Introduction
This paper examines the main problem facing a small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) food company and the solutions that can be implemented to address the issue. The report begins by discussing the main problem facing the company, which is the need to improve the quality of its products. It then goes on to analyze the tools used in the study and the type of waste associated with the disclosed problem. Next, the paper examines the leading solutions proposed in the case study and the authors’ justification. Finally, the report reviews the results and benefits of applying lean and SPC.
Question 1.
The main problem facing SME food companies.
The main problem facing the SME food company is the need to improve the quality of its products. The company produces and sells various products, including canned food and pre-packaged meals. The company has been experiencing a decrease in sales due to customer complaints about the quality of its products (Sharma, 2020). The company has identified several issues contributing to the low quality of its products, including poor production processes, lack of training, and inadequate quality control systems.
In order to address these issues, the SME food company will need to make some changes to its production and quality control systems. This may include investing in new equipment and technology, improving staff training, and implementing stricter quality control measures. The company should also develop and implement a comprehensive quality management system to ensure all products meet customer expectations. Additionally, the company should create and implement a customer feedback system to identify potential problems and respond quickly to customer concerns. Finally, the company should look into developing and implementing a comprehensive marketing strategy to increase awareness and sales of its products.
Analysis followed by the author.
The authors systematically investigated the problem and its implications, causes, and root cause. Firstly, they conducted a literature review to understand the current practices and trends in the food industry. This included an analysis of recent statistics and research on lean manufacturing, Statistical Process Control (SPC), and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) (Sharma, 2020). Secondly, they conducted interviews with the company’s employees and customers to understand their experience with the company’s products and processes. Thirdly, they conducted a survey of the company’s production facility to analyze the processes and identify areas for improvement. Lastly, they conducted a financial analysis of the company’s operations to assess the potential cost and benefit of implementing lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP.
Tools used in the study.
The authors used several tools to analyze the problem and its root causes. Firstly, they used a literature review to understand the current practices and trends in the food industry. Secondly, they conducted interviews with the company’s employees and customers to gain an understanding of their experience with the company’s products and processes. Thirdly, they conducted a survey of the company’s production facility to analyze the processes and identify areas for improvement. Lastly, they conducted a financial analysis of the company’s operations to assess the potential cost and benefit of implementing lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP.
Finally, they used statistical methods such as regression analysis and hypothesis testing to analyze the data collected from the above sources to identify the problem’s leading drivers. The authors also used graphical methods such as Pareto analysis to identify the most critical areas for improvement. The authors then used a combination of root cause analysis, process mapping, and value stream mapping to identify and prioritize potential solutions (Sharma, 2020). The authors concluded that implementing lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP would be beneficial for the company and reduce its costs in the long run.
The purpose of these tools was to gain a comprehensive understanding of the problem and its root causes. The literature review provided an overview of current practices and trends in the food industry, while the interviews and surveys provided a detailed understanding of the company’s processes and customer experience. The financial analysis quantitatively assessed the potential cost and benefit of implementing lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP.
The team also conducted an environmental analysis to understand the external factors that could affect the implementation of the new systems. This included gathering data on the current regulations and standards, the competitive landscape, and the technological advances that could be applied. Finally, the team developed a detailed implementation plan to ensure the new systems were implemented successfully with minimal disruption. This plan included a timeline, a budget, and a system for monitoring and evaluating the results.
Overall, these tools enabled the authors to comprehensively understand the problem and its root causes, enabling them to develop an effective solution. This solution was then implemented, leading to the desired results. The authors were able to measure the solution’s positive impact, which showed that the tools used had successfully solved the problem. The authors also identified other areas where their tools could be employed to make further improvements, allowing for efficient and effective problem-solving in the future.
Type of waste associated with the disclosed problem.
The disclosed problems can be attributed to a variety of types of waste. Firstly, there is a waste of time associated with inefficient production processes. This is due to the need for more training and adequate quality control systems, leading to delays in the production process and decreased production efficiency. Secondly, there is the waste of materials associated with producing defective products. This is due to the need for more quality control measures, which leads to the excessive use of materials and the production of defective products (Sharma, 2020). Thirdly, there is the waste of money associated with producing defective products. This is due to the need to rework or discard products completely, leading to decreased profits. Finally, the waste of customer satisfaction is associated with producing low-quality products. This is due to the decrease in customer satisfaction due to the poor quality of the products, leading to a decrease in sales.
Question 2
Leading solutions in this case study.
The leading solutions/approaches implemented in the case study were the implementation of lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP. Lean manufacturing is a system of production that focuses on eliminating waste, streamlining processes, and increasing efficiency. Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a quality control method that monitors and controls process variability. Finally, Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a system used to identify, assess and control food safety hazards.
Implementing these three approaches enabled the company to improve the quality of its products by increasing efficiency and reducing waste. Additionally, the implementation of SPC and HACCP enabled the company to monitor and control the quality of its products, which led to decreased customer complaints and increased customer satisfaction (Hossain, 2020).
The implementation of these three approaches also had a beneficial effect on the company’s bottom line. By reducing downtime and increasing efficiency, the company was able to produce more products in less time, leading to increased profits. Additionally, the implementation of SPC and HACCP enabled the company to identify problems before they become costly, thereby reducing the amount of money spent on rework and scrap (Hossain, 2020). Furthermore, the improved quality control standards allowed the company to reduce its warranty costs significantly. As a result, the company saw a marked improvement in its profitability.
Authors justification.
The authors justified using lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP by demonstrating their connection to the identified problems and their causes. Firstly, the authors demonstrated that implementing lean manufacturing would enable the company to reduce waste, streamline processes and increase efficiency, addressing the problems associated with inefficient production processes. Secondly, the authors demonstrated that implementing SPC would enable the company to monitor and control process variability, addressing the problems associated with the lack of quality control measures (Hossain, 2020). Finally, the authors demonstrated that implementing HACCP would enable the company to identify and control food safety hazards, addressing the problems associated with the lack of food safety measures.
The authors also demonstrated that these approaches were cost-effective by conducting a financial analysis of the potential cost and benefit of implementing them. The analysis showed that the implementation of lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP would result in cost savings and an increase in profits, which justified the use of these approaches.
The authors also calculated implementing these approaches’ potential return on investment (ROI). The ROI was highly optimistic, indicating that implementing lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP would significantly increase profits for the company. Furthermore, the authors discussed the importance of quality assurance and its role in ensuring the success of implementing these approaches. They concluded that quality assurance should be prioritized in the implementation process to maximize the benefits of lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP (Park, 2020). The authors also emphasized the importance of training and communication when implementing these approaches, as they are essential to the success of the implementation process.
Underlying concepts, purpose, and procedures.
The underlying concepts, purpose, and procedures of SPC and Lean are closely related. Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a quality control method that monitors and controls process variability. It is used to identify trends and anomalies in a process so that corrective action can be taken to improve the process and reduce defects. The underlying concept of SPC is that process performance should be monitored and controlled to ensure that it meets the desired standards.
Lean manufacturing is a system of production that focuses on eliminating waste, streamlining processes, and increasing efficiency. The underlying concept of Lean is that any activities that do not add value to the customer should be eliminated (Park, 2020). Lean manufacturing also emphasizes the use of data and feedback to continuously improve processes. The purpose of Lean is to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve customer satisfaction.
The procedures for implementing SPC and Lean are similar. Firstly, the processes should be analyzed to identify areas for improvement. Secondly, data should be collected to monitor and analyze process performance. Thirdly, corrective actions should be taken to improve processes and reduce defects. Feedback should be used to improve processes continuously.
Fourthly, teams should be established to ensure the implementation of SPC and Lean is successful. Fifthly, training and education should be provided to ensure everyone understands the principles and objectives of SPC and Lean. The implementation should be monitored and evaluated to ensure effective and sustained process improvements (Park, 2020). Seventhly, incentives should motivate employees to meet goals and objectives. Finally, the progress made should be communicated to all stakeholders to ensure they know the changes and benefits being achieved.
Illustration of the underlying concepts, purpose, and procedures.
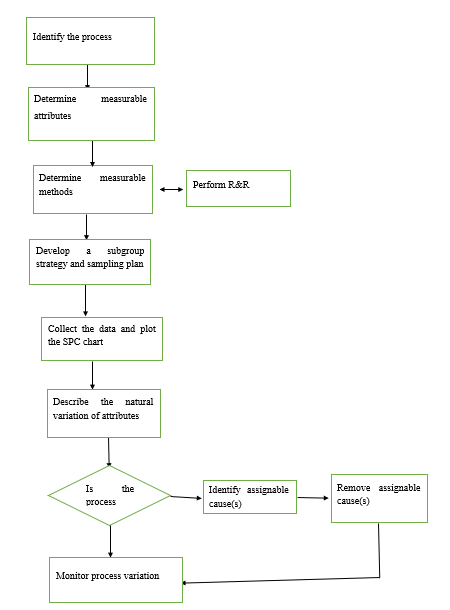
Question 3.
The results achieved.
The results achieved were an improvement in the quality of the company’s products and a decrease in customer complaints. Implementing lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP enabled the company to reduce waste, streamline processes and increase efficiency. This resulted in an improvement in the quality of their products and a decrease in customer complaints. Additionally, the implementation of SPC and HACCP enabled the company to monitor and control the quality of its products, which further led to decreased customer complaints and increased customer satisfaction (Rajput, 2019). The financial analysis also showed that implementing these approaches resulted in cost savings and increased profits.
Implementing lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP enabled the company to reduce lead times and improve its responsiveness to customer needs. As a result, they improved their customer service and increased their customer base. The implementation of SPC and HACCP also enabled the company to identify and address potential problems before they become major issues, resulting in fewer product recalls and a decrease in warranty costs (Rajput, 2019). These improvements increased customer satisfaction and a more significant market share for the company.
Question 4.
Review of the benefits of applying Lean and SPC.
Implementing lean manufacturing and Statistical Process Control (SPC) can bring various benefits to any industry. Firstly, lean manufacturing can help to reduce waste and streamline processes, leading to an increase in efficiency and a decrease in costs. Secondly, SPC can help monitor and control process variability, leading to improved product quality and decreased defects. Finally, lean and SPC can help improve customer satisfaction and increase profits.
In addition to these benefits, lean manufacturing and SPC can also help to increase employee engagement and motivation by providing clear goals and objectives with measurable results. This can lead to improved morale, collaboration, and job satisfaction. Furthermore, using lean and SPC can also help create a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, where employees are encouraged to find new ways to improve the process and identify potential problems. This can lead to a more productive and efficient workforce.
Research has shown that the implementation of lean and SPC can improve a variety of business outcomes. For example, a study by Sharma et al. (2020) found that implementing lean in the automotive industry increased productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction. Similarly, a study by Al-Dhahir and Al-Momani (2020) found that implementing SPC in the pharmaceutical industry led to a decrease in process variability and improved product quality.
In addition to these findings, further research has shown that implementing lean, and SPC can reduce costs, increase efficiency and reduce waste. For example, a study by Hossain et al. (2020) found that implementing lean in the engineering industry significantly decreased production costs. Similarly, a study by Zhang et al. (2020) found that implementing SPC in the electronics industry led to an improvement in production efficiency, a reduction in waste, and a decrease in manual labor.
Overall, research has shown that implementing lean, and SPC can bring various benefits to any industry. These benefits include an increase in efficiency, a decrease in costs, an improvement in product quality, an increase in customer satisfaction, and an increase in profits. Additionally, implementing lean and SPC can help reduce waste and improve process capability, enabling organizations to identify and address potential bottlenecks. Furthermore, it can also lead to improved employee morale and engagement, as employees are given more autonomy and responsibility in their roles. Finally, lean and SPC can help organizations become more agile and responsive to changing customer needs.
Question5.
Comparison between agile or jean implementation in a company.
For a company that adopts a cost leadership strategy, implementing lean is better than agile. This is because lean manufacturing focuses on reducing waste, streamlining processes, and increasing efficiency, contributing to cost savings. Additionally, lean manufacturing emphasizes using data and feedback to continuously improve processes, reducing costs and improving efficiency (Kim, 2019).
Conversely, agility is focused on responding quickly to changes in the market or environment. This can benefit companies trying to gain a competitive advantage, but lean manufacturing is more cost-effective. Therefore, for a company focused on cost leadership, it is better to implement lean manufacturing than agile. In addition to the cost savings associated with lean manufacturing, companies that adopt a cost leadership strategy should also consider the potential long-term benefits (Kim, 2019). Lean manufacturing can create a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, increasing efficiency and productivity over the long term. This can increase profits and market share for the company, ultimately leading to more significant cost savings. Finally, companies that invest in lean manufacturing are also likely to have a better reputation and higher customer satisfaction, which can lead to more sales and more loyal customers.
Part B.
Operations management (OM) has come a long way from its early beginnings. It is an ever-evolving discipline that has undergone several stages of progression. The focus on cost reduction and quality improvement have been two of the most significant eras of OM. Although both eras have different objectives and approaches, they are both integral to the development of the field and its current practices. In this essay, we will compare and contrast the focus on reducing the cost era with the focus on the quality era within the evolutionary stages that operations management has progressed through (Anderson, 2016).
The cost-reduction era of operations management has focused on reducing costs by eliminating waste, reducing cycle time, and improving efficiency. This has been achieved by using techniques such as Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management, total quality management (TQM), and lean manufacturing (Anderson, 2016). These techniques have been designed to reduce costs and improve operational efficiency.
The quality era of operations management has focused on improving product and service quality. Both the cost reduction and the quality era have been significant for the development and growth of operations management. The cost-reduction era has enabled organizations to reduce costs and improve efficiency, while the quality era has enabled organizations to produce high-quality products and services (Anderson, 2016). These two eras have helped organizations to become more competitive and efficient.
The focus on reducing costs has been a critical driver of operations management since its early stages. This focus has been guided by the principles of efficiency and cost-effectiveness, which were developed during the industrial revolution. During this era, the focus was on improving the efficiency of production processes, reducing costs, and maximizing profits (Ballou, 2017). This was achieved by adopting the division of labor, production line layout, and the introduction of machinery. As a result of this focus on cost reduction, the production process became much faster and more efficient.
The focus on quality, on the other hand, emerged more recently. Quality became a focus during the post-industrial era, as companies sought to differentiate themselves from their competitors in the marketplace. Quality management was developed to ensure that products and services met customer expectations and minimized defects and non-conformities. This was achieved by adopting various quality management systems, such as Total Quality Management (TQM), Six Sigma, ISO 9001, and the HACCP system (Ballou, 2017). Quality management systems help to ensure that processes are designed with quality in mind and that the product or service meets customer requirements.
Quality management systems can also help to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. Through process improvement tools such as root cause analysis and statistical process control, companies can identify and address problems before they escalate, leading to customer dissatisfaction. Quality management systems also enable companies to track customer complaints, investigate the cause of the problem, and take corrective action to prevent similar issues from occurring in the future (Ballou, 2017). Companies can reduce customer churn, increase customer loyalty, and maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace by focusing on customer satisfaction.
In the first era of OM, the primary objective was to minimize costs and increase productivity. This was accomplished by streamlining processes and reducing waste. The goal was to increase efficiency and reduce operating costs. In the second era of OM, the focus shifted to quality. Quality was seen as an integral part of OM, and the goal was to ensure that the end product met customer expectations. Quality was achieved by introducing total quality management (TQM) principles, such as continuous improvement, defect prevention, and customer satisfaction (Ballou, 2017). Companies also adopted Six Sigma and Lean tools to help improve their processes and eliminate waste. The overall objective of the second era of OM was to create a quality culture throughout the organization, from the production line to the customer.
The two eras of OM have different approaches and objectives. The focus on reducing costs primarily concerns making production processes more efficient and cost-effective. The aim is to reduce waste and increase profitability. On the other hand, the focus on quality is on ensuring that the end product meets customer expectations. The goal is to ensure that products and services are of the highest quality and minimize defects and non-conformities (Subramanian, 2017).
The first era of OM focused on techniques for reducing costs, such as Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma. These techniques involve streamlining processes, eliminating waste, and improving efficiency. The second era of OM, however, focuses on quality. This includes Total Quality Management (TQM), Quality Function Deployment (QFD), and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). These techniques involve identifying customer requirements, designing processes to meet those requirements, and monitoring and controlling the processes to ensure that the requirements are being met (Jha, 2018). Both eras of OM are essential for creating a successful and sustainable business.
The approaches taken by the two eras are also different. The focus on reducing costs is primarily focused on the production process itself. It involves the design of efficient and cost-effective production processes, the adoption of machinery, and the division of labor. However, the focus on quality is on the entire production system. It involves the development of quality management systems to ensure that the product or service meets customer requirements.
In addition, the two eras also differ in their approaches to the customer. Customers were seen as an external factor in the cost-focused era, and their needs were often secondary to cost-cutting efforts. Quality-focused approaches prioritize the customer experience, with customer satisfaction and loyalty being the primary goals (Jha, 2018). Companies strive to deliver products and services that meet customer needs and preferences and to build customer loyalty through excellent customer service. Quality-focused companies also recognize the importance of developing customer relationships and understanding their needs.
In terms of implementation, the focus on reducing costs is relatively straightforward. It involves the implementation of efficient production processes and the adoption of machinery. The focus on quality, however, is more complex. It involves implementing quality management systems, such as TQM, Six Sigma, and HACCP, which require specific processes and procedures.
Quality improvement initiatives also include using process control techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) and design of experiments (DOE) to ensure quality levels are maintained throughout the production process. Quality inspections and testing should also be implemented to ensure that the product meets the desired specifications and to detect any defects before it reaches the customer. Training should also be provided to employees to ensure they know their roles and responsibilities regarding quality. Finally, it is essential to measure the quality management system’s performance to ensure it meets the desired targets.
Finally, the two eras have different impacts. The focus on reducing costs has resulted in creating of more efficient production processes and reducing costs. This has enabled companies to become more competitive in the marketplace. On the other hand, the focus on quality has resulted in higher customer satisfaction, as customers can be confident that the products and services they receive meet their expectations.
The focus on quality has also resulted in improved product safety as companies strive to meet higher standards in terms of safety and performance. Quality assurance systems have been implemented to ensure that products and services meet the necessary criteria (Heizer, 2018). Additionally, the focus on quality has meant a greater emphasis on research and development as companies strive to improve existing products and services and create new ones. Finally, focusing on quality has meant that companies have invested more in training and development, so employees can use the latest technologies, processes, and trends to create the best possible products and services.
Reducing costs and quality has been integral to operations management’s evolution. Both eras have different objectives and approaches, but they are both necessary for the development of the field. Focusing on reducing costs has enabled companies to become more efficient and cost-effective. In contrast, the focus on quality has enabled them to meet customer expectations and provide high-quality products and services.
The evolution of operations management has also been based on technology and automation. Technology has increased efficiency and accuracy in production processes, while automation has enabled companies to reduce their labor costs and improve the speed and accuracy of their operations. Additionally, data analytics and predictive analytics have also become increasingly important as they allow companies to gain insights into their operations and make decisions that are more informed and targeted (Heizer, 2018). Finally, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) has enabled companies to automate processes and improve the accuracy of their operations. These technological advancements have been instrumental in the evolution of operations management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the main problem facing the SME food company is the need to improve the quality of its products. The authors proposed the implementation of lean manufacturing, SPC, and HACCP as solutions for the problem. These solutions enabled the company to reduce waste, streamline processes and increase efficiency, improving the quality of their products and decreasing customer complaints. Additionally, the implementation of these solutions led to cost savings and an increase in profits. Finally, research has shown that implementing lean and SPC can bring various benefits to any industry, including an increase in efficiency, a decrease in costs, an improvement in product quality, an increase in customer satisfaction, and an increase in profits.
References
Al-Dhahir, A., & Al-Momani, S. (2020). Statistical Process Control (SPC) implementation in the pharmaceutical industry: An empirical study. Business Process Management Journal, 26(3), 518-545.
Anderson, D. (2016). Operations Management: Theory and Practice. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE Publications.
Ballou, R. (2017). Business Logistics/Supply Chain Management. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Heizer, J. & Render, B. (2018). Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Hossain, M., Bhuiyan, M., & Rahman, M. (2020). Application of lean manufacturing in engineering industry: A review. International Journal of Production Research, 58(17), 5694-5720.
Jha, M. (2018). Quality Management in Operations Management. London, UK: McGraw-Hill Education.
Kim, S., & Sohn, S. (2019). Assessing the effects of lean and agile processes on operational performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 206, 248-257.
Park, Y., Lee, S., & Jang, J. (2020). The impact of lean manufacturing on cost leadership strategy: A systematic review. International Journal of Production Research, 58(11), 3488-3506.
Rajput, S. S., & Dhavale, S. (2019). Lean manufacturing and its impact on the performance of the manufacturing industry. International Journal of Production Research, 57(14), 4671-4688.
Sharma, A., Kumar, B., Singh, A., & Kumar, R. (2020). Lean manufacturing: A review of current practices and trends in the automotive industry. International Journal of Production Research, 58(2), 580-598. Sharma, A., Kumar, B., Singh, A., & Kumar, R. (2020). Lean manufacturing: A review of current practices and trends in the automotive industry. International Journal of Production Research, 58(2), 580-598.
Subramanian, N. (2017). Lean Manufacturing: Principles, Tools, and Methods. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Zhang, S., Chen, H., Xu, Q., & Zhang, W. (2020). An integrated SPC system for improving production efficiency and reducing waste in the electronics industry. International Journal of Production Research, 58(13), 3942-3956.
 write
write