The Military disagreement between Ukraine and Russia has changed the whole world’s history. The awareness of a paramount war breaking in Europe after eight years of a tumbling dispute caused a political group of three divergent nations. According to a study by (Heath et al., 2020), There were those groups that promised to support Ukraine, those who supported Putin’s Russia, and those who resisted fully participating. Since there was less harmony in Ukraine, Putin sought the support of longtime allies like Iran and Bashar al-Assad of Syria. He also forged tighter strategic ties with Aleksandra Lukashenka of Belarus. The Russia-Ukraine war started in February 2014, and the Maidan uprising protests resulted in the rioting of dignity and the shifting of Ukraine’s President Viktor Yanukovych. At the same time, the unmarked Russian soldiers invaded Ukraine’s Crimea and got hold of the infrastructure, strategic sites, and the government’s buildings. In this discussion, we will see the factors that accounted for the current military conflict between Russia and Ukraine, its causes and consequences, how the conflict has affected the Russians, Ukrainian, and the rest of the world, and measures for resolving the conflict.
Factors that Accounted for the Current Military Conflict between Russia and Ukraine
The Ukraine-Russia war is the most unruly war that Europe has experienced since 1945. Many people view the Ukraine-Russia war as a war of choice by Russian president Vladimir Putin. Putin states that the 2008 North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) resolutions favored ultimate Ukrainian belonging that brought a verifiable warning to the Russian border (Marten, 2023). For many years, Putin and other Russian leaders have repeatedly stated that they regard the United States’ approach toward Ukraine as an existential danger. The Biden administration was dubious about ending that danger subtly and recapitulated its dedication to Ukraine’s NATO membership in 2021. On February 24 of this year, Putin invaded Ukraine in retaliation. Factors that contributed to the conflict between Russia and Ukraine were Political, Economic, and Military factors.
Political Factors
In recent history, Ukraine has been regarded as an independent nation with a different political system from Russia. This shifted when the government of Russia authorized the invasion of the military group into the Ukrainian area on February 24, 2022. Due to these efforts, Russia began a full-scale seizure of Ukraine. This invasion shocked the entire world as it was so blatant and because it affected nearby sovereign governments. Russia wanted to include Ukraine within its region because they share the same cultural history but different political systems (Marten, 2023). Also, the Americans wanted to make Ukraine the western parapet on Russia’s border. The master plan of this idea was to incorporate Ukraine into the European Union, turn off Ukraine into a pro-western unprejudiced democracy, and also to embrace Ukraine into NATO.
A Russian military growth on Ukraine’s border in 2021 and 2022 exacerbated tensions and deteriorated bilateral relations between Russia and Ukraine, ultimately leading to Russia’s full-scale invasion. The European Union made so much effort to help Ukraine with financial and compassionate assistance as the war would affect the stock market returns. The strategic location of Ukraine benefitted countries such as Slovakia and Poland because it aided so much assistance with their refugees. In addition, NATO motivated the remittance of harmless and compassionate help (Marten, 2023). The figure below shows how Ukraine has changed in the past year.
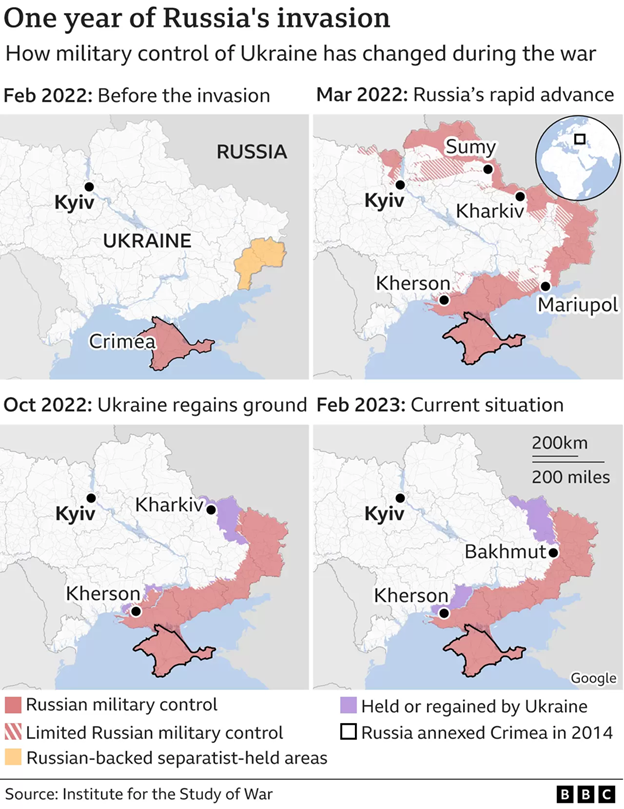
Figure 1: Ukraine in maps: Tracking the war with Russia
Source: Brown, D. (2022, February 24). Ukraine invasion: Russia’s attack in maps. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-60506682
Economic Factors
New measures that were confusing the provision of some essential commodities were experienced, especially in Europe. Therefore, some of the most influential trade association with Russia still subsists, despite the already rigid correlation between the West and Russia since the Russian invasion of Crimea in 2014. The foreign ministry of Russia demanded that NATO and the United States end their military running in Central Asia and Eastern Europe, pledged to put an end to any more NATO enlargement toward Russia, and outlawed Ukraine from ever attaching itself with NATO. In reaction to Russia’s ultimatum, the US and other NATO members repudiated and menaced them to apply raucous economic measures (Ptaschсenko et al., 2019).
Military factors
As Russian forces had arrived in the southern port cities of Odesa and Mariupol, military regime headquarters in Kyiv and Kharkiv in the northeast had been hit by projectiles. Ukraine’s border guard service uttered that the Russian troops invaded Ukraine from Belarus and Russia with Belarusian service (Shah & Gedamkar, 2022). A seizure was also being started from Crimea, which had been captured. Russian commercial flights at airports close to the border with Ukraine were suspended until March 2, while Ukraine closed its airspace to public flights because of an elevated danger to citizen safety.
Ways the Russia-Ukraine Military Conflict Has Affected Russia, Ukraine, and The Rest of the World.
Since Russia invaded Ukraine in February 2022, its consequences have resonated worldwide. The Ukraine war has not only transformed its geopolitical setup but also led to economic hardships far from the main core of fighting. This essay will discuss several impacts of the Russia-Ukraine military war, such as the Displacement of people and food security, slow economic recovery, cyber-attacks, and the China-Europe route blocked (Shah & Gedamkar, 2022).
Displacement of people and Food Security
By the Russian government’s urge to invade Ukraine, more than eight million people have run from Ukraine due to the hostile environment. Some have been forced to relocate to Russia, leaving their daily activities (Behnassi & El Haiba, 2022). Due to the current war between Russia and Ukraine, food insecurity pointed out some inherent fragility in global food security. The Russia-Ukraine disagreement has put more force on pre-existing challenges, such as the Covid 19 pandemic causing increased international hunger.
A Slow Economic Recovery
The Global Economic growth of Ukraine was stable before its invasion by Russia. Russia- Ukraine war was a vast and historical zeal shock that slowed economic growth to a percentage of 3.1. The disagreement between Russia and Ukraine has resulted in instability in the capital markets and sharply raised uncertainty about the future of the global market. The threats have caused the anticipation of unrelenting high escalation, which raises the probability of economic decline and societal instability, boosted by higher product prices. Russia ranks in the top 5 aluminum, nickel, and steel producers and is the world’s third-largest oil-producing nation. Moreover, Russia sells oversee the most wheat globally. According to a study by (Nasir et al., 2022), Ukraine is among the top ten manufacturers of sugar beet, barley, soy, and rapeseed. It is also a significant producer of corn, wheat, sunflowers, and sunflower oil.
Destructive Cyber-attacks Against the West
Executives have given a warning for some time now that Russia will cause cyber-attacks. The Cyber-attacks will cause communication and trade damage where they will improvise systems that will cause physical damage resulting in loss of life. Despite Russia’s idea of planning cyber-attacks against Ukraine, the attack could have minimal impact on Ukraine or the west. According to a study by Guchua et al., 2022, “Russia is actively using its cyber capabilities in the Russia-Ukraine war to restore vectors of influence in the territories of the former Soviet Union.”
China –Europe Routes Blocked
The transportation route that connects China and Europe is one of the losses caused by the invasion of Ukraine since it was blocked (Jakóbowski & Nieczypor, 2021). China is one of the leading countries that export electronic goods globally; hence, it is a significant loss for Europe since it has no access to China. Not all routes have been disrupted, such as water transport, but it takes a long time before the goods are transported to where they are needed, especially in far countries or continents.
Diplomatic and Military Solutions to the Russia-Ukraine Squabble
The Russia-Ukraine dispute caused much damage both internally and externally. The European Union and its members were not happy with the actions of Russia. Therefore, the European Union had to strike a deal between the two countries where both sides would make a promise to observe the terms laid out. It is possible to say that the dispute between Russia and Ukraine could end in peace if they agree to make peaceful terms with each other (Åtland, 2020). Russia’s President Vladimir Putin is determined to withdraw himself from the war by putting in too much political and military capital without success. However, Ukraine might not be ready to accept the terms of Putin since that is equivalent to political suicide.
Through Putin’s repeatedly nuclear ultimatums on Ukraine, NATO has chosen to intervene (Mongin, 2022). The use of nuclear weapons by the Russian government has bigger risks, especially if they are exploded in areas that Putin claims to be Russian territories. Even so, it is still uncertain whether NATO will still involve itself in stopping Russia from using nuclear weapons, as this could cause war in other countries such as China.
Also, Russia and Ukraine could also agree to end the war without showing their weakness. This would only work if the Ukrainians do not disgrace Russia, but also, the West should show that their military antagonism will be met with motivation. It would be ideal for Kyiv to have a way into the four emancipation of the European Union’s intramural market without imperatively becoming a full member. However, Ukraine could simultaneously have a common concurrence with the Eurasian Union (Cross & Karolewski, 2017).
Conclusion
The Russia-Ukraine war started in February 2014, and the Maidan uprising disagreements led to the rampage of regality and the elimination of Ukraine’s pro-Russian president Viktor Yanukovych. Some factors include the desire of Russia to invade Ukraine because they share the same cultural history but different political systems, Russia’s foreign ministry demanding that NATO and the US terminate their military duties in Central Asia and Eastern Europe, and Russian troops invading Ukraine from Belarus. Russia, Ukraine, and the rest of the World have been affected by the military conflict in several ways, such as people being displaced from their home countries, countries experiencing a slow economic recovery, experiences of cyber-attacks, and the China- Europe route being blocked. However, some measures have to be taken for this long-term conflict to end. They include NATO intervention, the European Union striking a deal between Russia and Ukraine, and Russia and Ukraine agreeing to terminate the war without showing their weaknesses.
References
Åtland, K. (2020). Destined for deadlock? Russia, Ukraine, and the unfulfilled Minsk agreements. Post-Soviet Affairs, 36(2), 122-139.
Behnassi, M., & El Haiba, M. (2022). Implications of the Russia–Ukraine war for global food security. Nature Human Behaviour, 6(6), 754-755.
Cross, M. A. K. D., & Karolewski, I. P. (2017). What type of power has the EU exercised in Ukraine–Russia crisis? A framework of analysis. JCMS: journal of common market studies, 55(1), 3-19.
Guchua, A., Zedelashvili, T., & Giorgadze, G. (2022). Geopolitics of the Russia-Ukraine War and Russian Cyber Attacks on Ukraine-Georgia and Expected Threats. Ukrainian Policymaker, 10, 26-36.
Heath, A., Davidov, E., Ford, R., Green, E. G., Ramos, A., & Schmidt, P. (2020). Contested terrain: explaining divergent patterns of public opinion towards immigration within Europe. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies, 46(3), 475-488.
Jakóbowski, J., & Nieczypor, K. (2021). Under the radar of big politics: cooperation between China and Ukraine. OSW Commentary Number 395 2.06. 2021.
Marten, K. (2023). NATO enlargement: evaluating its consequences in Russia. In Evaluating NATO Enlargement: From Cold War Victory to the Russia-Ukraine War (pp. 209-249). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Mongin, D. (2022). War in Ukraine, a new nuclear crisis? Esprit, (7), 129-139
Nasir, M. A., Nugroho, A. D., & Lakner, Z. (2022). Impact of the Russian–Ukrainian Conflict on Global Food Crops. Foods, 11(19), 2979.
Ptaschсenko, L., Glushko, A., Volkova, N., & Volkova, V. (2019, September). Ukraine’s depressive national economy destructive factors. In 6th International Conference on Strategies, Models, and Technologies of Economic Systems Management (SMTESM 2019) (pp. 82-86). Atlantis Press.
Shah, P., & Gedamkar, P. P. (2022). Effects of Russia-Ukraine war. International Journal of Scientific Research in Engineering and Management, 6(03), 1-5.
 write
write