LIST OF TABLES, CHARTS AND FIGURES
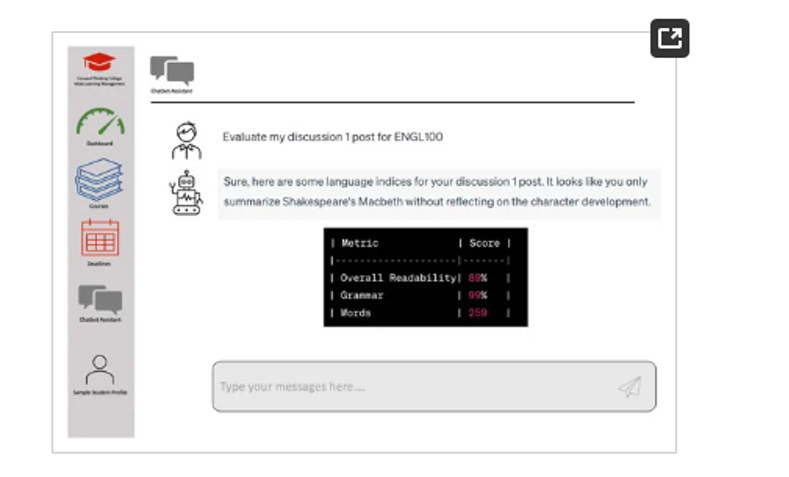
Fig 1: Example of a chatbot, an AI-assisted tool, automatically generating content on learning analytics (Chang et al., 2023)
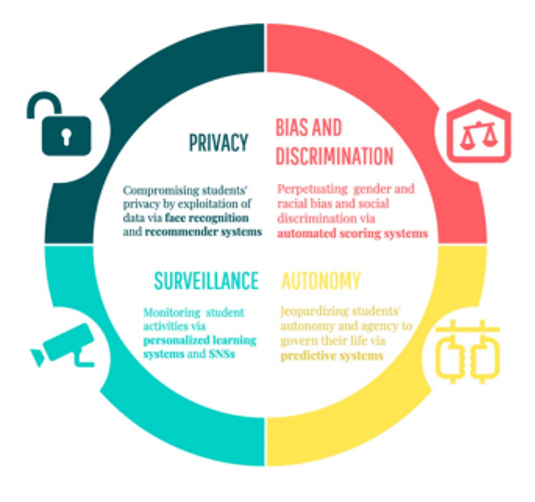
Fig 2: A potential ethical and societal risk of AI application in education (Akgun & Greenhow, 2021)
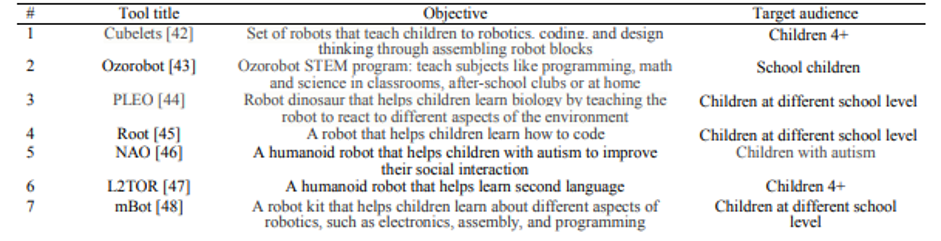
Fig 3: A table on typical examples of robots used in education (Chassignol,et al., 2018)
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
AI-assisted tools significantly refines educational experiences, including enhancing efficiency and proficiency in high school mathematics learning. This report places a significant emphasis on the vital role and challenges of leveraging AI-assisted tools in enhancing the efficiency and proficiency of high school mathematical learning. First, this report overviews the nature of AI in education, pinpointing that the presence of AI-powered tools in education, such as computers and bots, enhances educational efficiency and proficiency. Second, the report point out that the current high school mathematics has been grappled with complexities and difficulties, serving as a clarion call for the leverage AI-assisted tool such as chatbots to enhance learning efficiency. The report point out that these AI-assisted tool enhances learning experience by fostering tailored and individualized learning, enhancing educational engagement and retention and facilitates intuitive tutoring experiences. Whereas these AI-assisted tools hold these benefits, it equally poses significant challenges to education such as raising privacy concerns and increasing risk of technological overreliance. In real life, these AI-assisted tools, such as chatbots, have been used in educational data mining and foster educational and learning interaction.
INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved as a significant tool vitally shaping educational and learning experiences. Grounded on computer science, AI involve developing digital systems and structures that can execute a task that requires human cognition and intelligence (Benbya et al., 2020). These AI systems have been masterfully employed in education setting and have continued to significantly strengthen student learning, development and performance. As part of AI, AI-assisted tools have constantly evolved as significant elements in fostering students’ efficiency and proficiency and strengthening their knowledge in crucial subjects such as high school mathematics. The vital role of these AI-assisted tools goes past the conventional teaching methods and practices, providing a more individualized and flexible educational experience that considers individual preference, needs and learning paces in learning mathematics. Whereas AI-assisted tools continue to enhance proficiency in learning mathematics, they equally pose significant challenges in enhancing the efficiency of high school mathematics learning. Therefore, this report’s purpose is to explore the role and challenges of AI-assisted tools in enhancing high school students’ efficiency in learning mathematics. The intended audience for this report is Chinese educators, Chinese school administrators, global policymakers and Chinese high school mathematics teachers. This report begins by providing a comprehensive overview of AI education, the evolution of AI-assisted learning tools and the current state of high school mathematics education. After that, this paper explores the effectiveness of AI-assisted tools in enhancing learning, challenges and ethical considerations, case studies and real-world applications. The paper concludes by providing a summary of the report while providing comprehensive report recommendations at the same time.
BACKGROUND INFORMATION
Overview of AI in education
AI has refined education by introducing significant tools and approaches that enrich learning experiences. Its incorporation in the education systems and structures fosters educational efficiency and proficiency, enhancing individualized learning and setting students ready for the ever-changing demands and needs of learning, which are technology-based. Currently, AI tools and systems are being used in several significant ways, including chatbots, which offer endless student support to individualized learning algorithmic notations that align with every individual’s needs and preferences (Yildirim & Celepcikay, 2021). Besides these chatbots, there is an increased use of computers and mobile phones, which are powered by AI to offer significant educational solutions such as research. Similarly, AI systems and tools are leveraged in creating individualized quizzes that enhance student engagement. The existence of automatic content generative AI tools such as Scribe and Jasper revolutionizes educational research, as it processes and analyzes vast data amount effectively and efficiently. Additionally, these AI tools and systems exhibit the capability and ability to offer significant response to questions from various evaluative tests and exams.
Evolution of AI-assisted tools
AI-assisted learning tools have undergone significant evolution over the years. In the initial years, society heavily depended on the traditional basic structures and systems. However, the evolution of AI-assisted tools has led to more complex machine learning, significantly refining the educational space. Currently, there are several significant AI-assisted tools which continue to refine education and learning experience. One of these AI-assisted tools is Chatbot, which is used to answer numerous questions. Another AI-assisted tool is Grammarly, which is used to correct grammatical errors within a text (Fitria, 2021). Here, these AI-assisted tools facilitate deep learning, process the natural language, and are able to perform tasks and functions that require human intelligence, such as mathematics.
Current state of high school mathematics
The current state of high school mathematics is characterized by complexities and challenges, which reflect the ever-evolving changes in the educational system. Here, this curriculum has seemingly gone past the traditional topical concerns to encompass diverse topics such as calculus and statistics that require increased individual engagement. With this complex state of high school mathematics, students are required to master both the basic and the complex mathematical concepts. According to Hwang and Tu (2021), learning mathematics has proved to be a significant challenge for many students. The percentage of students proactively engaging in repeated learning has been on the rise, and nearly one-third of students in a mathematics class drop perceived complex topical concerns such as calculus (Rasmussen et al., 2011). However, the current high school mathematics has witnessed technological integration, particularly AI-assisted tools. These existing AI-assisted tools, such as calculators and computers, eminent in the current high school mathematics space, actively engage high school students, fostering a comprehensive understanding of these mathematical concepts effectively. Here, student has leveraged these AI-assisted tools to perform complex operation and calculations that require human intelligence.
DISCUSSIONS OF FINDINGS
Effectiveness of AI tools in enhancing learning
The integration of AI-assisted tools refine and enhance learning experience, particularly in high school mathematics. One of the vital aspects of these AI-assisted tools is their ability to foster student engagement in ever-changing and interactive learning. Enhancing student engagement, retention, and interaction is crucial for successful learning. The conventional teaching methods and practices have often struggled to effectively enhance student learning engagement of the high school students’ because of overreliance on outdated and paper-based techniques. However, the introduction and usage of AI-assisted tools have fostered student interaction and engagement, especially when it comes to learning mathematics. According to Rd et al. (2023), the AI systems have programmed instructions with new concepts that enhance learners’ engagement. Here, it is the comprehensive visualizations charged by AI that make complex mathematical concepts substantial, facilitating easier understanding. For example, the virtual realities offer students engaged and simulative learning experiences, enabling them to dig deeper to unravel various mathematical conceptions and topical concerns in a manner that surpasses book explanations. Additionally, chatbots, an AI-assisted tool, foster interactive and flexible learning experiences, ultimately enhancing positive student learning experiences (Chang et al. 2023). As such, the incorporation of these AI-assisted tools in learning mathematics makes the experience more exciting. This, in the long run, improves learning engagement while at the same time enhancing long-term content mastery.
In addition to enhanced student learning engagement and knowledge retention, AI-assisted tools foster individualized learning experiences, which is critical to enhancing mathematical learning. One of the vital roles of AI-assisted tools in education and learning space is their capacity and capability to offer individualized learning experiences. The traditional learning sphere has often failed to take into consideration the varied student individual needs, preferences and paces, especially when it comes to learning vital subjects like mathematics. These traditional educational and learning space have subscribed to a universal learning approach, which perceive these student needs, preferences and pace from a single point of view. In this traditional learning system, the teacher would employ the same method in teaching students (Akyuz, 2020). However, the introduction of AI-assisted tools has facilitated learning adaptation, with these high school mathematics students having a more remarkable ability to personalize learning to align with their preferences and needs. According to Müller and Massaron (2021), AI-assisted tools serve as adaptive learning platforms that personalize learning experiences, enabling students to progress with learning at their personalized pace. AI-assisted tools acclimatize and create learning paths that adapt to every student’s needs and preferences by employing algorithmic notations as well as machine learning mechanisms to evaluate student performance and the subsequent data (Baskara, n.d). In this sense, AI-assisted tool bridges the existing learning gap, enabling high school students’ to comprehensively learn mathematics according to their paces. This, in the long run, fosters content mastery and flexibility in learning mathematics.
AI-assisted tools also play a vital role in enhancing efficiency and proficiency in high school mathematics by offering intuitive tutoring approaches different from those provided within the classroom space. Individualized tutoring that is different from that which is provided in the classroom enables students to stay in line with what they are learning. AI-assisted technological tools foster intuitive and engaging tutoring approaches, which contributes to greater learning experiences in mathematics. This aligns with the assertion that Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools and systems offer students intelligent tutoring systems, which are computer programs devised to integrate techniques from the AI space to “provide tutors who know what they teach, who they teach and how to teach it” (Nwana, 1990, p. 252). These AI-assisted tools provide individualized support to these students learning mathematics. With these tutoring systems, mathematics students stand in a greater position to strengthen their knowledge and efficiency in learning mathematics, as they are able to supplement the mathematical concepts that have already been taught in class. In the same sense, these AI-assisted tools enable these learners to conserve teachers, as the student already has substantial information. Contextually, one of the AI-assisted technological tools contributing to intuitive tutoring systems is the Jasper chatbot, where individuals can explore vital information around the topic and generate answers, which serve as a supplement to the mathematical concepts taught in the physical classrooms. Thus, AI-assisted tools pivotally enhance mathematical learning by facilitating intuitive learning approaches.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
One key challenge of AI-assisted tools in the learning space is the increased risks of technological overreliance. As entities in the education space, including high school institutions, continue to depend on technology, particularly AI-assisted tools, for enhancing learning experiences, there is an increased speculation that it might make students more glued to technology. As a consequence, this stands to interfere with their educational and learning experiences. One of the key concerns is that it stands to erode the students’ ability and capacity to think critically in finding solutions to various problem within the educational sphere. As a matter of fact, these AI-assisted tools employ numerous algorithmic notations to develop content that aligns with the students’ abilities and needs. According to Chen et al. (2020), AI-assisted tools like computers foster adaptive learning, which is grounded on personalized needs. This overreliance on AI-assisted tools because of their ability to enhance adaptive learning is what results in increased risks of technological overreliance. This overreliance discourages students from actively engaging in developing personalized thoughts. In the case of mathematics learning, an increased risk of technological overreliance tends to inhibit critical and creative thinking among high school mathematics students. For example, the constant use of chatbots to generate a mathematic solution limits students’ ability to engage in proactive critical and creative thinking, ultimately impeding enhanced high school mathematical learning. Therefore, AI-assisted tools pose a threat to enhanced learning and education because they increase the risks of technological overreliance.
Another ethical challenge of AI-assisted tools in education and learning space is reduced privacy. The use of AI-assisted tools threatened educational and learning experiences because it reduced privacy. According to Baidoo-Anu and Ansah (2023), there has been an increasing concern regarding privacy and data security, especially when individuals are using AI generative tools and models. In the event that students utilize and interact with AI systems and structures, large amounts of data amount is obtained and processed. Sometimes, this AI-assisted tools goes overboard to collect individual sensitive information such personal biodata. This poses the risk of data breaches, raising ethical regarding its efficiency. The intrusive ability of these AI-assisted tools, which manifests through the collection of student personal biodata and related sensitive information, tends to manipulate personal details, resulting in misuse and abuse of data privacy. Additionally, the AI-assisted tools are often follow the manner in which they are trained, meaning that it lack creativity, which fuel privacy concerns. Thus, integrating AI-assisted tools in education and learning space, particularly in mathematics learning poses a challenge to enhanced education and learning experience because it it reduces data privacy.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications of AI-assisted tools
In high schools, AI-assisted tools have been incorporated to facilitate learning, including high school mathematical learning. According to Eguchi et al. (2020), the AI-assisted technologies have been used in K-12 curriculum, with students the students using the AI-assistants and AI smart devices like Google enhance smart speaker. Contextually, the Japanese national curriculums mandate computer education system in all its elementary schools starting 2020 (Eguchi et al., 2020). This served as the foundation for the subsequent AI-assisted technologies that are commonly used in teaching critical subjects like mathematics. A similar case of the integration of AI-assistive tools in enhancing high school mathematical learning manifest in the Turkish curriculum for secondary schools, which has leveraged the AI-assistive tools to offer solutions to the mathematical problems (Cunska, 2020). With these AI technologies an individualized learning is fostered with the machines using algorithmic notations to develop content, including high school mathematical content that conforms to the students’ needs, preferences and learning paces.
Besides enhancing mathematical learning, including high school mathematical learning experience, the AI-assisted tools have facilitated educational data mining (Yildirim & Celepcikay, 2021). In the broadest sense, educational data mining entail acquiring significant student educational data to tailor education in line with students, while simultaneously generating new learning conception, ideologies and topical concerns. Various entities within the educational space have employed these AI-assistive tools to mine student educational data. This helps in generating educational concepts and content that comprehensively conform to individual needs, preferences and interest. This equally manifest in the high school mathematical learning, where AI-assistive devices such as the Oracle data mining have been used to collect data and information regarding students’ abilities, interests and preferences, which are used to develop learning practices that equally subscribe to the interests, abilities and capabilities.
Additionally, AI-assistive tools, particularly AI chatbots, have been used to foster interactive and engaging learning experiences. With these chatbots, students can easily obtain answers to their questions at any time and convenience. This stands to strengthen high school mathematical experience as they students get answers from mathematical concepts they haven’t understood. In university of Murcia in Spain, students use these AI chatbots to socialize and interact with other students (Yildirim & Celepcikay, 2021). A similar case is experience in the Staffordshire University in the United Kingdom that has leveraged chatbots to respond to students’ questions at any time (Yildirim & Celepcikay, 2021).
CONCLUSION
In a nutshell, AI-assisted tools have proved to be significant elements in revolutionizing education systems. Specifically, these AI-assisted tool has played a vital role when it comes to enhancing high school mathematical learning. Essentially, this report has emphasized the the role and challenges of AI-assisted tools in enhancing the efficiency of high school mathematics learning. Among the roles includes enhancing learning engagement, facilitating tailored and individualized learning and fostering intuitive tutoring systems. Whereas AI-assisted tool stands to enhance learning, including high school mathematics learning, it present significant challenges, which includes reduced privacy and increased risk of technological dependency and reliance. Besides students, teacher also add up as the beneficiaries of these assisted technologies in the sense that it allows them to generate new content and understand new ideologies associated with the topic of interests and thematic concerns.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Whereas this report unravels significant information surrounding the role of AI-assisted technologies in enhancing mathematical learning, future research conducts a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the implications and ramifications of integrating these AI-assisted systems in education. This emphasis should be placed on the cost and maintenance of these AI-assisted items in education. The future report should emphasize the ease of integrating these AI-assisted tools in education, while simultaneously comparing the effectiveness and efficiency of these AI-assisted tools in enhancing educational experiences.
REFERENCES
Akgun, S., & Greenhow, C. (2021). Artificial intelligence in education: Addressing ethical challenges in K-12 settings. AI and Ethics, 1-10.
Akyuz, Y. (2020). Effects of intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) on personalized learning (PL). Creative Education, 11(6), 953-978.
Baidoo-Anu, D., & Ansah, L. O. (2023). Education in the era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): Understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. Journal of AI, 7(1), 52-62.
Baskara, F. R. PERSONALISED LEARNING WITH AI: IMPLICATIONS FOR IGNATIAN PEDAGOGY. International Journal of Educational Best Practices, 7(1), 1-16.
Benbya, H., Davenport, T. H., & Pachidi, S. (2020). Artificial intelligence in organizations: Current state and future opportunities. MIS Quarterly Executive, 19(4).
Chang, D. H., Lin, M. P. C., Hajian, S., & Wang, Q. Q. (2023). Educational Design Principles of Using AI Chatbot That Supports Self-Regulated Learning in Education: Goal Setting, Feedback, and Personalization. Sustainability, 15(17), 12921.
Chassignol, M., Khoroshavin, A., Klimova, A., & Bilyatdinova, A. (2018). Artificial Intelligence trends in education: a narrative overview. Procedia Computer Science, 136, 16-24.
Chen, L., Chen, P., & Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: A review. Ieee Access, 8, 75264-75278.
Cunska, A. (2020). Effective learning strategies and Artificial Intelligence (AI) support for accelerated math acquisition. In European Proceedings of International Conference on Education and Educational Psychology. European Publisher.
Eguchi, A., Okada, H., & Muto, Y. (2021). Contextualizing AI education for K-12 students to enhance their learning of AI literacy through culturally responsive approaches. KI-Künstliche Intelligenz, 35(2), 153-161.
Fitria, T. N. (2021). Grammarly as AI-powered English writing assistant: Students’ alternative for writing English. Metathesis: Journal of English Language, Literature, and Teaching, 5(1), 65-78.
Hwang, G. J., & Tu, Y. F. (2021). Roles and research trends of artificial intelligence in mathematics education: A bibliometric mapping analysis and systematic review. Mathematics, 9(6), 584.
Müller, J., & Massaron, L. (2021). Artificial Intelligence for Dummies. Wiley.
Nwana, H. S. (1990). Intelligent tutoring systems: an overview. Artificial Intelligence Review, 4(4), 251-277.
Rad, H. S., Alipour, R., & Jafarpour, A. (2023). Using artificial intelligence to foster students’ writing feedback literacy, engagement, and outcome: a case of Wordtune application. Interactive Learning Environments, 1-21.
Rasmussen, C., Heck, D. J., Tarr, J. E., Knuth, E., White, D. Y., Lambdin, D. V., … & Barnes, D. (2011). Trends and issues in high school mathematics: Research insights and needs. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 42(3), 204-219.
Yildirim, Y., & Celepcikay, A. (2021). Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications in Education. Eurasian Journal of Higher Education, (4), 1-11
Yildirim, Y., & Celepcikay, A. (2021). Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications in Education. Eurasian Journal of Higher Education, (4), 1-11.
 write
write