1. Change Management and Digital Transformation
The digital transformation process is critical to organizational development and competitive advantage in today’s technology-driven, fast-paced corporate environment (Langer & Yorks, 2018). Enterprises are radically altering their operational landscapes, customer interaction models, and strategic objectives as they adopt cutting-edge technologies, from big data analytics and the Internet of Things to cloud computing and artificial intelligence. The success of these revolutionary projects depends on their efficient administration. Change management’s function becomes crucial at this point. It provides companies with the structural support they need to navigate the challenges of digital transformation successfully. Change management ensures that technology innovations are smoothly incorporated into business processes and are consistent with company objectives and values by methodically planning, carrying out, and overseeing the change processes. Ultimately, this methodical approach improves the organization’s Ability to fully utilize digital advancements by reducing opposition and promoting an adaptive culture.
Change Management is essential to digital transformation because it ensures a smooth and systematic change in company operations, culture, and strategy. This discipline’s significance is increased because it serves as a uniting force and successfully aligns stakeholders and workers with the overall aims of digital transformation. It helps to methodically close the gap between new technological integrations and current processes by carefully planning and executing change projects. This congruence is essential to lowering the innate resistance that transformational processes frequently meet. Furthermore, cultivating an atmosphere of acceptance and adaptation is crucial for the effective integration of digital projects, and this is where Change Management comes in. According to Kraus et al. (2022), it guarantees that the shift is technically solid and strategically and culturally aligned with the organization’s mission.
In the context of digital transformation, there are several benefits to having an efficient change management strategy. It is a driving force behind improving an organization’s Ability to adapt, putting it in a position to react quickly and skillfully to the ever-changing markets and technology environments. It gives the workforce the abilities and perspective required to accept new technology and changing market trends by fostering a culture of change. This adaptability enables organizations to stay ahead in an ever-evolving business landscape and empowers them to seize opportunities as they arise. Additionally, Change Management safeguards against the inherent risks associated with digital transformation. It ensures that changes are effectively implemented and sustained in the long term, minimizing disruptions and maximizing the benefits. Coron and Gilbert (2021) noted that this approach is pivotal in safeguarding the organization’s investments and ensuring that the digital transformation journey yields lasting and favorable outcomes.
2. Change Management Model/Framework
2.1 ADKAR Model
For Digital Transformation projects, the ADKAR Model, developed by Prosci, is highly suitable. This model emphasizes individual change and ensures that each level of the organization is ready and willing to embrace technological changes.
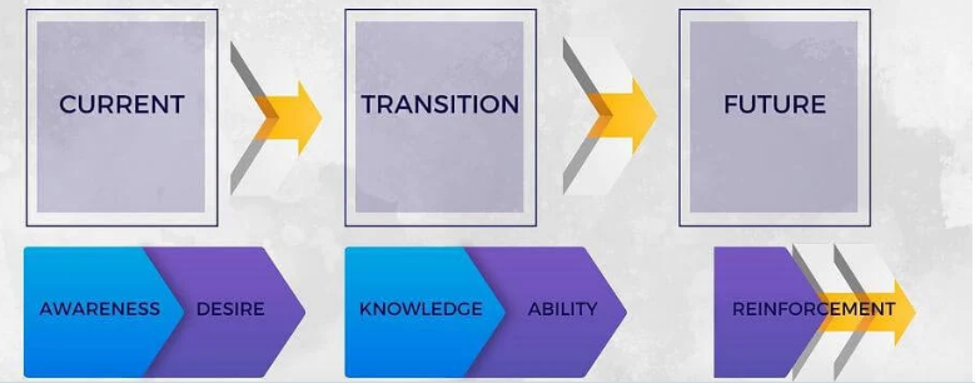
Figure1: ADAKAR Model
Source: (Johnson-Woods, 2023)
2.2 Justification
The choice of the ADKAR Model for Change Management in Digital Transformation projects is firmly justified by its meticulous alignment with the specific requirements of this transformative endeavor. The five key components of the ADKAR Model—Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement—act as a comprehensive framework that precisely caters to the multifaceted human aspect of change. In digital transformation, where technological advancements are integrated into every facet of an organization, addressing the human element becomes paramount. The model begins with creating Awareness, ensuring that individuals understand the need for change, and kindling a Desire for this transformation, motivating them to participate actively. Knowledge acquisition ensures that employees possess the necessary skills and understanding, while Ability guarantees their capability to implement new technologies effectively. Reinforcement reinforces these changes, ensuring their longevity. This systematic approach ensures that each organization member is on board and equipped to adapt to the evolving digital landscape, as underlined by Johnson-Woods in 2023, making the ADKAR Model an ideal fit for digital transformation endeavors.
3. Change Management and Disruptive Technologies
3.1 Differences in Approach
Distinguishing between Change Management approaches for disruptive technologies and non-disruptive digital transformation is essential, as the nature of these initiatives presents contrasting challenges. Disruptive technologies, characterized by their potential to revolutionize industries and alter conventional practices, necessitate a distinctively agile and flexible approach. Unlike non-disruptive digital transformations, which often involve incremental changes, disruptive technologies introduce fundamental shifts that demand unparalleled dynamism and innovation in managing change. This is primarily because disruptive technologies can swiftly render existing processes, products, and business models obsolete. Therefore, change management needs to be proactive and flexible in disruptive technologies, ready to welcome unanticipated advances and use innovation to forge new paths. The necessity of this dynamic approach is emphasized by Roberts (2023), who emphasizes that successful Change Management is characterized by the capacity to quickly adjust and react to disruptive forces in the era of disruptive technology. Top of Form
3.2 Key Differences
The differences between change management and disruptive technologies are very noticeable, and this calls for a change in emphasis to innovation, quick adaptation, and an ongoing learning culture. Disruptive technologies bring about changes of a never-before-seen scope and speed, in contrast to non-disruptive digital transformation, which may involve gradual and controlled adjustments. Change management needs to place a high priority on innovation and create a culture that actively supports new ideas in order to handle this instability properly. It becomes critical for firms to adapt quickly to keep up with new technology and changing market conditions. Furthermore, it takes a culture of continuous learning to remain ahead of disruptive forces since it shows a dedication to gaining new skills and information. The pace and scale of change are typically far more substantial in disruptive technology scenarios, demanding a robust and proactive Change Management approach that can not only navigate the turbulence but also harness it for competitive advantage.
3.3 Key Success Factors (KSFs)
Key Success Factors (KSFs) play a pivotal role in determining the effectiveness of Change Management in digital transformation projects. Firstly, effective communication stands as a linchpin among these factors. Transparent and clear communication is essential in disseminating digital transformation’s objectives, progress, and benefits to all stakeholders. It fosters understanding and buy-in from employees and stakeholders at every level of the organization. Furthermore, it ensures that any concerns or doubts are addressed promptly, reducing resistance and increasing acceptance. Communication becomes essential for establishing alignment and trust in the quickly changing digital transformation world, where ambiguity can stoke opposition (Islam & Evans, 2020).
Secondly, activities to bring about digital change can only be successfully guided with strong leadership. The attitude of an organization toward change is determined by its leaders. Their dedication to the change, participation, and unified messaging highlights how important the project is. Good leaders energize and excite their groups, fostering passion and commitment to the objectives of the digital transition. They are also essential in deciding how best to allocate resources, make strategic decisions, and handle problems that may arise during a shift. Put, capable leadership offers the direction and foresight required to negotiate the challenges of digital change successfully.
Engaging stakeholders is another essential KSF. It is ensured that the transformation aligns with the demands and interests of important stakeholders by including internal and external parties. It encourages a feeling of responsibility and dedication to the project’s accomplishment. Stakeholders can also offer insightful comments and insights that help guide decisions and course corrections, improving the transformation effort’s overall efficacy (Samadhiya et al.,2023). Finally, constant feedback methods must be included for continual development and modification. Since digital transformation is dynamic, feedback loops help firms spot obstacles, adjust to changing conditions and improve their tactics. Frequent feedback helps firms keep on course and shows that you are committed to agility and responsiveness, which are critical traits in the digital age. Together, these KSFs help ensure that new technologies are successfully adopted and that transitions go smoothly, resulting in the successful completion of digital transformation projects and the desired outcomes.
4. References
Coron, C., & Gilbert, P. (2021). Managing Technological Change. Digital Transformations in the Challenge of Activity and Work, 225–236. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119808343.ch17
Islam, S., & Evans, N. (2020). Key Success Factors of PRINCE2 Project Management Method in Software Development Project: KSF of PRINCE2 in SDLC. International Journal of Engineering Materials and Manufacture, 5(3), 76–84. https://doi.org/10.26776/ijemm.05.03.2020.02
Johnson-Woods, C. (2023). What is the ADKAR Model of Change Management? [Review of What is the ADKAR Model of Change Management?]. Resonance. https://www.resonanceglobal.com/blog/what-is-the-adkar-model-of-change-management
Kraus, S., Durst, S., Ferreira, J. J., Veiga, P., Kailer, N., & Weinmann, A. (2022). Digital transformation in business and management research: An overview of the current status quo. International Journal of Information Management, 63(4), 102466. ScienceDirect. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2021.102466
Langer, A. M., & Yorks, L. (2018). Strategic Information Technology: Best Practices to Drive Digital Transformation. In Google Books. John Wiley & Sons. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=1_xlDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR11&dq=digital+transformation+stands+at+the+forefront+of+organizational+development+and+competitive+edge&ots=V-mfe_-R0Y&sig=btEr7ZGpne2nXZ4ofSppcBHzy3M
Roberts, D. P. (2023). Managing Change from Disruptive Innovation: United States Property & Casualty Insurance (Doctoral dissertation, Franklin University). https://search.proquest.com/openview/62e593c915cdc2c61b6eb9abc21221f7/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y
Samadhiya, A., Agrawal, R., & Garza-Reyes, J. A. (2023). Investigating the influence of total productive maintenance key success factors on the social sustainability dimension of manufacturing SMEs. Benchmarking: An International Journal. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/BIJ-05-2022-0287/full/html
 write
write