1. Introduction
1.1. Introduction to Gymshark
Known for its innovative designs and robust web presence, Gymshark, a well-known fitness wear business, was formed in 2012 and has expanded quickly. Around the world, exercise enthusiasts have grown to love the brand (Gymshark, 2017).
1.2. Rationale for Selection
Gymshark was chosen as the case study because of its reputation as a disruptor in the fitness wear market. Gymshark is a fascinating topic for examination because of its dynamic business model and strategic choices (Accountancy Cloud, 2021). Furthermore, Gymshark’s dedication to innovation is consistent with this assessment’s emphasis on strategy and employability.
1.3. Main Strategy Themes
The CSR theme will examine Gymshark’s current community involvement, environmental sustainability, and ethical sourcing efforts and practices. Concurrently, the leadership analysis will examine the brand’s present leadership initiatives closely, which will highlight the brand’s inclusive and dynamic approach (Siegel et al., 2020). The section on the external environment will provide insight into how Gymshark responds to outside influences that affect its strategic choices while navigating the cutthroat and dynamic market. The brand’s final analysis will evaluate its internal capabilities, examining Searshark’s resources to support its competitive advantage. This article aims to offer a thorough analysis of Gymshark’s strategic environment by breaking down the essential components that determine its current standing in the industry. We want to dissect Gymshark’s unique business model by examining these strategic topics, highlighting the company’s achievements and possible directions for future expansion.
2. CSR Analysis
Gymshark has demonstrated a multidimensional commitment to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) consistent with the brand’s principles and culture. Gymshark is currently running itself as a responsible player in the fitness wear business by implementing several several activities.
2.1. Current CSR Strategy
Gymshark has made ethical material sourcing a top priority and placed a strong emphasis on supply chain transparency. Due to the brand’s commitment to fair labour practises, workers engaged in the production process are guaranteed ethical treatment (Gymshark, 2023). Furthermore, Gymshark’s emphasis on environmental sustainability is demonstrated by its attempts to reduce the environmental impact of its business operations by using eco-friendly packaging and materials (sustainability.gymshark.com., n.d.). The company’s CSR approach includes community involvement in addition to production methods. Gymshark supportactively s health and wellness activities activelbecause they fit its target market’s fitness-focused lifestyleparticipation entails joint ventures with fitness influencers and cooperation on physical activity-promoting events (central.gymshark.com., n.d.).
2.2. Future CSR Strategies
In the future, Gymshark has the chance to increase the effect of its CSR initiatives. In order to ensure a more widespread adoption of eco-friendly practices throughout the supply chain, future initiatives might entail forming relationships with suppliers who share a commitment to sustainability (Noring & Nygaard, 2018). To reduce environmental impact, this can entail looking into novel materials such as recycled fabrics (Chowdhury et al., 2022, p. 100674). In order to improve community involvement, Gymshark should consider creating programmes that deal with more general social issues. This may be using its platform to promote mental health awareness. This subject is becoming increasingly important in today’s society, or it could entail funding health and wellness initiatives in underprivileged areas (Ford et al., 2021, p.592237).
- CSR Strategy Models (Tables)
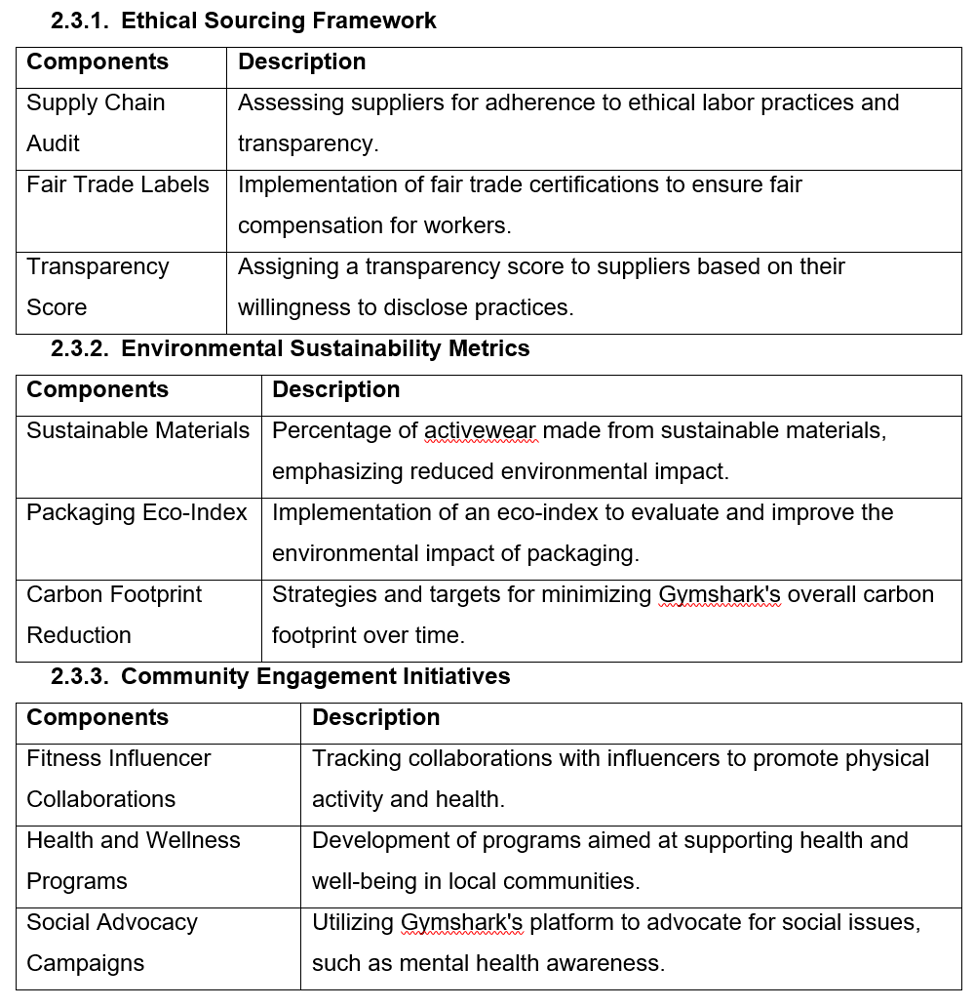
2.3.1. Ethical Sourcing Framework
| Components | Description |
| Supply Chain Audit | Assessing suppliers for adherence to ethical labour practices and transparency. |
| Fair Trade Labels | Implementation of fair trade certifications to ensure fair compensation for workers. |
| Transparency Score | Assigning a transparency score to suppliers based on their willingness to disclose practices. |
2.3.2. Environmental Sustainability Metrics
| Components | Description |
| Sustainable Materials | Percentage of activewear made from sustainable materials, emphasising reduced environmental impact. |
| Packaging Eco-Index | Implementation of an eco-index to evaluate and improve the environmental impact of packaging. |
| Carbon Footprint Reduction | Strategies and targets for minimising Gymshark’s overall carbon footprint over time. |
2.3.3. Community Engagement Initiatives
| Components | Description |
| Fitness Influencer Collaborations | Tracking collaborations with influencers to promote physical activity and health. |
| Health and Wellness Programs | Development of programs aimed at supporting health and well-being in local communities. |
| Social Advocacy Campaigns | Utilising Gymshark’s platform to advocate for social issues, such as mental health awareness. |
3. Leadership Analysis
Gymshark’s dynamic leadership techniques play a are vital role in the tompany’s success in the highly competitive fitness gear business. The brand’s leadership strategy is distinguished by its dedication to creativity, diversity, and empowering culture.
3.1. Current Leadership Strategy
The leadership team at Gymshark uses a transformational leadership approach to encourage and inspire staff members to go beyond what they think they are capable of. Ben Francis, the company’s creator, has been instrumental in fostering an environment encouraging innovation and taking calculated risks. This strategy fosters a sense of ownership and dedication among the workforce by encouraging employees to submit ideas and actively engage in decision-making (Avolio, 2010). Recognising the value of varied viewpoints in fostering innovation, Gymshark’s leadership team also strongly emphasises diversity (Northouse, 2021). This inclusive leadership approach fosters a cooperative atmosphere where people from all backgrounds are encouraged to contribute their special perspectives and feel appreciated. Consequently, Gymshark’s management has been effective in developing a workfan imaginative and flexible workforce—qualitiesl in the quick-paced fashion sector.
3.2. Future Leadership Strategies
In the future, Gymshark will have the chance to improve its leadership techniques even further. In the future, the organisation may use mentorship programmes to help with knowledge transfer and skill development. This could support the spirit of entrepreneurship essential to Gymshark’s success. To findLeadership development initiatives can also be implemented tond develop future leaders inside the company, leade 2023, p. 48). Gymshark can guarantee a strong leadership pipeline capable of handling the constantly changing demands of the industry by making investing in its staff members’ professional development ship Strategy Models (Tables)
3.3. These leadership
strategies illustrate Gymshark’s present and prospective leadership philosophies. These models provide direction for enhancing leadership tactics to maintain creativity, diversity, and flexibility inside Gymshark as it develops.
3.3.1. Transformational Leadership Model
| Components | Description |
| Inspirational Motivation | Leaders inspire and motivate employees by creating a compelling vision for the future. |
| Intellectual Stimulation | Encouraging innovation and creativity by challenging employees to think outside the box. |
| Individualised Consideration | Recognising and valuing each employee’s unique strengths and contributions. |
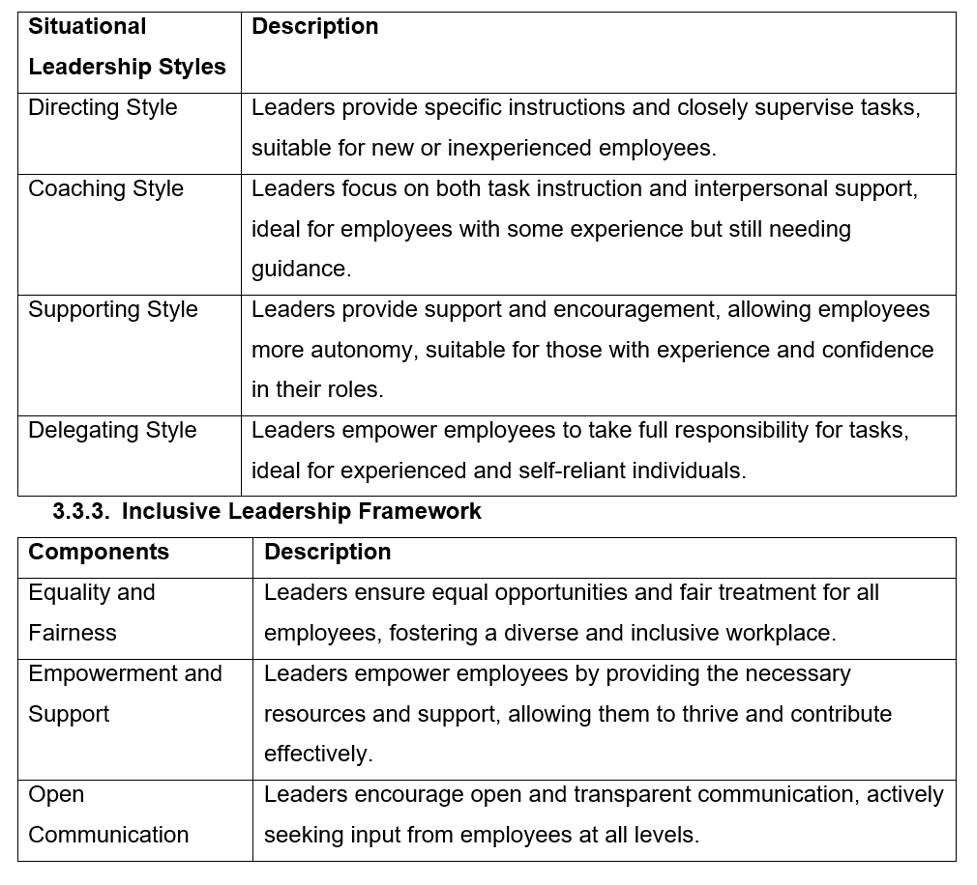
3.3.2. Situational Leadership Model
| Situational Leadership Styles | Description |
| Directing Style | Leaders provide specific instructions and closely supervise tasks suitable for new or inexperienced employees. |
| Coaching Style | Leaders focus on task instruction and interpersonal support, which is ideal for employees with some experience but still need guidance. |
| Supporting Style | Leaders provide support and encouragement, allowing employees more autonomy, suitable for those with experience and confidence in their roles. |
| Delegating Style | Leaders empower employees to take full responsibility for tasks, ideal for experienced and self-reliant individuals. |
3.3.3. Inclusive Leadership Framework
| Components | Description |
| Equality and Fairness | Leaders ensure equal opportunities and fair treatment for all employees, fostering a diverse and inclusive workplace. |
| Empowerment and Support | Leaders empower employees by providing the necessary resources and support, allowing them to thrive and contribute effectively. |
| Open Communication | Leaders encourage open and transparent communication, seeking employee input at all levels. |
4. External Environment Analysis for Gymshark
Gymshark functions under a constantly changing external milieu influenced by multiple elements that affect the fitness gear sector. A thorough examination entails examining market trends, the competitive environment, and the technological and regulatory factors affecting Gymshark’s strategic choices.
4.1. Impact of External Environment
Fitness apparel is fiercely competitive, with many firms fighting for consumers’ attention. Gymshark’s success can be ascribed to its aptitude for navigating and adapting to outside obstacles. External factors that impact Gymshark’s strategic direction include evolving fashion trends, shifting consumer tastes, and technological breakthroughs in the fitness industry. Market trends, like the increased focus on wellness and health, have presented Gymshark with opportunities and difficulties. Gymshark’s innovative strategy is consistent with the rise of athleisure fashion and the tech integration of sportswear. However, Gymshark must continue to be adaptable and change to meet the needs of its customers because of how quickly the market is evolving.
4.2. Gymshark’s Response to External Factors
By leveraging its web-based business strategy, Gymshark has shown to be strategically flexible. The company’s direct-to-consumer approach allows for quick reaction to changes in the market, efficient inventory management, and transparent communication with its customers. Gymshark’s robust online presence has proven essential in mitigating external factors, such as the impact of global events on conventional retail.
4.3. External Environment Strategy Models (Tables)
Gymshark can seize opportunities and proactively address challenges in the competitive exercise equipment business by utilising strategic models and conducting extensive external environment research.
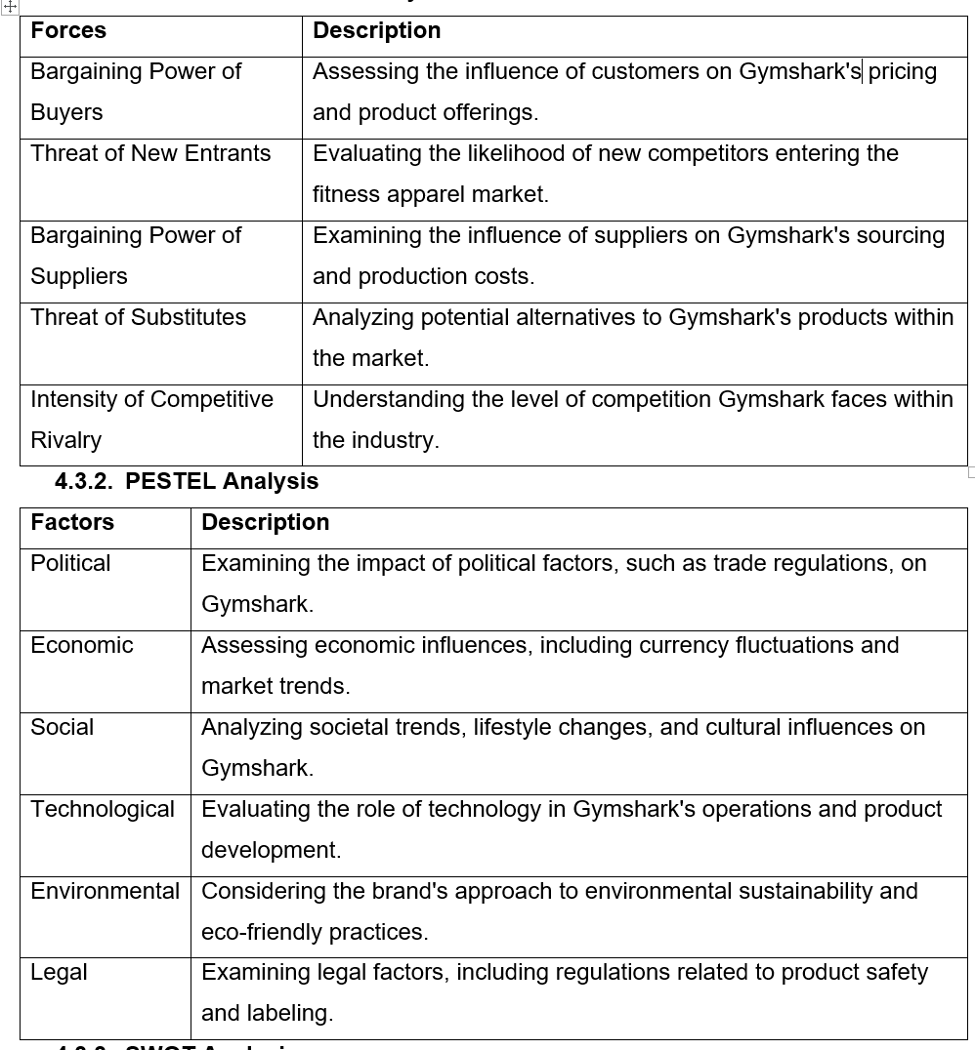
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
| Forces | Description |
| Bargaining Power of Buyers | Assessing the influence of customers on Gymshark’s pricing and product offerings. |
| Threat of New Entrants | Evaluating the likelihood of new competitors entering the fitness apparel market. |
| Bargaining Power of Suppliers | Examining the influence of suppliers on Gymshark’s sourcing and production costs. |
| Threat of Substitutes | Analysing potential alternatives to Gymshark’s products within the market. |
| Intensity of Competitive Rivalry | Understanding the level of competition Gymshark faces within the industry. |
4.3.2. PESTEL Analysis
| Factors | Description |
| Political | Examining the impact of political factors, such as trade regulations, on Gymshark. |
| Economic | Assessing economic influences, including currency fluctuations and market trends. |
| Social | Analysing societal trends, lifestyle changes, and cultural influences on Gymshark. |
| Technological | Evaluating the role of technology in Gymshark’s operations and product development. |
| Environmental | Considering the brand’s approach to environmental sustainability and eco-friendly practices. |
| Legal | Examining legal factors, including regulations related to product safety and labelling. |
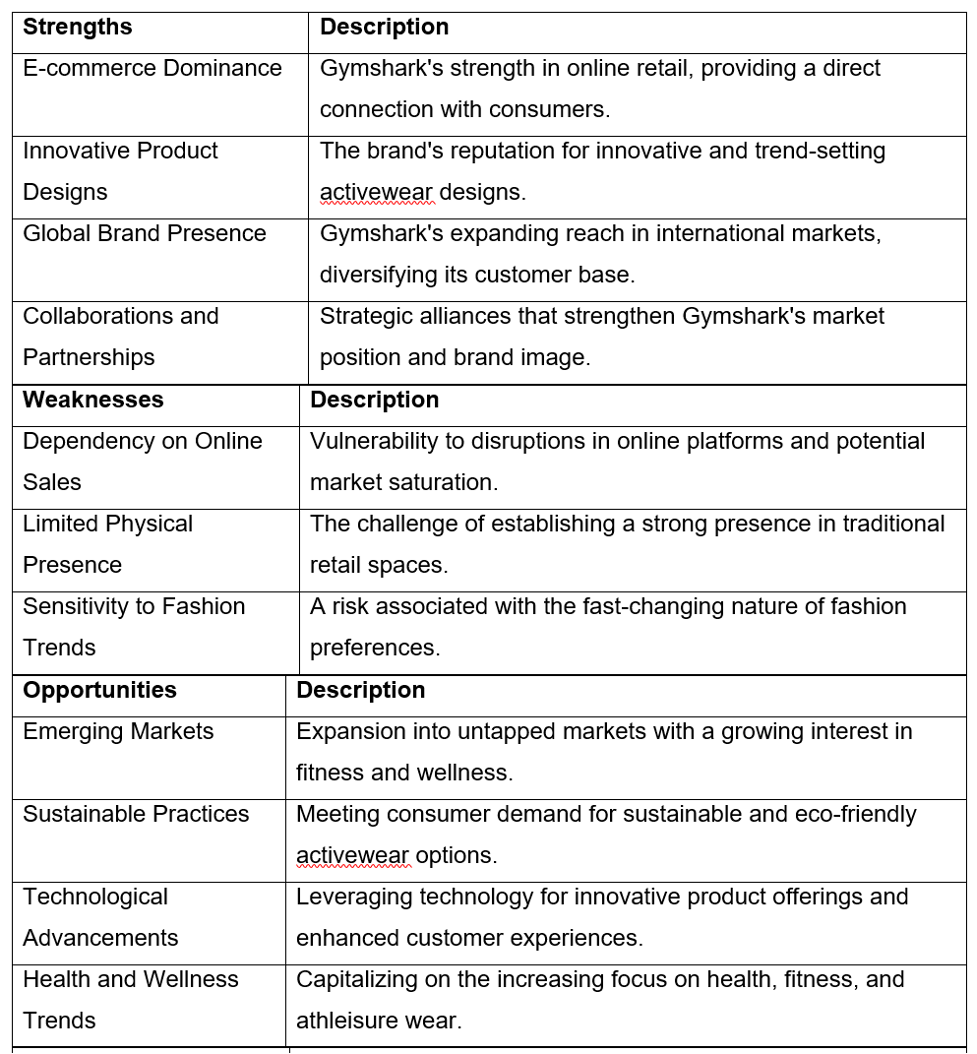
4.3.3. SWOT Analysis
| Strengths | Description |
| E-commerce Dominance | Gymshark’s strength in online retail providing a direct connection with consumers. |
| Innovative Product Designs | The brand’s reputation for innovative and trend-setting activewear designs. |
| Global Brand Presence | Gymshark’s expanding reach in international markets, diversifying its customer base. |
| Collaborations and Partnerships | Strategic alliances that strengthen Gymshark’s market position and brand image. |
| Weaknesses | Description |
| Dependency on Online Sales | Vulnerability to disruptions in online platforms and potential market saturation. |
| Limited Physical Presence | The challenge of establishing a strong presence in traditional retail spaces. |
| Sensitivity to Fashion Trends | A risk associated with the fast-changing nature of fashion preferences. |
| Opportunities | Description |
| Emerging Markets | Expansion into untapped markets with a growing interest in fitness and wellness. |
| Sustainable Practices | Meeting consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly activewear options. |
| Technological Advancements | Leveraging technology for innovative product offerings and enhanced customer experiences. |
| Health and Wellness Trends | Capitalising on the increasing focus on health, fitness, and athleisure wear. |
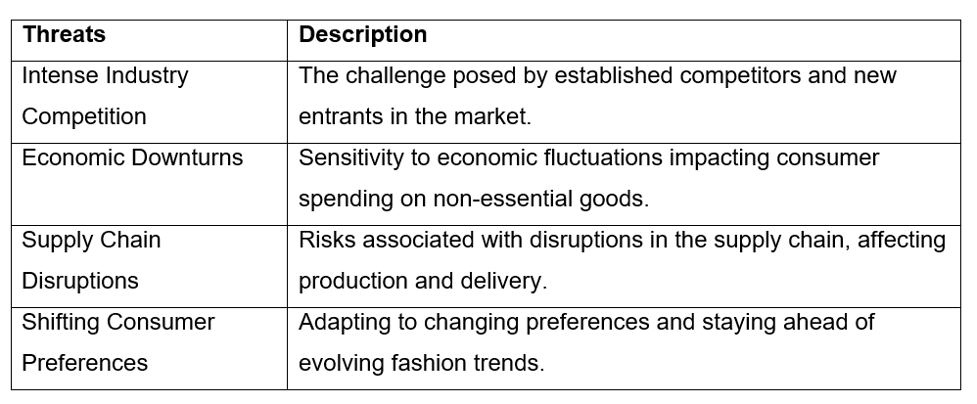
| Threats | Description |
| Intense Industry Competition | The challenge posed by established competitors and new entrants in the market. |
| Economic Downturns | Sensitivity to economic fluctuations impacting consumer spending on non-essential goods. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Risks associated with disruptions in the supply chain, affecting production and delivery. |
| Shifting Consumer Preferences | Adapting to changing preferences and staying ahead of evolving fashion trends. |
5. Internal Resources Analysis for Gymshark
Gymshark’s internal resources play a significant role in shaping its competitive edge in the fitness wear industry. Analysing its internal resources in-depth entails looking at essential areas, including organisational capacities, human capital, and technology infrastructure.
Organisational Capabilities
Gymshark’s success can be attributed to the unique organisational skills it has developed. The organisation’s key competencies are its quick response to market changes, quick product development cycles, and effective supply chain management (Teece, 2007, p.1330). Gymshark has established itself as a trailblazer in the industry and has drawn a devoted following because of its ability to bring cutting-edge products to market quickly. Furthermore, Gymshark’s direct-to-consumer business strategy is a tactical advantage that permits the company to keep command of the whole value chain, from distribution to design (Bock, 2023, p. 16). Gymshark’s competitive position is strengthened by this integrated strategy, which improves efficiency and responsiveness to client demands.
Human Capital
The talent and expertise of Gymshark’s staff make them an essential internal resource. The company’s founder, Ben Francis, has significantly fostered an inventive and enterprising culture (Gupta, 2018). The company’s emphasis on hiring individuals who align with its fitness-focused culture produces a team that understands and connects to Gymshark’s target clientele. The commitment to innovation, teamwork, and an uncompromising pursuit of perfection characterise Gymshark’s internal culture. This aspect of the company’s culture aids in attracting and retaining top personnel in industries like technology, marketing, and design.
Technological Infrastructure
Gymshark’s internal resource that enhances customer satisfaction and operational effectiveness is its infrastructure investment in technology. The business uses cutting-edge technologies for data analytics, e-commerce platforms, and supply chain management. Gymshark’s technology-driven approach enables them to gather valuable client data, optimise inventory management, and personalise the online shopping experience (Bharadwaj et al., 2013, p. 475).
Internal Resources Strategy Models (Tables)
This internal resources analysis demonstrates that Gymshark’s competitive advantage in the fitness equipment market may be primarily ascribed to its strengths and capabilities. By using and enhancing these internal resources, Gymshark can carry on innovating and growing the business.
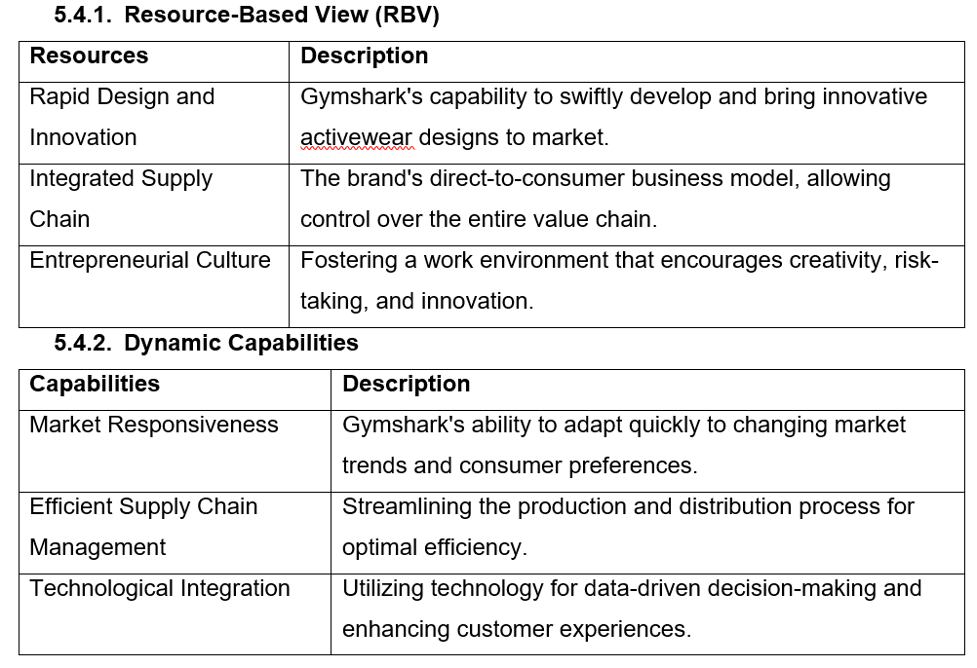
Resource-Based View (RBV)
| Resources | Description |
| Rapid Design and Innovation | Gymshark’s capability to swiftly develop and bring innovative activewear designs to market. |
| Integrated Supply Chain | The brand’s direct-to-consumer business model allowing control over the entire value chain. |
| Entrepreneurial Culture | Fostering a work environment that encourages creativity, risk-taking, and innovation. |
5.4.2. Dynamic Capabilities
| Capabilities | Description |
| Market Responsiveness | Gymshark’s ability to adapt quickly to changing market trends and consumer preferences. |
| Efficient Supply Chain Management | Streamlining the production and distribution process for optimal efficiency. |
| Technological Integration | Utilising technology for data-driven decision-making and enhancing customer experiences. |
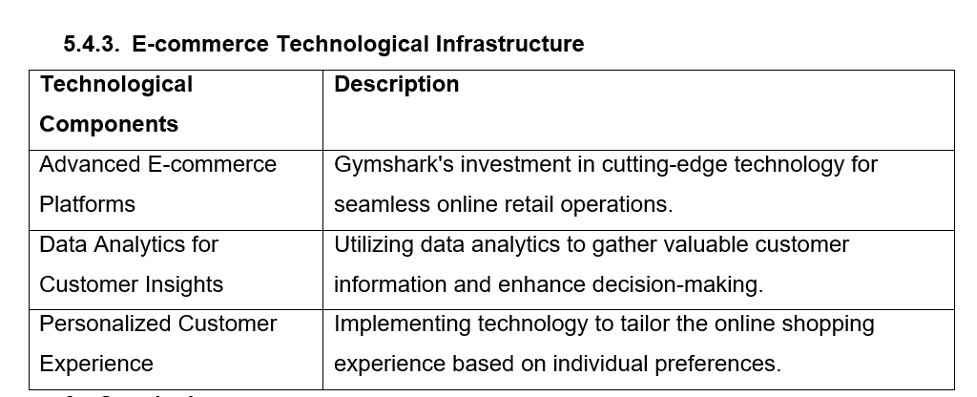
5.4.3. E-commerce Technological Infrastructure
| Technological Components | Description |
| Advanced E-commerce Platforms | Gymshark’s investment in cutting-edge technology for seamless online retail operations. |
| Data Analytics for Customer Insights | Utilising data analytics to gather valuable customer information and enhance decision-making. |
| Personalised Customer Experience | Implementing technology to tailor the online shopping experience based on individual preferences. |
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, the strategic environment analysis of Gymshark shows how the company has developed from a 2012 startup to a significant participant in the exercise gear market, indicating its disruptive influence in the industry. Gymshark’s path may be fully understood by looking at the important themes of leadership, internal resources, external environment, and corporate social responsibility (CSR). Gymshark demonstrates their dedication to corporate social responsibility (CSR) through community involvement, environmentally sustainable practises, and ethical sourcing. A responsible mindset is reflected in current activities like fair labour practises and environmentally sustainable operations. Gymshark has the capacity to grow by forming long-term alliances and taking on more significant social issues.
The success of Gymshark is intricately tied to its transformational leadership style, notably driven by founder Ben Francis. This leadership fosters a culture of innovation and inclusivity, pushing employees beyond perceived limits. To further enhance leadership, investments in mentorship programs and leadership development are recommended, ensuring a continuous flow of innovative ideas. Operating in a competitive external environment, Gymshark strategically leverages its online-centric model, as revealed by Porter’s Five Forces, PESTEL, and SWOT analyses. Proactive strategies, such as global expansion and sustainability practices, position Gymshark to navigate industry dynamics successfully. Moreover, Gymshark’s internal resources, encompassing organisational capabilities, human capital, and technological infrastructure, constitute the core of its competitive advantage. The Resource-Based View and Dynamic Capabilities frameworks underscore Gymshark’s agility and innovation. Sustaining its leadership involves ongoing investments in technology and maintaining an entrepreneurial culture.
Bibliography
Northouse, P.G., 2021. Leadership: Theory and practice. Sage publications.
sustainability.gymshark.com., n.d. our impact. [online] Available at: https://sustainability.gymshark.com/ourplanet/ourimpact.
Abad-Segura, E., Cortés-García, F.J. and Belmonte-Ureña, L.J., 2019. The sustainable approach to corporate social responsibility: A global analysis and future trends. Sustainability, 11(19), p.5382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195382
Accountancy Cloud, 2021. The Rise of Gymshark – How it turned into an over £1bn brand. [online] Accountancy Cloud. Available at: https://theaccountancycloud.com/blogs/the-rise-of-gymshark.
Avolio, B.J., 2010. Full range leadership development. Sage Publications.
Bharadwaj, A., El Sawy, O.A., Pavlou, P.A. and Venkatraman, N.V., 2013. Digital business strategy: toward a next generation of insights. MIS Quarterly, pp.471-482.
Bock, M., Wiener, M. and Saunders, C., 2023. Non-ownership business models in the manufacturing industry: Uncertainty-exploiting versus uncertainty-mitigating designs and the role of context factors. Electronic Markets, 33(1), p.16.
central.gymshark.com., n.d. Gymshark x Steve Cook | Gymshark Central. [online] Available at: https://central.gymshark.com/article/steve-cook-x-gymshark-the-collection.
Chowdhury, N.R., Chowdhury, P. and Paul, S.K., 2022. Sustainable practices and their antecedents in the apparel industry: A review. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, p.100674.
Ford, E., Shepherd, S., Jones, K. and Hassan, L., 2021. Toward an ethical framework for the text mining of social media for health research: a systematic review. Frontiers in Digital Health, 2, p.592237.
Geissdoerfer, M., Vladimirova, D. and Evans, S., 2018. Sustainable business model innovation: A review. Journal of cleaner production, 198, pp.401-416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.240
Gupta, G., Tan, K.T.L., Ee, Y.S. and Phang, C.S.C., 2018. Resource-based view of information systems: Sustainable and transient competitive advantage perspectives. Australasian Journal of Information Systems, 22.
Gymshark., 2017. About Us. [online] Gymshark US. Available at: https://www.gymshark.com/pages/about-us.
Gymshark., 2023. Home. [online] sustainability.gymshark.com. Available at: https://sustainability.gymshark.com/.
Noring, L. and Nygaard, J.J., 2018. Partnerships for Improved Sustainability: A Case Study Method Applied to Partnerships in the Transport Industry. research.cbs.dk. [online] Available at: https://research.cbs.dk/en/publications/partnerships-for-improved-sustainability-a-case-study-method-appl [Accessed 14 Nov. 2023].
Siegel, E., Glaeser, E.L., Kozyrkov, C. and Davenport, T.H., 2020. Strategic Analytics: The Insights You Need From Harvard Business Review. Harvard Business Press.
Teece, D.J., 2007. Explicating dynamic capabilities: the nature and microfoundations of (sustainable) enterprise performance. Strategic management journal, 28(13), pp.1319-1350.
UMOH, U.E., 2023. CHARISMATIC LEADERSHIP AND ITS ROLE IN ORGANISATIONAL EFFECTIVENESS. In 3rd International Conference on Institutional Leadership and Capacity Building in Africa (p. 48).
Appendices
 write
write