Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic is bringing unprecedented challenges to the global financial sector, and the banking industry is no exception. With the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic on December 30, 2019, most businesses face many challenges; their resilience and adaptability are tested, and banks are no exception to falling profitability. This analytics report engages with the management of Barclays Bank, highlighting the unique characteristics that make banks an important institution in the financial sector. Critical aspects of bank management, such as liquidity, capital structure, and regulatory framework, are examined, as well as how these aspects play an important role in determining the risk associated with the pandemic. Furthermore, the report analyzes risks in the banking industry and examines the adoption of business strategies and the nature of capabilities required to overcome such challenges.
Introduction
The banking sector plays an important role in global financial services (Allen et al. (eds), 2019), acting as a key financial control system, promoting economic growth and development, and meeting the financial needs of businesses for a stable and sustainable business environment. The year 2020 was a turning point for global financial institutions as the COVID-19 pandemic continued, bringing unprecedented challenges to the banking sector. This study focuses on Barclays Bank and examines the strategies and risks associated with the COVID-19 pandemic. The insights are drawn from the July 2020 Financial Performance Report, which provides a snapshot of Barclays Bank’s resilience and flexibility during periods of high economic uncertainty.
Performance and Risk Development – 2019 vs. 2020:
To gauge the impact of the pandemic on Barclays, a comparative analysis of performance and risk development in 2019 and 2020 is imperative. The impact of the pandemic is evident in various aspects, including revenue, profitability, and asset quality. Net income, for instance, may have been affected by increased provisions for loan losses and reduced economic activity. A comparison of key financial metrics will provide insights into the extent of these effects.
| Financial Metrics | 2019(£ Millions) | 2020 (£ Millions) | % Change |
| Net income | 9407 | 8122 | |
| Total Assets | |||
| Loan loss provision | |||
| Return on Assets (ROA) | |||
| Return on Equity (ROE) |
Table: Barclays Bank Performance Comparison (2019 vs. 2020)
Performance: In 2019, Barclays exhibited robust financial performance with steady revenue growth and sound asset quality. However, the pandemic-induced economic downturn in 2020 posed challenges. A detailed examination of the financial statements reveals any significant fluctuations in key performance indicators such as revenue, net income, and return on equity.
The risk landscape in 2019 was relatively stable, with the emergence of the pandemic dramatically altering the scenario in 2020. Operational risks, credit risks, and market risks are areas of particular interest, and a thorough examination of risk exposure and management strategies is crucial.
Barclays Bank Operations and Risk
Treasury management to ensure day-to-day operations include strategic decision-making, operational efficiency and risk mitigation measures. According to (2017), Banks are unique institutions that play an important role in financial intermediation, which includes transferring funds from savers to borrowers. These intermediary roles expose banks to a variety of risks, including credit, market, operational and liquidity. The COVID-19 pandemic has triggered realities about the importance of effective risk management strategies.
In retail banking, Barclays has shown agility in meeting the changing needs of its customers during the pandemic. Digital approaches to banking transactions, provision of flexible financial solutions and advanced customer engagement channels play an important role in maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. Corporate banks have evolved through risk exposure reviewed disclosure and support for businesses facing pandemic challenges. Partnerships with government incentive schemes and proactive risk management programs have made Barclays a reliable partner for businesses going through financial difficulties.
The investment bank has leveraged its global presence to identify emerging opportunities and effectively manage risks in the face of market volatility. The Strategy developed in investment allocation and client-oriented advisory services has helped maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly growing economic environment. Wealth management has increased the demand for advisory services as clients seek guidance in uncertain market conditions. Barclays’ commitment to personalized wealth management solutions and a customer-centric approach has helped drive confidence and satisfaction among high-net-worth individuals.
2.1 Why banks are different
Barclays is a universal global bank, reaching out to many communities and meeting individual financial needs as a unique institution (Saunders et al., 2017). It acts as a financial intermediary because it is the primary source of external financing, so unlike other financial institutions that borrow from collectors, lenders, and spenders, Barclays Bank accept deposits from the public in order to carry out money banking through fractional reserve. The process converts short-term liabilities, such as deposits, into long-term assets, such as debt (Casu et al., 2015). This unique characteristic allows many banks to play a dual role as custodians and lenders of public deposits, making their activities inherently linked to the macroeconomic environment. This change in time exposes banks to interest rate risk, as changes in interest rates can affect the profitability of their operations. In addition, Barclays Bank plays an important role in financial stability by providing a safe and secure environment for financial transactions by acting as custodians of payment systems.
2.2 Bank Management
Liquidity and Asset-Liability Management at Barclays Bank
Liquidity management is a vital element of bank operations, especially throughout instances of crisis, inclusive of the COVID-19 pandemic. Asset-liability control is a strategic degree of dealing with liquidity chance and hobby fee hazards in order to attain long-term intention, with the flexibility to handle any changes (Mushkin, 2016). The pandemic’s unexpected monetary downturn and marketplace volatility challenged banks’ liquidity positions. Effective liquidity management involves balancing property and liabilities to ensure a bank can meet its quick-term duties.
Barclays’ goals are to optimize the risk-return profile, liquidity, and capital adequacy via effective ALM by employing sophisticated threat evaluation fashions to discover and mitigate numerous dangers, consisting of interest rate danger, credit score chance, and liquidity threat. In addition, the financial institution diversifies its asset portfolio to beautify returns whilst managing attention dangers, leveraging superior technology and facts analytics for real-time tracking, and improving choice-making in ALM (Allen et al. (eds), 2019).
Barclays Bank’s approach to Asset-Liability Management is complete, emphasizing hazard control, diversification, and technological improvements (Casu et al., 2015). While facing challenges inherent inside the financial area, the financial institution stays well-positioned to navigate uncertainties and capitalize on possibilities for sustainable growth. Continuous tracking and variation to dynamic market situations could be key for Barclays to preserve a resilient and profitable ALM framework.
Table 2.0 shows the comparison of the grand summation of Barclays Bank Group management of income flow in the year 2019 vs. 2020
2.3 Capital and Regulatory Architecture
Capital is a buffer in opposition to unexpected losses and has been crucial to a financial institution’s resilience. Regulatory bodies impose capital requirements to ensure banks can absorb losses without jeopardy (Basel Committee On Banking Supervision, October).
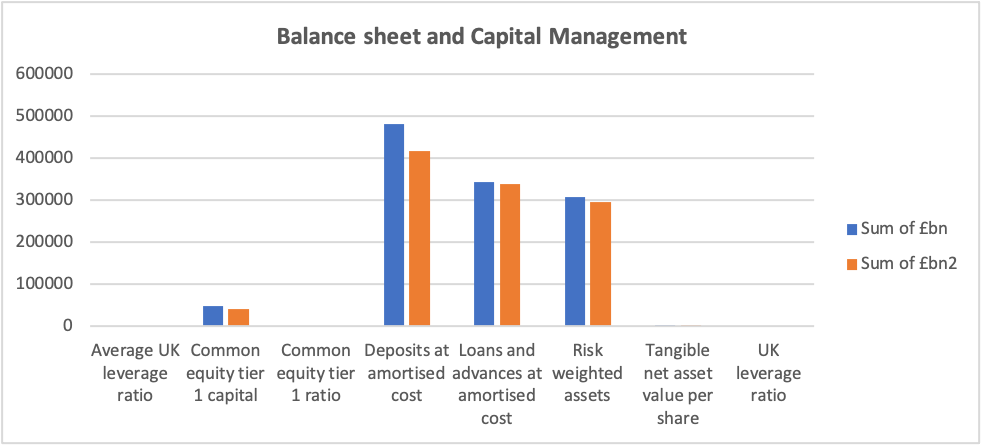
Diagram 2.0 Demonstrates the distribution of Balanced sheets
The blue bar represents the year 2019, while the orange bar represents the year 2020, indicating a slight drop in cash flow as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Risks in the Banking sectors
Barclays Bank is one of the banking industries, has been exposed to numerous dangers, starting from credit score chance, hobby charge danger, liquidity hazard, marketplace danger to operational threat (Saunders et al., 2017), and the COVID-19 pandemic has amplified those dangers globally. Understanding the nature of these risks is critical for effective change management and strategic choice-making. Barclays Bank operates in a tough environment with a mess of risks. Effectively coping with the market, credit score, operational, liquidity, regulatory, and reputational dangers is critical for sustained fulfilment. Continuous monitoring, adaptive threat control techniques, and a commitment to regulatory compliance are important factors in navigating the complicated panorama of the banking sector. As Barclays continues to evolve, it should stay vigilant and agile in addressing emerging risks to safeguard its economic health and popularity inside the marketplace (Margaerts et al., 2016).
3.1 Business Model and the Nature of Competence
Barclays Bank’s business model comprises a range of financial services, including banking and trading, investment banking, and wealth management. The bank’s July 2020 Financial Business Report highlights a customer-centric and digital approach with an emphasis on change processes to increase operational efficiency. Banks adopt distinct business fashions with every risk. Universal banks, investment banks, and retail banks have wonderful chance profiles. During the pandemic, shifts in consumer behaviour, economic uncertainties, and market disruptions examined the resilience of various enterprise models. The nature of competence required in banking includes a blend of monetary acumen, regulatory compliance, technological adaptability, and disaster control competencies.
Pros and cons of the business model in pandemic response:
Pros
- Diversification: Barclays’ diversified business model provides a hedge against the effects of economic shocks in specific sectors.
- Digitization: The bank’s robust digital infrastructure facilitated seamless remote collaboration during closed hours and increased customer engagement.
Cons
- Underlying economic downturn: Because it relies on sectors, Barclays is exposed to economic fluctuations, causing downturns in specific sectors
- Regulatory challenges: Stringent regulatory requirements can pose challenges in order to adapt and implement new solutions quickly.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Barclays Bank Management
The COVID-19 pandemic offered a multifaceted task to Barclays Bank, requiring rapid and strategic responses to ensure continuity and stability. This phase explores the precise effects of the pandemic on liquidity, capital adequacy, and regulatory compliance.
- Digital transformation: Barclays’ emphasis on digital banking and technology-driven services enables it to meet changing consumer behaviour and preferences accelerated by the pandemic.
- Diversification: Barclays, the global financial institution, operates across the banking and commercial banking, investment banking and wealth management sectors. This diversity of products provides a counterbalance to the effects of the epidemic in different areas.
Requirements for Use during COVID-19
- Customer support and flexibility: Understanding the financial challenges faced by customers, Barclays showed a tendency to provide bespoke finance solutions, deferred payments and support schemes to mitigate the financial impact of the pandemic at the bottom of the table.
- Accelerating digital banking: Barclays has been quick to adapt to the increasing demand for digital banking services. The bank has expanded its banking and mobile banking capabilities to ensure customers can transact with ease from the safety of their homes.
- Remote work systems: Barclays invested in robust remote work systems, enabling employees to work effectively from home. These requirements ensured productivity and maintained service levels during lock-in periods and restrictions.
4.1 Liquidity Challenges
The financial fallout from the pandemic brought about increased uncertainties, affecting banks’ liquidity positions. Withdrawals decreased monetary activity, and disruptions in financial markets created liquidity-demanding situations. Maintaining adequate liquidity is crucial for Barclays to satisfy its brief-term responsibilities. Sudden withdrawals, unexpected market disruptions, or regulatory modifications can pressure liquidity. The bank should strike stability among profitability and liquidity, ensuring it is able to fund its activities without compromising its financial stability. Banks had to hire numerous tools, together with important bank facilities and emergency investment measures, to preserve liquidity.
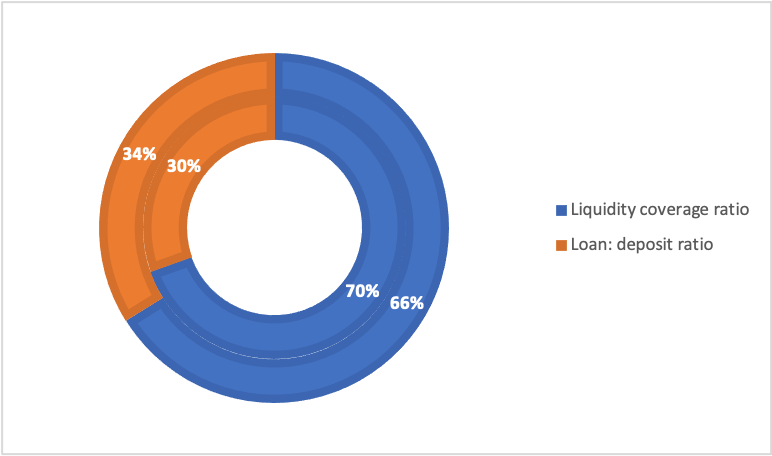
Table 2.2 shows the difference in Liquidity coverage and Loan deficit ratio
| Row Labels | Sum of 2020 | Sum of 2019 |
| Group liquidity pool (£bn) | 211000 | 266 |
| Liquidity coverage ratio | 1.6 | 1.62 |
| Loan: deposit ratio | 0.82 | 0.71 |
| Grand Total | 211002.42 | 268.33 |
Diagram 2.1 Represents the difference in the percentage of liquidity coverage ratio and loan deposit ratio.
4.2 Capital Adequacy Concerns
As a result of a high call for monetary sports contracts, the loan defaults improved, growing the emergence of capital adequacy. Barclays Bank confronted the twin strain of maintaining sufficient capital buffers to take in losses while helping the economy through lending. In reaction to the limitations, Regulatory authorities were able to provide transient comfort measures and versatility in capital requirements to ease the strain. Barclays has demonstrated its ability to meet unprecedented challenges by leveraging digital transformation, supporting customers and adapting to a dynamic regulatory environment to continue to build on customer-centric transformation and innovation that will ensure Barclays continues its success in the post-pandemic era.
4.3 Regulatory Adaptations
The regulatory landscape changed in reaction to the pandemic. Regulators achieved measures to address instantaneous issues even as thinking about the lengthy-term implications of the catastrophe. Flexibility in regulatory frameworks, collectively with the postponement of specific requirements and strain finding out, aimed to stability and help for monetary healing. Strategies for Mitigating Risks and Ensuring Resilience: In navigating the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, banks carried out numerous strategies. The nature of competence in the banking zone shifted in the direction of digital knowledge, agility, and the capacity to navigate an evolving panorama. Adapting to these adjustments required strategic, imaginative, prescient, and proactive management.
Despite improvements in capital and regulatory frameworks, Barclays continues to face challenging conditions, including a changing regulatory environment, cyber threats and geopolitical uncertainty. Barclays must adhere to a multitude of global and local regulations, including those mentioned in Basel III, Dodd-Frank, and the European Banking Authority (EBA) hints. The bank’s compliance framework is designed to meet these regulatory necessities, with ongoing tracking and reporting mechanisms in the region
5.2 Diversification of Revenue Streams
The financial uncertainties brought about with the aid of the pandemic highlighted the importance of diversifying revenue streams for banks. Institutions closely reliant on unique sectors faced greater larger demanding situations, prompting a reevaluation of business models. Diversification strategies included expanding product services, getting into new markets, and leveraging the era to explore revolutionary financial offerings.
5.3 Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis
Stress trying out and situation evaluation have become vital gear for banks in assessing their resilience to adverse monetary conditions. The pandemic underscored the want for robust threat management frameworks to resist unexpected shocks. Banks conducted state of affairs analyses to version the ability effects of extended financial downturns, allowing them to regulate strategies and capital allocations accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the landscape of bank control, emphasizing the want for adaptability, resilience, and modern techniques. As banks continue to navigate the demanding situations posed by the ongoing crisis, the instructions found from this experience will, in all likelihood, affect destiny threat control practices and regulatory frameworks. The significance of a strong and dynamic banking sector in helping financial recuperation highlights the crucial function banks play in shaping the economic well-being of countries.
The complex interplay of liquidity, capital adequacy and regulatory compliance defines the essence of bank management. The risks associated with the COVID-19 pandemic enhance the unique characteristics that make banks an important institution in the financial sector. As the banking sector continues to evolve, the lessons learned from the pandemic will undoubtedly shape the future direction of bank supervision and risk mitigation strategies.
References
Allen, N., Berger, A.N., Molyneux, P., Wilson, J.O.S.(eds). (2019). The Oxford Handbook Of Banking, 3rd Edition. Oxford University Press.
Ayunku, P. (2017). Bank Management and Regulations. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing.
Basel Committee On Banking Supervision. (October). The Basel Committee’s response to the financial crisis: report to the G20.
Casu et al. (2015). Introduction to Banking. Pearson International Content.
Margaerts, F., Vander Vennet, R.,. (2016). Business Models and Bank Performance: Along-term perspective. Journal of Financial Stability, 22, 57-75.
Mushkin, F. (2016). The Economics of Money, Banking, Financial Markets. 11th Edition, Global Edition. Pearson International Content.
Saunders et al. (2017). Financial Institutions Management: A Risk Management Approach. McGraw-Hill Education.
 write
write