SECTION ONE
Introduction
The goal of this section is to compare the financial performance of Associated British Foods Plc against that of its competitor, J Sainsbury Plc, using financial ratios derived from five-year financial information from 2017 to 2021. Associated British Foods is an international corporation majoring in ingredients, food, and retail business based in London, England, with 128,000 employees, £13.9 billion in revenue, and operating in more than 53 nations globally (ABF Corporate, 2021). It is part of the London Stock Exchange and the FTSE 100 indexes.
J Sainsbury Plc is a significant product and food retailer in the United Kingdom, with headquarters in London (Reference for Business, 2021). Sainsbury’s is a FTSE 100 company with a London Stock Exchange listing (J Sainsbury, 2021). The Sainsbury family established it in 1869. (J Sainsbury, 2021). The shop began by providing retailed fresh food, but as time went on, it expanded to include packaged goods. As a result, the goal of this component of the research is to analyze and contrast ABH’s and Sainsbury’s financial characteristics. Sainsbury’s has dabbled with real estate and financial services, in addition to its main retail food business (Financial Times, 2022). The four business segments of the corporation are retail food, real estate, general retailing clothes, and financial services.
Ratio analysis
By examining a company’s financial statements in absolute terms, it is impossible to acquire a critical understanding of its financial health. Quantifiable metrics are used to compare a company’s current financial position to its historical financial statements, rivals, or the whole industry (Barnes, 1987). The current performance of ABF Plc is compared to Sainsbury’s, its competitor over the past four years by calculating, evaluating and comparing their financial ratios. In this section, I’ll examine Current Ratio, Net Profit Margin, Total Asset Turnover and Debt Ratio, Ratios.
Net Profit Margin
Net Profit margin is a term for the percentage of net sales that a company retains after all costs have been removed and distributed. Following the deduction of all costs and expenses, the ratio measures the percentage of sales that remain as profit. Effective pricing and solid cost management are reflected in an NPM that is higher. In order to assess an organization’s overall performance, the NPM is used. Due to the similarity of the cost structures, and customers and business environment, it is useful in assessing similar organizations (Bragg, 2021). A company’s net profit margin (NPM) is determined by dividing net income by total sales. The NPM of ABF Plc and Sainsbury Plc were calculated and examined as shown in the following table and graphs.
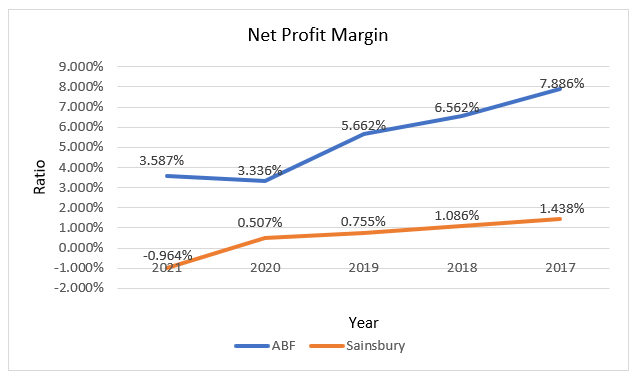
In 2017, 2018, 2019, and 2021, ABF’s net profit margins were 7.89 percent, 6.56 percent, 5.66 percent, 3.34 percent, and 3.58 percent, respectively. Within the same time period, the corresponding ratios for Sainsbury are 1.44 percent, 1.09 percent, 0.76 percent, 0.51 percent, and -0.96 percent. ABF Plc’s NPM is on the decline, with a major fall in 2020 and a little gain in 2021. Because the share of COGS in those years was 91.7 percent, 91.3 percent, and 92.3 percent, which is an increasing trend that consistently reduced gross, operating, and net profits, as shown in the vertical analysis, profitability declined consistently between 2017 and 2019. Furthermore, a greater proportion of COGS (94.7%) impacted the significant fall in NPM in 2020, whereas a decrease in COGS proportion (93.7%) influenced the increase in 2021. Sainsbury’s NPMs, on the other hand, declined throughout the time, with a major drop in 2021. Because Sainsbury’s has a bigger proportion of COGS than ABF, its NPMs are smaller. Furthermore, although ABF’s current NPM increased, Sainsbury’s fell, meaning that ABF’s performance is increasing while Sainsbury’s is declining. As a result, ABF outperforms Sainsbury in terms of profitability because its NPM is larger and grown over the previous year.
Current ratio
A company’s capacity to satisfy its short-term financial obligations without running into major financial problems is measured using the current ratio, which is one of the liquidity ratios. This metric is frequently employed to gauge a company’s short-term liquidity. In order to determine whether a firm is worth investing in, lenders and investors might look at the debt-to-equity ratio. The current ratio shows that current liabilities can be liquidated to pay current assets since current assets are divided by current liabilities (Bragg, 2022). According to the graph and table presented in the graph and table below, current assets are divided by current liabilities to calculate the ratio.
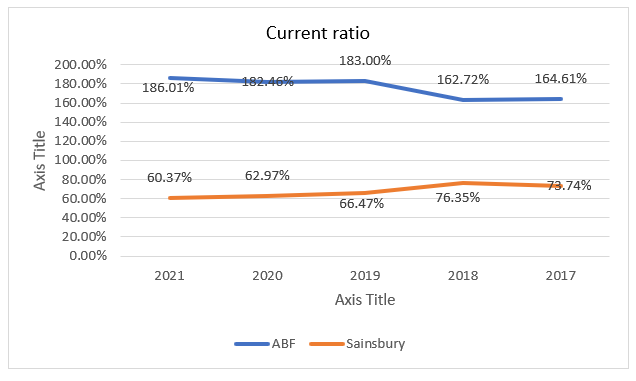
From 2017, 2018, 2019, and 2021, ABF Plc’s current ratios were 164.61 percent, 162.72 percent, 183.00 percent, 182.46 percent, and 186.01 percent. 73.74 percent, 76.35 percent, 66.47 percent, 62.97 percent, and 60.37 percent are the same current ratios for Sainsbury’s. Current ratios for ABH have been changing, with decreases in 2018 and 2020 followed by increases in 2019 and 2021. The decreases were due to a greater increase in current liabilities than current assets, whilst the increases were impacted by a decrease in current liabilities. Sainsbury’s current ratios rose in 2018, but then fell in the years after that. ABF’s liquidity ratios are higher than Sainsbury’s, for example. In addition, ABF’s recent current ratio grew, whereas Sainsbury’s fell. Because ABF’s current ratios are more than one, it may be inferred that its current assets are sufficient to cover current liabilities, whereas Sainsbury’s current assets are insufficient to cover all of its current liabilities. As a result, ABF has a stronger liquidity position than Sainsbury’s, which is growing.
Debt ratio
The debt ratio is a measure of a company’s solvency and leverage that shows the percentage of assets purchased with borrowed money, indicating that the same percentage of assets might be sold to pay off all of the debt. More leverage is indicated by a larger ratio, while less leverage is indicated by a lower ratio (Indeed, 2022a). The following chart depicts the debt-to-asset ratio of a business.
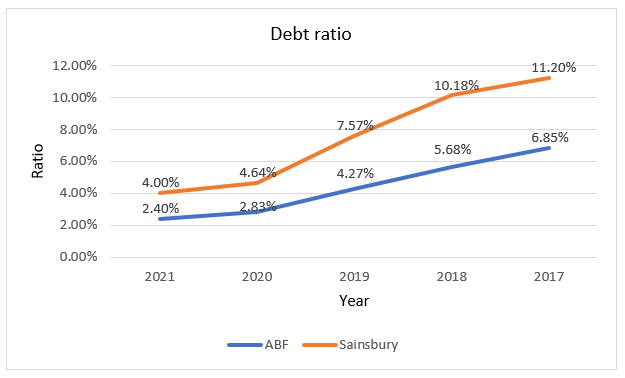
In 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, and 2021, ABF’s debt ratios are 11.20 percent, 10.18 percent, 7.57 percent, 4.64 percent, and 4.00 percent, respectively. For the same period, Sainsbury’s ratios are 6.85 percent, 5.68 percent, 4.27 percent, 2.83 percent, and 2.40 percent. Both companies have declining debt ratios, which are produced by a decrease in indebtedness and a matching gain in asset value. This pattern indicates that both organizations are meeting their debt obligations and, as a result, lowering their debt. However, Sainsbury’s debt ratios are greater, indicating that a larger percentage of its assets were bought with debt, as opposed to ABF’s assets, which are largely financed by equity. As a result of its decreased leverage, ABF is less likely to go bankrupt. Furthermore, ABF has lesser debt and higher profitability, implying that its capital structure is optimal, maximizing shareholder value, but Sainsbury’s higher leverage may be costly, resulting in shareholder value not being maximized. As a result, when capital structure is taken into account, ABF outperforms Sainsbury.
Total asset turnover
One of the efficiency ratios for assessing a company’s ability to generate income from its assets is the total asset turnover. As measured by TAT, this section examines how well a company makes use of its assets to generate income (Best, 2021). A company’s asset turnover can be estimated by dividing net sales by total assets, as shown in the table and graph below.
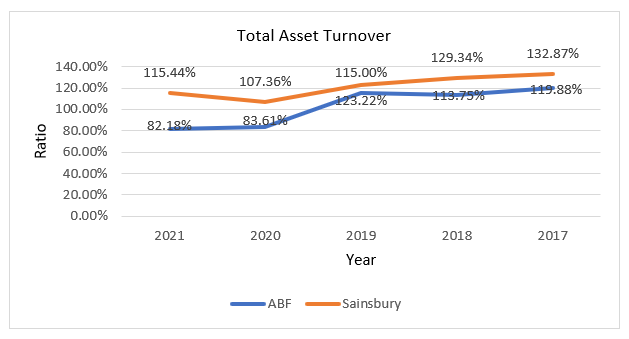
119.88 percent, 113.75 percent, 123.22 percent, 83.61 percent, and 82.18 percent were the current ratios for ABF. The increase in TAT in 2019 was due to increasing revenue, whereas the decreases in previous years were due to increased assets. Sainsbury’s total asset turnover, on the other hand, drops between 2017 and 2020 before increasing in 2021, with figures of 132.87 percent, 129.34 percent, 115 percent, 107.36 percent, and 115.44 percent. The decline was due to assets increasing at a faster rate than sales, but the increase in 2021 was due to lower assets. Because Sainsbury’s TAT is higher than ABF’s, it is clear that it is more efficient. As a result, when efficiency is taken into account, ABF is less competitive than Sainsbury.
In comparison to Sainsbury, ABF has a greater NPM, greater current ratio, lesser debt ratio, and lesser asset turnover. According to this analysis, ABF has stronger profitability and liquidity, as well as reduced leverage and efficiency. Lower leverage, on the other hand, is advantageous because it aids in the development of an ideal capital structure that boosts profitability. As a result, ABF outperforms its competition in terms of financial performance. ABF’s management must devise measures to increase the company’s efficiency.
SECTION TWO
Budgeting: Advantages
For a given time period like yearly, quarterly or monthly, a budget provides an estimate of spending and income. By creating a budget for the company, owners may plan their expenditures for the year and predict any operational changes that may be required in order to keep the firm running. A budget is used to monitor a company’s performance and to better understand its operational expenditures. The following are advantages of budgeting according to Indeed (2022b).
Decision making – The majority of owners of businesses are responsible of making more broad business decisions that affect the company’s cash flow in and out. A budget allows a company to make more informed judgments about how much it can increase remuneration, whether incentives are possible for employees, what benefits it can offer employees, and if it has the capacity to expand business activities.
Performance evaluation – According to Prasanna (2022), employees can work with management to set goals for a budgeting season, as well as bonuses based on their achievement. A budget versus real report could be created to offer staff with information on how they are performing in relation to their goals. Financial and operational goals can be integrated into the budget for performance evaluation purposes using responsibility accounting systems. In addition, evaluation aids in the monitoring and control of the actual outcome. Performance evaluation also aids in the implementation of many activities such as altering business operations over time or changing the budget if it is unrealistic.
Financial planning – Companies should establish financial goals that, if met, indicate whether they performed well and are able to continue operating regularly or expand as needed. It is impossible to know how a firm is going if its management lacks a budget, and you may discover after the year is over that it isn’t generating any money. A budget can help a business stakeholder achieve their goals by giving a clear overview of the sources and uses of business’ money.
Budgeting: Disadvantages
Making a budget is a crucial step in ensuring that your business has the resources it requires to run smoothly. A budget, on the other hand, can sometimes have drawbacks that prevent your business from reaching its full potential. Here are some of the disadvantages of budgeting according to Indeed (2022c) and O’Hoyt (2014).
Based on assumptions – There are normally certain assumptions which are similar to the way the budget was established at the time of writing. Even a minor shift in the business environment could have a significant impact on the company’s income or cost structure, causing budget expectations to swiftly shift. An economic downturn can make this a difficult situation to deal with, as the budget allows for some spending that is unaffordable when there is less income. As a result, the company will lose money if management doesn’t take action swiftly to revise or adjust the company’s budgeting policies. It is also possible that changes in commodity prices, currency exchange rates, and interest rates can alter a project’s performance. (O’Hoyt, 2014).
Rigid decision making – A lot of attention is only paid to strategy at this time of year when they are making their budgets for the next year. We won’t be rethinking our strategy for the rest of the year because we don’t have to do that. Thus, if there is a major shift in the market right after a budget is done, there is no formal way to assess the situation and make changes. This puts a company at a big disadvantage to its more agile competitors.
It is time consuming – It can take a long time to make a budget, particularly in a bad-organized place where many changes to the budget may be needed. If there is a properly-designed budgeting process, employees are used to the process, and the company uses budgeting software, the amount of time it takes is less. If business conditions are volatile, the work can be more extensive. This means that the budget model needs to be changed over and over again (Bag, 2022).
Considers financial results alone – As a result of the numerical structure of the budget, management tends to focus on the quantitative components of a company, which shows a conscious effort to expand or maintain profitability. Customers will only buy from a company if they receive good service and fairly priced goods, and customer satisfaction is more important than a company’s earnings. Qualitative rather than quantitative aspects make it more difficult to budget for these concepts. Thus, budgeting does not always match the client’s requirements.
Budgeting Approaches
Zero-based budgeting – Zero-based budgeting starts from scratch without any reference. As a result, all budget categories begin at zero balance unlike in increamental budgeting. As a result, every business segment is examined, and all expenses, not just the extras, must be approved. Zero-based budgeting guarantees that resources are directed to the areas of your business that require them the most. It accomplishes this by requiring managers to justify everything they do in their departments, knowing that their budget will not be spent otherwise. If they fail to do so, they will lose money and resources, and their job would come to an end. This type of unjustified spending is expected to come to an end (ACCA, 2022).
Top-down Approach – The top-down budgeting process is used to develop the company’s high-level budget. The budget is developed by top management in accordance with the company’s goals and then passed to department heads for implementation. Budgeting should be done first, according to managers. Following the budget preparation, management distributes precise budget allocations to specific divisions, which must subsequently develop budgets in conformity with their objective and budget allocations for budgeting.
The Bottom-up Approach – Bottom-up Budgeting begins at the divisional level and progresses to the executive level. Every department of an organization must submit a list of all resources it requires, as well as a list of all projects it plans to pursue in the coming fiscal year, along with cost estimates. The forecasts for each division are summed up and multiplied by 100 to get the overall budget of the company. Because they are familiar with the project’s cost projections, each department’s management is required to provide feedback.
Relevance of budgeting to performance management
A budget is a financial plan that outlines how funds will be allocated to different purposes. Because of this, a company’s budget comprises a variety of sub-categories in addition to income and expenses. Real, budgeted, and discrepant amounts are shown in three columns in each subsection. Performance is measured using the “difference” column (Benge, 2014).
A company’s labor and material costs, as well as the number of services offered or units produced, are all determined by its budget. After allocating resources to various budget divisions, the approach is utilized to compare planned money to actual utilization. The initial estimate budget is a fixed budget. A flexible budget is created by modifying the static budget. After then, the budget can be used to produce new ones. The aims and resources of the organization must be understood in order to use budgets to assess business performance. It is reasonable to assume that any discrepancies between actual results and budgeted figures are the result of events beyond management’s control.
By analyzing the budget, management can make adjustments to production, inventory, and shipping in order to better serve customers. In addition to enhancing channels of communication with suppliers and consumers, it also encourages management to conduct performance evaluations and strengthen internal channels of communication.
Every day, management reviews evaluation reports to evaluate if the company’s objectives are being met. It is necessary to do a frequent budget review if goals are not being met. If the corporation chooses, they can alter their strategy, operations, and/or other aspects. Additional changes would be made to the next budgets, if necessary.
SECTION THREE
Investment Appraisal
Net Present Value
The intrinsic value of a project with a stream of future cash flows is determined using the Net Present Value (NPV) approach. N PV the sum of all predicted cash flows during the investment’s lifetime, discounted to the present. This strategy, which emphasizes the time worth of money, is in line with the company’s goal of maximizing shareholder wealth. In the NPV approach, the WACC is frequently used as the discounting factor. An investment, a project, or a sequence of cash flows can all be valued using NPV analysis.
Because it includes all of the initial investment, expenses, and income costs involved with a particular investment, Free Cash Flow is an all-inclusive method. The timing of each cash flow can have a significant impact on an investment’s present value. The cash inflows should be watched first, followed by the cash withdrawals.
In an NPV analysis, cash flows are discounted to account for inflation and the risk of the investment. The need for risk adjustment derives from the fact that some projects and investment opportunities are risk-free. To account for risk, the discount rate is lower for less risky assets and higher for riskier ones. The temporal value of money must be examined because of issues such as interest rates, inflation, and wasted opportunities. If the NPV is positive, management should embrace the investment.
Illustration
The management of ABF is deliberating on the purchase of a knitting machine at a cost of £50 000 000. The machine will be useful for ten years and then it can be disposed of as scrap for £6000000. The forecasted cash flows of the machine from the first to the tenth year are £12500000, £13000000, £13000000, £10500000, £9600000, £7900000, £5400000, £3600000, £2400000, and £1500000 respectively. The Net Present Value of the project is: NPV = £5744316.1
The discounting rate that brings the NPV to zero is known as the Internal Rate of Return. The internal rate of return (IRR) compares the value of discounted future cash flows to the amount invested initially. If the IRR surpasses the cost of capital, management approves an investment. Management should approve a project if the IRR exceeds the company’s cost of capital. IRR = 13.50486% The company should adopt the project because its NPV is positive and its IRR has surpassed the cost of capital.
References
ABF Corporate. (2021). ABF at a glance. [online] Available at: https://www.abf.co.uk/about-us/abf-at-a-glance#:~:text=Associated%20British%20Foods%20is%20a,the%20Americas%2C%20Asia%20and%20Australia. [Accessed 20 Apr. 2022].
AACA (2022). Comparing budgeting techniques | F5 Performance Management | ACCA Qualification | Students | ACCA | ACCA Global. [online] Accaglobal.com. Available at: https://www.accaglobal.com/ie/en/student/exam-support-resources/fundamentals-exams-study-resources/f5/technical-articles/comparing-budgeting-techniques.html [Accessed 28 Apr. 2022].
Aragwal, R. (2015). Advantages and Limitations of Budgeting. [online] Your Article Library. Available at: https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/accounting/budgeting-accounting/advantages-and-limitations-of-budgeting/52793 [Accessed 16 Apr. 2022].
Barnes, P. (1987). The Analysis and Use of Financial Ratios: A Review Article. Journal of Business Finance & Accounting, [online] 14(4), pp.449–461. Available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1468-5957.1987.tb00106.x [Accessed 14 Nov. 2021].
Benge, V. (2014). Budgets as a Basis for Evaluating Performance. [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/budgets-basis-evaluating-performance-82027.html [Accessed 16 Apr. 2022].
Best, R. (2021). Asset Turnover Ratio: Explanation & Formula. [online] SeekingAlpha. Available at: https://seekingalpha.com/article/4454199-asset-turnover-ratio?external=true&gclid=Cj0KCQjwr-SSBhC9ARIsANhzu17Cf3N5lCJy2G03ejSf2AUp14hZIAd1MVYr5dJkImlZS-Ns4OYrBmgaAl1qEALw_wcB&utm_campaign=14926960698&utm_medium=cpc&utm_source=google&utm_term=127894704186%5Eaud-1171917839511%3Adsa-1427141793820%5E%5E552341146729%5E%5E%5Eg [Accessed 16 Apr. 2022].
Bragg, S. (2021). AccountingTools. [online] AccountingTools. Available at: https://www.accountingtools.com/articles/what-is-net-profit-margin.html [Accessed 15 Apr. 2022].
Chcom (2013). J Sainsbury. [online] CompaniesHistory.com – The largest companies and brands in the world. Available at: https://www.companieshistory.com/j-sainsbury/ [Accessed March 28. 2022].
Indeed (2022a). Debt Ratio: Types and How to Calculate | Indeed.com. [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/debt-ratio-types-and-how-to-calculate [Accessed 15 Apr. 2022].
Indeed (2022b). 7 Reasons Why Budgeting Is Important. [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/why-budget-is-important [Accessed 27 Apr. 2022].
J Sainsbury. (2021). Forbes. [online] Available at: https://www.forbes.com/companies/j-sainsbury/?sh=1479845022d8 [Accessed 28 Mar. 2022].
Kibet, L. (2021). Current ratio: A liquidity measure that assesses a company’s ability to sell what it owns to pay off debt. [online] Business Insider Africa. Available at: https://africa.businessinsider.com/personal-finance/current-ratio-a-liquidity-measure-that-assesses-a-companys-ability-to-sell-what-it/r5sxe57 [Accessed 15 Apr. 2022].
O’Hoyt, B. (2014). The Disadvantages of Budgeting. [online] Cpapracticeadvisor.com. Available at: https://www.cpapracticeadvisor.com/accounting-audit/blog/10951056/the-disadvantages-of-budgeting [Accessed 27 Apr. 2022].
Onyschuk, M.J. (2020). The advantages and disadvantages of budgeting. [online] Mjobookkeeper.com. Available at: https://www.mjobookkeeper.com/business-management/article/the-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-budgeting/ [Accessed 16 Apr. 2022].
Prasanna (2022). Advantages And Disadvantages Of Budget | What is Budget?, Advantages and Limitations of Budget. [online] A Plus Topper. Available at: https://www.aplustopper.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-budget/ [Accessed 16 Apr. 2022].
Reuters Editorial (2022). ABF.L – Associated British Foods plc Profile | Reuters. [online] Reuters.com. Available at: https://www.reuters.com/companies/ABF.L [Accessed 20 Apr. 2022].
Wsj.com. (2022). Associated British Foods PLC. [online] Available at: https://www.wsj.com/market-data/quotes/UK/XLON/ABF/financials/annual/income-statement [Accessed 20 Apr. 2022].
 write
write