern that incorporates beliefs, self-talk, and imagined experiences in order to redesign their mental reality. Emotional intelligence is the product of a leader’s mental world. Emotional intelligence is defined as a person’s ability to detect, assess, and manage one ’s own emotions as well as the feelings of others or groups (Stewart, Courtright, & Manz, 2019). The most personal essential intelligence traits are knowing oneself, my thoughts, goals, actions, and reactions, as well as comprehending other people and their emotions. To be an effective leader, emotional intelligence is essential. Leaders who lack emotional intelligence are unable to evaluate the needs and goals of those they manage.
Leaders must be conscious of their mental world in order to avoid reacting emotionally. Without filtering their emotions, situations of mistrust arise among their team, and the leader’s working relationship is jeopardized (Hanna et.al, 2021). As a result, as a leader, I practice mental awareness so that I can assess how my emotions and behaviors affect those around me. I’ve also used my beliefs and imagined experiences, as well as self-talk, to develop a picture of my personal strengths and shortcomings, and then struck a balance to guarantee that the weaknesses don’t overwhelm the strengths. Self-control is also crucial to me since without it, I wouldn’t be able to avoid verbal attacks or make rash emotional decisions (Harari et.al, 2021).
Team Self-leadership
In his or her leadership style, a leader must always consider the components of “me” and “us.” A leader should be able to lead both individual team members and a larger group. I consider myself to be a transformational leader. This form of leadership draws on the foundations of transactional leadership, but adds four new attributes: idealized influence and charisma, which indicate that the leader is revered, admired, and respected; intellectual stimulation, inspirational motivation, and concern for others (Jensen, Beaulieu & Neck, 2018). As a transformative leader, I believe that supporting the corporate goals while also articulating subordinates’ goals is necessary to obtain their acceptance and dedication (Stewart, Courtright, & Manz, 2019). As a transformative leader, my behaviors may also be consistent. These leaders are also said to be honest, to have ethical ideas and values, and to be able to adapt to change.
Transformational leaders, in my view, have vision and the ability to excite and encourage their colleagues to share their goal. Complex moral ties between people are formed through obligations, trust, empathy, dedication, and a shared vision (Hanna et.al, 2021). On the other hand, ethics entails determining what is right and wrong in human behavior. As a result, ethics is at the heart of all human interactions. I believe I am able to use transformational leadership style to have an influence on an organizational and personal level because of the team-self leadership dimension.
Natural Reward Strategies
Natural reward strategies seek to create situations in which a person is motivated or rewarded by intrinsically enjoyable aspects of their profession or hobby. There are two types of natural reward techniques. The first entails introducing more pleasant and engaging qualities into a task so that it becomes naturally pleasurable. In order to shape impressions, the second strategy includes shifting attention away from the task’s disagreeable elements and toward the task’s intrinsically gratifying features. Both strategies are likely to develop feelings of competence and self-determination, which are two of the most fundamental intrinsic motivation strategies (Stewart, Courtright, & Manz, 2019). I use the notion of natural reward systems to instill a sense of competence and self-determination, which has been shown to motivate task-related behaviors that improve performance. I make sure to use self-control when assessing the workplace environment so that everyone, including myself, feels at ease. In addition, I use the natural reward approach to have a feeling purpose, which is linked to the behavior focus strategy because I typically want to make everyone around me feel better, which is an achievement.
Personal and Team Effectiveness
Self-leadership is a strategy of consciousness aimed at improving one’s own effectiveness. Self-leadership, which is based on the self-management concept, combines behavioral rewarding, goal-setting, intrinsic motivation, and positive thinking pattern tactics to increase people’s self-control and self-direction (Hanna et.al, 2021). Through enhanced self-focus, accurate feedback perceptions, appropriate goals, and higher levels of self-efficacy, self-leadership tactics are aimed to support effective personal self. The capacity to identify both individual and team goals is necessary for personal and team efficiency. Because self-leadership tactics allow team members to be more efficient in their resource allocation to achieving individual goals, self-leading team members should have more extra resources to devote to achieving team goals (Oxarart & Houghton, 2021). Given that personnel have limited resources (e.g., energy, time), self-leadership can help team members overcome time and resource constraints that could otherwise prevent them from participating to the team’s mission.
As a leader, I have personal ambitions based on personal effectiveness. Applying ethical values and spiritual well-being to make a big change in the world is one of my goals. Personally, I think that a person cannot lead everyone else if they do not have a clear understanding of who they are and what they strive to achieve. To strike a balance of the morality required to become a leader, my balance implies developing ethical standards and spiritual welfare. Another goal is self-efficacy, which includes my level of effectiveness in coping with the existing reality, as well as my view of my ability to handle difficulties and challenges. Its significance within the self-leadership framework is that when I am able to achieve success, my self-perceptions tend to improve, allowing me to improve current behaviors in a more intelligent, purposeful, and behavior-oriented manner, allowing me to lead others in the same manner.
World Altering Strategies
Complex and adaptable organizational structures, emancipated work structures, and employees’ professional self-directing conduct are all characteristics of significant changes in the nature of work in the 21st century (Oxarart & Houghton, 2021). Self-leadership – team members who set priorities, take charge, and resolve issues while taking personal ownership — is more crucial than ever in this collaborative, decentralized context. As a self-leader, I must cultivate self-influence in order to establish self-direction and self-motivation to achieve results. As a result, I’ve developed personal behavioral and cognitive tactics to help me be more effective. The purpose is to concentrate on success-oriented goals and objectives (Jensen, Beaulieu & Neck, 2018). I adopt a behavior-focused self-leadership method to support positive acceptable habits that bring success while inhibiting negative unwanted behavior that lead to failure. I am always well-informed about current behavior and performance levels so that, as an individual, I can be more effective in creating tough and precise goals that will considerably improve individual performance levels.
Self-Imposed Strategies
One of my self-imposed strategies is a behavior-focused method that incorporates self-observation, goal setting, reward, and punishment. For me, self-observation includes becoming more aware of when and why I engage in specific acts. This level of self-awareness is required before changing or removing ineffective and wasteful behaviors. Self-rewards can range from something as simple as mentally congratulating myself on a great accomplishment to something more serious, such as a specific vacation after completing a difficult project. Self-punishment is a constructive, introspective evaluation of failures and undesirable behaviors that results in their reformation (Oxarart & Houghton, 2021). I believe that my self-leadership paradigm is intended to improve goal and objective attainment through behavior-focused self-leadership strategies.
Conclusion
Every company has a chair, board chairman, or leader. In most cases, we agree that someone must be self-sufficient in order to lead enterprises and social groups. The leader of any organization is expected to fulfill his or her position by addressing the ideals of the institute that he or she represents. Managers must have leadership skills in order to work effectively at a planned level, and a competent manager will be capable of assessing personal skills in order to achieve strategic judgments and manage own leadership growth in order to assist achievement of scheduled aspirations. A superiority culture is promoted when a leader is capable of measuring the performance of the leadership strategy and promoting a healthy and benign environment. Therefore, self-leadership is intended to have a positive impact on one’s personal effectiveness.
References
Daud, Y. M. (2020). Self-leadership and its application to today’s leader-A review of literature. The. Strategic Journal of Business & Change Management, 8(1), 1-11.
Hanna, A. A., Smith, T. A., Kirkman, B. L., & Griffin, R. W. (2021). The emergence of emergent leadership: a comprehensive framework and directions for future research. Journal of Management, 47(1), 76-104.
Harari, M. B., Williams, E. A., Castro, S. L., & Brant, K. K. (2021). Self‐leadership: A meta‐analysis of over two decades of research. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 94(4), 890-923.
Jensen, J. R., Beaulieu, R. J., & Neck, C. P. (2018). The Self-Ac-tion Leadership Model: A Qualitative, Nomological Expansion of Self-Leadership Theory Rooted in Action Research. Journal of Lead-ership and Management, 2(11), 10-30.
Oxarart, R. A., & Houghton, J. D. (2021). A Spoonful of Sugar: Gamification as Means for Enhancing Employee Self-Leadership and Self-Concordance at Work. Administrative Sciences, 11(2), 35.
Stewart, G. L., Courtright, S. H., & Manz, C. C. (2019). Self-leadership: A paradoxical core of organizational behavior. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 6, 47-67.
 write
write