A tax cut denotes a decrease in the amount of money from taxpayers to revenue. Tax cuts increase the disposable income of the taxpayers but decrease government revenue. Tax cuts represent reductions in the amount of tax paid for services, goods, and income. Tax cuts leave taxpayers with more usable money and thus are examples of expansionary fiscal policy (Tax Foundation, 2021). Moreover, tax cuts involve a decrease in tax in other aspects, such as tax credits. The implications of tax cuts on the economy depend on the type of tax cut. Policies that increase usable income to low and middle-income people are likely to increase general consumption and thus stimulate the economy.
Since a tax cut shows a decline in the amount of tax a taxpayer is required to pay, it results in increased disposable income. The increase in income can be used to buy extra goods and services that would not have been bought without the tax cut. Tax cut ensures that money remains in the hands of the consumer, and thus a taxpayer can afford to buy more. Tax cuts give workers better financial muscles to invest and spend more money. When consumers have more money, they are expected to spend it. When consumers spend more money, then it leads to an increase in aggregate demand. Increasing demand for commodities and services can lead to increased economic growth.
Tax cuts implemented on income, such as salaries, increase the money used for investment savings, thus increasing people’s productivity and economic growth. On the other hand, if direct spending cuts do not fund tax cuts, they can lead to increased national budget shortage. The national budget deficit can hamper economic growth in the long-term via prospective negative impacts on investment, such as increased interest rates (Nwafor & Wright, 2021). Moreover, it can lead to a decline in a country’s savings and impact the income of a country’s posterity. Implementing tax cuts regarding its structure and financing is critical to spurring economic growth.
A decrease in tax rates means that people have a higher income they can use. The economy’s significant aspect is the money people are willing to save and can use to purchase extra products and services. This aspect is best explained using the multiplier effect. The multiplier effect shows the relationship between money used on economic activities and the volume of money reduced in taxes or increased government expenditure(The Balance, 2023). Tax cuts and spending increases are not fixed but depend on the economic condition of a country.
Tax cuts have short-term economic impacts if the economy is near its perspective, and the zero interest rates do not impact the Federal Reserve. The short-term economic impact is due to the fiscal stimulus being outdone by interest rate increases. On the other hand, if the economy does well and surpasses its economic potential leading it to be bound by zero interest rates, the impact of fiscal stimulus is increased. However, a better way of enhancing a country’s economy is through increased government spending. When government spends, more money is in circulation because more employment is created, leading to more people getting money that they can spend and circulate in the economy.
Tax cuts have two distinct financial and economic impacts. Firstly, tax cuts have incentive impacts of minimized corporate rates. Secondly, tax cuts impact government borrowing by minimizing tax revenue. Higher interest rates and investments should be the main impact of tax cuts. Corporate tax rate reduction increases after-tax investment returns and minimizes corporate investment costs. Tax cuts should lead to additional investment in the capital leading to productivity and salary increments (Nwafor & Wright, 2021). However, the country should give time for the enhanced investments’ benefits. A government takes time to partake in investment projects and will be distributed with time.
When tax cuts minimize government revenue while government expenditure remains intact or even increases, public debts will increase, perhaps leading to increased government borrowing. The less money that can be used to finance individual investment, the more a country borrows. When government uses more money, households have minimal money to use and save (Tax Foundation, 2021). This means that taxpayers can notice when taxes pay for the expenditure. For example, when the government uses tax to perform a construction project, the people will notice because they will be taxed more to cater for the project.
During times when the expenditure is increased while taxes are lower, the government expenditure costs are underestimated by the taxpayers. More government expenditure means additional money must be taken from the taxpayers to finance the expenses. Also, the government may get into debt as more money will be used. Thus, the government should use additional means to get money, such as borrowing from financial institutions and other external sources. The government also implements other money-creation strategies to cater to the resulting deficits. These impacts lead to less money in circulation and, thus, a decline in the economy.
The federal government gets its revenue majorly from payroll taxes. The payroll taxes have grown faster than income taxes because government rates and income constraints have been increased. The Federal Insurance Contributions Act(FICA)payroll tax is used to pay social security advantages. Corporate taxes, which comprise 10.6% of total income, and exercise tax are another source of government revenue. Exercise taxes are a form of government tax imposed on products such as cigarettes and fuel. The exercise taxes represent about 3.1 percent of the total income taxes. Such taxes are necessary because they assist the government in collecting much-needed money to run various government activities and deliver services to the citizens. In service delivery, the government hires and pays people, thus contributing to the circulation of income to the economy.
Decreasing marginal tax rates would spur economic growth. The approach is to give people more money after being paid. This additional money is essential to people because they can use it to buy more products and services at minimal tax rates. Such an approach is an expansionary fiscal stimulus and a demand-side argument to enhance a decrease in tax rates. Moreover, the tax rates are advantageous because they enable people to have more savings and invest money in the economy. The investments create more job opportunities and enhance money circulation, thus growing the economy.
Different consumers perceive tax cuts in various ways. Consumers who pay the most taxes also benefit more from easier dollar terms. For example, If the government cuts tax by 0.5 percent, a Chevrolet buyer can save about $100, while a Mustang buyer can save up to $2000. Although the tax cut is a similar percentage in both items, the Mustang buyer benefits more in easy dollar terms. However, due to the progressive nature of a tax, reducing income taxes is emotive. Minimizing taxes by 12.5 percent on a $3000 adjusted Gross Income(AGI) family can help a consumer save about $802.Using the same formulae will always benefit high-income earners.
Tax cuts will likely impact the economy positively in the long run by increasing benefits to work, make savings, and do investments. Minimized individual income tax rates denote that workers can retain more money from every extra dollar of their salaries. These tax cuts will encourage people to work for long hours and attract fresh people to work. Thus, the tax cuts will encourage people to work harder to have more salaries with fewer taxes, thus retaining more money that can be used to build the economy. Thus, more tax cuts contribute positively to the growth of the economy.
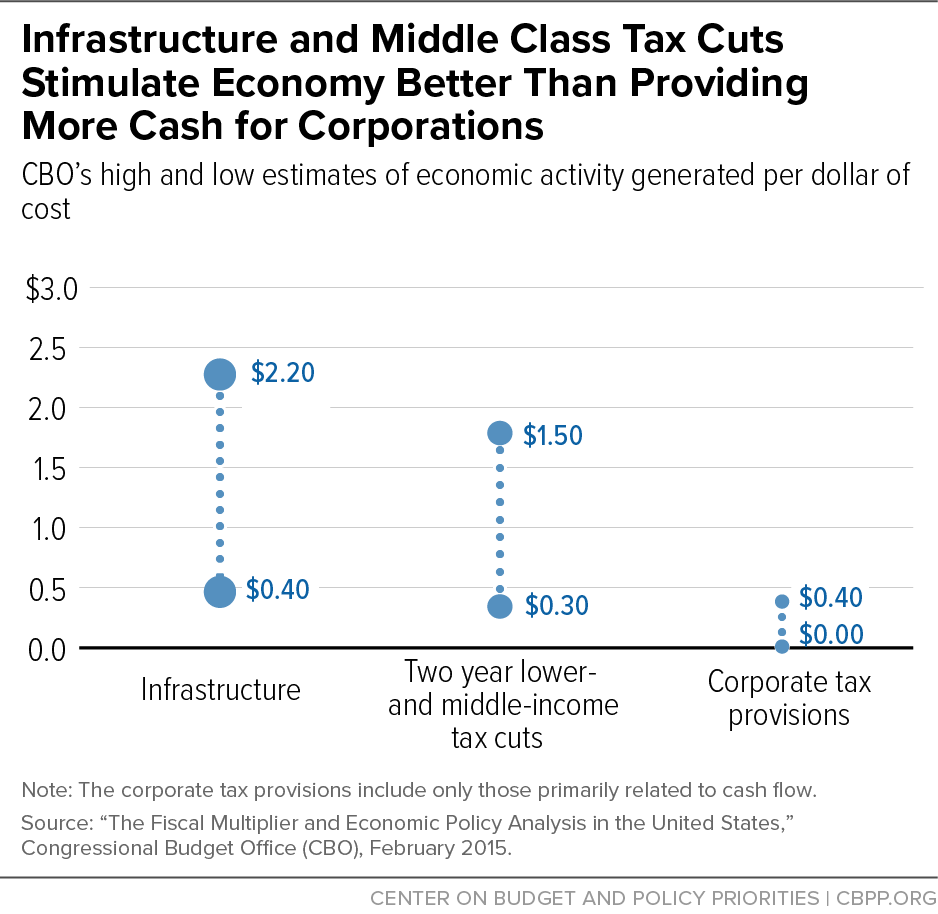
Reduced individual tax rates, capital investment usage, lower corporate tax rates, and other deductions in the corporate tax rates will increase after-tax savings returns. This will encourage households to save. Moreover, reduced corporate taxes will encourage companies to have more money for business expansion and corporate social responsibility. Additionally, businesses will have fewer costs necessary for investment. The reduced investment costs will enable corporations to have more money and encourage economic growth in the country. Tax cuts result in more significant investment, production, and excellent capital stock, contributing to economic growth.
How tax cuts impact the economy depends on the type of tax being cut. However, tax cuts stimulate economic growth by putting more money into circulation. Also, tax cuts expand the deficit if they are not relieved by spending cuts. Thus, tax cuts lead to the economy’s growth in the short term. On the other hand, tax cuts can depress the economy in the long run if they increase the federal debt. When tax cuts are implemented, the decision is difficult to revert because it can lead to economic pain among taxpayers.
References
Nwafor, F. C., & Wright, I. D. (2021). The 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act in the USA: An Economic Perspective. Journal of Applied Economics & Business Research, 11(1).
Tax Foundation(2021).Reviewing the Impact of Taxes on Economic Growth. Retrieved 21 April 2023, from https://taxfoundation.org/reviewing-recent-evidence-effect-taxes-economic-growth/
The Balance(2023).The Truth About Tax Cuts. (2023). Retrieved 21 April 2023, from https://www.thebalancemoney.com/tax-cuts-definition-types-and-how-they-work-3306328
 write
write