2.1 Overview
Chapter 2 is a further discussion of the research approach relating to cloud accounting in public governance. This chapter covers the definitions, current theoretical framework, theories and models that are equipped to explore the readiness to accept digitalization. These theories used to predict people’s acceptance behaviour over the years. TAM, UTAUT and TRI are trusted models in IT-related contexts with high accuracy in the employee’s nature. The models assist in measuring the direct impact of adopting cloud accounting whilst combating fraud. The key indicators and moderators of theories are also discussed in this section. Accordingly, this study initiates a thorough investigation of Selangor’s state government preparation in the accounting sector.
2.2 Empirical studies
Empirical studies provide a better understanding of the study that mainly examines the intention to adopt cloud accounting technology in the public sector taking keen consideration of the government organizations in the Selangor area in Malaysia. Raid & Alzoubi (2021), examined the of employees who mainly work in the public sector concerning the use of cloud accounting systems. The study used questionnaires to collect data from a large sample group in Selangor with the participants giving a variety of views. The outcome shows that the participants were well satisfied with the cloud computing systems in their organizations. The system was found to enhance the accessibility of financial data and hence play a crucial role in the productivity of the organization.
Lim et al. (2020) examined various aspects of using cloud accounting among government organizations in Malaysia. The study was mainly qualitative hence data was mainly collected through the help of the interviews which were provided to various managers and employees. The results show that the implementation of the technology led to improved data accuracy even though there were many obstacles. Another study by Ramdzuan (2021) evaluates the role of cloud accounting systems in the effectiveness and performance of workers in the organization among organizations. The study, mainly collected data through the use of questionnaires that enhanced effective completion of the research. The study found that cloud accounting technology has led to significant changes in the efficiency of organizations.
Khaliq et al. (2021) conducted a comprehensive study on the implementation of cloud computing in the management of organizations in Selangor. Based on the study, various factors including support provided by the organization and the perceived security are significant factors that enhance effective implementation of the technology. The findings showed that although cloud accounting technology adoption was generally highly desired, worries about data security and privacy continued to be major roadblocks. The study emphasized how critical it is to address these issues and offer sufficient guidance and assistance to promote successful adoption.
2.3 Research Gap
Despite the important information that is collected from the existing studies on the adoption of cloud computing, various gaps remain addressed. To begin with, there is a lack of enough research on the adoption of cloud computing technology specifically in Selangor state government organizations hence this might provide unique characteristics compared to other regions. Even though many studies have talked about the adoption of cloud computing in the public sector in Malaysia, few have targeted specific places in Selangor state which is one of the growing cities in the country.
Additionally, there is a lack of longitudinal studies regarding the adoption of cloud accounting technology over time. Longitudinal studies could provide a more thorough understanding of the factors influencing adoption dynamics. Even though many cross-sectional studies provide for snapshot of cloud accounting adoption at a single point in time, longitudinal research could address these issues more thoroughly.
Consequently, most of the existing studies have focused mainly on the internal factors that influence the adoption of cloud accounting, such as perceived utility, organizational support as well as ease of use. There is however less attention on the external factors that could also impact adoption decisions, like market competition, industry standards, and regulatory compliance requirements, A more sophisticated knowledge of the intricate adoption process and the development of focused treatments to aid in its implementation may result from investigating the interactions between internal and external influences.
2.4 Theoretical Framework of Technology Adoption
The underpinning theory of this research study is the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) will be discussed in the following section.
2.4.2 Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT)
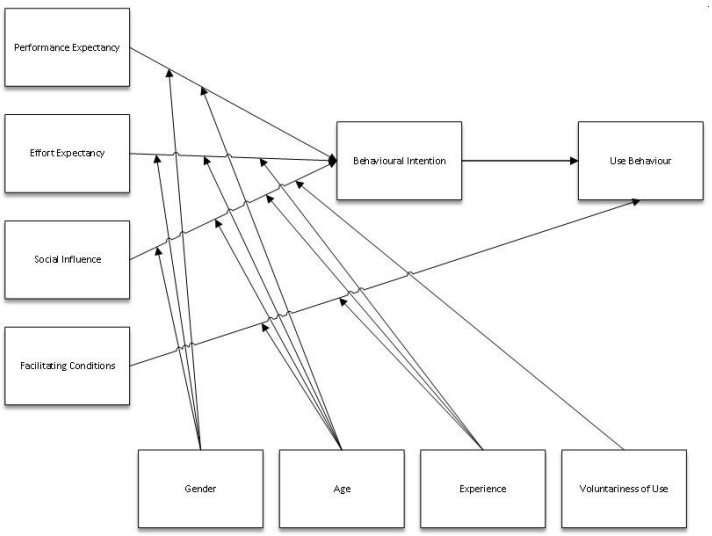
Figure 1: Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model (Venkatesh et al., 2003)
Venkatesh et al. (2003) formulated UTAUT from several other theories to develop a new framework. The framework encompasses behavioural intention that drives performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence and enabling conditions driven by the behaviour of the user. Gender, age, education and intention to use are influenced by the aforementioned formulation. In this study, UTAUT is used to examine which factors contribute largely to the intention to adopt cloud technology.
The enabling conditions are perceived to brace novel software. It includes a surveillance organization system, a supported server until the end-user and can run the database remotely ( Cota et al., 2023). Additionally, the UTAUT theory is executed thoroughly in studies relating to technology adoption and behaviour ( Popova & Zagulova, 2022). Thus, UTAUT is employed to delve into the managers’ and professionals’ acceptance of cloud accounting in local state public organizations.
2.5 Conceptual Framework
The illustration below provides the conceptual framework that enhances a significant understanding of the relationship between the dependent variables and the independent variables of the study. Performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence and facilitating conditions are the independent variables while behavioral intention to use cloud computing is the dependent variable.
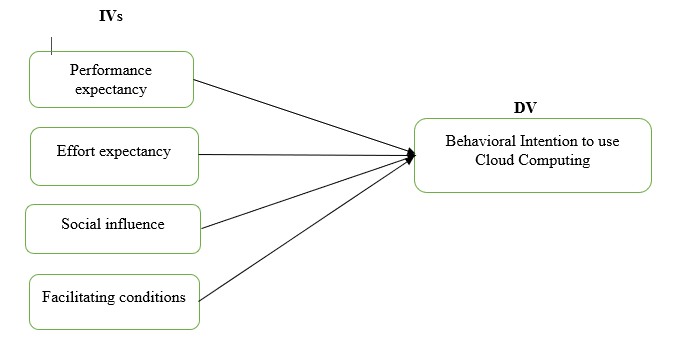
Figure 2: Conceptual framework
2.6 Literature Review
2.6.1 Performance expectancy
Performance expectancy is of significance in the adoption of technology especially the cloud accounting systems within the organizations. According to Venkatesh (2022), performance expectancy is a scenario in which people believe that they are using specific technology to enhance their productivity at work. Based on cloud computing, performance expectancy mainly consists of the perception of the usefulness of the technology in enabling efficient financial management processes and effective performance of the organization. Many studies have been provided by past researchers related to the significance of performance expectancy in enabling the effective adoption of cloud computing technology.
Qasem et al. (2020) provide a study on the the perception of workers regarding cloud computing systems in the public sector basically in Selangor. The findings of the study show that most of the respondents agreed that cloud computing systems are of great significance for their performance at work and that they had high behavioural intentions towards the adoption. This mainly implies that perceived usefulness has a significant effect on the intentions and attitudes towards the adoption of cloud computing systems.
Ramdzuan (2021) conducted a detailed study on the implementation of cloud accounting in the Selangor state government agency. The study mainly collected data through the help of interviews that were conducted among the major stakeholders. The results show that employees had a perception that cloud accounting systems were important in supporting their work hence all were willing to adopt it within their organizations. The aforementioned results underscore the significance of perceived utility in propelling user acceptance and adoption of cloud accounting technology within corporate environments.
According to Tırpan & Bakırtaş (2020), perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use of cloud computing systems have a significant influence on performance expectancy. People who tend to perceive technology as useful tend to find it easy to use it. Ali & Osmanaj (2020) provided that the employees in the public sector who found it easy to use cloud computing systems had a belief that the technologies would greatly impact their performance at work. This demonstrates how crucial training programs, system usability, and user interface design are in influencing how employees view their expected levels of performance.
A study by Porath (2023) provides that performance expectations for the implementation of cloud accounting are significantly shaped by organizational support and leadership endorsement. A technology that is strongly supported by organizational leaders and managers is most likely to be perceived as of great significance Kaushik & Guleria (2020) discovered that workers were more likely to think that technology will enhance their ability to accomplish their jobs if they felt management was strongly in favour of cloud accounting adoption. This emphasizes how crucial it is to use leadership communication and efficient change management techniques to promote favourable attitudes towards technology adoption.
2.6.2 Effort Expectancy
In the context of technology adoption, effort expectancy mainly provides for the perceived ease of use that is mainly brought about through the use of some given technology. Expectancy of effort is necessary to facilitate wise decision-making on the deployment of cloud computing systems in businesses. Lutfi (2022) provides for different impacts that cloud accounting systems have on organizations in Vietnam. The study mainly collects data through the use of the questionnaires hence the results show that interfaces and designs of the system played a significant role in creating positive perception regarding the use of cloud accounting technology.
Another study by Nguyen & Luu (2020) examines the effects that have been caused by the adoption of the cloud accounting system among SMEs in China. The outcome shows that the ease of use of the technology has enabled effective implementation. Participants who had a perception that the technology was easy to use had a higher intention of adopting cloud accounting solutions.
A study by Menon & Shilpa (2023) provides the view of the users concerning the amount of worth that is needed to enhance the effective implementation of cloud accounting. Based on the study, proper training and support from the management they tend to believe that the technology is user-friendly. Yang & Gu (2021) take keen consideration of understanding the effect of training initiatives on the intention to use cloud accounting systems. The study shows that employees who were given proper training on the use of cloud accounting technology had a good aspiration for its implementation.
A study by Ali et al. (2021) examines the perception of the users regarding the effort expectation and its effects on the performance of the system. The study provides that the technology that mainly satisfies the operations of the organization consistently will look easy to use. Consequently, Ali & Osmanaj (2020) take keen consideration of how effort expectancy affects the adoption of accounting systems in large businesses in the US. The study shows that effort expectancy had a significant effect on the effectiveness of the technology. This highlights how system stability and performance optimization impact users’ perceptions of effort expectations.
2.6.3 Social Influence
Social influences are mainly the level at which the decisions and behaviour of individuals are influenced by the opinions and perceptions of others within their social network. Social influence is important in the adoption of technology as it helps in enhancing decisions and intentions to use various technology types including cloud computing systems. This aspect mainly consists of different factors including social norms, peer influence and perceived views hence they tend to impact the decisions of the users to adopt the technology. Hsu (2022), examines various factors that tend to influence the intention to adopt cloud accounting systems among the accounting professionals basically in Taiwan. The findings show that cloud accounting has a strong influence on the social influence among the consumers with a higher percentage of the participants showing high intention to adopt the technology. This mainly; provides for an efficient understanding of how crucial peer relationships and social networks are in influencing how users view social impact.
Similarly to this, Tan (2022) looked at how social influence affected Malaysian small- and medium-sized businesses’ (SMEs’) adoption of cloud accounting systems. The results mainly show that cloud accounting was of great significance in enabling peer support among employees at work. The employees who were fully supported by their managers had a strong intention to use cloud computing technology.
Diener & Špaček (2021) provide for various external factors that tend to affect the view of individuals regarding social influence. Based on the study, regulatory guidelines and government policies have a significant effect on the adoption of cloud computing technology among public organizations. Chohan & Hu (2020) take a keen look into the factors that lead to the adoption of cloud accounting systems in government organizations basically in Singapore. Based on the study, the social influence of the employees is mainly determined by the initiatives that are implemented by the government. This primarily suggests that attitudes regarding a given technology are often affected by different external factors.
Heslina & Syahruni (2021) examines the role of corporate culture in enabling a positive influence on the adoption of technology. The study provides that clear guidelines and communication within the organization influence how the users view the technology whether desirable or undesirable. Liu (2023) carried out a detailed study regarding the effect that has mainly been caused by proper communication on the intention to adopt cloud computing technology. Based on the study, social influence led to great effects on the perception of the employees to adopt the technology. This study provides for a better understanding of the role of effective communication in enabling how users perceive social influence.
2.6.4 Facilitating Conditions
Facilitating conditions are those support structures that are provided to enhance the proper implementation of technology within an organization. In the context of cloud accounting adoption, the facilitating conditions include technical support and access to hardware and software that are necessary (Xu & Boudouaia, 2023). The conditions are important in enhancing the feasibility of adopting cloud accounting technology among organizations.
Different studies have been reviewed regarding the past studies on the effects of facilitating conditions on the effective adoption of cloud computing. Heslina & Syahruni (2021) provided a detailed study on various factors that tend to affect the intention of adopting the use of cloud computing technology in different organizations in South Korea. Based on the study, employees know how technical support affects their attitude towards using cloud computing. Many workers show good intentions about adopting the technology if they feel they have access to sufficient hardware and software, as well as competent technical assistance. This emphasizes how crucial it is to create favourable conditions to influence users’ opinions about the viability and preparedness of adopting new technologies.
Skafi et al. (2020) took keen consideration of the effects of facilitating conditions on the performance of SMEs in adopting the use of cloud computing technology. Based on the study, the readiness of the organization affects how cloud computing technology is implemented in the organization. Various factors including the privacy and security level affected the intention of the workers to gain a positive attitude towards adopting the technology among SMEs. This mainly provides for a better understanding of the significant ways of enabling efficient adoption of the technology.
A study by Walker (2024) examines the facilitating conditions that are mainly affected by sufficient knowledge and training. The study shows that employees who are given enough training opportunities have a high intention of using the technologies as they perceive them to be user-friendly. Jackson & Allen (2023) provided various ways in which the training initiatives affect the adoption of cloud account technology among public organizations in Singapore. The results showed that workers were more likely to believe that cloud accounting systems are realistic and to exhibit good intentions towards adopting them if they had received thorough training on how to utilize them. This emphasizes how crucial technical know-how and training are to creating favourable impressions of favourable conditions.
2.7 Hypotheses Development
This study intends to predict the future use of technology based on the integrated theories of TAM, TRI and UTAUT. TAM is defined as measuring an individual’s intention to use cloud accounting based on two variables namely perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use (Davis, 1989). The purpose of perceived ease of use is to predict the perceived usefulness of cloud accounting. Therefore, the hypotheses are developed as follows.
2.7.1 Performance Expectancy Towards Intention To Use Cloud Computing
Performance expectancy is determined as user acceptance and behaviour that reflects the user’s perception believed technology enhances job performance and productivity (Venkatesh et al., 2003). In this study, performance expectancy is defined as managers’ and professionals’ trust in cloud technology’s ability can perform daily work tasks superiorly.
Studies such as (Phuthong, 2022b; Islam et al., 2023; Jebreel et al., 2023; and Sallehudin et al., 2020) discovered a positive impact on ease of use and usefulness in routine. Thus, it is anticipated that organizations require cloud services to support task completion in operating productively, especially when data stored are relatively connected with other authorities (Islam and Karlsson, 2021). In this research, performance expectancy on perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness is also tested as moderators. Based on this notion, this research proposes the hypothesis related to performance expectancy:
Performance expectancy has a positive relationship towards the intention to use cloud computing
2.7.2 Effort Expectancy Towards Intention to Use Cloud Computing
In the context of technology adoption, effort expectancy mainly provides for the perceived ease of use that is mainly brought about through the use of some given technology. Effort expectancy is essential in enabling effective decision-making towards the use of cloud computing systems within organizations.
Studies such as Lutfi 2022; Ali & Osmanaj 2020; Ali, et al., 2021; Menon & Shilpa, 2023; Yang & Gu 2021 and Nguyen & Luu (2020) discovered a positive impact on effort expectancy and intention to use cloud accounting systems. Based on this notion, this research proposes the hypothesis related to effort expectancy:
Effort expectancy has a positive relationship towards the intention to use cloud computing
2.7.3 Social Influence Towards Intention to Use Cloud Computing
Social influences provide for the level at which the decisions and behaviour of individuals are influenced by the opinions and perceptions of others within their social network. Public institutions are monitored by social and regulatory factors when implementing technology. The absence of relevant laws to govern Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) and apprehension over safeguarding cloud-stored data from external vulnerabilities impact decision-making in the public sector (Hsu, 2022). Studies by Chohan & Hu, 2020; and Tan (2022) discovered social influence impacted positively the convenience of use and benefits for organizations. So, the following hypotheses are proposed:
Social influence has a positive relationship towards the intention to use cloud computing.
2.7.4 Facilitating Conditions Towards Intention to Use Cloud Computing
Xu & Boudouaia (2023) defined facilitating conditions in the context of technological factors as technical readiness to support networking, PCs and less time constraint to offer better working performance. A study by Skafi et al., (2020) found to support this notion. An individual’s experience using a set of technologies to enhance accuracy in decision-making contributes to its utilization as it only needs stable internet and devices (Jackson & Allen, 2023). Hence, the below hypotheses are formulated:
Facilitating condition has a positive relationship towards intention to use cloud computing.
2.8 Chapter Summary
This chapter emphasized the initiatives by the Selangor state government, underpinning theories used in this research, cloud accounting theories, and cloud accounting adoptions in public sector organizations. A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) was performed to examine empirical research on the adoption of cloud accounting. The objective was to identify the elements that influence the adoption of cloud accounting and classify them into technological, organizational, social, human, and environmental aspects. This chapter investigated 18 theoretical frameworks and frameworks. The research is desired to seek the appropriate theories to be adopted in this research based on the problem statement defined and the review of illustrated literature.
References
Ali, O., & Osmanaj, V. (2020). The role of government regulations in the adoption of cloud computing: A case study of local government. computer law & security review, 36, 105396. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0267364920300017
Ali, O., Shrestha, A., Ghasemaghaei, M., & Beydoun, G. (2021). Assessment of complexity in cloud computing adoption: A case study of local governments in Australia. Information Systems Frontiers, 1-23. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10796-021-10108-w
Chohan, S. R., & Hu, G. (2020). Success factors influencing citizens’ adoption of IoT service orchestration for public value creation in smart government. IEEE Access, 8, 208427-208448. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9248990/
Cota, D., Martins, J., Mamede, H., & Branco, F. (2023). BHiveSense: An integrated information system architecture for sustainable remote monitoring and management of apiaries based on IoT and microservices. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 9(3), 100110. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2199853123002123
Diener, F., & Špaček, M. (2021). Digital transformation in banking: A managerial perspective on barriers to change. Sustainability, 13(4), 2032. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/4/2032
Heslina, H., & Syahruni, A. (2021). The influence of information technology, human resources competency and employee engagement on the performance of employees. Golden Ratio of Human Resource Management, 1(1), 01-12. https://goldenratio.id/index.php/grhrm/article/view/100
Hsu, P. F. (2022). A deeper look at cloud adoption trajectory and dilemma. Information Systems Frontiers, 24(1), 177-194. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10796-020-10049-w
Jackson, D., & Allen, C. (2023). Technology adoption in accounting: the role of staff perceptions and organisational context. Journal of Accounting & Organizational Change. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JAOC-01-2023-0007/full/html
Kaushik, M., & Guleria, N. (2020). The impact of pandemic COVID-19 in workplace. European Journal of Business and Management, 12(15), 1-10. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Neha-Guleria-2/publication/353659460_The_Impact_of_Pandemic_COVID_-19_in_Workplace/links/6109085c1ca20f6f86f718be/The-Impact-of-Pandemic-COVID-19-in-Workplace.pdf
Khaliq, A., Umair, A., Khaniukova, R., Iqbal, S., & Abbas, A. (2021). Leadership and decision making among SMEs: management accounting information and the moderating role of cloud computing. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ansar-Abbass/publication/353134201_Leadership_and_Decision_Making_among_SMEs_Management_Accounting_Information_and_the_Moderating_Role_of_Cloud_Computing/links/60e94f980fbf460db8f5f62d/Leadership-and-Decision-Making-among-SMEs-Management-Accounting-Information-and-the-Moderating-Role-of-Cloud-Computing.pdf?_sg%5B0%5D=started_experiment_milestone&origin=journalDetail&_rtd=e30%3D
Lim, S. B., Malek, J. A., Hussain, M. Y., & Tahir, Z. (2020). Participation in e-government services and smart city programs: A case study of Malaysian local authority. Planning Malaysia, 18. https://mail.planningmalaysia.org/index.php/pmj/article/view/794
Liu, H. Y. (2023). Digital Taylorism in China’s e-commerce industry: A case study of internet professionals. Economic and Industrial Democracy, 44(1), 262-279. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0143831X211068887
Lutfi, A. (2022). Understanding the Intention to Adopt Cloud-based Accounting Information System in Jordanian SMEs. International Journal of Digital Accounting Research, 22. http://www.uhu.es/ijdar/10.4192/1577-8517-v22_2.pdf
Menon, D., & Shilpa, K. (2023). “Chatting with ChatGPT”: Analyzing the factors influencing users’ intention to Use the Open AI’s ChatGPT using the UTAUT model. Heliyon, 9(11). https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4340207
Nguyen, X. T., & LUU, Q. K. (2020). Factors affecting adoption of industry 4.0 by small-and medium-sized enterprises: A case in Ho Chi Minh city, Vietnam. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business (JAFEB), 7(6), 255-264. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/4102/8bd066f3aa789ff68616aa5514e394f3f2b6.pdf
Popova, Y., & Zagulova, D. (2022, March). UTAUT model for smart city concept implementation: use of web applications by residents for everyday operations. In Informatics (Vol. 9, No. 1, p. 27). MDPI. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9709/9/1/27
Porath, U. (2023). Advancing managerial evolution and resource management in contemporary business landscapes. Modern Economy, 14(10), 1404-1420. https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=128338
Qasem, Y. A., Abdullah, R., Yaha, Y., & Atana, R. (2020). Continuance use of cloud computing in higher education institutions: A conceptual model. Applied Sciences, 10(19), 6628. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/19/6628
Raid, M. A., & Alzoubi, H. M. (2021). The interplay among HRM practices, job satisfaction and intention to leave: An empirical investigation. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24(1). https://research.skylineuniversity.ac.ae/id/eprint/137/
Ramdzuan, I. H. M. (2021). Standard Accounting System For Government Agencies (SAGA) Implementation Readiness In Dungun Municipal Council (MPD) Dungun, Trengganu. http://library.oum.edu.my/repository/1384/
Tan, K. Y. (2022). Determining factors for the adoption of cloud computing among small and medium-sized enterprises during the covid-19 pandemic (Doctoral dissertation, UTAR). http://eprints.utar.edu.my/4971/
Tırpan, E. C., & Bakırtaş, H. (2020). Technology acceptance model 3 in understanding employee’s cloud computing technology. Global Business Review, 0972150920957173. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0972150920957173
Venkatesh, V. (2022). Adoption and use of AI tools: a research agenda grounded in UTAUT. Annals of Operations Research, 1-12. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10479-020-03918-9
Xu, Q., & Boudouaia, A. (2023). A study on technology use for sustainable graduate education internationalization at home: Chinese teachers’ experiences and perspectives. Sustainability, 15(13), 10621. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/15/13/10621
Yang, F., & Gu, S. (2021). Industry 4.0, a revolution that requires technology and national strategies. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 7, 1311-1325. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40747-020-00267-9
Walker, K. (2024). Employee feedback: how to provide feedback and recognition regularly. Strategic HR Review. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/SHR-12-2023-0069/full/html
 write
write