Abstract
Supply chain management is essential to achieve operational excellence, customer happiness, risk mitigation, cooperation, strategic advantage, innovation, sustainability, and social responsibility since it acts as the driving force behind these objectives. It allows firms to successfully negotiate the intricacies of global marketplaces, adapt to difficulties, and capitalize on opportunities, which is critical in guaranteeing organizations’ long-term performance and profitability. This function is essential because it is crucial in ensuring organizations’ long-term performance and profitability.
Over the last several years, Walmart has been subjected to tremendous changes, most of which have been brought about by globalization. As a direct consequence of this, Walmart has broadened the scope of its operations and now engages with a broader consumer base in a variety of locales all over the globe. This growth in new areas has brought many benefits to Walmart, including a reduction in operating expenses and an improvement in the effectiveness of the supply chain. These advantages are a direct result of the firm’s expansion and increased capacity to efficiently manage and improve its supply chain. To deal with the challenges that affected the overall supply chain system during the beginning of the pandemic, some of the actions Walmart took were hiring additional staff to ensure they could move inventory throughout facilities as swiftly as possible and chartered ships to divert shipments through less congested ports these are just a few of the things which were done to assist with dealing with challenges. This paper will analyze the Global Supply Chain Challenges Walmart faced during the pandemic and how it streamlined its SCM processes during Covid-19.
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving global marketplace, supply chain management is critical in ensuring an organization’s long-term performance and profitability. Particularly in times of unforeseeable global events, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, the importance of supply chain management cannot be overstated (Collings et al., 2021). Walmart, one of the world’s largest retail giants, faced several critical challenges in managing its supply chain amid the pandemic. These challenges range from supply chain disruptions, workforce safety concerns, inventory management, and reduced consumer demand (Banker, 2022). Despite these challenges, Walmart adopted various innovative strategies to streamline its supply chain management processes. The objective of this paper is to analyze the global supply chain challenges Walmart faced during the pandemic and how it streamlined its SCM processes during Covid-19. Particularly highlighting the key methods and practices Walmart adopted to optimize its supply chain management processes amidst the pandemic’s unprecedented difficulties. Through comprehensive research and data analysis, this paper intends to shed light on the significance of effective supply chain management in ensuring business continuity and resilience amid unforeseeable global challenges.
Walmart’s Supply Chain Structure Overview
Walmart is renowned for its robust and efficient SCM system, which significantly ensures product availability and competitive pricing for its customers. This intricate network begins with manufacturers, moves through distribution centers, and passes through logistics operations and retailers, eventually reaching consumers. Finally, overseeing and ensuring smooth operations is the company headquarters (Check Appendix 1).
Manufacturers
Walmart has formed potent alliances with thousands of suppliers from all over the world. These partners manufacture products spanning various categories to satisfy the needs of Walmart’s vast and varied customer base. The retailer sources items from domestic and global manufacturers who comply with Walmart’s rigorous ethical and sustainability requirements to secure cost efficiency and top-notch quality (Francis, 2021). The positive relationships allow Walmart to acquire the desired goods at more reasonable prices, thus diminishing expenses along the supply chain and shielding buyers from any extra financial burden. Consequently, consumers reap the fruits of savings that result from these partnerships. However, the unprecedented pandemic proved challenging for many, especially Walmart’s suppliers and manufacturers. They had to navigate several issues to continue doing business, such as workforce disruptions, transportation challenges, and even raw material shortages (Rose et al., 2023). To top it off, they were under immense pressure to ensure their operations continued with little hindrance. Moreover, all changes had to be actioned at lightning speed so that business could go on as normal – or close as possible – despite unprecedented challenges.
Distribution Centers
Walmart boasts a wide and complex distribution network encompassing more than 150 strategically located distribution centers in the United States. These fulfillment centers store and manage inventory before sending it to related retail outlets. Additionally, Walmart has consolidation centers that accept merchandise directly from manufacturers equipped with advanced technology, enabling them to consolidate shipments expeditiously (Rose et al., 2023). On top of that, their Cross-Dock system minimizes storage times and dramatically lowers inventory costs by directly transitioning products from inbound to outbound trucks. As the world grappled with the pandemic, Walmart’s distribution centers were burdened with handling unprecedented levels of goods. This massive shift resulted in a surge of pressure, forcing Walmart to make operational adjustments. Not only did this involve a complete restructuring of organizational processes—but the company also had to ensure that minimum standards for service were met while providing an acceptable level of customer satisfaction (Lauchlan, 2020). As lockdown orders spread around the country, supply chains needed to adapt quickly and efficiently to handle volatile changes in demand volumes. Walmart representatives acknowledged supply chain challenges amid this sudden spike, taking appropriate steps to modify their practices and remain agile. To match rising output needs, thus increasing their responsiveness and efficiency, Walmart optimized several operational parameters.
Logistics
Walmart’s supply chain efficacy is anchored upon its logistics management. Boasting one of the largest private truck fleets on the planet, plus expansive rails around the globe, Walmart further secures its distribution capability. A sophisticated satellite communication system embeds their trucks, stores, and distribution centers, ensuring that deliveries arrive on time and routes are planned with astuteness (Francis, 2021). These are all main contributors to Walmart pushing the boundaries regarding shipment speed and reliability. During the COVID crisis, this sector has seen numerous impediments, including deficiencies in the driver labor force and a choppy course of delivery. Moreover, further requests from the unprecedented use of e-commerce services gave new difficulties that makers need to address.
Retailers
Touted for its ‘Everyday Low Prices’ mission, Leonard (2021) notes that Walmart has established an expansive network of 11,000 retail locations worldwide. This network spans multiple formats, such as Supercenters, Neighborhood Markets, and Sam’s Club warehouses, to guarantee that customers are afforded quality services and the most competitive prices on the market. Furthermore, Walmart has capitalized on e-commerce capabilities allowing customers the convenience of shopping online and services such as curbside pickup and home delivery (Ashcroft, 2022; Alwan et al., 2023)). With over 11 thousand outlets sharing a commitment to accessible value, Walmart continues to foster a strategy for success.
Inventory Management and Store Operations
Walmart’s inventory management teams ensure that the desired products arrive in the right stores at adequate levels. Building on data analytics and forecasting, their responsibility has become more multifaceted as it is their job to calculate demand and surpass it accordingly (Leonard, 2021). Unpredictable shifts in shopper patterns entailed by the pandemic altered this dynamic significantly, necessitating increased flexibility within the department. At the retail level, Walmart store personnel made up a core component in leading operations during these uncertain conditions (Francis, 2021). They met quotas for what should go on shelves while being aware of safety protocols; additionally, they had to contend with heavier than usual foot traffic, all before this same unit was attributed an even bigger part due to the unpredicted boon that online orders received.
E-Commerce and Online Fulfillment and Third-party Vendors and Partners
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a dramatic shift in consumer shopping habits. Industries worldwide experienced an influx of online shoppers as measures like lockdowns and social distancing put a halt to in-person store visits (Ashcroft, 2022). To capitalize on this change, Walmart saw the opportunity to invest heavily in expanding its e-commerce platforms and introduce new services, such as curbside pickups and same-day delivery. Additionally, by collaborating with third-party vendors, Walmart has provided other essential services that become even more important during a pandemic. These include financial services, pharmacy operations, and healthcare solutions, which have opened up physical access limitations many customers experience due to measures put in place by governments responding to the pandemic.
Consumers
Walmart has an ambitious mandate for its supply chain strategy – to enable customers to have optimal shopping experiences. They strive to offer broad, varied assortments of products and the lowest prices available to accomplish this. Their comprehensive data monitoring system makes such successes possible; customer needs and preferences are regularly analyzed to readjust inventory and repeatedly respond quickly to customer demands (Rose et al., 2023). With intelligent data analytics and diligent product stocking, Walmart can be ready for any consumer circumstance requiring quick solutions.
Company Headquarters
Walmart’s corporate headquarters are in Bentonville, Arkansas. Various departments unite to achieve the overall organizational objectives of Supply Chain Management, Global Sourcing, Transportation, and Merchandising (Zhang, 2023). These divisions work together to form healthy global supplier-Shopper relations by maintaining convenient distribution pathways. Walmart holds sustainability at the forefront of its mission while leveraging technological infrastructure like Data Café and machine learning to monitor better and optimize its trajectories (Francis, 2021). This visionary approach is critical for successful supply chain management. Therefore, Walmart’s supply chain structure is an intricate network of manufacturers, distribution centers, logistics systems, retailers, and consumers. The company’s headquarters are pivotal in overseeing and continuously enhancing this efficient system, enabling Walmart to become a global retail leader.
Challenges Faced by Walmart During the Pandemic
Inventory Management Challenges
The onset of the pandemic proved an abrupt challenge for Walmart, one of the world’s largest retailers. Its inventory management team encountered irregular rate-shifted demand patterns and drastic changes in consumer behavior (Rose et al., 2023). With movement restricted across the globe, essentials such as groceries and cleaning supplies were prioritized while traditionally popular non-essential products such as clothing receded sharply in demand. The warehouse was expected to meet rush orders for necessary goods while struggling to avoid acquiring surplus stock for heavier selling items (Leonard, 2021). Consequently, Walmart juggled supply curves almost entirely antithetical inputs: immediate needs vs scarce anticipation. This shift in demand required Walmart to recalibrate its inventory strategies, striking a delicate balance between maintaining adequate stock levels of essential products and avoiding excess inventory of non-essential items.
The disruptions in the supply chain during the pandemic further compounded Walmart’s inventory management challenges. The global nature of the pandemic meant that supply chains worldwide were impacted. Many suppliers faced factory closures, reduced production capacities, and transportation delays due to lockdown measures and labor shortages (McKay, 2021). Consequently, Walmart experienced delays in receiving inventory from its suppliers, affecting its ability to restock popular items promptly. The uncertainties in the supply chain led to difficulties in accurately forecasting inventory needs, making it harder for Walmart to anticipate and address sudden fluctuations in demand. Also, the perishable nature of some products posed a particular challenge for Walmart’s inventory management during the pandemic. With disruptions in transportation and storage capabilities, there were instances of food spoilage and wastage (Zhang, 2023). Maintaining optimal stock levels of perishable items became more challenging as demand and supply fluctuations affected the availability of cold storage and distribution capabilities. Walmart had to enhance coordination with suppliers, distribution centers, and stores to minimize waste and manage perishable inventory effectively.
Furthermore, the pandemic presented Walmart with numerous supply chain obstacles. Countries put restrictions on movement and production, leading to significant delays and interruptions between suppliers and Walmart’s distribution centers. Consequently, the replenishment of goods sold could not be immediately prompted even though there was an increased demand for certain items (Sánchez-Flores & Serna, 2021). This issue was compounded by a startling reduction in demands on non-essential commodities, resulting in excessive inventory generated; Walmart’s stockpile incorporated holding charges and eventual wastefulness. The pandemic made it evident that reliable contingency plans and security inventory reserves are paramount strategies in countering the aftereffects of disturbance among outlets. Consequently, it became necessary for Walmart to acquire buffer stock which provided a safety net against Supply chain disturbances and unforeseen boosts in demand levels, although largely such backup comes with additional costs related to its storage setup (Segal, 2021). Balancing safety stock requirements while optimizing inventory levels became a delicate balancing act for Walmart’s inventory managers.
The COVID-19 pandemic saw a shift to more prominent e-commerce, thus bringing forth daunting inventory management challenges. Amid customers leaning toward online shopping, Walmart had to have an eagle-eye view of inventory to keep stockouts at bay and fulfill orders accurately (Locke et al., 2023). To enable these results, Walmart invested in sophisticated inventory tracking systems and integrated data across sources for maximum accuracy. These challenges brought on by the pandemic included sudden gaps in demand patterns and unforeseeable interruptions in the supply chain. Walmart, however, navigated these obstacles with adept use of technology and clever optimization of its supply chain through data-driven approaches. It was well-equipped to manage changes in the external environment (Sánchez-Flores & Serna, 2021). The lessons learned during this period likely informed and improved their future inventory management strategies, ensuring they remain adaptable and resilient even in uncertain times.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Risk Mitigation
The Covid-19 pandemic brought unprecedented disruptions to global supply chains, and Walmart, one of the world’s largest retailers, faced significant challenges in navigating these uncertainties. Many factors, including factory closures, transportation restrictions, labor shortages, and increased demand for essential products, caused supply chain disruptions. These disruptions impacted Walmart’s ability to promptly receive products and services from suppliers, leading to stockouts and inventory shortages (Jin et al., 2021). The sudden and severe disruptions in the supply chain made it difficult for Walmart to maintain consistent inventory levels and fulfill customer demands. Risk mitigation became a critical aspect of Walmart’s operations during the pandemic. As supply chain disruptions intensified, the company had to proactively identify and address potential risks to ensure the continued availability of essential goods. This involved diversifying the supplier base to reduce reliance on a single source for critical items. By working with multiple suppliers, Walmart aimed to mitigate the impact of supply chain disruptions caused by localized outbreaks or factory closures in specific regions (Zhang, 2023). Additionally, Walmart strengthened communication and collaboration with suppliers to gain better visibility into their supply chain capabilities and potential risks, enabling them to develop contingency plans.
One of the major challenges Walmart faced was predicting and planning for future disruptions. The Covid-19 pandemic was unprecedented, and the duration and severity of its impact were uncertain. This made it challenging for Walmart to forecast demand accurately and anticipate supply chain disruptions in the long term (Banker, 2022). The company leveraged data analytics and predictive modeling to assess various scenarios and simulate potential risks to address this. Using these advanced tools, Walmart aimed to gain insights into how different disruptions might affect their supply chain and inventory levels, allowing them to prepare for contingencies and plan accordingly. The pandemic also highlighted vulnerabilities in Walmart’s supply chain and distribution network. The company had to ensure that inventory was distributed efficiently and quickly from distribution centers to stores to meet changing demand patterns. With transportation disruptions and increased pressure on logistics services, Walmart had to optimize its distribution routes and explore alternative transportation options to avoid delays and bottlenecks. Moreover, with the shift towards e-commerce, the demand for online deliveries surged, putting additional strain on Walmart’s distribution network (Ashcroft, 2022). The company had to quickly adapt to these changes and invest in technologies and processes to enhance last-mile delivery capabilities and ensure timely order fulfillment.
Furthermore, consumer behavior changes during the pandemic further complicated risk mitigation efforts. As customers stockpiled essential items, the demand for certain products skyrocketed, leading to supply shortages and inventory imbalances (Ovezmyradov, 2022). On the other hand, the demand for non-essential items plummeted. Walmart had to adjust its inventory allocation and distribution strategies to ensure essential items were available while minimizing excess inventory of non-essential products. This involved dynamically reallocating inventory across stores and online platforms based on real-time demand data. Therefore, the Covid-19 pandemic presented numerous challenges for Walmart’s supply chain, including disruptions in sourcing, transportation, and distribution and uncertainties in demand and consumer behavior. Risk mitigation efforts became crucial for the company to navigate these challenges successfully (Zhang, 2023). By diversifying suppliers, leveraging data analytics, optimizing distribution networks, and adapting to changing consumer demands, Walmart aimed to strengthen its supply chain resilience and ensure a steady supply of essential goods to meet customer needs during the pandemic and beyond. The lessons from this experience likely informed Walmart’s strategies to enhance risk management and supply chain preparedness for future unforeseen events.
Abrupt Increase in Demand
The sudden increase in demand posed a major challenge for Walmart’s supply chain management during the COVID-19 pandemic. As the virus spread and lockdown measures were implemented in various regions, consumers began buying panic, stocking up on essential items like toilet paper, sanitizers, and canned goods (OECD, 2021). This unprecedented surge in demand led to a massive strain on Walmart’s supply chain, initially designed to handle more predictable and steady demand patterns. The rapid and unpredictable increase in consumer buying behavior overwhelmed the company’s ability to maintain adequate inventory levels, resulting in empty shelves in many of its stores (Mrozek, 2022). One of the primary difficulties Walmart faced was the unpredictability of consumer behavior. Traditional demand forecasting models, which relied on historical data and patterns, became less reliable as the pandemic brought about sudden and drastic changes in purchasing habits. The lack of accurate forecasting made it challenging for Walmart to accurately anticipate the surge in demand and proactively adjust its inventory levels (Luo, 2022). Consequently, the company had to react in real-time to the evolving situation, which sometimes led to shortages of essential items, causing customer frustration and dissatisfaction.
The sudden increase in demand also put immense pressure on Walmart’s supplier network. With consumers rushing to purchase essentials, suppliers experienced a surge in orders and requests from multiple retailers, including Walmart. The global nature of Walmart’s supply chain meant that many of its suppliers were located in regions heavily affected by the pandemic, such as China and other Asian countries (Rose et al., 2023). Lockdowns, factory closures, and labor shortages in these regions disrupted production and shipment schedules, further exacerbating the supply chain challenges. Another significant issue that arose from the surge in demand was inventory allocation. With consumers in different regions panic-buying various items, Walmart had to prioritize and allocate inventory to the hardest hit areas by the pandemic. Ensuring an equitable distribution of essential goods across its vast network of stores while considering the varying severity of the pandemic’s impact on different communities was a delicate balancing act (Luo, 2022). This process required clear communication and collaboration with suppliers to coordinate the timely delivery of products to the right locations.
Walmart recognized that investing in technology and automation would aid its operations as it faced the challenge of labor shortages during the COVID-19 outbreak. Automated checkouts, inventory management systems, and robots taking on repetitive tasks acted as replacements for manual labor, optimizing efficiency even with a reduced workforce (Rose et al., 2023). These detailed precautions allowed the company to remain in operation during this time of heightened demand and constant alarm while adequately serving its customers. By anticipating how this situation might impact them, Walmart leveraged technology to streamline operations and minimize any consequential effects of the deficiency of human resources they relied on before COVID-19.
Labor Shortages
Labor shortages presented a significant challenge for Walmart’s supply chain management during the COVID-19 pandemic. As the virus spread, many employees fell ill or were required to quarantine due to potential exposure. This decreased the available workforce, affecting various parts of the supply chain, including distribution centers, stores, and fulfillment centers. Walmart was rocked to its core when workforce reductions in its distribution centers and warehouses led to operational disruptions. With fewer workers able to pick, pack, and ship products, the efficiency and throughput of these facilities were seriously impacted (Chaturvedula, 2022). This decreased replenishment rates for stores, causing shortages of essential items across the board. On top of everything else, panic buying from concerned consumers contributed even further to the inventory issues that Walmart was experiencing, making it near impossible for them to restock quickly enough to meet steadily increasing demands.
The COVID-19 pandemic reduced Walmart’s staffing, causing existing employees to be tasked with heavier workloads. This additional pressure resulted in concerning levels of fatigue, which in turn consumed valuable mental energy otherwise needed for daily workflows; small execution errors due to physical and emotional burnout are highly likely (Collings et al., 2021). Furthermore, immense weight was laid upon the shoulders of individuals picking and packing items separately for distinct customers with high expectations from their shopping experiences. Consequently, thorough quality checks and powerful performance are essential to the now more labor-intense Walmart system. Also, the pandemic intensified the surging demand for e-commerce orders driven by customers spending more time shopping online. Walmart’s supply chain labor force needed additional workforce and resources to fulfill and deliver these orders, creating a burden due to the increased volume accompanied by labor shortages (Ashcroft, 2022; Lauchlan, 2020). This spike in e-commerce demanded greater focus on last-mile delivery and more strategic approaches toward fulfillment not to strain the existing workforce.
Moreover, Walmart faced significant labor shortages and needed to recruit and train additional staff amid an international pandemic. Finding suitable applicants was challenging due to constantly evolving health and safety guidance. Ensuring all onboarding factors stayed compliant with necessary regulations and guidelines substantially complicated the training process for new employees (Zhang, 2023). Content those uncertainties, Walmart achieved a successful onboarding process that enabled fresh talent ready to begin working as quickly as possible. In Walmart’s brick-and-mortar stores, the effects of labor shortages caused by the coronavirus pandemic constantly shifted (Check Appendix 2). Staffing levels vary between stores, causing a turbulent atmosphere and problems driving consistent customer service. The flux in manpower inevitably resulted in a lack of operational continuity, leading to store closures when a disproportionate amount of employees fell ill or were placed into quarantine (Banker, 2022). This eventually led many Walmart locations to reduce hours significantly as an additional risk mitigation measure.
Government Regulations
As the impacts of Coronavirus spread across the globe, many government regulations were put in place to limit its transmission. These included lockdowns, curfews, and taxes, which presented several significant challenges for Walmart’s supply chain management as they attempted to navigate the ever-evolving environment (OECD, 2021; Banker, 2022; Chaturvedula, 2022). These measures had a far-reaching effect on almost every facet of Walmart’s day-to-day activities, with the potential and ongoing changes requiring swift action and strategic agility from Walmart’s leadership team to maintain operations effectively and without disruption.
Walmart felt the impacts of government-imposed restrictions on international trade and cross-border movement on their sourcing and procurement processes. Though suppliers were located in different countries, delays and disruptions forced the company to find alternative, efficient solutions (Locke et al., 2023). To reduce supply chain obstacles, goods that were essential for Walmart had been restricted from shipment, pushing them towards stronger relationships with local suppliers while offering alternative sourcing methods. Crafting these ties was essential so stores would be graced with ample products despite all outside challenges. Also, the pandemic brought about tremendous change across the various transportation and logistics networks worldwide. Lockdowns and other types of restrictions on movement caused considerable strain on transport and logistics (McKAY, 2021). With sea freight and air freight capacity significantly reduced along with several borders shutting down, moving goods became ever more difficult and costly for Walmart and other companies.
Store Operations experienced drastic changes due to governmental restrictions. Walmart stores had to adjust their opening and closing times and limit the number of shoppers allowed inside at any given time (Xu et al., 2022). This emergency protocol also affected employee schedules, creating difficulties for managers tasked with organizing efficient staffing protocols. Existing procedures had to be reworked to meet legal regulations and protect customer safety. Therefore, government regulations impact most of the components of Walmart’s supply chain. It affected the transportation and distribution of commodities because of lockdowns and curfews (OECD, 2021). Also, they disrupted store operations resulting from safety concerns and low workers turnout. As a result, the corporation had to adjust its supply chain system to meet the current market demands.
Communication and Collaboration
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Walmart faced various significant challenges related to its supply chain management. The unexpected nature of the pandemic meant a lack of preparedness in terms of communication strategies and collaboration. With global logistics partners, coordinating essential information became difficult since teams had to work remotely (Ovezmyradov, 2022). Furthermore, face-to-face interactions were restricted, making expressing intricate supply chain concerns more challenging via virtual communication tools. This again posed complications in ensuring the effectiveness of essential exchanges. Also, the pandemic caused a demand for essential products, like food items, cleaning supplies, and PPE. With an abrupt increase in consumer needs, all eyes fell on Walmart’s supply chain to keep up. As missing products, low stock levels, and changes in customer behavior arose—it became clear that quick communication channels were needed across its manufacturer partners, suppliers, distribution centers, and stores (Segal, 2021). Unfortunately, the pre-existing means of communication between these various stakeholders were inadequate for this unprecedented shift in needs.
Many suppliers faced production halts, decreased employees available for work, and issues with international shipments led to delays and uncertainty. Because of this, Walmart was tasked with adapting quickly to the changes while effectively coordinating efforts with their suppliers to come up with viable alternatives. Despite these measures, communication deficits and compartmentalized processes created challenges regarding the flow of critical information that would have helped promptly identify potential issues along the chain and expedite solutions (Rose et al., 2023). Also, the unexpected nature of the pandemic meant a lack of preparedness in terms of communication strategies and collaboration. With global logistics partners, coordinating essential information became difficult since teams had to work remotely. Furthermore, face-to-face interactions were restricted, making expressing intricate supply chain concerns more challenging via virtual communication tools (Locke et al., 2023). This again posed complications in ensuring the effectiveness of essential exchanges.
Moreover, as the global Covid-19 pandemic developed, so too did the regulations by numerous governments and health authorities. This was particularly impactful for a large organization like Walmart, which needs to coordinate operations among multiple regions worldwide. Each region found the need to adhere to an increasingly complex set of guidelines, creating the challenge of communicating those changes efficiently across such a wide structure (Chaturvedula, 2022). With no unified communication platform and additional complexities associated with disseminating information, Walmart had faced one of its biggest challenges yet – ensuring everybody within their network remained updated on regulations and steered clear of compliance in light of these ever-changing regulations. Therefore, the COVID-19 pandemic posed several obstacles to Walmart’s supply chain management. Not only was the rapid onset of the crisis extremely challenging, but many essential products were in higher demand due to isolated circumstances (Jin et al., 2021). Additionally, disruption in much of their supplier networks and the need to continually adhere to updated regulations hurt necessary communication infrastructure– making cooperation throughout their supply chain difficult.
How Walmart Adjusted to Deal with These Challenges
Inventory Management
In the face of customers stocking up on essentials and supplies, Walmart encountered unprecedented inventory management challenges. To meet the growing consumer demand while avoiding possible losses due to overstocking, the company rolled out a sophisticated system combining advanced analytics with tracking of buying patterns. This new, data-driven approach allowed Walmart to modify its supply chain, reducing empty shelves both online and in their stores — all to keep customers gratified (Alwan et al., 2023). Also, Walmart channeled strategic investments toward addressing the issues arising from the pandemic, including revamping its inventory management strategy to set up a new system for guided auto ordering by sales analysis. All measures contributed to maintaining product availability on the shelves and attaining optimal supply chain discernibility. Walmart’s success in weathering these pandemic times highlighted the importance of making decision data dependent during this current crisis and when contingency plans are established for the future (Luo, 2022). Ultimately, Walmart puts at ease its customers by successfully upholding an efficient stock turnover and reliable supply chain network.
The company prioritized increasing its ability to analyze data. Mindful of the competitive edge of advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning, Walmart invested time and funds in its development aggressively. During times of crisis, like the pandemic seen in recent months, this investment has manifested into a useful instrument to anticipate demand oscillations and gain insight into consumer behavior, allowing Walmart to adjust inventory levels accordingly promptly (Ashcroft, 2022). With real-time information at their disposal, they can have all variables when determining which products they will stock up on while arriving at a sensible estimate for their replenishment process, not forgetting wisely appropriation across its scores of overflowing stores and distribution centers. Also, Walmart had to adapt truly and pivot to a more flexible and agile approach to inventory management for their stores. The traditional forecasting models were not designed to adjust quickly to abrupt moderate peaks in customer demand during the pandemic. To allow better customization, they explored opportunities with dynamic inventory replenishment systems (Lauchlan, 2020). This would help them adjust stock levels more frequently and provide avenues for improved efficiency. Moreover, the company kept track of consumer behavior through accurate data tracking and trend analysis of customer preferences. Thereby predicting inventory needs well in advance. Moreover, this assisted in managing unwanted surpluses while avoiding out-of-stock situations.
Despite lockdown and restriction restrictions, Walmart ramped up its e-commerce capabilities and leveraged its extensive store network for order fulfillment. Consumers noticed the shift online, translating into a surge in online orders. Walmart quickly met such increased demand by optimizing its inventory management system to ease consumer buying power. But having an effective inventory management system was not enough. As such, Walmart took the next step in providing customers with the ultimate seamless shopping experience– they utilized their physical stores as distribution centers, allowing customers to enjoy options like curbside pickup and same-day delivery when desired (Segal, 2021). This creative approach helps further distinguish Walmart from competitors regarding customer service and digitalizing the shopping experience. Also, Walmart rose to the challenge of improving its inventory management system to ensure a smooth supply of products and services. Walmart partnered closely with its suppliers and vendors to find creative solutions to ensure an unbroken supply. The partnership looked at alternative sourcing options, increased safety stock levels for critical items, and navigated logistics challenges that arose (Luo, 2022). By working collaboratively with its partners, Walmart identified disruptions and found ways to ensure the availability of these essential items for customers during this critical period.
As a solution to the inventory management challenges caused by the pandemic, Walmart invested in its workforce. The company suffered from widespread shortages in the past year due to various factors, such as employees falling ill or needing to quarantine. Recognizing its unprecedented challenge, Walmart decided to cross-train its employees to maintain operations and protect against future employee issues. Apart from offering workers benefits like cross-training opportunities, Walmart also looked for additional ways to attract and motivate them while work became challenging amidst these trying times (Leonard, 2021). Therefore, Walmart tackled the inventory management challenges posed by the pandemic with a multifaceted approach. To ensure success during uncertainty, they utilized advanced data analytics to guide decisions, implemented a flexible replenishment system, collaborated closely with their suppliers, heightened ecommerce capabilities, and invested in their workforce (Ashcroft, 2022). These efforts were not just helpful for surviving immediate disruptions — Walmart crafted strategies that positioned them for a more resilient future when dealing with inventory amid potential future obstacles. With these initiatives, they met their customers’ needs while adapting to rapidly evolving demands and established an infrastructure that helps establish long-term stability.
Supply Chain and Risk Mitigation
The COVID-19 pandemic posed unique challenges for Walmart’s supply chain. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, factory closures, and surging demand for certain products all resulted in an unsettled environment. To guard against and protect its operations from these risks, Walmart developed proactive strategies to impede disruptions. One such strategy was to diversify the explicit suppliers it worked with to reduce physical difficulty regarding those countries or regions more heavily impacted by the virus (Zhang, 2023). Specifically, Walmart sought multiple other sourcing options in multiple geographic locations. This allowed them to rapidly transition production in the event of a disruption or shortage of supplies at any given supplier. Evidently, this moved as a defense into Walmart’s arsenal in response to contending with supply chain Roadblocks resulting from COVID-19. Additionally, Walmart’s wide product range allowed the company to adapt to changes in consumer demand as customer preferences shifted in response to the pandemic (Molly Kinder et al., 2020). For example, the company rapidly scaled up its delivery and pickup services to meet the surge in online orders during the pandemic.
Moreover, Walmart took swift action in response to the pandemic’s disruptions to the supply chain. To evaluate the risks posed by the pandemic, they established a COVID-19 task force comprised of interdisciplinary experts from their company’s logistics, procurement, and legal divisions. This specially appointed task force was responsible for continuously analyzing and responding to risks throughout the crisis (Luo, 2022). Walmart implemented several measures to minimize disruptions. They increased inventory levels across warehouses and altered routes of shipments to help during substantially chaotic times. Direct connections with domestic suppliers allowed Walmart to expedite certain products during this uncertain interval in the supply chain. Also, the corporation sought to take a collaborative approach with its suppliers to improve communication and visibility throughout the supply chain. Accomplishing this required consistent team dialogue, allowing Walmart to more quickly anticipate problems and address situations as a joint effort whenever possible (Zhang, 2023). Furthermore, Walmart displayed high transparency between them and their suppliers. Sharing sales figures and inventory forecasts enabled them to appropriately plan for future needs from manufacturing to distribution, thus greatly minimizing the risk of stockouts.
Walmart showed an exemplary commitment to the security of their staff and also the wider community. The company explicitly invested in tactics to protect individuals employed in the distribution centers and shops, such as delivering Personal Safe Guards equipment (PPE) and finalizing social distancing rules (Zhang, 2023). These preventive activities were fundamental not only for taking care of the well-being of its workers but also crucial for guaranteeing supply chain management during these critical outbreak moments. Usually, protecting workers generated an efficient network for Walmart so that displays were kept vibrantly open and goods secured, ready to go up to customer request. Also, Walmart was aware of the potential risks posed by a specific kind of emergency, such as an outbreak or pandemic, and had incorporated many different contingency plans to help mitigate those dangers. Before facing this crisis, these steps were already in place, allowing the massive company to adapt its practices immediately to go with the continually shifting circumstances (Grace, 2022). Specifically, it altered its dynamics to prioritize e-commerce while augmenting its delivery contributions simultaneously; furthermore, Walmart modified underlying supply chain protocols. Moreover, additional protection was available through enlisting strategies centered around safeguarding against port complications, closedowns, and service alterations resulting from unexpected savings shortages.
Labor Shortages
As the novel Coronavirus spread across the globe, so did its effects- impacting businesses like Walmart, which encountered unrestrained labor shortages. Causes of these scarcity issues lacked variety: disease outbreaks causing some employees to fall ill, imposed quarantines requiring workforce absence, and difficulty accessing various childcare options (Jin et al., 2021). Walmart weathered this unique predicament by applying a bevy of crucial strategies to fulfill the demand for depleting relief items while dispensing critical functions.
Amid the pandemic, Walmart was determined to keep its workforce safe. The company heavily invested in sustainable measures and protocols, with employee safety at the core of its operations. Comprehensive safety standards were implemented both in store locations and distribution centers. This encompassed supplying personal protective equipment such as masks and gloves, promoting social distancing practices among employees, and recovering high-touch points with frequent disinfectant use (Xi et al., 2022). All measures are driven by the commitment to firmly establishing an environment where everyone can feel safe by continuing their work in all spheres of stores’ functioning, even amidst a global crisis. Also, to attract and retain employees during the stark labor shortages, Walmart offered various incentives and benefits. In addition to providing additional pay or hazard pay for frontline workers who vowed to stay in service even while at risk from the pandemic, Walmart drastically expanded its benefits programs (Zhang, 2023). Encompassing innovations such as enhanced sick leave policies and childcare assistance, the features gave their employees assurance during these trying times. Not only did this hold present employers in place, it successfully drew new talent to match up with gaps in staffing.
Moreover, Walmart was determined to keep its workforce safe during the pandemic. The company heavily invested in sustainable measures and protocols, with employee safety at the core of its operations. Comprehensive safety standards were implemented both in store locations and distribution centers. This encompassed supplying personal protective equipment such as masks and gloves, promoting social distancing practices among employees, and recovering high-touch points with frequent disinfectant use (Zhang, 2023). All measures are driven by the commitment to firmly establishing an environment where everyone can feel safe by continuing their work in all spheres of stores’ functioning, even amidst a global crisis. Also, the company sought out partners in temporary staffing agencies to meet their labor demands at peak times. This approach allowed the retailer to promptly and readily hire extra help when employees were unavailable, or more hands were needed, particularly during holidays or the most frantic pandemic (Luo, 2022). Each temp began with fixed skills that qualified them for essential tasks, allowing Walmart to remain operational without being hampered by shortages in the workforce.
Government Regulations
Walmart addressed Government regulations sensitively during the COVID-19 pandemic to improve supply chain management. Taking compliance and safety measures paramount, the company collaborated with government agencies, distributed essential goods adeptly, dealt with transport constraints courageously, and developed emergency response plans flexibly. All of this was enabled by its adoption of technology and data analytics tools (Alwan et al., 2023). These strategies put Walmart in a pivotal position to meet future disruptions, facilitating better service to their customers even as they intricately observed laws entertaining societal activities yet still maintained a strong commitment towards citizens’ health and welfare.
Walmart quietly prioritized strict compliance with government regulations and guidelines related to health and safety while doubling down on its commitment to public health. To ensure the safety of its employees and customers, it implemented protocols throughout its stores, distribution centers, as well as logistics operations, including things like enforcing social distancing requirements, mandatory mask usage, more frequent sanitization of high-touch surfaces, and limiting the number of shoppers inside each store at a single time (OECD, 2021; Zhang, 2023)). By meeting and, in most cases exceeding established safety standards and governmental body guidance about health and safety, Walmart proved their dedication towards abiding by protocol while significantly reducing any potential risks from non-compliance.
Collaboration with Government Agencies has been a major priority for Walmart. The company undertook many initiatives to ensure compliance with the latest governmental regulations and guidelines surrounding the supply chain during this pandemic (Segal, 2021). This included engaging in regular dialogue with health authorities and policymakers, where Walmart could share its experiences and best practices regarding successfully managing its supply chains. With these conversations, Walmart acquired valuable insights into potential policy changes. It positively influenced said policy decisions, guaranteeing that its global supply chain remained efficient and resilient in the long term.
Abrupt Increase in Demand
Walmart faced the rapid increase in consumer demand caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, which necessitated an extensive response strategy. To address this challenge, the company collaborated with suppliers and established new supply chains; invested in technology and logistics capabilities; adapted a flexible pricing approach to accommodate changing market dynamics; and prioritized its employees’ and consumers’ health and safety (Forehand et al., 2021). These collaborative efforts enabled Walmart to respond to mounting pressure from the pandemic more effectively while pricing goods competitively and ensuring continued access to essential supplies.
Walmart implemented a dynamic pricing strategy to accommodate changes in market conditions. This allowed the company to tailor its prices and promotions in real-time and stay price competitive. Walmart compared competitors’ rates to bolster its competitive advantage and promptly adjusted its prices. Walmart introduced certain customer incentives to increase sales, such as waiving delivery fees and minimal order requirements (Luo, 2022). Additionally, discounts were offered on bulk purchases of essential items, which strongly encouraged consumers to stock up during these uncertain times of heightened precautionary measures and lockdowns. Also, Walmart set up new supply chains to guarantee customers had the supplies they needed under any circumstances. Walmart formed integral connections with new producers and vendors outside its usual community to compensate for insufficiencies (humanimpact.org, 2021). Additionally, Walmart shipped their products more quickly by ship and plane from countries less affected by the pandemic. In addition, to guarantee that vital commodities came directly to customers’ hands, the mortgage credit letter template Walmart created further conduits for curbside pickups and residence delivery.
Walmart implemented a far-reaching strategy to optimize inventory management and order fulfillment. This included investing heavily in logistics and technology, with significant innovation across automation, AI, and machine learning algorithms that enabled forecasting customer needs and demand criteria to divvy up resources more accurately. The deployment of robots in the picking and packing orders significantly increased accuracy for customers receiving their deliveries on time (Luo, 2022). Walmart additionally leveraged its expansive network of physical stores to facilitate order fulfillment, thanks to rapid delivery between these regional distribution centers. To ensure employees felt secure and protected during the COVID-19 pandemic, Walmart altered worker incentives, providing sick leave cover alongside inflationary bonuses for those going above and beyond regarding understaffed tasks (Grace, 2022). Communal safety also received due attention from Walmart in their rollout of technological upgrades that minimized cause for viral detection risk transmission throughout their property infrastructure aboard thermal scanners and contactless card payment systems at all stores associated with the company.
The role of Walmart’s Supply Management of its Performance and Profitability during Covid-19
Amidst the Covid-19 pandemic, Walmart’s supply chain management team was challenged to maintain product availability. Consumer behavior shifted to panic buying and stockpiling groceries leading to an extraordinary surge in demand for essential products. The supply chain team developed measures to ensure optimal stock levels at their distribution centers and stores to combat this shift in buying patterns (Leonard, 2021). At the forefront was efficient inventory management, a strategy that requires tracking up-to-date sales data, consumption trends and assessing supplier performance from a data perspective. Only with diligent oversight could Walmart replenish inventory accordingly and ensure customers had access to vital goods. The importance of demand forecasting in anticipating consumer needs cannot be underestimated. Walmart’s supply chain team employed extensive historical sales data, market trends, and insights from various sources to predict variations in demand and adjust their inventory appropriately and accurately. Establishing positive relationships with suppliers was another key factor in product availability. Through these channels of open communication, Walmart was able to share pertinent information regularly and identify potential areas of concern in the supply chain promptly (Chaturvedula, 2022). This collaborative network enabled Walmart to devise effective strategies to tackle disruptions conveniently and look elsewhere if a main supplier struggled with exigencies.
Walmart could sustain its illustrious professionalism and remain consistent in supplying essential products. This proved reassuring to existing customers and all new prospecting ones searching for a solid and dependable retail provider. Greater stock availability encouraged more people to shop in Walmart stores, and retailing with worldwide customers sustained static shopping through Walmart, giving them confidence despite rocky times (Forehand et al., 2021). This enabled Walmart’s perseverance during an unpredictable economic climate many others struggled against. The efficient inventory management, accurate demand forecasting, and careful collaboration with suppliers all rocked the policymaking decision processes so well that it allowed Walmart far into profit during such moments of vast contact scarceness from buying perceptive relating enterprises, helping complete certainty with Walmart’s strategic continuity.
Moreover, during the Covid-19 pandemic, managing disruptions and demand surges was a paramount challenge for Walmart’s supply chain management team. The global supply chain faced significant upheaval, with various regions experiencing factory closures, transportation restrictions, and labor shortages (Banker, 2022). Walmart’s supply chain team had to act swiftly and decisively to address these disruptions. They closely monitored the evolving situation and proactively identified potential bottlenecks in the supply chain. By doing so, they could develop contingency plans to ensure a continuous flow of goods to their stores and distribution centers. One of the key strategies Walmart’s supply chain team employed was identifying alternative suppliers. They worked closely with existing suppliers to assess their capabilities and explored options with new suppliers locally and internationally. By diversifying their supplier base, Walmart could reduce dependency on a single source and mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions (Segal, 2021). This adaptability allowed the company to respond quickly to changing conditions, ensuring a steady supply of essential products to meet heightened customer demand.
The corporation’s vast network of suppliers and distribution centers was essential in handling disruptions. An extensive presence enabled the company to draw upon multiple supply chain resources to redirect its goods through different pathways whenever an existing supply channel was compromised (McKAY, 2021). The agility presented by this approach allowed Walmart to surmount any transportation issues quickly while continuing to get goods to their stores. This proactive strategy enabled them to retain a competitive advantage over other retailers facing similar problems with their supply chains during the pandemic. Customers preferred Walmart for required products since it depended on keeping shelves stocked and promptly delivering online orders (Ovezmyradov, 2022). It thus thoroughly enhanced its reputation as a retailer that put customers first, drawing in more customers and ultimately positively impacting the company’s profitability and overall performance.
Furthermore, Walmart’s supply chain management team identified e-commerce and last-mile delivery as critical elements to guarantee steady growth. With social distancing measures and lockdowns impacting individuals’ ability to shop at a store, there was a dramatic increase in consumer demand for online services (Luo, 2022). As such, Walmart perceived the need and its importance to shift its infrastructure towards serving this need. To accomplish this goal, considerable investments were made in further developing digital capabilities. Their website and mobile app received several upgrades; additionally, the entire process, from ordering to wait times of receiving merchandise, was optimized so that consumers had a seamless experience when shopping. Also, Walmart focused on scaling up its last-mile delivery capabilities to meet the rising demand for home deliveries. Last-mile delivery pertains to the last leg – getting a product to a customer’s doorstep. To succeed, the corporation had to expand its fleet of delivery vehicles and partner with third-party logistics providers for greater outreach (Ross, 2020). Delivery routes were optimized, and cutting-edge algorithms were employed so customer orders arrived quickly and efficiently. This meant that Walmart stayed profitable due to its ingenious practices and resourceful capacity, enjoying discernable expansion milestones.
As the growth of online shopping increased during the pandemic, Walmart found success by committing to enhancing its e-commerce platform and offering last-mile delivery services. This ‘strategic move’ allowed them to retain existing customers who preferred to rely on convenient online shopping demand and capitalize on the new customers joining their platform – leading to a considerable increase in sales through their e-commerce channels. Consequently, Walmart’s dedication to meeting customer needs in terms of timely and reliable deliveries boosted profitability and customer satisfaction ratings while driving continued success even during these trying times. As demonstrated through these efforts, Walmart plays a significant role by solidifying itself as one of the top choices for online shopping – attributed to its excellent performance and profitability even during a pandemic.
Since its inception, Walmart has implemented effective supply chain management, contributing to increased growth and profitability. Relying on a robust global supply system, the chain retailer has quickly grown into one of the world’s largest. In response to the current pandemic, Walmart ensured the safety and welfare of customers, staff, and partners through rigorous maintenance of its supply chain standards (Zhang, 2023). Promoting compliance during this critical time reaffirmed the prized brand of Walmart as a reliable resource for customers—enhancing customer loyalty and evolving their revenue stream positively. Also, the organization’s supply chain management was critical in ensuring essential goods were available and accessible during the pandemic. The system enabled Walmart to manage inventory outcomes with responsiveness, which made supplies accessible through physical stores and online outlets. This effective use of supply chain management is reflected in the staggering fact that there was a 97% upsurge in online sales by Walmart during this difficult period (Ashcroft, 2022). Moreover, more significantly, it allowed Walmart to provide goods for customer delivery and have products arrive at their doorstep – heightening customer satisfaction and fortifying brand loyalty.
Additionally, the company’s supply chain management proved increasingly crucial during the pandemic. To ensure the safety and compliance of employees, customers, and partners, Walmart executed a stringent set of safety measures. Mandatory mask-wearing and social distancing, contactless delivery options, and enhanced sanitation procedures were implemented companywide to promote stakeholders’ health and well-being (Zhang, 2023). This successful implementation towards proactively mitigating risk enabled Walmart to maintain customer trust and loyalty. The symbiotic relationship between employee health and client satisfaction led to inspiring growth and profitability for the duration of the crisis and looking ahead. Effective supply chain management allowed Walmart to safeguard its resources while simultaneously providing essential goods – increasing profits while forming an indestructible bond with its core customers throughout these unprecedented times (Mrozek, 2023). By investing in safety and compliance within its supply chain management, Walmart demonstrated a keen understanding of the pandemic’s potential impacts and proved itself as an industry leader in crisis response and resilience.
Growth During the Pandemic Resulting from Effective Pandemic Measures
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted individuals and businesses all over the world. While many have been forced to shut down operations entirely, a limited number of corporations have thrived despite the economic crisis, with Walmart being a prime example. These retail giants achieved substantial financial growth amidst the pandemic, surpassing their closest competitors, Amazon, Costco, Lowe’s, and Home Depot. According to an analysis conducted by the Brookings Institute, Walmart’s profits for January to July of 2020 outpaced those from the same period in 2019 by an astounding $(USD) 5.1 billion, a growth rate of 80% (View appendix 3) (Molly-Kinder & Kinder, 2020). Amazon followed closely behind at an impressive 53%, while Lowe’s and Home Depot grew by 50% and 24%, respectively – compared to a comparatively modest 18% increase by their close rival Costco (Mrozek, 2022). That indicates steady growth despite the challenges that the pandemic presented.
Walmart’s impressive growth rate can be attributed to its diversified product portfolio. This includes various essential goods, notably groceries, household supplies, and personal protective equipment (PPE) (Zhang, 2023). During the 2020 pandemic, shoppers increasingly gravitated toward these items, resulting in overwhelming demand. Consequently, the company reported an incredible 97% jump in e-commerce sales during Q2 2020 (Ross, 2020). Walmart had long recognized the important role online retailing could play in its success. The company strategically invested heavily in improving its cyber capabilities before the global health crisis. They acquired Jet.com and broadened options for grocery deliveries and curbside pickups, lumbered with this foresight, and put them significantly ahead of competitors throughout the period of disruption (Lauchlan, 2020). As a result of these smart decisions, Walmart was excellently equipped to cater to the suddenly skyrocketing demand for ecommerce services during the COVID timeframe.
Walmart’s unique position as an essential business has been a major advantage during the pandemic. The company maintained its physical store presence while following safety guidelines, meaning consumers could continue shopping in-store and online. Despite this impressive growth, Walmart has been criticized for not rewarding its frontline workers accordingly. According to the Brookings Institute, the company allocated only $0.71 extra per hour in additional wages and bonuses to its non-managerial workforce throughout the pandemic (Molly-Kinder & Kinder, 2020). In stark contrast, Amazon invested over $9 billion in additional employee pay and benefits. As such, Walmart’s growth during the COVID-19 pandemic has been exceptional, surpassing its competitors Amazon, Costco, Lowe’s, and Home Depot (Ross, 2020). While the company’s diversified product portfolio, robust e-commerce capabilities, and status as an essential business have contributed to its success, it is important to note that Walmart has faced criticism for not adequately compensating its workers.
The Impact of Globalization on Walmart’s Supply Chain Operations during the Pandemic
The expansion of Walmart’s supplier base through globalization has been pivotal to its success and growth. By sourcing suppliers from diverse locations, Walmart has gained access to top-quality products and raw materials, promptly fulfilling customer orders (OECD, 2021). They have built up an expansive network across countries, allowing the retail chain great cost advantages through favorable contract terms. Moreover, regional suppliers give them the agility necessary to react swiftly to changes in consumer sentiment and market trends. Subsequently, they offer customers a remarkable selection of products attuned to their tastes across borders (Rose et al., 2023). Whether it is sourcing trendy fashion items, innovative gadgets, or specialty food products from different corners of the world, Walmart’s expanded supplier base has positioned it as a one-stop shop for diverse consumer needs.
However, this globalization-driven expansion also comes with challenges. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2019 challenged Walmart’s supply chain operations, especially given how quickly the virus spread worldwide. Furthermore, managing many far-away suppliers is intricate – substantial supply chain management and coordination become paramount to ensure on-time and top-quality deliveries (Banker, 2022). Additionally, working with international partners also carries certain risks – for instance, suddenly changing regulations, currency variabilities, and political instabilities can cause problems if not meticulously planned. Strong supplier relationships must be developed to minimize these potential risks and full transparency in sourcing moves alongside investments in ethical and sustainable strategies.
Additionally, the corporation employed cost optimization by accessing external suppliers to ensure profitability. Strategic sourcing from countries where labor and manufacturing costs are lower has enabled Walmart to attain significant savings; the savings can then be passed along to customers through competitive prices (Luo, 2022). Also, Walmart can secure favorable terms with suppliers stationed in multiple nations, allowing them to utilize economies of scale and capitalize on cost differentials. This competitive edge in price has invited an extensive customer base who range from individuals looking for budget items to customers seeking good value. Utilizing attractive pricing, Walmart has accomplished appealing to a vast demographic and cemented itself as one of the shapers of modern retailing (Check Appendix 4). Also, Walmart has utilized cost optimization through international sourcing, allowing them to remain agile and responsive to shifting market conditions and consumer demands. With the global reach of Walmart, they can alter their procurement strategies in response to disparities in demand, emergent purchasing tastes, or supply line hindrances. Flexibility has been a core attribute for Walmart during economic unpredictability and abrupt geopolitical alterations, which affect the accessibility and pricing of goods (Chaturvedula, 2022). Moreover, they can diminish susceptibilities related to dependency on any one segment or vendor by diversifying across suppliers distributed in various regions worldwide.
However, cost optimization through international sourcing also comes with ethical and sustainability considerations. While seeking lower production costs, Walmart must ensure that its suppliers adhere to responsible labor practices and environmental standards. The company has faced scrutiny in the past regarding the working conditions of some of its suppliers, leading to efforts to enhance supply chain transparency and promote responsible sourcing practices (Zhang, 2023). Balancing cost optimization with ethical responsibilities is a continuous challenge for Walmart and other multinational corporations, but it remains essential for maintaining a positive brand image and meeting the increasing consumer demand for socially responsible business practices.
Supply chain efficiency was critical for Walmart’s enormous success, and globalization had a pivotal role in its development. The retail giant’s access to new international markets created opportunities to use sophisticated supply chain technologies, greatly enhancing its logistics and inventory management capabilities (Ashcroft, 2022). Advanced logistic systems, such as automated warehouse management technology and transportation tracking systems, enabled smooth coordination within the Walmart supply chain so that products could be reliably and speedily replenished. This optimized its route way and timetable operations, significantly cutting down on transportation time and costs without jeopardizing arrival times in stores or at distribution centers. Ultimately, globalization enabled Walmart to revolutionize its supply chain processes. It could source products from different countries and leverage regions with lower labor and manufacturing expenses, allowing Walmart to optimize production costs and maintain competitive customer pricing. With an efficient flow of goods between suppliers, distribution centers, and stores, Walmart was able to meet customer demands timeously (Leonard, 2021). This streamlined process optimized operational efficiency and the customer experience, ultimately fostering trust in the brand and reinforcing Walmart’s position in the global retail industry.
Market expansion through globalization has been seen as a crucial growth strategy for Walmart. This strategy enabled them to increase significantly their retail presence across numerous international markets. By merging the extended opportunities offered by the globalized world, Walmart could identify and enter attractive supply markets in varying regions; both developed and developing economies. Over time, this global expansion allowed Walmart to expand its consumer base, diversify its revenue streams, and decrease its dependence on any region or market (Luo, 2022). This acted as a method of equilibrating risk and augmenting business resilience. A pivotal component that has played a role in its successful market development is the capability Walmart has had to customize product offerings in accordance with regional preferences and credentials. The company immediately recognized how significantly shopping conductors, cultural ethos, and user tastes differ not only between countries but also between states within those countries. To satisfy customers of varying ethnic backgrounds around the globe, Walmart developed an individualization design that necessitated molding product catalogs that fit each particular demand of that particular market it was entering (Zhang, 2023). By offering products that appeal to local customers, Walmart could establish a deeper connection with the communities it serves, building consumer trust and loyalty. This adaptability facilitated market entry and fostered long-term success by creating a strong brand presence in various countries and reinforcing Walmart’s commitment to serving its customers globally.
Conclusions
How other Companies can use These Strategies
The measures implemented by Walmart to address various challenges in their global supply chain management during the pandemic can serve as valuable guidelines for other companies to improve their supply chain practices today. Adopting Walmart’s intelligent approach to inventory management can bring invaluable cost-saving benefits to businesses today. By utilizing real-time data and predictive analytics, firms can use data from orders, sales volumes, manufacturing capabilities, supplier deliveries, and more to inform decisions that will achieve an optimum balance between supply and demand (Locke et al., 2023). This means companies can increase efficiency by reducing their inventory carrying costs and guarding against stockouts that come with sudden changes in market servicing power capacity or third disturbances. Additionally, by applying predictive analytical models paired with such real-time data collection strategies as scanning barcodes through a ‘day of sale’ system, teams can extract value from otherwise negligible bits of information and adjust accordingly to respond swiftly to situational variations such as customer behaviors or varying levels of demand.
Companies can look to Walmart’s strategies of diversifying their supplier base and improving supply chain visibility to mitigate disruptions and risks. Alternative sourcing gives the option to maintain flow in the event of localized crises or political events. When suppliers are formed with different regions, reliance on one diminishes, making disruption less severe when financial losses could be intended otherwise (Metzger, 2021). Technologies and data analytics gain insight into vulnerabilities that are not accessible openly, allowing organizations to recognize any potential issues which can then be addressed in anticipation, offering solutions both securely and promptly. With an understanding of the risks involved just as much as the rewarding factors of establishing partners from afar, potential economic derailment is avoided if required risk management and alternatives are established (Alwan et al., 2023). Therefore, an integrated relationship with suppliers near or abroad and real-time issue alerts sufficiently prepares companies for any foreseeable supply chain disruptions or crisis occurrences.
With the current characteristically low labor market growth, it is beneficial for companies to find ways of alleviating labor shortages. To address this issue, corporations like Walmart have implemented incentives and benefits to attract and retain employees, a strategy other companies could adopt (Forehand & Schaefer, 2021). Competitive wages can attract candidates looking for work, while bonuses or extra benefits encourage engagement without breaking the bank. Additionally, businesses should aim to fulfill jobs in an encouraging atmosphere that makes employees feel appreciated and fulfilled (Locke et al., 2023). Showing dedication to replacing staff turnover and retaining experienced personnel through enhanced policies could effectively address labor shortages and sustain a competent workforce. Effective communication and collaboration are essential to building resilient supply chains, as Walmart shows when it works with its suppliers and workforce. To make information sharing among stakeholders within the network smoother, companies can invest in robust communication platforms and collaboration tools (Alwan et al., 2023). Doing so allows for expedited decision-making, enriching coordination between stakeholders, and initializing prompt responses to disruptions or sudden shifts in demand. Walmart’s current endeavors demonstrate that organizations can use technology and automation to handle even abrupt increases in demand. Since robotics and automation improve the efficiency of warehouses and distribution centers, this process is useful for companies facing periods of soaring demand (Luo, 2022). The implications associated with quickly scaling operations grant automation a bright future.
References
Alwan, S. Y., Hu, Y., Al Asbahi, A. A. M. H., Al Harazi, Y. K., & Al Harazi, A. K. (2023). Sustainable and resilient e-commerce under COVID-19 pandemic: a hybrid grey decision-making approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(16), 47328-47348.
Ashcroft, S. (2022, February). Walmart’s supply chain is fed by Tech and e-commerce. https://supplychaindigital.com/logistics/walmart-supply-chain-fed-by-tech-and-e-commerce
Banker, S. (2022, October). Walmart’s Supply Chain Woes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/stevebanker/2022/08/17/walmarts-supply-chain-woes/?sh=193dd65d13d0
Chaturvedula, B. (2022). Disrupting the supply chain game – the Walmart way. Walmart Global Tech. https://tech.walmart.com/content/walmart-global-tech/en_us/news/articles/disrupting-the-supply-chain-game-the-walmart-way.html
Collings, D. G., Nyberg, A. J., Wright, P. M., & McMackin, J. (2021). Leading through paradox in a COVID‐19 world: Human resources comes of age. Human Resource Management Journal, 31(4), 819-833.
Forehand, K., Roman, J., & Schaefer, T. (2021). Supply Chain Efficiency in the Discount Store Industry Post COVID-19: Applying the Supply Chain Efficiency Ratio. Operations and Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 14(4), 423-430.
Francis, A. (2021, March). Case study: Wal-Mart’s distribution and Logistics System. MBA Knowledge Base. https://www.mbaknol.com/management-case-studies/case-study-of-walmart-logistics-management/
Grace, C. L. (2022, February). After hits from Omicron and supply-chain costs, Walmart eyes a brighter year. Winsight Grocery Business. https://www.winsightgrocerybusiness.com/retailers/after-hits-omicron-supply-chain-costs-walmart-eyes-brighter-year
humanimpact.org. (2021). Walmart’s role in the COVID-19 pandemic – human impact partners. humanimpact.org/Walmart. https://humanimpact.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Walmarts-role-in-the-COVID-19-Pandemic-How-lack-of-paid-sick-time-prolongs-the-pandemic-and-increases-mortality.pdf
Jin, Y., Xu, W., & Zheng, N. (2021, September). Analysis of COVID-19’s Investment in Corporate Value. In 2021 International Conference on Financial Management and Economic Transition (FMET 2021) (pp. 146-152). Atlantis Press.
Lauchlan, S. (2020, May). Walmart’s e-commerce soared during the COVID-19 crisis, but online profitability remains a longer-term challenge. diginomica. https://diginomica.com/walmart-e-commerce-soars-during-covid-19-crisis-online-profitability-remains-longer-term-challenge
Leonard, M. (2021, May). Walmart boosts inventory, extends lead times to account for supply chain delays and stockouts. Supply Chain Dive. https://www.supplychaindive.com/news/walmart-inventory-stock-out-pandemic-pick-ecommerce-fulfillment-last-mile/600424/
Locke, R. M., Armstrong, B., Schaab-Rozbicki, S., & Young, G. (2023). Supply Chains & Working Conditions During the Long Pandemic: Lessons for a New Moral Political Economy?. Dædalus, 152(1), 131-142.
Luo, W. (2022, April). Research on the Way Walmart Succeeded during the Pandemic. In 2022 7th International Conference on Social Sciences and Economic Development (ICSSED 2022) (pp. 1210-1213). Atlantis Press.
McKay, S. (2021, September). Covid-hit supply chain struggling. Arkansas Online. https://www.arkansasonline.com/news/2021/sep/12/covid-hit-supply-chain-struggling/
Metzger, J. (2021, October). How Walmart is navigating the supply chain to deliver this holiday season. Corporate-Walmart. https://corporate.walmart.com/newsroom/2021/10/08/how-walmart-is-navigating-the-supply-chain-to-deliver-this-holiday-season
Molly Kinder, L. S., & Kinder, M. (2020, March). Amazon and Walmart have raked in billions in additional profits during the pandemic and shared almost none of it with their workers. Brookings. https://www.brookings.edu/articles/amazon-and-walmart-have-raked-in-billions-in-additional-profits-during-the-pandemic-and-shared-almost-none-of-it-with-their-workers/
Mrozek, M. (2022). Walmart Inc. in light of COVID-19 pandemic: the financial assessment. Catallaxy, 7(1), 23-32.
Nguyen, T. T. H. (2017). Wal-Mart’s successfully integrated supply chain and the necessity of establishing the Triple-A supply chain in the 21st century. Journal of Economics and Management, (29), 102-117.
OECD. (2021). E-commerce in the time of Covid-19 – OECD. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/e-commerce-in-the-time-of-covid-19-3a2b78e8/
Ovezmyradov, B. (2022). Product availability and stockpiling in times of pandemic: causes of supply chain disruptions and preventive measures in retailing. Annals of Operations Research, 1-33.
Rose, N., Rowe, F., & Dolega, L. (2023). How consumer behaviors changed in response to COVID-19 lockdown stringency measures: A case study of Walmart. Applied Geography, 154, 102948.
Ross, L. (2020). How Walmart beat Amazon during the supply chain crisis of covid-19. Thomasnet® – Product Sourcing and Supplier Discovery Platform – Find North American Manufacturers, Suppliers and Industrial Companies. https://www.thomasnet.com/insights/how-walmart-beat-amazon-during-the-supply-chain-crisis-of-covid-19/
Sánchez Flores, R., & Serna, G. (2021). The Impact of COVID-19 on Supply Chain Management, 1er Ed. England: ProudPen. England: ProudPen.
Segal, E. (2021, November 9). How Walmart is responding to covid-related challenges. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/edwardsegal/2021/09/01/how-covid-repeatedly-put-walmart-to-the-test/
Xu, X., Sethi, S. P., Chung, S. H., & Choi, T. M. (2022). Reforming global supply chain management under pandemics: The GREAT‐3Rs framework. Production and Operations Management, 32(2), 524-546.
Zhang, D. (2023). Understanding Enterprise Risk Management of the Retail Industry During the Pandemic-Case Study of Walmart. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 154, p. 01018). EDP Sciences.
Abbreviations
SCM: Supply Chain Management
AI: Artificial Intelligence
PPEs: Personal Protective Equipment
OECD: Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development
Appendix
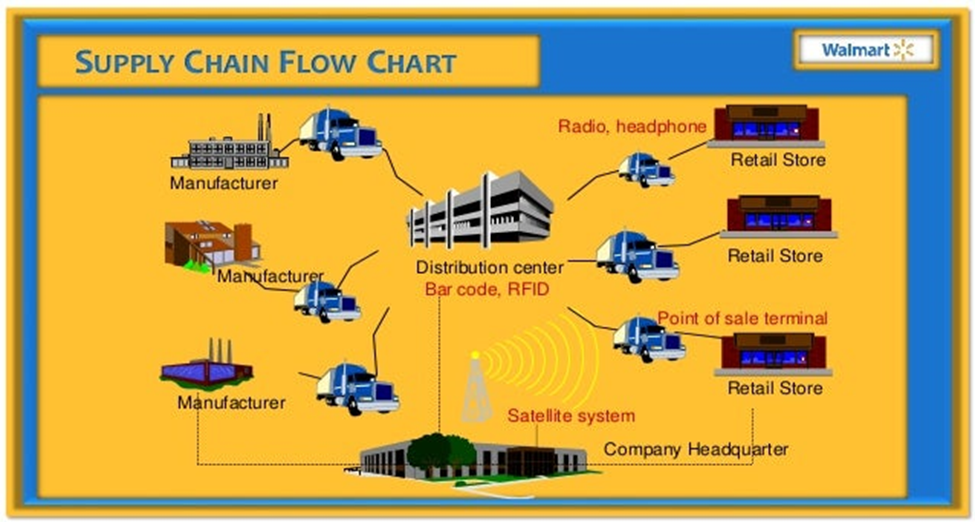
Appendix 1.0 Walmart’s Supply Chain Structure
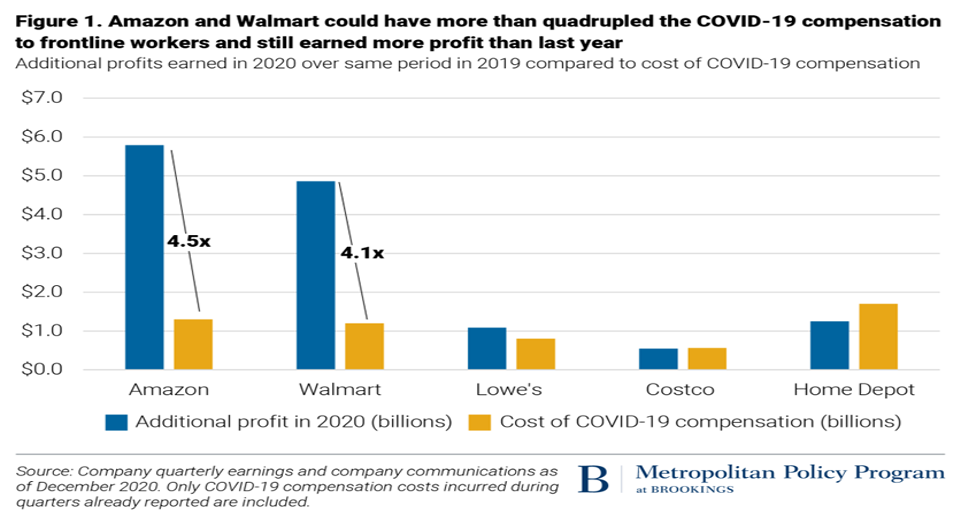
Appendix 2.0 Walmart’s growth compared to other companies during the Coronavirus
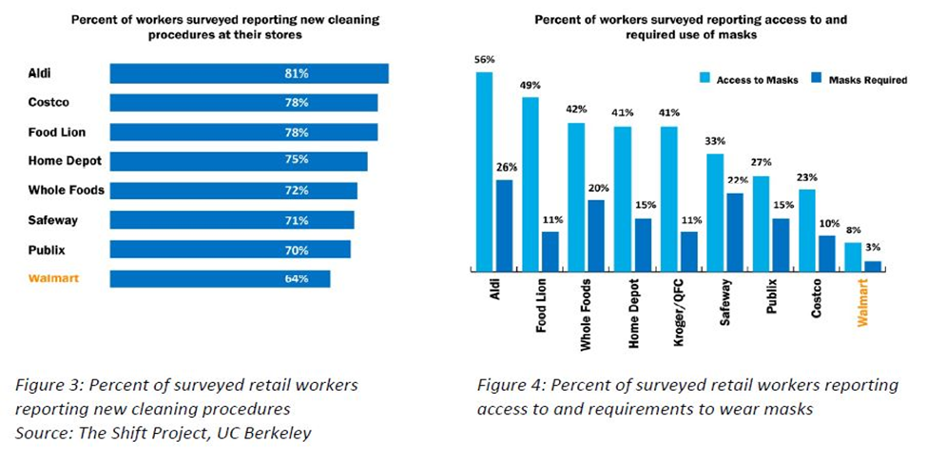
Appendix 3.0 Walmart’s protective measure immediately after Coronavirus outbreak
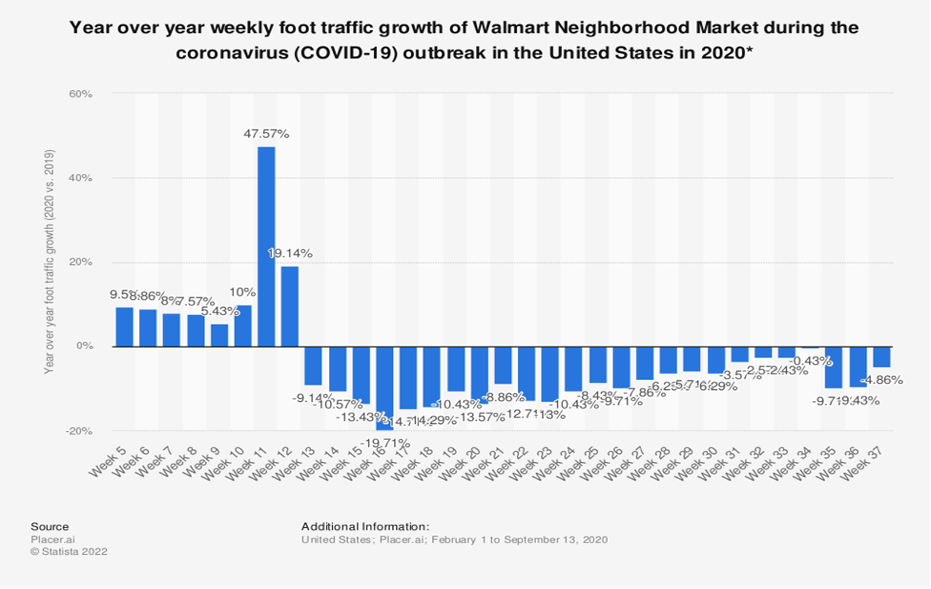
Appendix 4.0 Walmart’s market growth after implementation of effective precautionary measures during Coronavirus
 write
write