Staphylococcus aureus is the main human pathogen that results in a variety of medical contaminations. Staphylococcus is both a commensal bacterium and a human pathogen (Tong et al., 2015). Close to 30% of the human population carry the germ in their noses (Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2021). The infections resulting from staph infections are likely to be severe or fatal. Bacteremia is the best-described exhibition of aureus infection. Several studies document the prevalence, prognosis, and outcome of aureus. The organism is well-known for its capacity to gain opposition against a variety of antibiotic classes.
S.aureus is a gram-positive bacterium that appears to be spherical. The S. aureus cells appear in clusters, often resembling grapes, mainly when perceived under the light microscope following gram staining. The electron microscope shows unevenly sphere shaped cells with level surfaces. The electron microscope depicts thick cell walls, distinct cytoplasmic membranes, and amorphous cytoplasm. Close to all segregates of S.aureus produce coagulase enzyme, which is a virulence influence that aids in identifying the bacterium. The bacterium tends to be salt-tolerant and can develop in mannitol-salt agar medium. The bacterium tends to be oxidase-negative and catalase-positive.
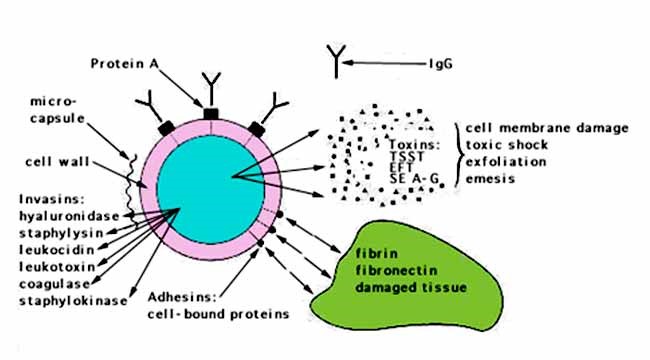
Virulence Factors and How They Affect the Host
Virulence factors refer to the factors a micro-organism produces that evokes diseases. S. Aureus produces several virulence factors. Some of them include hemolysis, proteases, leukocidins, exfoliative toxins, and immune-modulatory factors (Bien et al., 2011); aureus offers a combination of virulence factors that contain toxins, adhesins, and immunomodulatory molecules facilitating the infection of various host tissues. Staphylococcus aureus colonizes the host causing severe life-threatening ailments (Balasubramanian et al., 2017). The microbes live in and contaminate a widespread range of host tissues, from shallow surfaces to the skin and deep tissues for instance the heart and bones. Owing to the diverse regulatory networks in its possession, the pathogen can adapt to various environments modulating virulence.
Immunity
According to Zychinsky and colleagues, structures known as neutrophil extracellular traps, which contain histones, chromatin, and azurophilic granule proteins, can kill bacteria aureus. Human neutrophils use oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent means to kill ingested micro-organisms (DeLeo et al., 2009). Hence, the neutrophils, a kind of white blood cell, ensnare attackers in neutrophil extracellular traps(NETS). The NETs are web-like structures of proteins and DNA.
The seized microbe is then wrecked by the amoeba-like white blood cells, which are identified as macrophages. S. aureus takes part in activating adaptive and innate immune systems (Karauzum & Datta, 2016). The innate immune response is triggered by outline recognition paths that help discover markers of microbial infection that are not specific, thus activating neutrophils. On the other hand, the adaptive immune kicks in later in the disease depending on the exhibition of bacterial antigens by antigen-presenting cells (Karauzum & Datta, 2016). Hence, the prevalence of aureus implies a decline in the functionality of adaptive immune responses.
Infectious Disease Information
Staphylococcus aureus results in skin infections and, at times, may result in endocarditis, pneumonia, and pneumonia. The bacteria is likely to result in abscess formation. Once the bacteria get to an individual’s body, it is highly spread to other organs and tissues, such as bones, joints, lungs, the heart, and the brain (Medline Plus, 2021). The skin infections that are left untreated result in severe and fatal disorders of the blood and bones. Individuals are likely to experience recurring infections with S. aureus. The ailment is associated with acute infections, wherein biofilms they are linked with chronic infections. Several staphylococcus aureus species are opportunistic pathogens that result in significant diseases (Coates et al., 2017). Staphylococcus aureus is a bacteria that mainly occurs on the humanoid skin, armpit, groin, and other areas.
Epidemiology
Prevention
There is no present vaccine to S. aureus infection. Any individual stands the risk of acquiring Staphylococcus though certain groups are highly susceptible to the ailment. The groups include individuals with cancer, eczema, lung disease, and individuals who inject themselves with drugs. The best prevention method against infection is by maintaining good hygiene and ensuring the frequent washing of hands. The fatal strain of S. aureus is prevented through the maintenance of hygienic practices such as hand washing. Equally, individuals should avoid overly crowded places and also avoid contact with other individuals.
Treatment
Quinupristin-dalfopristin and linezolid are the two new antimicrobial agents available with action against drug-resistant staphylococci. The agents are efficacious against the organism as they are protein synthesis inhibitors with a gram-positive spectrum. Mechanism of action includes enzymatic hydrolysis of the beta-cell -lactum nucleus (Lowy, 2003). Also, there is the synthesis of dipeptide with a reduction in affinity for vancomycin. Other agents include glycopeptide, carbapenems, quinolones, oxazolidinones, and tetracyclines (Lowy, 2003). Also, several states are making an effort to come up with a vaccine against S. aureus. Also, there should be supportive care for individuals regarding medical advice on the preventative measures they need to put in place to evade infections.
Clinical Relevance
S. aureus silently stays in the body of humans and could at times subject their lives to danger. Besides its capacity to outsmart the immune system, the pathogen serves as a multidrug resistance phenotype making it the most obstinate pathogenic microbe in the antibiotic chemotherapy antiquity. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection results from a kind of staph bacteria that results in resistance to several antibiotics. MRSA is a strain that is known in healthcare-associated with pathogens. Individuals who stand higher risks of MRSA include athletes, school students, military personnel in the barracks, and individuals who are inpatients in the medical sector. Several antibiotics are used against the MDR strain, and they include Polymyxins, Aminoglycosicides, Tigecycline, Carbapenems, Fosmycin, Ceftazidime, Meropenem, and Ceftotozolone.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Staphylococcus is a bacterial infection that mainly affects the nose and other body organs such as the lungs. The effects of the disease may be acute and, at other times, chronic. The types of microscopes used in viewing the organism are light and electron microscopes. The pathogens possess virulence factors that affect the immunity of the persons. However, the neutrophils aid in defense against S. aureus. Some of the infectious diseases it results in are pneumonia and skin infections. A vaccine is yet to be developed to fight against the infection. Thus, individuals are advised to maintain high levels of hygiene, avoid contact with other individuals and shun overcrowding to curb the acquisition of the disease. Quinupristin-dalfopristin and linezolid are the two new antimicrobial agents available with action against drug-resistant staphylococci. There are drug-resistant strains, and one is Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection which is clinically recognized. The are several antibiotics used in the prevention of MDR strain, and they include, Polymxins, Aminoglycosicides, Tigecycline, Carbapenems, Fosmycin, Ceftazidime, Meropenem and Ceftotozolone.
References
Balasubramanian, D., Harper, L., Shopsin, B., & Torres, V. J. (2017). Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis in diverse host environments. Pathogens and disease, 75(1), ftx005.
Bien, J., Sokolova, O., & Bozko, P. (2011). Characterization of virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus: novel function of known virulence factors that are implicated in activation of airway epithelial proinflammatory response. Journal of pathogens, 2011.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Staphylococcus aureus in Healthcare Settings | HAI | CDC. Cdc.gov. https://www.cdc.gov/hai/organisms/staph.html.
Coates, R., Moran, J., & Horsburgh, M. J. (2014). Staphylococci: colonizers and pathogens of human skin. Future microbiology, 9(1), 75-91.
DeLeo, F. R., Diep, B. A., & Otto, M. (2009). Host defense and pathogenesis in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Infectious disease clinics of North America, 23(1), 17-34.
Karauzum, H., & Datta, S. K. (2016). Adaptive immunity against Staphylococcus aureus. Staphylococcus aureus, 419-439.
Lowy, F. D. (2003). Antimicrobial resistance: the example of Staphylococcus aureus. The Journal of clinical investigation, 111(9), 1265-1273.
Medline Plus. (2021). Pneumonia in adults – discharge: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Medlineplus.gov. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000017.htm.
Oogai, Y., Matsuo, M., Hashimoto, M., Kato, F., Sugai, M., & Komatsuzawa, H. (2011). Expression of virulence factors by Staphylococcus aureus grown in serum. Applied and environmental microbiology, 77(22), 8097-8105.
Tong, S. Y., Davis, J. S., Eichenberger, E., Holland, T. L., & Fowler Jr, V. G. (2015). Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clinical microbiology reviews, 28(3), 603-661.
 write
write