DEFINITION PHASE.
Change is a vital aspect required by the organization as it identifies the areas or activities the business needs to focus on to improve its efficiency and effective utilization of available resources such as time, labour and finances. A change driver, therefore, entails all the plans, designs, operations, products, services and strategies that the business adopts and enforces new standards and guidelines to improve the previous operations of the activities in the organization. Automation of services has rendered some methods of selling products, such as physically visiting the shops, obsolete because, with technological advancements, computerized purchasing systems allow for online ordering, payment and tracking of the online transactions made. This has led to time-saving and efficiency in dealings with customers. The organization should open branches in different locations for the shops to sell and distribute electronic equipment such as TVs, radios, mobile phones, tablets, computers, peripherals and other electronic gadgets to maximize profits from these commodities.
There will be short-term and long-term goals made for the electronic shop to maintain the focus of the business on the objectives that will enable efficiency in handling the operations. Short-term goals are likely to be achieved within a short time, like a period of less than one year, whereas long-term goals take more than one year to actualize. The short-term plans can involve the installation of power, security systems such as CCTV cameras to detect and prevent theft and also the structure of network cables that can enhance easy access of materials through the internet. Whereas the long-term goals can involve compatibility and upgrading of the organization’s machines to ensure they are up to date and also the opening of branches dealing with the sale of electronic devices. These goals need to be correctly planned, and practical strategies to be employed in the formulation as they foreshadow the business operations in the near future.
Functional specifications are based on the end user’s expectations regarding the usage of the machine developed. For example, a computer should be able to solve complex calculations easily using Microsoft Excel, and it should also have an easy connection to the internet. This will enable the user to quickly browse and get more materials from the internet concerning how the electronic shop is running its operations. On the other hand, technical specifications entail the skills and knowledge necessary to handle the electronic machines; for instance, an end user of the laptops should know how to install the software in a computer, for example, QuickBooks and SPSS. As the seller, I will also provide manuals, for example, for the TVs and CCTV cameras, to the customers, predominantly the illiterate, to enable them to adapt faster to the automation service.
For every business to thrive skillfully, a group of individuals must be assigned different roles to ensure that tasks are performed efficiently. Division of labour and specialization aids in reducing the time consumed and improves efficiency as other people are given to do various jobs in which they are competent. In this case, the customer care department will receive complaints about the system breakdown of the machines and also deal with repairs; the marketing and sales department will develop competitive strategies that can be relied upon for advertising the electronic shop’s products and its branch offering. All the team members should have integrity, honesty, truthfulness, cooperation and accountability.
PLANNING PHASE.
A work breakdown structure shows various activities that need to be done in the project. For example;
- Preliminary Study; identify the constraints and limitations of the website developed, for example, leakage of harmful data, the objectives and goals to be achieved through the use of the website. For instance, the provision of adequate data concerning the electronic devices dealt with in the shop.
- Feasibility study; test the technical capacity and the financial visibility of the system before the resources are fully employed.
- System investigation is an in-depth study to understand how the systems operate so that an individual can acquire adequate knowledge and skills to develop better websites.
- System development; The website is fully developed, and errors that might occur in progress should be corrected before the system is implemented.
- System implementation; this involves training, acquisition of the machines and installations, file conversion into new formats and changeovers on the machine usage.
- System maintenance; maintenance activities involve; corrective, perfective, adaptive and replacive maintenance.
Resource allocation entails the cost of raw materials and facilities, equipment, payment to contractors, cost of paying the rent house, cost of labour required, whether there are enough funds available for the completion of the project and the time available for the fulfilment of machine development. The training and development cost aims to provide adequate skills to the end users.
NETWORK ACTIVITY DIAGRAM.
Network analysis can be defined as a technique used for planning, scheduling and controlling large and complex projects. It is a graphical representation consisting of specific configurations of arrows and nodes for showing the logical sequence of various tasks to achieve the project objectives.
The critical path is the sequence of essential activities of a network. It is the longest path in the network from the minimum time required to complete the project. Therefore, it is the chain of activities with the most prolonged duration. These activities are critical in that delay in any of them results in a delay in the project’s completion.
Project duration entails the total time taken to complete a project.
Where the letters below represent the following activities in a network diagram;
- Preliminary Study
- Technical capacity
- Financial viability
- System investigation
- System development
- System implementation
- System maintenance
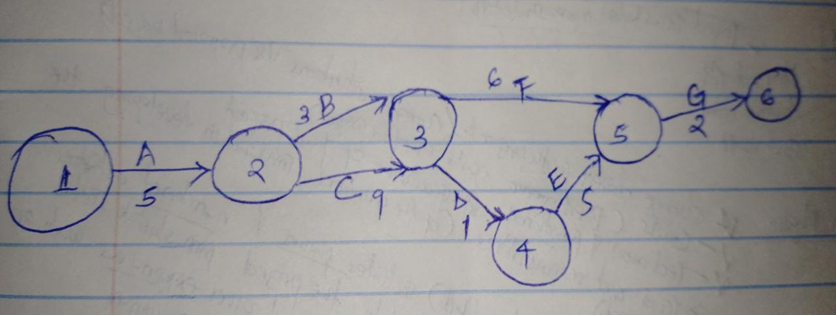
A-B-F-G =5+3+6+2= 16
A-C-D-E-G =5+9+1+5+2=22
Critical path =A-C-D-E-G
Project duration=22
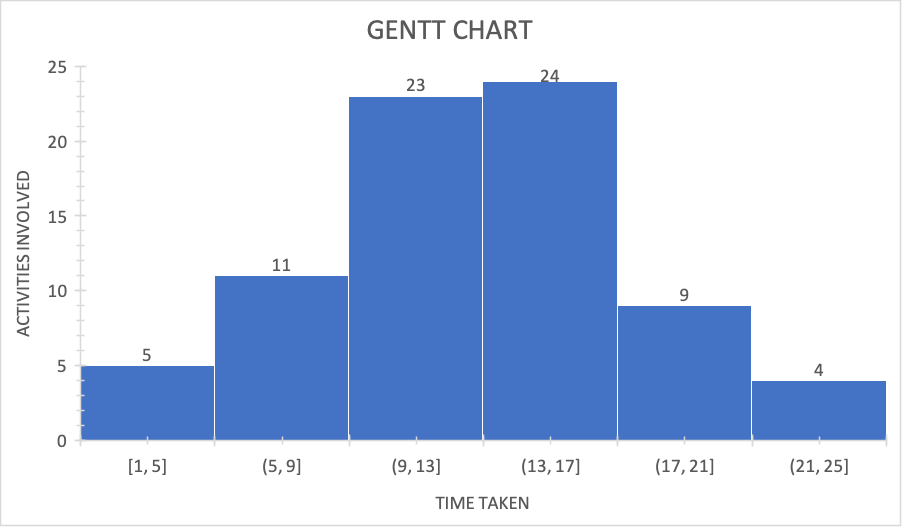
GENTT CHART.
This is a graphical representation of activities in a project against the time taken for each activity. The chart below shows the movements in developing the hardware; electronics used in the shop.
PERT DIAGRAM.
Project Evaluation and Review Techniques is a methodology used for planning, scheduling, allocation of resources and controlling. Planning involves splitting the total project into small projects, which are further divided into different activities and are analyzed by a department. Scheduling entails providing the earliest and the latest allowable start and finish times of each exercise and a relationship with other activities in the project. Allocation of resources is performed to achieve a desired objective. Resources involve labour, time, finances, office rental space and equipment.
| Project development. (Electronics shop) | |
| A) Preliminary Study; identify the constraints and limitations of the website developed, for example, leakage of harmful data, the objectives and goals to be achieved through the use of the website. For instance, the provision of adequate data concerning the electronic devices dealt with in the shop. | B) Feasibility study; test the system’s technical capacity and financial visibility before the resources are fully employed. |
| C) System Investigation is an in-depth study to understand how the systems operate so that an individual can acquire adequate knowledge and skills to develop better websites. | D) System development; The website is fully developed, and errors that might occur in progress should be corrected before the system is implemented |
| E) System implementation; Hardware installation, training on how to use the hardware, file conversion into the format of the new system, and changeovers which include parallel, direct, phased and pilot. | F) System maintenance includes the following operations; corrective, perfective, adaptive and replacive maintenance. |
REFERENCES.
Bagshaw, K.B., 2021. PERT and CPM in Project Management with Practical Examples. American Journal of Operations Research, 11(4), pp.215-226.
Chen, W., 2020. Intelligent manufacturing production line data monitoring system for the industrial internet of things. Computer communications, 151, pp.31-41.
Choudhary, G.R., Kumar, S., Kumar, K., Mishra, A. and Catal, C., 2018. Empirical analysis of change metrics for software fault prediction. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 67, pp.15-24.
Holm, L. and Schaufelberger, J.E., 2021. Construction cost estimating. Routledge.
Klein, L.M., Young, D., Feng, D., Lavezza, A., Hiser, S., Daley, K.N. and Hoyer, E.H., 2018. Increasing patient mobility through an individualized goal-centred hospital mobility program: a quasi-experimental quality improvement project. Nursing Outlook, 66(3), pp.254-262.
Laborie, P., Rogerie, J., Shaw, P. and Vilím, P., 2018. IBM ILOG CP optimizer for scheduling: 20+ years of scheduling with constraints at IBM/ILOG. Constraints, 23, pp.210-250.
Lai, S.T., Susanto, H. and Leu, F.Y., 2022. Project Management Mechanism Based on Burndown Chart to Reduce the Risk of Software Project Failure. In Advances on Broad-Band Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Broad-Band Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA-2021) (pp. 197-205). Springer International Publishing.
Marion, T.J. and Fixson, S.K., 2021. The transformation of the innovation process: How digital tools change work, collaboration, and organizations in new product development. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 38(1), pp.192-215.
Nevens, H., Harrison, J., Vrijens, F., Verleye, L., Stocquart, N., Marynen, E. and Hulstaert, F., 2019. Budgeting of non-commercial clinical trials: development of a budget tool by a public funding agency. Trials, 20(1), pp.1-10.
Soe, P.H. and Htike, T.M., 2018. Critical path analysis programming method without network diagram. In MATEC Web of Conferences (Vol. 192, p. 01027). EDP Sciences.
 write
write