Task 1: Theoretical meaning of Strategic Management Accounting (SMA) and strategic support provided by management accountants
Introduction
The evolution of such a corporate environment in the 1980s called into question the applicability of conventional management accounting practices. The phrase SMA has been coined to describe a set of methodologies designed to solve the issues of conventional management accounting. The supply and assessment of managerial accounting information on a company and its products inside the marketplaces, its pricing structure, including rivals’ expenses, along with the surveillance of such businesses and its competition’ strategic areas over the period, is defined as SMA (Nik Abdullah et al., 2022). SMA approaches could always deliver several advantages to enterprises. These strategies include competitive accountancy, customer financial reporting, strategic pricing, strategy development, oversight and achievement of goals administration, and strategic thinking. Even though SMA has great potential for long-term planning, there continue to be challenges with practical implementation and a need for more knowledge regarding applying SMA effectively to meet company objectives.
Discussion
Strategic management accounting is a subset of traditional management accounting, which aims to analyze the business’s internal and external performances to accomplish the emphasized objective based on organizational operations and growth projections. Strategic management accounting success of the company and its executives and managers in making sound decisions for such organization’s benefit (Nasab and Maddahali., 2022).
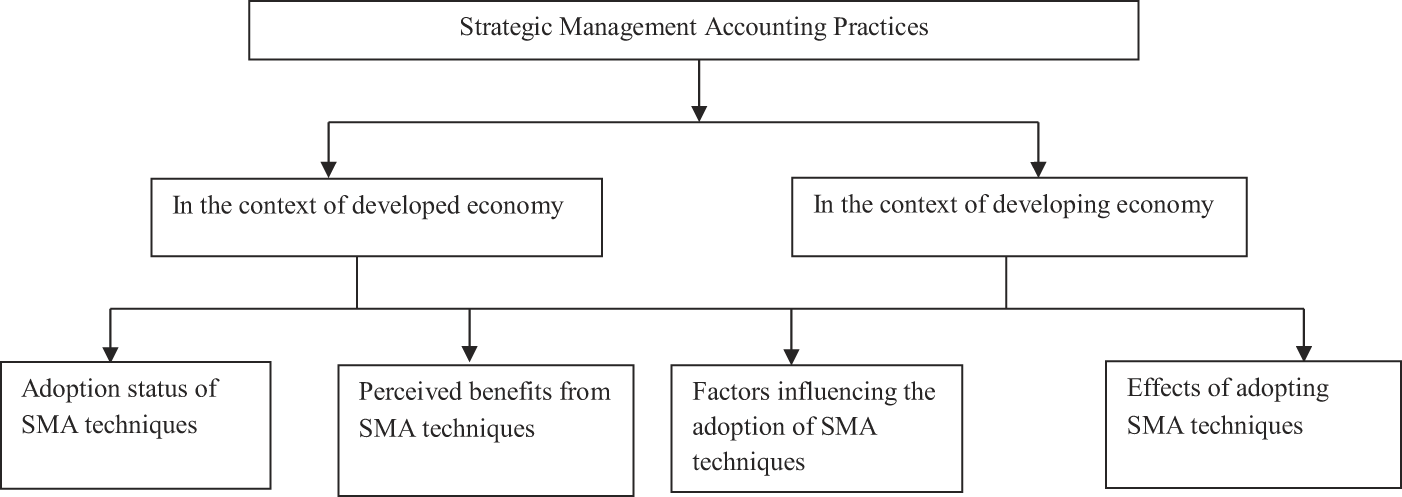
Figure: Strategic Management Accounting Theoretical Framework
Source: (Abanis et al., 2022)
The credibility of strategic management accounting theory could be more robust (Pitcher et al., 2015). An accountant’s knowledge base is aging, and a need for a more profound understanding of strategic management accounting. Strategic management accounting is more than just a simple, pure chance of financial management; it also represents several subject areas’ interconnection. Strategic management accounting is used for financial index calculation and a more detailed utilization of analytical techniques in various approaches (Almahairah et al., 2022). So the performance standards for accountants and auditors in strategic management accounting have been considerably large. Furthermore, accounting staff necessitates expertise in managerial, scientific knowledge, behavioral science, and economic history to comprehend their respective professional expertise, understanding of the marketing field, managerial accounting ways to successfully perform, and powerful expertise (Suarez., 2022).
Costing: The attribute costing method represents the most significant advancement in SMA. This emphasis on pricing the advantages connected to products and related qualities demands input from management accounting and marketing managerial functions inside a strategic management approach (Mpofu., 2022). Assessment of life cycles The SMA approach means assessing all linked expenses of a service or good across its entire lifespan, often known as the phases of the product’s life cycle. Conception, launch, development, maturation, decrease, and discontinuation are the stages of a product’s life cycle (Abanis et al., 2022).
Planning, control, and performance Measurement: This strategy seeks to discover best practices inside or outside the business. It entails comparing methods or events in all performance domains within an employee’s performance, such as strategic positions, operating procedures and operations, and client satisfaction (Mohamed and Saad., 2022). Integrated systems for measuring performance give financial and non-monetary achievement metrics that transcend several organizational viewpoints. This metric requires organizations to evaluate the aspects crucial to ensuring client satisfaction.
Strategic Decision-Making: Strategic costing is also referred to as Strategy Cost Management. This approach would examine the economic effect of different management styles, using cost information to create superior tactics that give a significant edge over competitors (Farhood et al., 2023). The material used to make price choices must be complemented with data concerning possible competition responses toward any planned price change policy. Brand recognition accountancy could emphasize that brand-related spending must be considered an asset instead of a liability, underlining the tools and lengthy focused perspectives.
Competitor Accounting: Because of its focus on rivals’ cost structures, such an approach might be considered a competitive situation measurement technique. Proponents of this method, including Simmonds and Bromwich, say that assessing a significant competitor’s relative price positioning could lead to a better understanding of an organizational future decision-making context. Inside the industry, competition positioning evaluation is performed by examining events that have the potential to rival purchases, customer base, volumes, input cost, and profit margins (Maelah et al., 2022). Financial statements representing rivals must be evaluated to determine what differentiates companies from the respective competition. Non-financial data and a competitive financial strategy would be necessary to sustain competitiveness.
Customer accounting: Individual consumers or groups of customers were also examined, and also the associated customer-specific expenses, including revenues to client accounts, were tracked appropriately. This entails calculating the profits made by such a single consumer (Shaban et al., 2023). This would cover the standard techniques for calculating revenue, earnings, and expenditures derived from consumers or customer categories. Such an approach entails reviewing and analyzing client economics over a longer duration to encompass future years, focusing on overall predicted future earnings potential, including expected expenditures associated with maintaining a specific customer (Pourahmadi and Kalkowska., 2022).
Management accounting facilitates making strategic choices by offering a financial assessment. However, the emphasis is still on delivering certain confidence that the recommended strategy will likely succeed, regarded as an essential part frequently given greater weight. Among the most significant ways management accounting helps strategy implementation is by giving correct monetary statistical information (Ebinaso and Ukwunna., 2022). This information may be used to track progress toward strategic objectives and determine where improvements are needed. Management accounting administration and compliance with strategizing, direction correcting, and making educated choices according to the investigation and understanding of financial information relevant to the company’s domestic processes. Management accounting is a digital instrument that assists an organization’s operations with steering toward its objectives.
Conclusion
Strategic management accounting has been regarded as both financial and non-financial in dynamics, and it’s frequently used for objectives including strategic planning, judgment implementation, and regulating choices to ensure they don’t exceed the boundaries of this kind of decision. Entrepreneurs use strategic management accounting to analyze the expenses connected with all these operations to guarantee that the business does not compromise its relative price advantage. Establishing a sustained price advantage is critical as organizations differentiate their goods from many other organizations inside the marketplace. Excluding one strategy development, successful strategic management continually prepares, analyzes, and evaluates an organization’s processes, leading to improved operational excellence and customer base, including revenue.
Task 2: Evaluation and ethical assessment of Activity Based Management (ABM) for organizations
Introduction
ABM is a technique for assessing the revenue from every area of an organization to ensure its advantages are strengthened, and its shortcomings can be remedied or removed entirely. “The goal of activity-based management (ABM), created in the 1980s, is to identify the areas where a firm is making losses so that these operations may be removed or modified to maximize profits” (Kim et al., 2022). To evaluate and allocate costs to activities, ABM examines the expenses of people, technology, buildings, transportation, administration, and other aspects of the company. Companies utilize ABM to examine the economics of each organization component, allowing companies to discover problematic areas and places of high durability.
Discussion
Businesses, providers, non-profit organizations, institutions, and government entities may all benefit from activity-based management. ABM may give cost data for every aspect of a firm’s management. ABM analysis results assist a firm in developing higher realistic budgets, including long-term economic predictions, and increase revenue and general financial stability (Anzola et al., 2022). Another example could pertain to a corporation that has created a secondary office. ABM could help managers assess the expenses of managing particular places, comprising people, equipment, and administration, and determine whether future earnings seem sufficient to cover or rationalize such expenditures.
ABM working steps
- Identification and analysis: Identification refers to locating and cataloging a firm’s major business operations, which is particularly significant given that most businesses engage in hundreds of operations on such a regular basis. Finding the activities with the greatest financial effect is a critical stage in activity-based management (Oyewo., 2022). The following process involves determining the actual costs for every activity according to the expenditures experienced throughout the operation. Cost drivers are the variables affecting the cost of an operation. For instance, when an activity establishes new devices, the cost driver is the number of devices established, which dictates each related external cost of personnel, material, and equipment component.
- Evaluation and Value chain analysis: “The management must also determine the expense from each action by allocating all indirect and direct expenses involved with the operation” (Biran et al., 2022). With exercise pricing, the valuable contacts from each action should be measured to be contrasted with its price and evaluated. This would be known as a value-chain assessment, examining such additional value generated by a specific operation.
- Identify opportunities to improve
Operational ABM: The expense of every action is scrutinized in operation ABM, while operational effectiveness is enhanced through strengthening value-generating operations and minimizing needless expenses and non-value-generating operations (Vărzaru., 2022). This allows management to discover and examine irregularities inside the costing system.
Strategic ABM: Strategic ABM analyses the economics of such an action, which could involve introducing novel products or acquiring a new client using activity-based pricing. This enables the firm to establish a long-term vision about which items and consumers to increase sales and revenue (Vitale et al., 2022). Strategic ABM is employed to make strategic decisions about promoting via a particular network, introducing an innovative product, or addressing a single population consumer base.
Advantages of ABM
Management is critical to the development as well as operation of enterprises. As a result, adopting the proper management technique is crucial. This is important to remember that firms operate within changing contexts (Amstrong., 2002). As a result, business executives must implement environmental reforms to improve profitability and sustainability. ABM is a management strategy wherein process managers have been provided authority and accountability to enhance operational execution and oversight by concentrating on core operational functions (Quesado and Silva., 2021). As a result, administrators, as well as politicians, utilize accounting data to comprehend as well as enhance organizational actions. Among the most impressive aspects of ABM is the ability to allocate costs to actions. For each specific cost paid in completing duties in enterprises, the approach employs multiple features of data tagging.
By enabling executives to enhance value-generating operations, it also has the chance to enhance the user experience, enhancing long-term revenue (Ahmed Mohamed Ghandour., 2021). Additionally, activity-based accounting data may be utilized to estimate and identify critical economic data for subsequent financial periods, allowing the organization to build a more affordable option throughout subsequent years. Such a management style has proven effective in eliminating waste, enhancing quality, and minimizing production time, including quickly releasing new items (Amiri and Khmidi., 2019). ABM had first been utilized mostly in industrial organizations. ABM can currently be used for many sorts of businesses as well as separated together into a variety of tasks. Such activities may be evaluated using a cost comparison.
Another advantage of activity-based management is the dedication to thoroughly examine every costing system, position, and time spent on every work. Obtaining this information is an important initial step in determining every costing system’s fundamental advantages and disadvantages and positioning (Ibrahim et al., 2021). With activity-based management, organizations may identify new approaches to save expenses. Activity-based costing identifies and allocates indirect costs to individual operations inside the manufacturing method (Naureen et al., 2020). Activity-based management makes judgments regarding individual processes and associated advantages and shortcomings using activity-based budgeting.
Risk Of ABM
The challenge with this management style is that specific tasks have hidden worth, making them difficult to identify as additional monetary value. The nice atmosphere may assist in attracting good workers, yet this cannot be considered an added advantage in practical Terms (Alsorkheee., 2019). despite the reality that strategy ABM labels him as a poor value client, a consumer who fails to create revenue may open up fresh leads and opportunities. Managers must become acquainted with and evaluate such implicit assumptions and utilize ABM as an impartial preliminary step. ABM allows leaders to comprehend expenses and assists groups in making choices that improve the whole business rather than just its operations.
Conclusion
Organizations prefer ABM to conventional methods owing to its effectiveness and simplicity in working overall managerial accounting, particularly in light of current changes in the international corporate environment. ABM is a management style that provides administrators with the duty and power to achieve continual improvement in both scheduling and operational controls by concentrating on operating processes, according to the materials discussed in the paper. Since day-to-day operations are portrayed through the lens of happenings that are recognizable to all stakeholders, the ABM method of administration connects with several interested parties inside any organization. Companies implementing all ABM methods are more likely to value essential data outputs, such as knowledge of activity/operational prices, non-value-added operational expenses, activity-based productivity methods, actual item expenses, and cost objects.
Task 3: The ways Of organizations can incorporate sustainability into Strategic Investment Decision Making
Introduction
The strategic decision-making process supports business organizations in making effective decisions to support organizational growth, create opportunities, and analyze threats. The strategic investment and the decisions support incorporating the advanced schools and technology to develop the organizational capability and who is the product installation of the new advanced manufacturing system (Mohr and Thissen., 2022). Researchers effectively focus on the decision and the substantial investment to achieve long-term growth and organizational performance because they analyze the strategic investment and the decision-making programs support to incorporate the advanced technology to shift the product more effectively as well as develop the capability with the new advanced manufacturing system (Mohr et al., 2021). “The car manufacturing company successfully uses the three most important approaches to managers’ capital budgeting: the internal rate of return (IRR) and the net present value (NPV).” Every year the company successfully communicates with the different departments of the organization to understand the financial development and the organization’s position to create the budget for long-term success and growth and manage the operational activities in the organization (Alkaraan and Northcott, 2007). Capital budgeting support the organization in achieving the long-term financial plan to generate better revenue and forecast sale.
Discussion
The process supports the car manufacturing company in the successful utilization of the tools to understand capital budgeting and choses the payback period (PB), internal rate of return (IRR), and Net present value (NPV) are the most important and effective methods, and approaches that support the company to bring the ideal capital budgeting solutions and the three matrices support the business leaders to make the effective decisions and investing planning to achieve success and growth (Rosa et al., 2022).
Payback period
The payback period calculation successfully provides the proper calculations and the length and time required to understand the original investment support the company to understand the initial gas outlay and how many years the company needs for the cash inflows to achieve success and growth (Pemsl et al., 2022).
| Investment | Inflows | ||
| Year 0 | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| 1,000,000 | 25,000,0 | 25,000,0 | 25,000,0 |
“In this example, it is clear that the capital budgeting project demands an initial cash outlay of $1 Million and how much time it needs to understand the one million dollar outflows”. Additionally, it supports understanding the ‘pay for itself’ within a small time frame.’ The payback period (PB) Better understands the liquidity present (Connors et al., 2021). Moreover, It supports the company in understanding the financial concern and helps the managers make effective decisions to understand the limited amount of funds before undertaking the major project. Hence, The company better develop the investment decisions and Undertaker one major project at a time and understand to recover the initial investment from undertaking subsequent projects.
The car manufacturing company successfully analyzed the payback to calculate the cash flow and forecast the sale, established a better management system, and made effective capital budgeting decisions (Sangiorgi and Schopohl., 2021). But at the same time, the payback period does not provide the time value of money (TVM) because it simply calculates the payments received in one or two years. The companies easily identified the errors by implementing the discount payback period model.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
IRR estimates use the same methodology as NPV analyses. The IRR shouldn’t represent the program’s real financial worth. The yearly profit brings the NPV equal to zero (Kukulska-Hulme et al., 2022). IRR is consistent across expenditure kinds and may be used to compare possible expenditures or initiatives on nearly service-level agreements (Caeiro et al., 2020). The transaction with the largest IRR will likely be the best when examining investing decisions with similar features.
This methodology computes the average ‘rate of return’ on an investment. The IRR offered by international investment strategy as a ‘rate of return (a compound interest rate).’ The anticipated return on investment is the risk premium where equal marginal rewards equal the forecasted costs (Abhayawansa and Adams., 2022). The transaction with the largest return on equity is chosen as the condition for choosing among options. Typically, the ‘rate of return’ is estimated by a test-and-error procedure. The net revenue is estimated for special discounted amounts until everything’s valuation is lowered to zero.
Apart from the advantage, it is similar to the payback method because IRR does not provide the two senses of the project’s value in the organization (Gonguet et al., 2021). The company does not understand the benchmark figure that the project should be accepted analyzing based on the forms cost of capital.
Net present Value (NPV)
This approach gives the company an accurate understanding and valuation approach to managing capital budgeting problems. It determines whether the project will be profitable or not. It provides the appropriate knowledge of how profitable a project will be compared to the alternatives project. The NPV rule supports the car manufacturing company’s understanding of the projects to bring effective outcomes and the overall usefulness in analyzing the direct measure to add profitability (Mendoza et al., 2019). An operation’s ‘Net Present Value’ (NPV) is the sum of all the future earnings (good and bad) decreased to the current. NPV evaluation is a financial analysis widely used in financial reporting and finance circles to determine the worth of a company, investment property, funds management, business partnership, cost-cutting program, or any other activity that includes profitability.
NPV valuation is employed to evaluate the worth of a bet, initiative, or any sequence of working capital (Wang et al., 2020). It considers not only all the earnings and expenses but also the time of each cash reserve, which can significantly influence a fund’s present value. In contrast, it is preferable to observe cash earlier and money transfers later than the contrary.
Conclusion
Strategic asset allocation is financial resources that greatly impact intermediate and long revenue and organizational outcomes and their comparative superiority. Strategically expenditures usually impact a company’s range of goods and services and its activities’ international breadth and spread. The ‘payback period’ (PBP) is the years required for the complete cash inflows to equal the original cash outflow. This is a decent approach for determining how fast the initial cost quantity will be recovered. Still, it is heavily criticized since it considers just cash rather than the time value of money. The anticipated future financial outflow opportunity cost is subtracted from the book value of predicted cash flows to determine the NPV. Existing values are estimated by depreciating the future profits with a suitable necessary return ratio, which is usually. When the NPV is favorable, the purchase is justified; also, will there be options with varying NPVs? The one with the greatest NPV should be selected.
References
Task 1
Abanis, T., Natwijuka, C., Sunday, A. and Byamukama, E.M., 2022. Cost and Management Accounting Practices, ICT Usage and Performance of Secondary Schools in Uganda: A Case of South Western Uganda.
Almahairah, M.S., Saroha, V.K., Asokan, A., Umaeswari, P., Khan, J.A. and Lourens, M.E., 2022. Strategic management accounting practices between developed and emerging economies using Machine Learning. Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results; Vol. 13, Issue 9.
Ebinaso, U.K. and Ukwunna, C.F., 2022. The Usefulness Of Modern Management Accounting Techniques On Management’S Decision Making: Case Of The Nigerian Manufacturing Industry.
Farhood, A.S., Abd Ali, A.R. and Abdulkareem, S.K., 2023. The impact of environmental management accounting on the strategic planning of budgets in the economic entity: Case Study in Wassit Co. in Iraq. resmilitaris, 13(1), pp.1978-2002.
Maelah, R., Mohammed, B.A.H. and Amir, A.M., 2022. Strategic Management Accounting Information and Performance: Mediating Effect of Knowledge Management. The South East Asian Journal of Management, 16(1), pp.1-25.
Mohamed, Z.E. and Saad, M., 2022. The Impact of Digital Transformation and Corporate Governance in the Relationship of Strategic Management Practices and the Firm’s Performance: The Case of the Egyptian Petroleum Sector. Journal of Business, 10(4), pp.192-209.
Mpofu, CM, 2022. Lean Accounting: a Connection to Strategic Partnership & Collaboration Between Management Accountants and Operations Managers (Doctoral dissertation, University of Missouri-Saint Louis).
Nasab, V.B. and Maddahali, A., 2022. The Impact of Management Accounting Network and Strategic Emotions of Management Accountants on Strategic Management with Emphasis on the Modifying Role of Organizational Culture and Information Systems. International Journal of Business Management and Entrepreneurship, 1(2), pp.1-35.
Nik Abdullah, N.H., Krishnan, S., Mohd Zakaria, AA and Morris, G., 2022. Strategic management accounting practices in business: A systematic literature review and future research directions. Cogent Business & Management, 9(1), p.2093488.
Pourahmadi, B. and Kalkowska, J., 2022. Characterizing the Relationship between Growth and Development in the Context of Strategic Management via Systems Thinking: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability, 14(9), p.5561.
Shaban, O.K., Beshr, B.A.H., Al-Shakrchy, E. and Raheem, HAA, 2023. Integration of Corporate Sustainability Valuation through Management Accounting System, Control, and Reporting System. resmilitaris, 13(2), pp.2139-2152.
Suarez, J., 2022. The Hallmarks of Strategic Management Accounting: seeking to support decision-making processes. Journal of Business Management, 20.
Pitcher G. S. (2015) Management Accounting in support of the Strategic Management Process. London: CIMA.
Task 2
Anzola, D., Barbrook-Johnson, P. and Gilbert, N., 2022. The Ethics of Agent-Based Social Simulation. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 25(4).
Biran, O., Feder, O., Moatti, Y., Kiourtis, A., Kyriazis, D., Manias, G., Mavrogiorgou, A., Sgouros, N.M., Barata, M.T., Oldani, I. and Sanguino, M.A., 2022. PolicyCLOUD: A prototype of a serverless cloud ecosystem for policy analytics. Data & Policy, 4, p.e44.
Kim, E., Jang, G.Y. and Kim, S.H., 2022. How to Apply Artificial Intelligence for Social Innovations. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 36(1), p.2031819.
Oyewo, B., 2022. Contextual factors moderating the impact of strategic management accounting on competitive advantage. Journal of Applied Accounting Research, 23(5), pp.921-949.
Vărzaru, A.A., 2022. Assessing Digital Transformation of Cost Accounting Tools in Healthcare. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(23), p.15572.
Vitale, E., Lupo, R., Fortunato, S., Gualano, A., Giammarinaro, M.P., Bardone, L., Mea, R., Calabrò, A., D’Anna, G., Della Pietà, C. and Germini, F., 2022. Correlations between performance and shift work in the nursing activities: A pilot approach. Acta Bio Medica: Atenei Parmensis, 93(3).
Ahmed Mohamed Ghandour, D., 2021. Analytical Review of the Current and Future Management Accounting and Control Systems Directions. European Journal of Accounting, Auditing and Finance Research, 9(3), pp.42-73.
Alsorkheee, M., 2019. Activity-based costing, management and budgeting, with an application to the hospitality sector (Master’s thesis, Lisansüstü Eğitim Enstitüsü).
Amiri, N. and Khmidi, S., 2019. Implementing Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing (TDABC) in the out-patient nursing department: A case from UAE. Management Science Letters, 9(3), pp.365-380.
Ibrahim, A.E.A., Elamer, A.A. and Ezat, A.N., 2021. The convergence of big data and accounting: innovative research opportunities. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 173, p.121171.
Naureen, Z., Beccari, T., Marks, R.S., Brown, R., Lorusso, L., Pheby, D., Miertus, S., Herbst, K.L., Stuppia, L., Henehan, G. and Falsini, B., 2020. Ethics committees for clinical experimentation at the international level with a focus on Italy. Acta Bio Medica: Atenei Parmensis, 91(Suppl 13).
Quesado, P. and Silva, R., 2021. Activity-based costing (ABC) and its implication for open innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(1), p.41.
Amstrong, P. (2002) The costs of activity-based management. Accounting, Organisations and Society, 27 (2002) pp 99-120.
Task 3
Abhayawansa, S. and Adams, C., 2022. Towards a conceptual framework for non-financial reporting, including pandemic and climate risk reporting. Meditari Accountancy Research, 30(3), pp.710-738.
Caeiro, S., Sandoval Hamón, L.A., Martins, R. and Bayas Aldaz, C.E., 2020. Sustainability assessment and benchmarking in higher education institutions—A critical reflection. Sustainability, 12(2), p.543.
Connors, E.H., Douglas, S., Jensen-Doss, A., Landes, S.J., Lewis, C.C., McLeod, B.D., Stanick, C. and Lyon, A.R., 2021. What gets measured gets done: How mental health agencies can leverage measurement-based care for better patient care, clinician support, and organizational goals. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 48, pp.250-265.
Gonguet, M.F., Wendling, M.C.P., Sakrak, O.A. and Battersby, B., 2021. Climate-Sensitive Management of Public Finances—” Green PFM .”. International Monetary Fund.
Kukulska-Hulme, A., Bossu, C., Charitonos, K., Coughlan, T., Ferguson, R., FitzGerald, E., Gaved, M., Guitert, M., Herodotou, C., Maina, M. and Prieto-Blázquez, J., 2022. Innovating pedagogy 2022: exploring new teaching, learning and assessment forms to guide educators and policymakers.
Mendoza, J.M.F., Gallego-Schmid, A. and Azapagic, A., 2019. A methodological framework for implementing circular economy thinking in higher education institutions: Towards sustainable campus management. Journal of cleaner production, 226, pp.831-844.
Mohr, J. and Thissen Mohr, J. and Thissen M., Powell, S., Parkin, D. and Farrier, A., 2021. Health-promoting universities: effective leadership for health, well-being and sustainability. Health Education.
Mohr, J. and Thissen, C., 2022. Measuring and Disclosing Corporate Valuations of Impacts and Dependencies on Nature. California Management Review, 65(1), pp.91-118.
Pemsl, D.E., Staver, C., Hareau, G., Alene, A.D., Abdoulaye, T., Kleinwechter, U., Labarta, R. and Thiele, G., 2022. Prioritizing international agricultural research investments: lessons from a global multi-crop assessment. Research Policy, 51(4), p.104473.
Rosa, W.E., de Campos, A.P., Abedini, N.C., Gray, T.F., Huijer, H.A.S., Bhadelia, A., Boit, J.M., Byiringiro, S., Crisp, N., Dahlin, C. and Davidson, P.M., 2022. Optimizing the global nursing workforce to ensure universal palliative care access and alleviate serious health-related suffering worldwide. Journal of pain and symptom management, 63(2), pp.e224-e236.
Sangiorgi, I. and Schopohl, L., 2021. Why do institutional investors buy green bonds: Evidence from a survey of European asset managers. International Review of Financial Analysis, 75, p.101738.
Wang, T., Qu, Z., Yang, Z., Nichol, T., Clarke, G. and Ge, YE, 2020. Climate change research on transportation systems: Climate risks, adaptation and planning. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 88, p.102553.
Northcott, D. and Alkaraan, F. (2007) Chapter 10, Strategic investment appraisal. In: Hopper, T., Northcott, D., Scapens, R. eds. Issues in Management Accounting 3 rd edn. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited pp 199 – 221.
 write
write