One of the crucial parts of public health systems is data collection. For the purpose of raising the standard of their services, decision-makers, policy-makers, and providers of health services all require accurate and timely data. The demand for mobile-based data-gathering solutions to close information gaps in the developing world’s health sector has expanded due to the fast-expanding use of mobile technologies. This proposal examines the existing methods for gathering health data and the open-source technologies that might be used to enhance them. It also suggests a prototype employing open-source data-collecting frameworks to see if they may be used to improve health data collection in underdeveloped countries. The goal is to comprehend the issues and suggest technological solutions that can enhance the flow of information between various tiers of the healthcare system. The proposal goes over data collection technology in more detail and assesses how well they work for collecting health data in underdeveloped countries.
Socioeconomic limitations and geographic constraints have limited the availability of potential health data in developing countries. These obstacles have an impact on the primarily manual and paper-based data collection techniques. These manual approaches don’t produce consistent data, which makes them challenging to handle for analytical and data mining applications (Mechael, 2010).
Data Collection Plan
There are various methods for collecting data, including the qualitative approach, the quantitative approach, the design science approach, and the hybrid strategy (which combines qualitative and quantitative methodologies). Due to the nature of our research issues, which call for various techniques to be employed to address them, a combination of three methods has been used in this proposal. Combining methodologies offers considerable potential for flexibility in the project. It draws advantages from several approaches, allowing the proposal to address broader concerns that are not limited to a single method (Yawson, 2021). The plan is to conduct a literature review, design and create, and then conduct a qualitative study to gauge how well our work turned out.
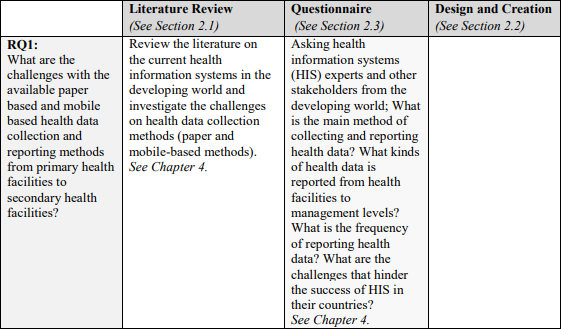
Figure 1: Connecting the research methodologies to the research questions.
This proposal aims to create a mobile health data gathering and reporting prototype for underdeveloped regions. This employs a design and creation methodology to produce items that serve human needs; it is technological in nature. Makri has developed a research framework to model research processes in studies that use a design and creation methodology (Makri, 2020). The four primary actions in this framework are matched to the four main artifacts. Constructs, models, methods, and instantiation are the artifacts (Sanders, 2018). Build, Assess, theorize, and justify are the tasks. To correctly understand and portray all of the strategies used to solve the problem in this study, it was necessary to adhere to the framework.
The activities are building and testing the prototype for mobile health data gathering in underdeveloped countries. The process of creating a prototype began with researching the open data kit structure, which was then followed by the design of unique features for collecting mobile health data.
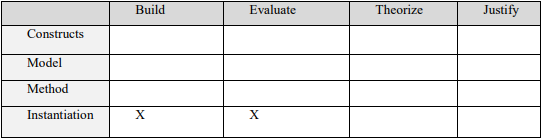
Figure 2: Summary of the activities undertaken in this proposal
The proposed prototype was designed using a four-step prototyping method (Fusco Girard, 2014). Through a scenario of the data collection and reporting systems in the poor world and a literature review, it was necessary first to identify the stakeholders (users). By examining the literature and applying the author’s knowledge of the health systems in developing nations, it was possible to determine the users’ needs. The prototype was subsequently created by modifying, testing, and debugging the source code to accommodate health data collection. Due to time constraints, it was not possible to test the prototype in its intended setting (health systems in developing countries). Assessed the prototype using a questionnaire, asking experts in health information systems from the developing world about its usability and viability in respective nations.
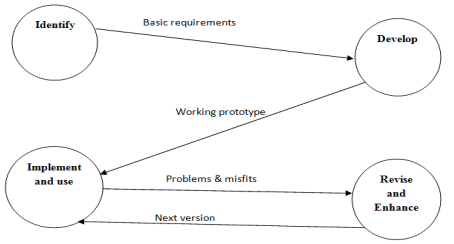
Figure 3: Procedure for Prototype Development
To help respondents understand the prototype before responding to the questions, a questionnaire was made that included a prototype description. The questionnaire was broken into three pieces. The introduction and a brief description of the proposed prototype were contained in section one to help the respondents become familiar with the prototype’s principal goal and capabilities. The generic questions in the second section were intended to help comprehend health data systems’ difficulties and gauge the viability of mobile data collection applications. The procedure of gathering health data and the suggested prototype were subjected to a series of evaluation questions in the third section.
Data Security Plan
A validity threat could limit a qualitative study’s ability to understand its data and draw conclusions. At least three major types of validity need to be protected from these dangers. Three kinds of validity exist: construct, internal, and external (Perry et al., 2000). By adding descriptions and screenshots of the proposed prototype in the evaluation of the proposed prototype, threats have been minimized to construct validity and reduced ambiguity in the formulation of questionnaire questions to aid participants in understanding the purpose of the study. The bulk of the participants in the evaluation study had no prior direct experience or involvement with health information systems in developing nations, posing an external danger to the validity of our evaluation results. Due to time restrictions, it was necessary to accept this threat to perform this proposal with actual stakeholders in a real scenario. More work is required to test the prototype with genuine stakeholders in the future.
Benchmarking Plan
The systems for gathering and processing health data from multiple sources are known as health information systems (HISs). HISs are becoming essential to improving developing nations’ health systems (Siribaddana, 2014). These systems have expanded significantly over the past few years due to the global technological improvement that has been occurring. The development of HIS has thus caused a shift in how health information is processed, from paper-based to computer-based. The potential for effectively manipulating patient data has expanded due to this change (Haux, 2010).
Health data are being used for more than just administrative and patient care; they are also used for planning and decision-making to enhance healthcare. Today’s health care professionals work with a lot of data, which increases the cost of accessing and interpreting the data and poses a high risk of inaccuracy. It is essential and pertinent to improve the performance of health professionals to demand technology-based tools that might simplify the data input and manipulation procedure (Siribaddana, 2014). New health information systems may now be able to capture various types of data anywhere, thanks to the ubiquitous network infrastructure that is now widespread.
Quality and Change Management Strategies
Understanding the necessary information flow will help to improve coordination between levels of the health care system. Reliable data from the lower level are required to transfer health information from the lower level (primary health facilities) to the higher level (secondary facilities). Strategies and plans are created at higher levels and rely on data gathered at lower levels (operational level) (White, 2015). Improving strategic plans for managing the primary facilities depends on having adequate and timely information at the organization’s top level. Lack of sufficient information could have detrimental effects on the health system, such as underreporting crucial data (Siribaddana, 2014). Operational data collection units need to be outfitted with the right technology to make sufficient and timely information available. Health data systems in remote developing nations have had issues with data reliability, which has hampered the provision of high-quality medical care.
Implementation
It was essential to decide on the technology before designing the suggested prototype. The prototype could be created using a variety of technologies. J2ME or Java-Android are available for the mobile client, and the administration module, PHP or JSP. But since the prototype was built on top of the ODK framework, it was restricted to following its requirements for implementation languages and development toolkits.
Conclusion
The statistical data reported from primary health facilities to secondary health facilities are the main emphasis of the suggested prototype. The overarching goal is to enhance data-driven decisions and policy-making to improve the health service. For decision- and policy-making processes to be successful, timely and appropriate data are crucial. The lack of reliable communication infrastructure in the poor world makes it challenging to manually report health data from distant health facilities, which delays plans and decisions. The concentration was on open-source frameworks and mobile technologies that might facilitate data collection and reporting. The proposed prototype has been created to examine how well open source and mobile technologies may be applied to enhance the reporting process.
References
Haux, R. (2010). Medical informatics: Past, present, future☆☆☆. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 79(9), 599-610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2010.06.003
Makri, S. (2020). Information informing design: Information Science research with implications for the design of digital information environments. Journal of The Association for Information Science and Technology, 71(11), 1402-1412. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.24418
Mechael, P. (2010). “Barriers and Gaps Affecting mHealth in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Policy White Paper. Mhealth Alliance, 1-79.
Sanders, K. (2018). Media Review: Research Design: Quantitative, Qualitative, Mixed Methods, Arts-Based, and Community-Based Participatory Research Approaches. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 13(2), 263-265. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558689817751775
Siribaddana, P. (2014). Making Distance Learning an Effective Health Information Systems Training Strategy: A Combined Social Network Analysis and Content Analysis Perspective. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries, 61(1), 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1681-4835.2014.tb00434.x
White, F. (2015). Primary Health Care and Public Health: Foundations of Universal Health Systems. Medical Principles and Practice, 24(2), 103-116. https://doi.org/10.1159/000370197
Yawson, R. (2021). Transformativism: A paradigm whose time has come. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 32(1), 7-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrdq.21422
Fusco Girard, F. (2014). City-systems: A new development strategy to promote a new economic paradigm. Human Systems Management, 33(1-2), 35-45. https://doi.org/10.3233/hsm-140804
 write
write