Introduction
This report will examine the ownership structure and discuss the pros and cons of the corporate governance of the British multinational enterprise Burberry Group PLC. A component of this report will also outline and assess the challenges Burberry faces in the market in which it operates and propose ways to tackle such challenges.
Concept of Ownership
The legal authority to direct a company’s operations and policies are derived from ownership of the corporation. Initially held only by a family or a single person, a firm eventually becomes publicly traded by offering all or a portion of its shares in an Initial Public Offering (IPO) or employing a Special Purpose Acquisition Vehicle (SPAC). Highly dispersed ownership is a defining characteristic of large publicly listed organizations. These corporations’ management is chosen to make choices and operate in the best interests of the shareholders.
As stated in Berle and Means’ book Modern Corporation and Private Property, conflicts of interest between shareholders and management always result from the agency problem, better known as the information asymmetry between both parties (Means, 2017). There are a variety of outlooks on what the management’s objective should be: the two key ones are the Shareholder Wealth Maximization viewpoint, which promotes the notion that the administration should operate to maximize returns for its shareholders, and the Stakeholder Capitalism viewpoint, which supports the concept that there should be an unbiased link between increasing corporate wealth and the welfare of all stakeholders in the company.
Concept of Governance Structure
Corporate governance is imperative due to the division between ownership and management of the company.
Corporate governance is a framework for managing and directing businesses. The owner’s responsibility is to elect the board of directors and auditors while ensuring a suitable corporate governance structure is implemented. Companies and directors must build and maintain strong connections with many stakeholders to prosper in the long run. (2017) (Financial Reporting Council Responsibility, Fairness, Transparency, and Accountability.) The Financial Regulatory Counsel (FRC) established the UK’s Corporate Governance Code in 2018. It has since been updated regularly to reflect the country’s growing need for a corporate governance framework. The code’s guiding principles have successfully achieved strong corporate governance practices and encouraged long-term investing.
If they are built on mutual respect, trust, and benefit, these relationships will succeed and be rewarding. In light of this, a company’s culture should encourage honesty and transparency, appreciate diversity, and be receptive to the opinions of shareholders and other stakeholders. The code allows flexibility rather than laying down a rigid set of regulations by applying principles and requiring compliance or by outlining provisions and providing supporting information. Boards must utilize this freedom prudently, and investors and their advisors must carefully consider deferring company purchases. The code applies to all companies with a premium listing, whether incorporated in the UK or elsewhere. A multinational enterprise is an enterprise that controls and manages production establishments in at least two countries.
Burberry Group Overview
Burberry Group Plc is a British luxury design house and apparel company headquartered in London, England. The business, founded in 1856 by Thomas Burberry, first focused on outdoor clothing before branching out to the high fashion market and expanding internationally. Burberry is “one of the most valuable luxury brands in the world” (Subanoglu, 2022). Burberry is well-known for its trench coats and distinctive tartan lining pattern. In 2022, the firm made over 2.8 billion GBP in worldwide income, with “most of it coming from the Asia Pacific area”
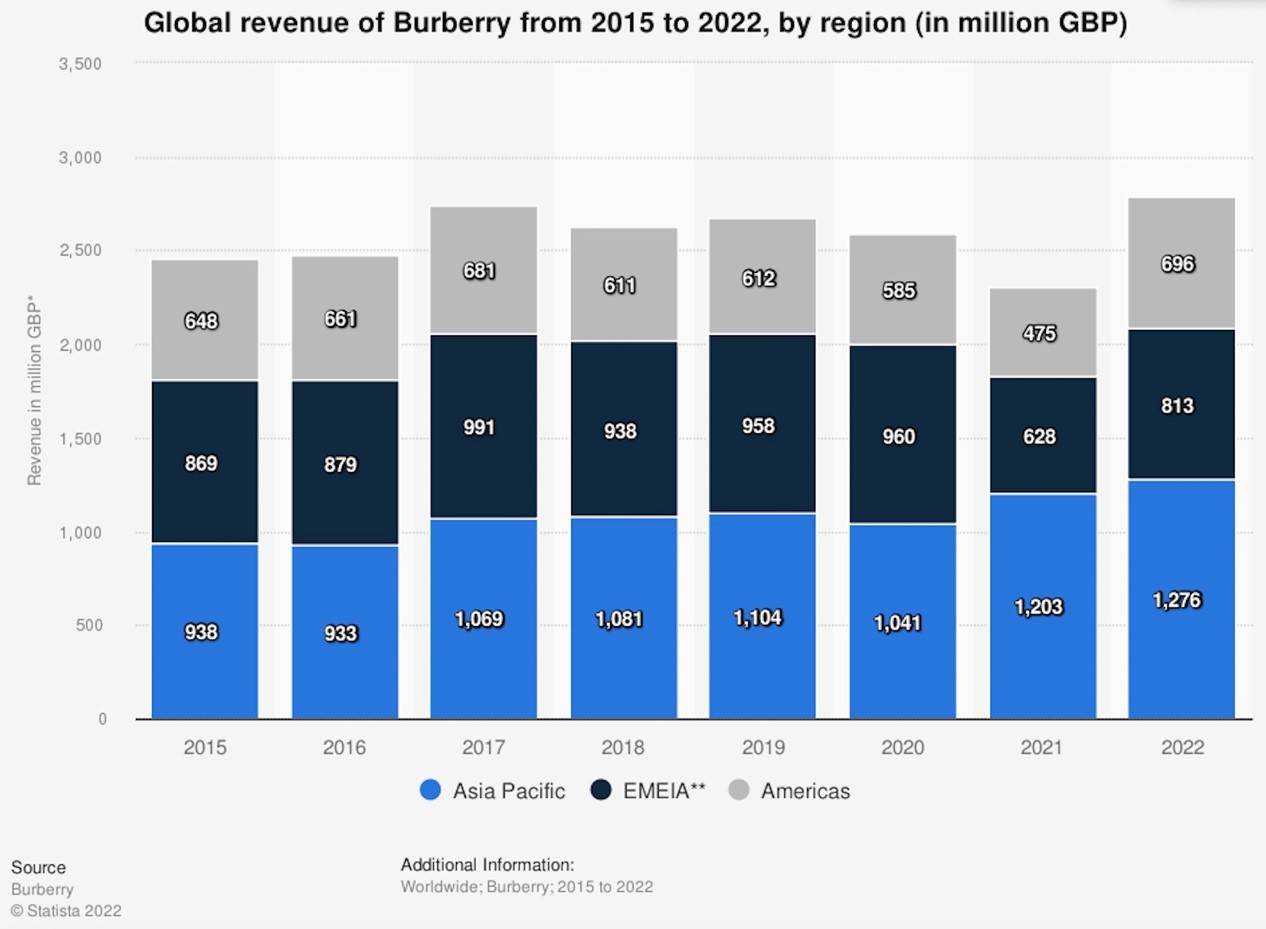
(Subanoglu, 2022), demonstrating how much it benefits from its international operations.
Burberry Group Ownership Structure
Publicly listed on the London Stock Exchange since 2002, Burberry Group PLC is a member of the FTSE 100 Index, with a market capitalization of 7.12 billion GBP (Bloomberg).
Burberry was an independent family-controlled company until 1955 when Great Universal Stores (GUS) assumed ownership until the demerger in 2005. Where at this point, holding majority ownership, institutional investors became the majority in ownership by owning 81.18% of Burberry Group’s shares. Therefore, it suggests that no single shareholder has significant control over the company. The largest shareholder, however, is Massachusetts Financial Services Co, an investment management fund with 9.24%, BlackRock Inc at 8.85%, Baillie Gifford & Co at 7.40%, Vanguard Group Inc 5.45%, and Sun Life Financial Inc at 5.32%.
Ownership History of Burberry Group PLC
Burberry Group PLC is a British luxury fashion house headquartered in London, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. The company was founded in 1856 by Thomas Burberry, who revolutionized rainwear with the invention of gabardine (Kaolawanich et al., 2020). The company is led by Christopher Bailey and is known for its trench coats, initially designed for soldiers fighting in the First World War, and its distinctive check pattern, which has been used on various products, including clothing, accessories, and home furnishings. Burberry is one of the leading luxury fashion houses in the world, with a strong presence in Europe, the Americas, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East. The company has a portfolio of over 500 stores and concessions globally, including flagship stores in London, New York, Milan, Paris, and Hong Kong. Burberry is majority-owned by GUS plc, a British conglomerate. GUS plc also owns several other businesses, including Experian, a credit reporting agency, and Home Retail Group, a home improvement retailer.
Advantages of Burberry Group Ownership Structure
Several advantages can be associated with Burberry Group’s ownership structure. One of the key advantages is that the company has centralized and unified control over its operations. The company is wholly owned by a single entity, the holding company Burberry Group plc, which means there is no need for the company to consult with or answer to any other shareholders or stakeholders when making decisions about its operations. The company has continued integrating more Britishness into its primary supply chain to restore its corporate heritage and fundamental brand values and reorient its operations towards a brand-led and customer-centric strategy (Robinson & Hsieh, 2016). The increased independence contributes to a greater level of efficiency and coordination within the company and a greater level of control over its strategic direction.
The second advantage of the ownership structure is that it provides Burberry Group with a greater degree of flexibility when it comes to making decisions about its business. One of the principles of good corporate governance is that it should be flexible and avoid rigidity. The company does not have to consider the wishes of many different shareholders when making decisions. The flexibility allows the company to be more agile and responsive to market changes in the broader business environment. The company employed a responsive supply chain strategy making it more flexible to the dynamics of the emerging consumer’s needs and wants (Robinson & Hsieh, 2016). Third, the ownership structure of Burberry Group can also provide the company with a greater degree of financial stability. Any corporation must be stable to facilitate proper governance of all its entities. The reason is that the company does not have to worry about the possibility of a hostile takeover from another company or group of shareholders. The flexibility gives the company greater security and allows it to plan for the future with greater certainty.
Disadvantages of Burberry Group Ownership Structure
One of the cons of the ownership structure is that Burberry company is only owned by a small number of shareholders which means that there is less diversity in the ownership structure and that the company is more vulnerable to the whims of a small group of investors. In addition, there is a lack of control, given that Burberry is a publicly traded company subject to the whims of the stock market and shareholders’ actions (Robinson & Hsieh, 2016). The company faces difficulties pursuing long-term strategies or making decisions that may be unpopular in the short term but beneficial in the long term. Secondly, the company is also highly geared, with a large proportion of its capital being provided by debt, making it more susceptible to interest rate changes and economic downturns. The changes in interest rates are uncertain and create capital fluctuations and alter the profits obtained by the company from its sales.
Third, the company has a relatively low level of free float, meaning that a relatively small number of shares are available for trading, which makes it difficult for investors to buy and sell shares in the company and can make the share price more volatile. Burberry Group is also subject to increased regulation from governmental agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission, which can add compliance costs and make it more difficult for the company to respond quickly to changes in the marketplace (Stevenson & Cole, 2018). Fourth, the company has a relatively high level of insider ownership, meaning that a significant proportion of the shares are owned by directors and other senior executives, which makes the company less responsive to the wishes of outside shareholders. Publicly traded companies are often under pressure from shareholders to produce short-term results, which can lead to a focus on short-term strategies that may not be in the best interests of the company or its long-term shareholders.
The fifth demerit is that Burberry company is listed on the London Stock Exchange, which imposes certain restrictions on the company’s ownership structure. For example, the company must have a minimum of two directors, and the public must hold a certain proportion of its shares. The ownership structure can also create conflicts of interest between the different shareholders (Burberry, 2018). For example, suppose one shareholder wants to sell their shares. In that case, this may not be possible if the other shareholders do not want to sell, which can lead to a stalemate within the company and may prevent it from being able to make decisions promptly. Additionally, the ownership structure can make it difficult for the company to raise capital. Finding investors willing to invest in a company with a complex ownership structure may be challenging. Burberry Group is also a potential target for takeover by another company which could result in a loss of control over the company’s direction and strategy.
Burberry’s Governance Structure
The company is managed by a board of directors headed by a chairman. The company has an executive committee for running daily affairs. The Chief creative officer is responsible for the company’s creative direction, and the chief executive officer oversees the business operations. Burberry has a dual- governance structure, with a supervisory board and a management board. The supervisory board is responsible for the company’s strategic direction, while the management board is responsible for its day-to-day operations (Burberry, 2022). Burberry has several subsidiaries, including several joint ventures. One is Thomas Burberry Limited, which holds the brand’s trademarks and licenses. Other subsidiaries include Burberry Group plc and Burberry Limited. Burberry aligns with the principles of corporate governance by having a Board of Directors responsible for the overall strategy and direction of the company and an Executive Committee responsible for the day-to-day running of the business (Burberry, 2022). The company also has several committees that oversee specific areas of the business, such as finance, audit, and remuneration.
Countries of Operations of Burberry Group PLC
The company has established operations in the UK, US, China, Latin America, the Middle East, Eastern Europe, Russia, Brazil, and India. In addition, the company also operates in other regions like South Africa and various places in South East Asia. The company is protected from economic uncertainty in such nations due to its broad, diverse worldwide market.
Opportunities of Burberry Group PLC
Burberry aims to communicate openly with the UK’s HMRC and the tax authorities in all other countries where they do business. They make an effort to make sure that all tax filings remain accurate and are sent as scheduled. Any unintentional mistakes in tax filings or communications with tax authorities are immediately disclosed. To foster a professional, cooperative working partnership with HMRC Client Compliance Manager and specialized HMRC groups in the UK, Groups Finance, the global tax, and trade compliance teams, and Group Finance have constant communication (Burberry, 2022). Burberry participates actively in developing UK and global tax policies, where appropriate, participating in official and informal conversations on its behalf or through fair trade and industry associations.
The second opportunity is the Supply chain transparency for Burberry, which demonstrates that the current network improves network and products relations for business in all countries of operations. Burberry places a strong emphasis on sustainability in addition to the calibre of its raw materials. For instance, Burberry uses cotton from Better Cotton Project (1st supplier), which is in touch with one million cotton growers (2nd suppliers) worldwide, to weave and seam fabric in their own factories in order to minimize environmental issues and create a long-term supply of raw materials (Burberry, 2019). Thirdly, Burberry operates through backward integration strategy that has enabled it to grow its business. In order to build a strategic business organization and expand into a new market, Burberry is able to attract new consumers from both Business to Business (B2B) and Business to Consumers (B2C) networks through relational collaboration (Iglesias and Schults, 2020). Burberry will be able to lower production and delivery expenses attributable to this investment. Additionally, it will provide Burberry control over the leather goods’ durability and material quality.
The fourth opportunity of Burberry is that it is the first company to leverage Snapchat and other social media platforms to give customers access to exclusive content at Burberry locations. To create an exclusive content for Snapchat, Burberry collaborates with Oscar-winning director Steve McQueen (Kaolawanich et al., 2020). The tactic has enhanced the value of the Burberry brand and given the consumer a novel experience. Additionally, by focusing on current Snapchat users, Burberry has been able to introduce the brand to a new, younger demographic. The Snapchat has also given Burberry the opportunity to potentially deepen its customer relationships. Therefore, collaborating on online marketing could boost Burberry’s chances of connecting with the Vietnamese fashion industry (Dinh et al., 2019). Additionally, Burberry has used a diversification strategy in its partnerships with organizations like Coty Inc., a pioneer in beauty products globally. Through such partnerships, Burberry has increased its market share, elevated its brand value, and successfully attracted new consumers in the Vietnamese market.
Challenges of Burberry Group PLC
The first challenge of Burberry Company is the increased competition from other luxury brands. International companies like Coach, Prada, Gucci and Louis Vuitton are among Burberry’s many rivals. Additionally, Burberry’s rivals include a number of UK labels like Alexander McQueen, Vivienne Westwood and Stella McCartney. Research has shown that the fashion industry is very competitive. The brands have been able to steal market share from Burberry due to their stronger financial position and more innovative designs (Kaolawanich et al., 2020). The second challenge is that Burberry has seen a decline in sales in its core markets of the United States and Europe. For instance, in the twelve months ending March 2018, Burberry’s sales in the US declined by 4%, while sales in Europe fell by 2%. The company has attributed the decline in sales to a number of factors, including the challenging macroeconomic environment, changes in consumer spending patterns, and increased competition from other luxury brands.
Third is that Brexit vote in June 2016 has had a significant impact on Burberry’s business. The company has warned that the UK’s decision to leave the European Union could have a number of negative consequences, including a decline in consumer confidence, higher costs, and disruptions to the supply chain (Jeary, 2019). In addition, the company in the recent years has also been affected by inflationary pressures. In particular, the rise in the price of oil has had a significant impact on the cost of raw materials used by Burberry, as well as the cost of transportation. As a result, the company has had to increase prices on some of its products in order to offset these rising costs. Fourthly, Burberry has also been impacted by changing consumer preferences, with more shoppers now opting for online channels and cheaper alternatives to luxury brands. The fifth challenge is that Burberry has also been impacted by the slowdown in the Chinese economy. For instance, sales in China fall greatly by 8% in the twelve months ending March 2018. The decline in the sales altered the revenue gains for the company.
Solutions to the Challenges
Burberry needs to intensify its competitiveness in the fashion industry by investing in its own digital capabilities and store experience, as well as launching new products. Burberry should concentrate on upholding its distinctive online marketing network, brand image, and trademarks which might provide a chance to enter a new market (Kaolawanich et al., 2020). The company needs to adjust its product mix and price points for the Chinese market, as well as increase its focus on digital channels to help deal with economic downturns during recession. The company needs to refocus on a new brand strategy, store closures, and job cuts to deal with declining sales. In addition, partnering with other online retailers is a solution to the challenge of changing consumers tastes and preferences.
Conclusion
Burberry has an outstanding ownership following its capability to manage the company both at the headquarters in the UK and also in the countries of operations. The governance structure is flexible and stable consisting of the board of directors, executive committee and other committees for various functions. The various players in the organization have roles and responsibilities in which they execute. The governance structure also conforms to the principles of corporate governance. However, the ownership structure lacks diversity due to a small number of shareholders. The company’s openness in communication and transparency in business provides it with opportunities in tax contributions, customers engagements, and digitization in business deals. The company is also confronted by competition, declining sales and inflationary pressures. Diversifying in online marketing and digital platforms would help in creating a market niche for the company worldwide.
References
Burberry. 2022. Tax policy, Burberry Corporate Website. Available at: https://www.burberryplc.com/en/company/governance/tax-policy.html (Accessed: October 29, 2022).
Burberry .2018. Annual Report – Burberry. Available at: https://www.burberryplc.com/content/dam/burberry/corporate/Investors/Results_Reports/2018/Burberry_AnnualReport_FY17-18.pdf (Accessed: October 29, 2022).
Burberry.2019. Product. Available from: https://www.burberryplc.com/en/responsibility/responsibilitystrategy/product.html?fbclid=IwAR0ilrNiARsxr57rXPK5Mu_OMJdqrbLas9dkDChQQk2EEHtcUqPOYwT4AU [Accessed 9 March 2020]
Dinh, H.P., Nguyen, P.V. and Hosseini, J.C., 2019. The impact of product diversification and capital structure on firm performance: evidence from Vietnamese manufacturing enterprises. Journal for Global Business Advancement, 12(1), pp.95-116. https://www.inderscienceonline.com/doi/abs/10.1504/JGBA.2019.099920
Iglesias, O., Ind, N. and Schultz, M., 2020. History matters: The role of history in corporate brand strategy. Business Horizons, 63(1), pp.51-60. History matters: The role of history in corporate brand strategy – ScienceDirect
-Jeary, N. 2019. Burberry warns on the impact of a no-deal Brexit, UK Investor Magazine. Available at: https://ukinvestormagazine.co.uk/burberry-warns-on-the-impact-of-a-no-deal-brexit/ (Accessed: October 29, 2022).
Kaolawanich, R., Oe, H., Yamaoka, Y. and Chang, C.Y., 2020. A discussion of a luxury apparel brand strategy in an emerging market: Conceptual model with network perspectives. Journal of Social, Cultural and Political Studies, 4(2), pp.58-72. *57-Article Text-119-2-10-20200922 (1).pdf
Means, G., 2017. The modern corporation and private property. Routledge. The Modern Corporation and Private Property | Gardiner Means | Taylor (taylorfrancis.com)
Robinson, P.K. and Hsieh, L., 2016. Reshoring: a strategic renewal of luxury clothing supply chains. Operations Management Research, 9(3), pp.89-101.
Stevenson, M. and Cole, R., 2018. Modern slavery in supply chains: a secondary data analysis of detection, remediation, and disclosure. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal.
 write
write