Lowe’s is the world’s second-largest hardware corporation, was founded in 1921, and is based in the United States. It was originally situated in North Wilkesboro. It expanded after World War II and by 1962 had 21 locations. Currently, it operates 2,355 locations across North America, Canada, and the former Mexican territory. Lowe’s products inspired customers to conduct do-it-yourself projects and remodel their houses, which allowed the store to weather the economic effects of the epidemic. The company has generated more money than projected in previous years, and it is in a great position to continue bringing in new customers and get additional revenue from its current clientele.
However, the company’s revenues and profits have been dropping, and given the surge in do-it-yourself and home repair expenses, its current financial situation could not be long-term viable. The business is expected to be worth $269 billion by 2025, according to recent research by the Harvard Joint Centre for Housing Studies; nevertheless, Lowe’s revenue growth is less rapid than the industry’s overall expansion.
Swot analysis
The SWOT analysis is a methodology for strategic planning that takes into account the positives and negatives of a project, organization, or person. The strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) analysis is a popular and adaptable framework for strategic planning and company operations. It contributes to successful strategic planning and decision-making by helping firms make informed choices, capitalizing on strengths, addressing weaknesses, exploiting opportunities, and mitigating dangers (Thacher et al., 2007).
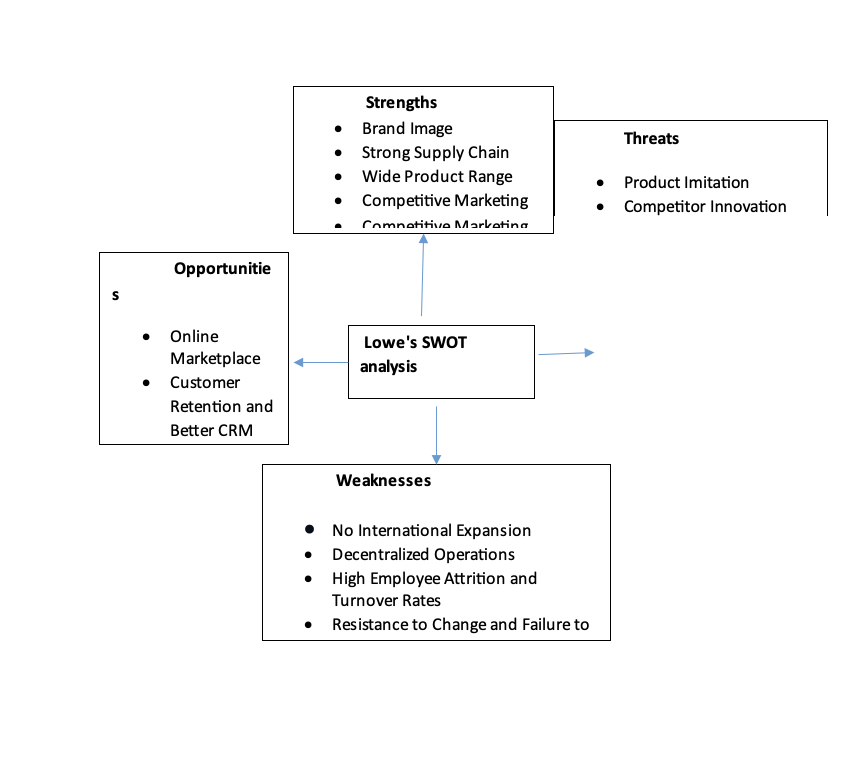
Strengths
Lowe’s, one of America’s major retailers, is known for its devoted customers and good reputation. Lowe’s, one of the nation’s largest retail businesses, has a good reputation, many stores, and dependable delivery. Due to the company’s effective supply chain, customers may employ real-time monitoring and low costs. This allows Lowe’s to provide in-store and home delivery. Lowe’s serves broad populations with thousands of items. Due to the company’s customer service, DIYers may expect excellent instructions and resources (Pinto, 2020).
Lowe also credits competitive marketing for its success. The company gave community initiatives significant attention during the pandemic. Lowe’s Bucket Brigade and #BuildThanks are two of several marketing campaigns that have helped it become a global hardware retailer.
Lowe’s frequent personnel reorganizations demonstrate their dedication to customer service. This increases customer satisfaction and revenue since they can find what they need for their projects. Despite expensive training, Lowe’s ensures its salesmen and customer service reps are ready.
Challenges
Lowe has several challenges, including its fragmented operations, high employee turnover and attrition rates, resistance to change, and incapacity to develop worldwide. The bulk of its revenue comes from North America since it has very few stores in Canada and no other markets due to the shutdown of its activities in Mexico in 2019. Customer satisfaction, a key performance indicator, is under-satisfied by the company’s decentralized business strategy. Lowe’s has had a serious problem with employee happiness, with personnel and compensation changes often contributing to poor morale. In 2017, Lowe’s reorganized its human resources division, eliminating middle management positions and providing staff members with the opportunity to transition to other areas within the company. The firm lost more money as a result of the high personnel attrition and turnover rates, which also had a detrimental effect on the customer experience.
The corporate culture at Lowe’s discourages innovation and change; actions like restructuring lower employee satisfaction and damage the business’s reputation. Their worries about their employment and rules may restrict their ability to handle any form of change, including changes to the business culture. Previous efforts by Lowe’s to become worldwide have failed, and in the one other foreign market where they are now present, Canada, they are hardly noticeable. All things considered, Lowe’s shortcomings are a factor in its general inability to satisfy customers and keep a competitive advantage in the market.
Opportunities
Lowe’s has been emphasizing innovation in the internet space, including alternatives for home delivery, in-store pickup, and augmented reality. Improved search features and personalized product suggestions, according to the corporation, would be advantageous to both clients and businesses. To make its items more available to a larger audience, Lowe’s may profit from continuing to enhance its online shopping platforms. Nevertheless, there is still potential for development in these capabilities. Because of its strong retail supply and transportation network, Lowe’s can sell items at a lower cost or convert those savings into profit. Since Lowe’s and rival Home Depot often charge comparable prices for their goods, Lowe’s may come out on top.
However, repeated store reorganization and the removal of middle management in 2017 have resulted in poor client retention rates. If these issues are resolved, the firm stands to make more revenue even if they are a contributing cause to poor client retention rates. Following the epidemic, more individuals want to upgrade their houses by adding desks and home offices, as well as by painting and beautifying the areas they spend more time in. This has led to an increase in hybrid and remote working. For businesses like Lowe’s, this anticipated expansion in the home improvement industry means more money.
Threats
Lowe’s faces several challenges in the home improvement market, including product imitation, competitor innovation, worker’s movements demanding higher pay, and the end of the lockdown. Product imitation involves imitation of high-quality products at lower prices, which can negatively impact the company’s bottom line. Competitors like Home Depot, Target, and Walmart are also in the market, posing a constant threat to Lowe’s. threats for the corporation may arise from worker movements like the Great Resignation, particularly when it comes to the high expenditures of staff training. With the return of programs like SPIFFS in 2019, Lowe’s is supposedly cutting expenditures in employee compensation. The rapid expansion of the business, however, raises concerns about worker rights groups.
A distinct product placement approach, larger shops, more positive marketing, an emphasis on customer service, and a broader assortment of items are all parts of Lowe’s competitive strategy. Additionally, there is a larger proportion of full-time employees, which means that clients have access to more assistance. Having a distinct identity also helps in keeping its current level of market share. The home improvement industry presents Lowe’s with several obstacles, including product copying, innovation from competitors, worker’s rights movements, and the eventual end of the lockdown. These obstacles won’t be able to derail Lowe’s sustained success because of its robust competitive strategy.
Conclusion
Lowe’s, a strong competitor in the home renovation industry, maintains its market position through brand recognition, a vast retail network, and competitive marketing. Despite facing challenges like staff attrition and resistance to change, it can achieve sustainable growth through cost leadership and online shopping innovations. To combat product copying and competition, ongoing strategic adaptation is necessary. In the dynamic home improvement market, Lowe’s can strengthen its performance by resolving internal issues, seizing opportunities, and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Visual Analysis Chart
Reference
Pinto, F. J. C. (2020). Equity Research-Lowe’s Companies Inc (Doctoral dissertation, Universidade de Lisboa (Portugal)).
Thacher, t., white, b., & sutorius, b. (2007). strategic report for Lowe’s Companies, inc. https://economics-files.pomona.edu/jlikens/SeniorSeminars/gotham2007/reports/lowes.pdf
 write
write