In contemporary society, most people drawn across all the demographic clusters across the globe have or will have tattoos implanted in their bodies. They are more popular among the students, especially college students as well as young adults aged between 18 to 35 years of age. Demographic statistics on tattoos demonstrate that close to 40 percent of 18 to 34 aged young adults have one or more tattoos on their bodies. Those aged 35 to 54 years old are have a tattoo accounting for at least 35 percent, while for those above 55 years old, at least 16 percent have a tattoo (Cassata, 2018). A rise in the number of tattoos implantations around the human body depicts that the myths regarding the taboo are decreasing. Some industries accept employees with tattoos and tend to prefer the employees. This essay aims to better understand the tattoo culture by focusing on how tattoos are perceived in contemporary society and describing the tattoos process.
Buffy case
Buffer’s parents should allow him to undergo the professional tattoo process. This is because it is safe and less risky than the traditional approach. Denying the opportunity may create some sense of discomfort and hatred amongst himself while interacting with peers. They should not be worried much since tattoos can be removed surgically in case complications arise.
Understanding of tattoo
Isaac, Ngwanya, & Lehloenya (2018) define a tattoo as the implantation of an exogenous pigment to a person’s mucous membranes. They argued that some tattoos on the human body are accidental and others intentional, short-term or permanent, professional or amateur, while others are decorative or for medical purposes. The purpose of tattoos implantation on a personal body thus plays a significant determinant to people taking tattoos or not. For instance, accidental tattoos often result from a traumatic situation because the victim endured uncontrollable scenarios. This may include inoculation into a wound of substances, including asphalt, graphite, ink, or gunpowder. Consequently, the victims do not have an alternative to allow tattoo implantation into their bodies.
Permanent tattoos entail a colorful pigmentation that is implanted below the derma-epidermal junction and are sustained by the macrophages as well as fibroblasts located in the dermis. The temporary tattoos that are short-term in nature have a similar outlook as permanent tattoos. However, these tattoos are mere paints or airbrushes on an individual skin’s surface, often lasting a few days.
Professional tattoos are another category usually implanted by well-trained personnel in a tattoos parlor and imprinted using a machine. In this category, tattoo implantation takes place in the skin’s dermis. The amateur tattoos are done at people’s residential areas, and one is only required to have a needle as well as one color ink. Depending on the person doing the implantation, the ink deposition is more superficial as well as variable.
Cosmetic tattoos are usually taken on an individual skin to enhance the body appearance of the body parts. They have an appearance of make-up or mask deformities. Such tattoos include permanent make-up, tattoos done against the surgical scars as well as nipple tattoos are usually done after the mastectomy. Medical tattoos are employed on an individual’s body with the sole intention of treating against certain medical conditions. They facilitate awareness of the specific medical information as well as mark the person’s body location intended for a patient’s surgery and other procedures and future review. The last category is the invisible tattoos, which are made with dyes. The dyes tend to fluoresce as well as glow visibly in ultraviolet light.
Brief history and epidemiology of tattoos
Tattoos can trace back more than 5000 years. In 1991, a 5300-year-old body of Otzi the Iceman was found in the Tyrolean Alps and tattooed across his arthritic joints. Since then, the epidemiology of tattooing depicts several evolutions throughout the time, which represents a series of changes in interpersonal, cultural, and political influences. In the recent past, tattoos that were majorly linked to prisoner’s prostitutes as well as seamen, some prominent people in the society, and respected leaders have been tattooed. Some tattooed leaders include Winston Churchill, his mother, Tsar Nicholas II, King George V, Theodore Roosevelt, and present global leaders. During the 1980s, tattoos were utilized to resist reforms against the middle-class conservative norms and practices in society. In the contemporary world, tattoo implantation has generally increased through several cultures, regional areas, social classes, and people from various educational backgrounds.
Tattoo implantation is generally increasing the modern society. The rise in tattoos is attributed to the increased digitalization as well as cultural commercialization. Isaacs, Ngwanya, & Lehloenya (2018) suggest that close to 100 million Europeans have been tattooed. A 2016 United States study explained a drastic change in the number of tattooed personnel. The number encourages people with higher education to recall their loved ones while others take it for entertainment. A study conducted in Germany explains the number of individuals tattooed averaged 35 years of age, lacked a history of drug and alcohol abuse, and were inactive employment.
Graphic images of tattoos

Source:https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fstylesatlife.com%2Farticles%2Ftattoo-designs-and-meanings%2F&psig=AOvVaw21p7AUxFBI7u2UYT3TToew&ust=1646825545491000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAsQjRxqFwoTCJCFvrK1tvYCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAD

Source: https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn2.stylecraze.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2013%2F05%2FBlackwork-Tattoos.jpg&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.stylecraze.com%2Farticles%2Famazing-tattoo-designs-and-their-meanings%2F&tbnid=VsM3s5wSc0yPLM&vet=12ahUKEwiugriutbb2AhUHzioKHQOwDukQMygOegUIARD7AQ..i&docid=bo5n3KJc6QtDBM&w=500&h=650&q=graphic%20representations%20of%20tattoos&client=firefox-b-d&ved=2ahUKEwiugriutbb2AhUHzioKHQOwDukQMygOegUIARD7AQ

Source: https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fmedia.istockphoto.com%2Fphotos%2Ftattoo-artist-back-picture-id147444721%3Fk%3D20%26m%3D147444721%26s%3D612x612%26w%3D0%26h%3D9MwUe_ZNu1tff16PZIwPPe_Pm6jT__yqKDbnxCOdz5M%3D&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.istockphoto.com%2Fphotos%2Fback-tattoo&tbnid=_aWnyJa1t3J6qM&vet=12ahUKEwiugriutbb2AhUHzioKHQOwDukQMygCegUIARDgAQ..i&docid=cCh027td49lddM&w=408&h=612&q=graphic%20representations%20of%20tattoos&client=firefox-b-d&ved=2ahUKEwiugriutbb2AhUHzioKHQOwDukQMygCegUIARDgAQ
Motivations for tattooing
There is a need to understand the motivations behind people taking part in tattooing, which assists in addressing any health concerns that may present themselves. There are varied reasons across different population demographics to opt for tattooing. Tattooing in historical times was mainly taken for therapeutic functionality alongside a mechanism to promote transmission of knowledge. However, religious groups such as Christianity and Judaism have always taken a different as well as unfavorable perception towards tattoos.
In recent years, those people tattooing ae motivated by personal identity since they want to be noticed by society members. This is the class of musicians and leaders who want to entertain people who are often tattooed. Another reason for tattooing is to display shared values within a given subculture and a quest for individuality, promoting self-attractiveness and impulsive tattooing when an individual is under the influence of alcohol, drugs, and substance abuse. Moreover, the motivations also vary among the individual social status and education levels. Unlike in the historical era, tattooed people, only 10 percent are under alcohol, drugs, or substance. The only educational level disproportionately represented in such a category is the high school.
Process of tattooing and Integumentary System
Tattooing procedures are usually invasive that inoculates probable hazardous chemicals into a human being’s body. The procedure used in traditional and amateur tattooing entails rubbing pigment into patterned cuts on individual skin (Levy 2008). It can also entail the hand trappings the ink to a human being’s skin using sharp objects. Traditional procedures are usually risky, and one can develop complications. Therefore, a traditional approach to tattooing may have adverse health implications hence the need to avoid it.
Modern professional tattoos are conducted using a tattoo machine that has a mechanized needle, which inoculates the pigment into a human being’s skin. The method ensures that ink quantities are well standardized controlled and the patterns maintained. The pigment is usually dispensed into the skin using controlled quantities and patterns. The method ensures that the pigment is carefully dispensed into the skin epidermis and dermis. The pigment found in the epidermis is eradicated through desquamation. On the other hand, pigment located at the dermal is generally absorbed by the macrophages alongside maintained at the fibroblasts. There are usually connective tissues that attempt to surround such ink containing fibroblasts, entrap them, and subsequently immobilize them.
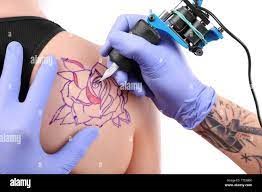
Source: https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fc8.alamy.com%2Fcomp%2FTTEMEK%2Fprocess-of-making-tattoo-closeup-TTEMEK.jpg&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.alamy.com%2Fprocess-of-making-tattoo-closeup-image256020315.html&tbnid=nVyIOJhcRenJ0M&vet=12ahUKEwjQiZO_t7b2AhXJ8bsIHWJOBJIQMygPegUIARDrAQ..i&docid=OcTaL9zc0fvvzM&w=1300&h=956&q=process%20of%20tattooing&client=firefox-b-d&ved=2ahUKEwjQiZO_t7b2AhXJ8bsIHWJOBJIQMygPegUIARDrAQ
Tattooing pigments
Several materials are utilized to ensure a successful tattooing operation is undertaken in tattooing. Carbon with shading additives, including titanium oxide, iron oxide, and excipients including the formulants, preservatives, fragrances, and dispersants, are employed to implant a black tattoo into human beings (Liao et al. 2014). On most occasions, the modern tattoos will contain organic pigments, including heavy metals such as titanium, barium, aluminum, and copper. It may also include other materials such as antimony, mercury sulfide, nickel contaminants, cobalt, lead, and chromium. Some of the inks that the professional tattooist are different in terms of purity as well as contain substances that are yet to be tested on for individual human consumption.
Amateur tattooists’ pigments include multiple inks such as India ink, pen ink, carbon particles collected from the burned wood, vegetable matter, cotton, shoe heels, paper, and molten rubber mixed with water sugar. Another component includes the mixture of ash and urine. This practice is widely used in prisons and attested that it lowers the probability of infections.
Complications of tattoos
Some underlying complications are closely linked to the tattooing processes. These complications are primary infections, non-infectious inflammatory, psychosocial, technique, and treatment-related miscellaneous. The complications tend to vary from one party to another with varying complexity. Some complications may be acute, delayed, or even chronic. The colored tattoos, red in red, are more likely to result in chronic complications than the black tattoos. The complications usually impact the individual’s skin, estimated at 70 percent, while 7 percent are believed to be systematic, and only 6 percent believed to be persistent.
Poor procedural, as well as individual hygiene, is responsible for the infectious complications. The infections from bacteria, viruses, and fungi are projected to complicate the tattoos. Whether amateur or professional, the tattooists must ensure that the materials they use to perform the tattooing procedures are well sterilized and clean to prevent infecting other people.
Tattoo removal
People may also seek to remove implanted tattoos from their bodies based on personal reasons and derive complications in tattooing. Personal reasons resonate with a person changing their religious affiliations, boredom, dissatisfaction with a tattoo, dissociation with certain groups, and relationship status (Sapp 2016). People seeking to reintegrate into society can be hampered due to prisoners or gang members with tattoos meanings they still prescribe the ideas of the group. The professional and social pressures have less impact on an individual’s ability to seek tattooing because some careers promote tattoos.
People’s desire to eradicate a tattoo from their bodies is usually more desired than a desire to implant it. A recent study suggests that people are not concerned about the health risks posed while removing a tattoo from their bodies. Most people want to seek complete medical surgery to remove the tattoos without alternative measures.
References
Cassata, C. (2018). Is President Trump Right? Should We Open More Mental Institutions?. Healthline. Retrieved 3 March 2022, from https://www.healthline.com/health-news/president-trump-should-we-open-more-mental-institutions.
Isaacs, T., Ngwanya, R. M., & Lehloenya, R. J. (2018). Tattoos: A summary knowledge for the practicing clinician. South African Medical Journal, 108(9), 714-720. Retrieved from https://journals.co.za/doi/abs/10.7196/SAMJ.2018.v108i9.13231
Levy, J. (2008). Tattoos in modern society. The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc.
Liao, P. A., Chang, H. H., & Su, Y. J. (2014). Is tattooing a risk factor for adolescents’ criminal behavior? Empirical evidence from an administrative data set of juvenile detainees in Taiwan. Risk analysis, 34(12), 2080-2088.
Sapp, J. L. (2016). Evaluation of tattoo artists’ perceptions of tattoo regulations in the United States.
 write
write