Nokia, established in 1865, is a Finnish multinational telecommunications corporation. With an annual net profit of $22 billion (Ali-Yrkkö et al., 2011), the firm has a long tradition of technology innovation and is one of the biggest in the telecommunications sector. However, being reluctant to adopt new smartphone technology, the corporation has lost its dominant market position to close rivals like Apple and Samsung.
Figure 1 Nokia net sales worldwide from 1999 to 2021
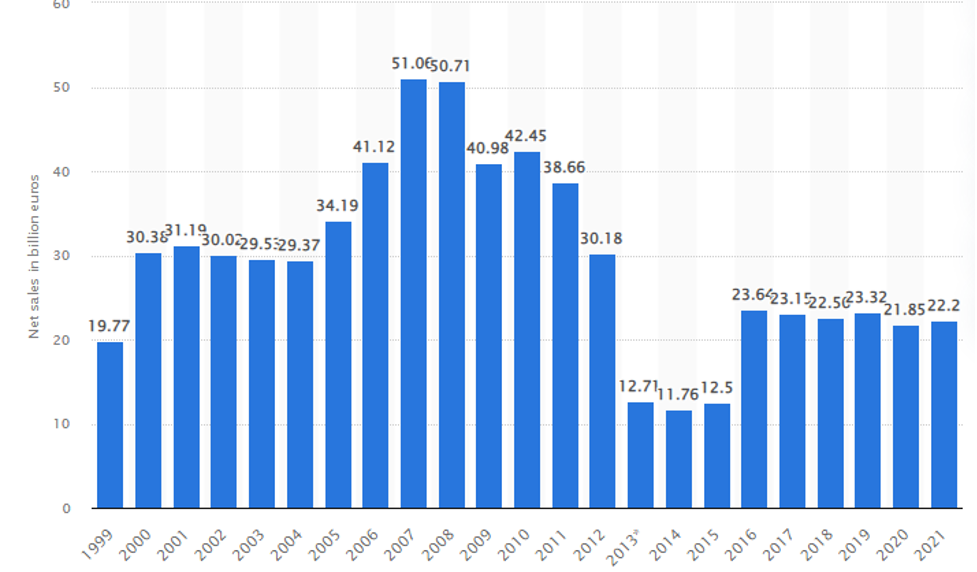
Source Statista (2021)
Nokia has more than 88,000 workers and works in many fields, such as network infrastructure, software, and licensing. Its main business is to provide mobile network owners all over the globe with the resources they require for managing their networks, such as 5G networks. Nokia is also a big player in the software business, with devices like the operating system it developed for mobile devices and licensing its technological copyrights. Nokia was selected as a case study of innovation, business, and technology transfer because the business has an extensive track record of developing innovative concepts that can change with the market. But the company has yet to be able to successfully add cutting-edge technology to its current offerings lately. As a result, it cannot compete with Apple and Samsung’s cutting-edge offerings. So, the organization is an ideal setting for starting this study.
One big problem Nokia has is ensuring that the latest technology operates effectively on its current product lines or platforms. This problem is important to the company because it impacts its capacity to stay competitive in competitive markets and satisfy the needs of its stakeholders. Users, shareholders, providers, workers, and government regulators are all interested parties in this issue. Customers require Nokia to have the newest and most cutting-edge technology, and shareholders desire to experience a return on their investment. Nokia requires its suppliers to give it the parts it needs to add new technology to its products, and its workers must learn how to use the new technology. Regulators also want to ensure that new technologies meet safety and environmental standards.
Figure 1 Nokia Good Interaction with Stakeholders
Source Nokia (2022)
Nokia risks losing market share, profitability, image, and the capacity to meet consumer demands if it is unable to effectively integrate new technologies into old product lines or platforms. New markets will open up, product features will be enhanced, and productivity will rise if Nokia properly incorporates new technology. If new technologies are successfully integrated, novel goods and services can be developed, opening up new markets for expansion and development. The business will also be able to satisfy the needs of its constituents and maintain its market standing.
Literature Review
Flexibility and Adaptability
Companies need more adaptability and flexibility when faced with ever-evolving markets, technologies, and customer demands. Such challenges may lead people to lose opportunities, become less competitive, and finally collapse. However, there are techniques for businesses to apply to overcome this obstacle. Developing a company-wide environment that encourages new ideas serves as an approach. McKinsey found that businesses that emphasize innovation outperform their competitors in terms of revenue expansion, profitability, and shareholder value. This is because innovative businesses are better able to adapt to the needs of their target audience.
Adopting agile methodology is another option. Agile project management is a method that encourages change, teamwork, and constant enhancement. The Project Management Institute found that businesses using agile approaches could better complete projects on time and adapt to customers’ needs. Technology-based increases in versatility and adaptability constitute a third approach. Cloud computing, for instance, enables businesses to effortlessly expand or contract their IT resources on the fly. This allows businesses to adapt to shifts in customer demand without buying expensive new equipment.
Amazon is a good example of a company that has overcome the difficulty of a lack of flexibility and adaptation. Amazon is known for its culture of innovation and its willingness to try new things. In 2006, Amazon created Amazon Web Services (AWS) to offer cloud computing services to enterprises. Since then, AWS’s popularity has skyrocketed, contributing more than $10 billion to Amazon’s bottom line every year. Spotify is another company that often updates its product using agile methods. Spotify regularly rolls out upgrades and new features, and the company uses data to monitor user activity and make informed decisions. Eighty-one percent of business leaders agree that organizational agility is important, per research conducted by Accenture. According to new research published in the Harvard Business Review, agile businesses increase their sales by 37% and their profitability by 30% more quickly than their less agile counterparts.
Partnerships and Alliances
Companies have struggled with weaker alliances and partnerships for a long time. Recent studies show, however, that businesses can succeed despite this limitation by focusing on innovative themes. One such concept is the “frenemy” approach, which entails working together on projects with rival businesses. The ability to share assets and knowledge while fostering a competitive environment has been proven to be a successful strategy for generating win-win results. In the technology business, for instance, Apple and Google have a frenemy relationship; the two companies compete in markets like cell phones and operating systems. They also collaborate on initiatives like making Google Maps available on Apple devices.
One concept that can be utilized to fortify otherwise vulnerable alliances and collaborations is “co-opetition.” Doing so requires firms to compete and cooperate with partners simultaneously, and it can help them overcome common partnership issues like clashing aims or unbalanced power relations. Co-opetition has been demonstrated to be especially useful in highly interdependent businesses like the aviation business. United, Lufthansa, and Air Canada are all members of the Star Alliance. This encourages healthy competition among its members while facilitating cooperation in shared lounges and frequent flyer programs. When comparing revenue growth and profitability, McKinsey showed that organizations with excellent partnerships performed 15% better than their competitors. PwC also discovered that 82% of CEOs consider alliances and partnerships crucial to their company’s success.
However, there may be negative outcomes if alliances and partnerships are weak. Seventy percent of partnerships, according to KPMG research, need to catch up to their goals. This can lead to lost time, money, and goodwill.
Marketing and Branding
To survive in today’s competitive corporate environment, innovation is a must. Organizations can use the distinctiveness of their products despite negative marketing and branding to make up for shortcomings in their alliances and relationships. The challenge is to incorporate low-income customers’ specific needs and viewpoints into the company’s overall branding and marketing efforts. Seventy-three percent of consumers, according to research by the marketing firm BBMG, are willing to pay a higher price for environmentally and socially responsible goods. Incorporating social and environmental concerns into product design and marketing is thus a potent strategy to set a brand apart and win over environmentally and politically aware consumers. Many businesses, however, need help getting the word out to customers about their social and environmental responsibility.
To overcome this obstacle, businesses might take cues from the advertising approaches of popular socially conscious brands. Patagonia, a clothing brand with a strong reputation for environmental responsibility, has created a marketing campaign highlighting the firm’s beliefs and objectives. The company promotes its products as sustainable and long-lasting, emphasizing decreasing waste and environmental effects, and its commercials frequently incorporate images of nature and wildlife. Not only may businesses gain from incorporating social and environmental factors into branding and marketing, but they can also work with communities with limited resources to jointly develop products and services tailored to their specific needs. Organizations like Unilever have employed this “inclusive innovation” strategy by collaborating with local entrepreneurs in emerging areas to create inexpensive and readily available products for those with modest incomes.
Increased customer loyalty, enhanced brand reputation, and entry into new markets are some of the many tangible benefits linked to inclusive innovation. Unilever’s Indian subsidiary, Hindustan Unilever, for instance, created a water purifier that people with lower incomes could purchase. Unilever broadened its customer base and increased its profits by copying the product and selling it in other developing countries.
Culture and Organizational Structure
The way a company operates is heavily influenced by its culture and its structure. When these two factors are balanced, they can foster an environment where innovation thrives and employees are encouraged to take risks and try new things. However, when they aren’t in sync, it can be a problem that stunts creativity and growth inside the company. The situation at Kodak is indicative of this difficulty. For many years, Kodak was the undisputed leader in the photography market. However, the company ultimately fell victim to the rise of digital photography. The company’s downfall can be attributed, in part, to its inflexible structure and culture, which made it difficult for employees to adopt new methods and ideas. Kodak struggled to innovate and adapt to shifting market conditions due to the company’s hierarchical structure and emphasis on retaining existing products and services.
To meet this challenge, businesses must cultivate an “innovation culture” that encourages novel ideas and calculated risks. Google is a great example of a company that has effectively established a culture of innovation. Google’s internal structure is set up to promote teamwork, exploration, and new ideas. Google’s “20% time” policy encourages workers to spend one day a week on personal projects; this has led to creation of some of the organization’s most popular services, including Gmail and Google News. Another company that fosters innovation and experimentation through its “customer obsession” culture is Amazon. The organizational structure of Amazon is made to encourage people to take the initiative and try new things. The company’s “two-pizza team” model encourages cooperation and adaptability by limiting teams to eight members at most.
McKinsey & company found that businesses that encourage new ideas have a better chance of succeeding than those that don’t. According to the poll results, businesses that foster a culture of innovation are more likely to increase their revenue, profits, and market share. The poll also discovered that innovative cultures were linked to increased employee dedication and loyalty.
Analysis and Findings
Companies in today’s fast-paced technology environment must constantly innovate to keep up with the competition. Integrating new technology into Nokia’s established product lines or platforms is crucial to the company’s continued success and innovation. To achieve this, Nokia must be adaptable and open to change, and one must form strategic connections and collaborations. Effective technology integration relies heavily on a company’s capacity to be flexible and adaptable to meet the ever-evolving demands of the market and its clientele. The fact that Nokia supplies networking and communication devices is proof of this. The company’s preparedness to adopt cutting-edge innovations like 5G wireless networks and the Internet of Things (IoT) paved the way for this change.
Nokia can increase its adaptability by cultivating a culture of innovation. Adopting agile development techniques that permit rapid prototyping and improvement can encourage staff to experiment with innovative technologies, stimulate innovation, and foster willingness to take risks. Partnerships and alliances are just as important as adaptability and flexibility when integrating technology successfully. By forming strategic alliances with other businesses, Nokia has found that it can gain access to technology, knowledge, and markets that would otherwise be out of reach. Nokia, for instance, has strengthened its position in the industry through agreements with major players like Microsoft, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud.
Nokia can get the most out of its alliances and partnerships by prioritizing partner communication and engagement. To do this, it is important to lay out a plan for the partnership, establish communication channels, and check in regularly to ensure everyone is on the same page. Nokia was formerly the industry leader in mobile phone production, but the company has struggled to incorporate new technologies into its old product lines and platforms. To overcome this difficulty, Nokia can use novel approaches to marketing, branding, and company culture and structure.
Nokia’s existing customer base can serve as a test market for the company’s new technologies and products if the company employs effective marketing and branding methods. Nokia’s marketing strategy might incorporate several channels to communicate more effectively with its intended demographic. The business may establish a solid brand identity and positioning by capitalizing on the company’s status as an industry leader and highlighting its dedication to innovation. Nokia’s recent partnership with Microsoft to create and sell the Windows Phone operating system is an example of a strategic decision that uses both firms’ respective technological and promotional advantages. Nokia established a brand identity with customers thanks to its partnership with Microsoft.
Integrating new technologies into Nokia’s current product lines can also benefit the company’s culture. Nokia has the potential to encourage its workforce to think creatively and try out innovative approaches to problems. By fostering an atmosphere that rewards originality and curiosity, Nokia can inspire its workforce to develop novel solutions that can be incorporated into its existing product lines. For instance, Nokia’s recent investment in 5G technology exemplifies the company’s dedication to innovation and openness to exploring new technologies. Nokia’s investment in 5G technology will allow the company to build upon its current portfolio of goods and services to provide innovative solutions for its client base.
Nokia’s organizational structure is vital for incorporating cutting-edge technology into its product offerings. By moving toward a more decentralized structure, Nokia will be better able to adapt to shifting market conditions. One way to accomplish this is to form cross-departmental teams to develop innovative products and services. The recent acquisition of Alcatel-Lucent, a telecommunications equipment manufacturer, by Nokia, for instance, has allowed the Finnish firm to broaden its product offering and service capabilities. Through the purchase, Nokia has gained access to Alcatel-Lucent’s expertise in telecommunications equipment, which it can now incorporate into its existing product lines.
Recommendations
The ability of Nokia to stay competitive in the industry and address the needs of its stakeholders has been negatively impacted by the company’s struggle to integrate new technologies into current lines of products or systems. First, Nokia’s consumers are extremely important and influential stakeholders. To solve the issue of incorporating new technologies into old product lines, Nokia must interact with its clientele and learn about their wants and needs. Nokia can better serve its customers’ requirements and stay ahead of the competition if it develops its products in response to those needs. Furthermore, stockholders are also important to Nokia since they have a vested interest in the company’s bottom line. Nokia must invest in R&D to keep up with the newest technological developments and solve the difficulty of incorporating new technologies into old product lines. This will allow Nokia to develop brand-new products and enhance existing ones, raising sales and earnings for the company’s investors.
Additionally, Nokia’s suppliers are an integral part of the business’s supply chain and an important stakeholder. Nokia must collaborate extensively with its suppliers to ensure they possess the resources and experience to offer the appropriate components and resources to solve the difficulty of incorporating cutting-edge innovations into old product lines. This will allow Nokia to create and sell innovative and affordable products in today’s market. Fourth, Nokia’s employees are a key shareholder and key to the company’s success. Nokia needs to invest in staff development and training initiatives to ensure its staff members have the expertise and abilities to deal with emerging technologies to solve the difficulty of incorporating new technology into old product lines. This will allow Nokia to create and sell innovative and affordable products in today’s market.
Reference
Ali-Yrkkö, J., Rouvinen, P., Seppälä, T., & Ylä-Anttila, P. (2011). Who captures value in global supply chains? Case Nokia N95 Smartphone. Journal of Industry, competition, and Trade, 11, 263-278. Available at (https://www.statista.com/topics/1183/nokia/#topicHeader__wrapper). It was accessed on 11th March 2023.
Nokia Company, (2022). Good Interaction with stakeholders. Available at (https://www.hypeinnovation.com/hubfs/content/case-studies/nokia-case-study-en.pdf). Accessed on 11th March 2023.
Statista, (2021). Nokia’s net sales worldwide from 1999 to 2021. Available at (https://www.statista.com/statistics/267819/nokias-net-sales-since-1999/). Accessed on 11th March 2023.
 write
write