Introduction
Apple Inc. is consistently ranked as one of the most financially viable corporations in the United States, as proved by its inclusion on the top performing corporations. The primary reason the corporation’s product lines, particularly the iPhone, were chosen as the subject of discussion is that, while they are extremely popular in North America, they are extremely unpopular in South America and Sub-Saharan Africa. North America is the company’s main regional market (Goodfellow, 2021). The market not only generates about 40% of net sales, but Apple-owned retail chains that sell a variety of products are the most concentrated. Apple Inc. sells iPhones, iPads, Apple Watches and many other products. The iPhone was the company’s most profitable product, so its choice as a product was intentional. iPhone sales make up about 45% of Apple Inc.’s total revenue. Through this emphasized reasons, iPhones sold by Apple Inc. are not only available in limited North American market, but also in the physical market.
Brand Analysis
Brand Introduction
The iPhone is Apple Inc’s most profitable single product. iPhone sales in 2021 accounted for 46.6% of total sales in the fourth quarter (Apple Inc., 2022). The development of the original iPhone model was kept secret primarily to protect its innovative concept (Lyytinen, 2021). Nonetheless, Apple Inc. announced the product’s launch in 2007 and started to sell it in the U.S. in June of that year. After that release, given its innovative mobile design, the product was very popular.
In contrast to previous products, the iPhone design features a touch screen with no physical hardware buttons, quad-band GSM mobile connectivity with features to enhance GPRS and EDGE data transfer, and provision for continuous internet access (Glimstedt, 2020, p.120). These features set it apart from Apple Inc.’s competing companies’ product lines. The iPhone was initially priced at $ 400 for the 4GB model and $ 500 for the 8GB model. Because of the evolutionary development of smart phones, the technology market is subject to substantial changes in customer preferences.
Products that may be attractive to consumers at some point may not provide consumers with similar value over time. One such issue was influenced by Apple Inc., on the innovative iPhone, which forced the suspension of sales of the original model in 2008. According to Silver (2018), the company had sold more than 6 million units, most of which were localized to the North American market when the suspension happened. Apple is well-known for its cutting-edge technologies and business models. The corporation was capable of overcoming this challenging task by strengthening the original version and creating better versions of the product over time, thanks to these innovative trends. The iPhone 13 Max Pro, iPhone 13 Pro, iPhone 12, and many other models and series are among the most popular (Lyytinen, 2021).
Brand Portfolio
The availability of a brand is a main factor of its success. This includes physical as well as mental availability. The physical presence of a commodity in a specific market is referred to as physical availability. In a buying situation, mental availability represents the likelihood that a consumer will think, notice, or recognize a specific company’s product. Although the iPhone has high intellectual and physical availability, the brand’s availability is primarily limited to the North American market. For example, in the United States, more than 100 million people use the iPhone, which accounts for about 47% of all smartphone users in the country (Reisinger, 2021). The availability of the brand in the market is critical to the performance of the corporation.
Apple’s strategic marketing and growth strategies have enabled it to achieve such a strong brand availability. The organization has been able to convince customers that the iPhone and its successive product lines are superior to their competing brands in terms of reliability and digital security through extended marketing (Vasylieva and James, 2021, p.18). In this way, the company was able to improve the mental availability of the iPhone in the US market. Because of Apple’s widespread distribution system in the country, iPhone products are now physically available in this market. These figures do not apply to other markets, particularly those in South America and Sub-Saharan Africa. In North America, iPhone brands are widely available, but this is not the case in these other marketplaces.
In South America and Sub-Saharan Africa, the most significant barrier to achieving mental and physical availability is the cost of this product. Consumers in these markets are unsure whether they are still getting good value for their money when purchasing an iPhone. As a result, when such needs arise, most consumers opt to purchase a smartphone sold by a different company. Apple’s limited distribution system in these market segments makes it difficult for the organization to physically make the iPhone accessible to clients (Kamnek and Klimánek, 2020, p.90). Customers find it difficult to obtain the product due to the limited number of retail stores in these markets. Apple releases the use of third party sales agents and retailers. However, this is further worsens the situation because it is exposed to consumers to raise the price of the iPhone.
Brand Elements
The iPhone is easy to identify, owing to its distinct logo. The company logo that designs and produces or sells smartphones is one of the first things customers notice when they see a phone. As a result, Apple ensures that the iPhone is a memorable product. This is the feature that has elevated the iPhone brand to the status of an icon and the most well-known brand (Perch, 2022). Sophisticated design that creates ease of use and aesthetic impact is Apple’s main focus. Consumers also associate the iPhone with special quality. Therefore, consumer have the willingness to buy the phone when looking to purchase a smartphone.
Brand Equity (Keller’s CBBE Model)
The worth associated with a firm’s or product’s brand is referred to as brand equity. Kevin Lane Keller created a model for enterprises to use to assess brand equity. His concept is structured in the shape of a pyramid, and the different levels within the structure highlight the key questions that customers frequently ask about the company or brand without realizing it (Tasci, 2018, p.145). The first question concerns brand identity. Combining Apple Inc.’s technological improvements with a range of marketing strategies will raise iPhone market awareness. When selling a product, the company should ensure that prospective and existing consumers are aware of the device’s remarkable and safe functionalities. The corporation is also identified with its advanced and innovative brands, such as the addition of a dual-lens camera in portrait mode to the iPhone 7 Plus. Because of their respect and admiration for the brand, all of these factors build customer loyalty to iPhone purchases. Even if Apple introduces a new iPhone model, consumers are eager to buying it since they more importantly have a favorable attitude towards the product, and also value its brand equity.
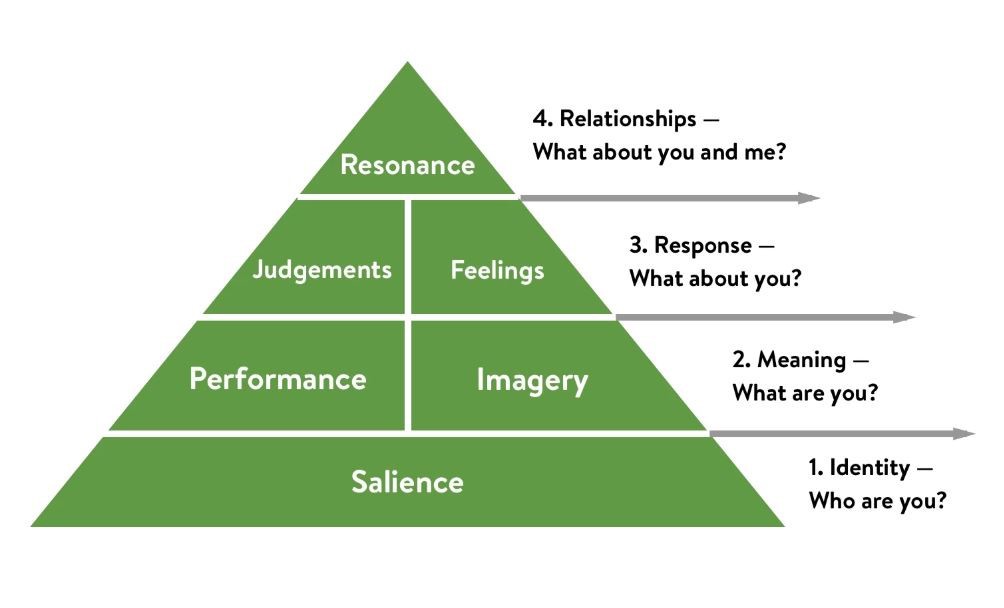
Figure 1: Keller’s Brand Equity Model
Brand Mantra
A brand mantra, also widely recognized as a brand essence, is an articulation that describes the significance of what a brand represents or the image it wishes to convey to buyers. It integrates and shares the key ideas behind branding and channeling within competitive standards (Lalaounis, 2017, p.356). All Apple Inc. products, including the iPhone, have a corporate brand called “Think Different.” Apple’s brand mantra is a complete integration of the company’s focus on creativity, emphasizing the creativity of the company as it creates its products.
International Market Analysis
Kenya
Social Factors
Kenya is one of the evolving marketplaces into which Apple Inc. should consider investing in to expand its operations. For the last ten years, the country’s population has increased at a two percent annual rate (Euromonitor International, 2021). Kenya’s growth in population means that there are more prospective consumers for purchasing iPhones. This, in conjunction with continuous growth and development over the same time frame, creates an opportunity for Apple Inc. The corporation must capitalize on its customers’ growing resources and consumer purchasing power in Kenya. These are prospective buyers who can now purchase Apple’s iPhone products.
Legal Factors
Kenya, unlike the majority of Sub-Saharan African countries, has a robust copyright protection framework (Euromonitor International, 2021). Not only does the nation have strict copyright laws, but it also has a strong legal system that protects the rights endorsed by such laws. Apple Inc.’s intellectual property (IP), which encompasses copyrights, trademarks, and patents, exemplifies its innovation. The level of security granted to such forms of intellectual property in Kenya signifies an opportunity for the firm to not only develop but also expand its customer base because the law protects their IP rights from infringement.
Economic Factors
Over the last couple of years, Kenya has consistently experienced strong economic growth. When combined with the nation’s liberalized trading platform, this means that there are still entry barriers that could hinder the acceptance and subsequent sale of the iPhone in the country (Euromonitor International, 2021). However, high inflation and the resulting volatility are a source of concern, given that as inflation rises, the prices of commodities in the market also rise, making it difficult for people to buy the iPhone. The high price of the iPhone in this case means that the customer is choosing to spend the money they have to meet their basic needs. Since the product price is high, there is almost no money left to inadvertently buy luxury goods, but the iPhone seems to be in such a situation.
Political Factors
Kenya has been relatively peaceful and stable, with the only major crisis being post-election conflict in 2007-2008 (Euromonitor International, 2021). A situation like this, combined with policy initiatives to liberalize trade, makes the state an appealing investment hub. However, by coming to market, Apple Inc. will be forced to deal with widespread corruption in its political sphere. This could be a problem because obtaining political backing for a large investment project, such as establishing a presence in Kenya, may necessitate bribery. This is contrary to the corporation’s ethical practices.
Technology Factors
Kenya is a technologically savvy country, as evidenced by the country’s overall internet access and the recent governmental plan to change Kenya into the digital realm. Despite this, rural areas have lower rates of adoption of technology and absorption than urban areas (Euromonitor International, 2021). As a result, entering the Kenyan market will necessitate Apple Inc. strategically locating its functions in the nation’s large cities and constituent municipalities, as these are the areas with the greatest number of consumers.
Competitor Analysis
Various organizations are present in Kenya’s smartphone market. However, Apple will face foreign competition from Tecno, which has a thirty percent market share, Samsung, which has a fourteen percent market share, and Huawei, which has a ten percent market share (Kibuacha, 2021). Local firms such as Safaricom will also compete with iPhones. Safaricom’s competition should be light, given the popularity of its Neon model in remote regions, which the corporation should avoid operations due to lack of sufficient technology acceptance rates and poverty levels, which means the value of iPhones is out of reach for the majority of people residing in these areas.
India
Social Factors
Despite the fact that India’s population growth has significantly slowed in the last decade, the nation’s large population combined with continuous economic growth makes it an appealing investment destination (Marmol, Feys and Probert, 2018, p.98). A large percentage of its residents are young adults. Smartphones are extremely popular among this segment of the population. The fact that many of them are completing their schooling, looking for employment, and accomplishing some level of economic independence means that Apple has created a profitable business opportunity that should be capitalized on. Financial freedom entails not only having money but also having the ability to spend it as one sees fit. As a result, these people are potential iPhone buyers in the wings.
Legal Factors
India has a strong employment protection program in place, with various laws aimed at protecting employee rights. Such an element works as an opportunity and an obstacles to market entry. On the plus side, establishing a presence in the country will necessitate the corporation’s compliance with all of these laws, and by doing so, Apple will improve its brand name in the market, as more consumers are holding organizations that promote employment discrimination accountable by boycotting their products (Beck, 2018, p.545). In the long run, strong brand image in the Indian market will result in increased smartphone sales. On the negative side, because the laws require employees to be paid a minimum wage, compliance with the legal frameworks will significantly raise the corporation’s wage costs.
Economic Factors
India, like Kenya, is continuing to pursue economic reform and liberalization. It means that there are some less barriers to trade that could impede Apple Inc.’s entry into the country and successive smartphone sales (Sundaram, 2019, p.493). During last two decades, the growth of the economy has also shown positive growth trends, demonstrating the economy’s stability and general well-being. This sort of atmosphere is advantageous for the firm’s management in this market. Apple Inc., on the other hand, will have to contend with the state’s wide economic disparities. Given the large economic disparity between rich and poor, India’s economic inequality is enormous. The primary reason for this is a lack of equitable access to technology and job opportunities.
Political Factors
A country’s political environment has a significant impact on economic development and increasing trade competitiveness. Because of its stable political system, economic development in India has been maintained consistently (Sundaram, 2019, p.493). As a result, foreign investors are more confident in investing in the economy, fueling economic growth. India has a well-structured and advanced tax structure, with the administration collecting revenue, sales, and services taxes and local governments collecting all other taxes. This, along with the country’s stable political system, makes it a viable iPhone market.
Technology Factors
Technology has a significant impact on product growth. 3G and 4G technology are currently available in India. Furthermore, the nation has one of the world’s strongest and dynamic IT sectors, which promotes continuous IT development, software upgrades, and other technological developments (Sundaram, 2019, p.493). As a result, many people place a high value on modern technology and related technological devices. Because of this, they are prospective consumers to whom Apple Inc. should sell its iPhone product. As a result, entering this marketplace will be reasonably simple.
Competitor Analysis
The Indian smartphone industry is equivalent to that of Kenya in that it is crowded, with fierce competition and shifting market shares. According to Jain (2022), Xiaomi controls the majority of the market, with a 27 percent market share. Samsung comes in second place with 18%, followed by Vivo (17%) and Real Me (16%). Given that none of them can be considered the market’s undeniable dominant force, these organizations have a fairly comparable market share. In such a case, the market’s intensity of competition is quite high.
Brazil
Social Factors
Brazil’s middle class is quickly increasing, both in population and in financial terms. This demographic is gradually becoming more familiar with present trends and, as a result, is aware of the key market brands selling such items (Rahman, 2021). Many Brazilians consider iPhones to be valuable beyond their smartphone functionality. Aside from being a smartphone device, Brazilians regard iPhones as a luxury item, and thus owning one is more of a fashion statement. Apple Inc. can capitalize on this tendency, as well as the nation’s increasing middle class’s affinity for costly products, to market iPhones to them.
Legal Factors
Over the last few years, Brazil has made some legislative changes that should make entrance and incorporation into its market moderately easy for Apple Company. In March 2017, the state passed legislation granting any business operating within its territory the right to decentralize any of its operations (Rahman, 2021). This type of restructuring makes things simpler for Apple Inc. to not only establish operational processes and sell iPhones, but also to develop a stable market position, allowing the company to make inroads into other regional markets.
Economic Factors
The country’s growth potential is very high due to its high population and rapid expansion of foreign direct investment. In addition, the country’s central bank has succeeded in controlling the country’s inflation rate as well as reducing the risk of currency devaluation. After all, Brazil’s corporate tax rate is 15% and foreign companies have no incentive to maintain profits domestically (Shaw, 2021). These factors significantly increase the profits from iPhone sales in this market, as low inflation leads to lower product prices and makes the iPhone very affordable. In addition, low corporate taxes combined with limited restrictions on investing some of the profits generated in the country will increase profitability.
Political Factors
The Brazilian administration is very active and is an aspect of the country’s relative political stability. As in Kenya, corruption is a problem in Brazil, and its level is increasing year by year. The situation is very dire, and even when starting a small business in the country, an individual or organization must give up paying money as a bribe to civil servants (Shaw, 2021). Entering the market means that Apple Inc. must fight the rampant corruption that plagues its political territory. Ensuring political support for investment ventures as large as Brazil may demand bribes can be an obstacle. This violates the corporation’s ethical values and standards.
Technology Factors
Brazil’s technological infrastructure is comparatively poor in comparison to India’s. Despite this, funds are being invested across Brazil to enhance the efficacy of technology centers (Rahman, 2021). Despite the fact that its current infrastructure is inadequate, the country’s growth opportunities make it a viable option for Apple to establish its operations. Improving the country’s technology capabilities will increase technology absorption and acceptance, a trend that the corporation can capitalize on to enhance smartphone sales in the market.
Competitor Analysis
Unlike in India and Kenya, where there is no dominant business influencing a significant portion of the market, Apple Inc. should be most concerned about Samsung in Brazil. Motorola has a twenty-one percent of market share, while Samsung controls slightly more than forty-five percent of the market. On the plus side, it means that Apple Inc.’s only competitor to be concerned about is Samsung. Given Apple’s competitive edge over Samsung, dealing with the corporation should be relatively simple.
Strategy for Market Entry
Selection and Justification for New Market to Enter
The Brazilian economy is the most appealing of the three potential nations. Apple can sell iPhones to potential domestic customers by leveraging its rapidly growing middle class and reputation for high-priced products. In addition, the domestic legal environment greatly encourages the types of commitments Apple needs to make (Rahman, 2021). In March 2017, the government passed a law granting the right to outsource all activities to companies under its jurisdiction. These reforms will assist Apple Inc. in not only launching and selling the iPhone, but also in establishing a stable position in the marketplace and moving forward in other market segments. Brazil has a corporate tax rate of 15%, so foreign companies have no incentive to keep profits in the country. Low corporate taxes, combined with limited restrictions on investing in some of the profits generated in the country, improve profitability.
Market Entry Strategy
Because the law allows for the outsourcing of functional activities, Brazil serves as the primary entry point for the iPhone in the larger South American markets. As a result, Apple Inc. can open a distribution center in Brazil, and the company can outsource iPhone manufacturing thanks to this specific law. When this occurs, Apple will be able to send the merchandise to Brazil and disburse it not only in Brazil but also in other South American countries. This outsources iPhone manufacturing to a much cheaper location, lowering operating costs and allowing the company to increase profits from selling iPhones (Shaw, 2021). One of Apple Inc.’s strengths is its extensive pool of resources available to its marketers. As previously stated, the tech company has a limited presence in the emerging economies, and thus in emerging markets. This strength can be used to vigorously sell smartphone products not only in the Brazilian market, but also in other South American markets. This presents an opportunity for Apple Inc. to dominate the South American market.
Marketing Mix Framework
Apple should concentrate its efforts in the Brazilian market on smartphone marketing and sales. However, given the wide income and wealth disparities, marketing must target the middle and upper classes. These people live primarily in the country’s metropolitan areas and are not only compatible with costly luxury products, but also have the financial means to make such purchases (Amaral et al., 2020, p.465). Apple Inc. primarily operates physical stores that sell its products. However, in the Brazilian market, you should think about selling your iPhone alongside an authorized seller, particularly in the early setup of operational processes. In Brazil, social media is relatively popular. Not only can the company promote the new iPhone model on various social media platforms, but it can also resolve customer complaints and queries.
Intended Points of Parity and Points of Differentiation
Brazil’s smartphone market is well-established and advanced, as well as price sensitive. As a result, in order to compete effectively and eventually dominate the market with iPhone products, Apple Inc. must highlight its differentiators. To accomplish this, the company must increase the availability of the iPhone brand in the Brazilian marketplace. Through widespread marketing, the firm can convince consumers that the iPhone and its successors are superior to their competitors in terms of functionality and data security (Amaral et al., 2020, p.470). This will increase the mental availability of the iPhone in the Brazilian market. Laws that allow the state to outsource operations make it easier for Apple to outsource manufacturing to existing factories and improve the physical availability of products. In addition, the establishment of local stores and the participation of authorized sellers will increase the availability of products on the market.
Conclusion
The iPhone is the most profitable product in Apple Inc.’s portfolio, and its popularity is a resultant of the innovation behind its creation. Apple’s strategic marketing and expansion strategies enabled it to achieve such high rates of product availability. The iPhone is Apple Inc’s most profitable single product. The availability of a brand is a main factor of its success. This includes physical as well as mental availability. Apple’s strategic marketing and growth strategies have enabled it to achieve such a strong brand availability. Through extensive promotion, the company was able to persuade consumers that the iPhone and its successive designs are superior to those sold by competing companies in terms of user experience and data protection. Nevertheless, the company was unable to enter certain markets other than North America, especially South America and sub-Saharan Africa. To stay competitive, Apple Inc. must enter such a market. In this paper, we have taken up three countries in these regions and decided that Brazil will ultimately serve as the gateway to the South American market and will be the preferred business hub.
References
Amaral, P., Lemos, M., Simões, R. and Chein, F., 2020. Regional Imbalances and Market Potential in Brazil. Spatial Economic Analysis, 5(4), pp.463-482.
Apple Inc., 2022. Apple Reports First Quarter Results. [online] Apple Newsroom. Available at: <https://www.apple.com/newsroom/2022/01/apple-reports-first-quarter-results/> [Accessed 24 March 2022].
Beck, V., 2018. Consumer Boycotts as Instruments for Structural Change. Journal of Applied Philosophy, 36(4), pp.543-559.
Euromonitor International, 2021. PEST Analysis: Kenya. [online] Euromonitor. Available at: <https://www.euromonitor.com/pest-analysis-kenya/report> [Accessed 24 March 2022].
Glimstedt, H., 2020. The iPhone and its antecedents: re-thinking entry and the evolution of platform strategies at Apple Inc. Entreprises et histoire, 98(1), p.120.
Goodfellow, J., 2021. Apple says it earned nearly one-third of 2021 revenue from emerging markets. [online] Campaignlive.com. Available at: <https://www.campaignlive.com/article/apple-says-earned-nearly-one-third-2021-revenue-emerging-markets/1731844> [Accessed 24 March 2022].
Jain, S., 2022. India Smartphone Market Records Highest Ever Shipments in 2021. [online] Counterpoint Research. Available at: <https://www.counterpointresearch.com/india-smartphone-market-shipments-revenue-2021/> [Accessed 25 March 2022].
Kibuacha, F., 2021. Mobile Penetration and Growth in Kenya – GeoPoll. [online] GeoPoll. Available at: <https://www.geopoll.com/blog/mobile-penetration-kenya/> [Accessed 24 March 2022].
Kamínek, J. and Klimánek, M., 2020. Mobile usage of digital geographical data in the Apple iPhone device. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 58(4), pp.89-96.
Lalaounis, S., 2017. Strategic Brand Management and Development. 5th ed. California: SAGE Publications.
Lyytinen, K., 2021. Understanding the Real Innovation behind the iPhone. [online] Scientific American. Available at: <https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/understanding-the-real-innovation-behind-the-iphone/> [Accessed 24 March 2022].
Marmol, T., Feys, B. and Probert, C., 2018. PESTLE analysis. New York: 50 minutes.
Perch, D., 2022. Brand Identity and Elements of Apple. [online] The Social Grabber. Available at: <https://thesocialgrabber.com/brand-identity-and-elements-of-apple/> [Accessed 24 March 2022].
Rahman, M., 2021. PESTEL analysis of Brazil (Brazil country profile). [online] Howandwhat.net. Available at: <https://howandwhat.net/pestel-analysis-brazil-brazil-pestel-analysis/> [Accessed 25 March 2022].
Reisinger, D., 2021. iPhones in use in the US rise to 94M, new study suggests. [online] CNET. Available at: <https://www.cnet.com/tech/tech-industry/nearly-100m-iphones-in-use-in-the-us-new-study-shows/> [Accessed 24 March 2022].
Shaw, A., 2021. PESTLE Analysis of Brazil | SWOT & PESTLE Analysis. [online] SWOT & PESTLE Analysis. Available at: <https://swotandpestleanalysis.com/pestle-analysis-of-brazil/> [Accessed 25 March 2022].
Silver, S., 2018. The story of the original iPhone, that nobody thought was possible | AppleInsider. [online] AppleInsider. Available at: <https://appleinsider.com/articles/18/06/29/the-story-of-the-original-iphone-that-nobody-thought-was-possible> [Accessed 24 March 2022].
Sundaram, N., 2019. PEST Analysis of Present Indian Telecom Sector. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 9(2), pp.493-494.
Tasci, A., 2018. Testing the cross-brand and cross-market validity of a consumer-based brand equity (CBBE) model for destination brands. Tourism Management, 65, pp.143-159.
Vasylieva, N. and James, H., 2021. Production and trade patterns in the world apple market. Innovative Marketing, 17(1), pp.16-25.
 write
write