Introduction
The passenger transportation service industry has grown significantly due to the demand for public transportation systems. This has been considered a fundamental sector in the economy that concentrates on moving people and products from one point to another. Generally, they include companies such as railroads, airlines, logistics firms, and those providing transportation infrastructure. However, other companies such as Uber, Bolt, Lyft, Cabify, and Ola cabs have emerged with technological advancements. These companies primarily use technology to connect the driver and the customer using mobile apps (Liu et al., 2021). This has made booking and paying for transportation services easier and more efficient, despite various limitations. For that reason, this report will explore Uber by highlighting the nature of its services, target market, perceived risks, and the different components of the service.
The Nature of the Service
Uber is a multinational transportation or mobility service provider company headquartered in San Francisco, United States. The organization was established in 2009 and hastily developed to become to most valuable star-up across the world. It is regarded as a technology firm whose mission and vision are to facilitate movement for both things and people (Uber, 2022). In order to achieve this, Uber uses exclusive innovation to establish and maintain multisided platforms, which provide various services to users, including linking potential consumers to service providers (Sthapit & Björk, 2019). As a result, the nature of the services Uber provides.
Table 1: The nature of the service Uber offers
| Nature of service | Specific service nature of Uber | Reasons |
| Act | Tangible |
|
| Relationship | Discreet delivery |
|
| Demand | High variability |
|
Source: Author (2022)
The Target Market
Table 2: The target market Uber explores
| Segmentation | Target market |
| Demographics |
|
| Psychographics |
|
| Geographic |
|
| Behavioral |
|
Source: (Sthapit & Björk, 2019; Uber, 2022)
Generally, Uber has two customer groups or segments, including drivers and riders. The drivers are normally called taxi drivers. They are people who have vehicles that move people and things from one region to another. On the other hand, the riders are the customers who need transportation services from the company. Hence, Uber mainly targets both riders and drivers. All the two parties benefit from the company. Nonetheless, the target market can be categorized into demographics, psychographics, geographic, and behavioral elements.
Figure 1: Positioning/Perceptual Map
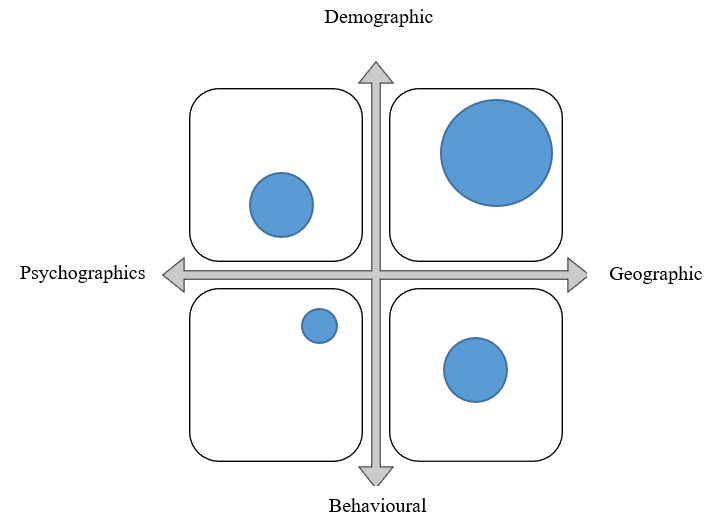
Source: Author (2022)
NB: The large circles represent the segments Uber targets most while the small circles represent where it targets least.
The Perceived Risks
- Theft and murder: This is among the most risk Uber drivers experience. A customer might pretend to order for an Uber to steal the car and kill the rider.
- Rape: This has also been a risk factor in the industry where either the rider or the driver forcefully involve in sexual behavior.
- Accountability: Often, the driver is responsible for car liabilities, including fuel, repairs, and general maintenance (Lovelock et al., 2015).
The Components of the Service
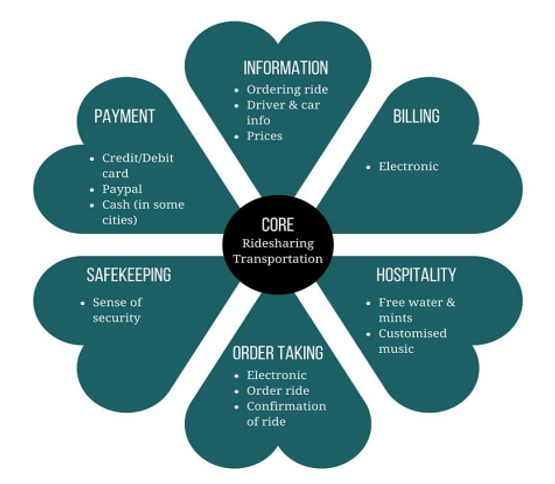
Figure 2: Flower of service model for Uber
Source: (Vale, 2016)
Conclusion
This report established that transportation companies such as Uber, Bolt, Lyft, Cabify, and Ola cabs have emerged with technological advancements. Hoverer, this report mainly explored Uber by highlighting the nature of services, target market, perceived risks, and the different components of the service. It was maintained that Uber is a multinational company that offers tangible and discreet delivery with high variability in demand. Also, Uber targets mainly drivers and riders from various demographics and geographic locations. Nevertheless, the report highlighted various perceived risks such as rape, theft, and murder.
References
Liu, M., Brynjolfsson, E., & Dowlatabadi, J. (2021). Do Digital Platforms Reduce Moral Hazard? The Case of Uber and Taxis. Management Science. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2020.3721
Lovelock, C., Patterson, P., & Walker, hett H. (2015). Services Marketing: An Asia-Pacific and Australian Perspective (6th ed.). Pearson.
Sthapit, E., & Björk, P. (2019). Sources of value co-destruction: Uber customer perspectives. Tourism Review, 74(4), 780–794. https://doi.org/10.1108/tr-12-2018-0176
Uber. (2022). About Us. Uber. https://www.uber.com/ke/en/about/
Vale, H. (2016). Uber Service Audit. https://zachariahmillerblog.files.wordpress.com/2016/06/report.pdf
 write
write