Abstract
This study intends to conduct an exhaustive inquiry into the idea of lunar tourism and current initiatives to make the Moon a welcoming and accessible vacation spot for everybody. This remarkable study improves the efficiency of accommodation and life support systems for tourists taking weeklong excursions to the Moon. Survival of astronauts in lunar isolation is a unique challenge that must be carefully planned. This project attempts to develop a detailed plan for a one-week tourist expedition to the Moon, with safety, comfort, and happiness as the overarching goals, based on scientific discoveries, past space missions, and contemporary technology. This project aims to enhance the visiting experience and deal with lunar problems via spacecraft design, lunar habitat construction, life support systems, spacesuit technology, and resource management. The goal is to provide scientific backing for space tourism to prepare astronauts better physically and emotionally. The program takes a scientific and practical approach to solving the problems specific to moon tourism in order to foster a love of space travel among the general public.
Literature Survey Research Mission
Introduction
Lunar tourism is an emerging industry that enables Earthlings to walk through lunar surfaces, feel the effects of lunar gravity, and enjoy the splendors of space. The research utilizes scientific studies, past space missions, and state-of-the-art technology to enhance these tourists’ quality of life on a lunar vacation that lasts for about seven days. We consider safety, well-being, and happiness in our focus areas, such as ship design, lunar habitat construction, life support, spacesuit technology, and resource management. Therefore, we aim to provide sound and applicable information to give astro-tourists a distinct moon experience.
Background Scenario
Improving habitat and life support systems for lunar visitor missions is critical in light of the burgeoning space tourism and exploration industries. The lofty goal is to allow humans to spend a week on the Moon, experiencing its unique terrain, lunar gravity, and astronomical marvels. This study mission addresses the unique and demanding challenge of building a one-week tourist journey to the Moon. This scenario offers a unique opportunity to study habitat and life support under actual lunar circumstances (Casalino et al., 2022). The mission’s strategy is to carefully examine vital components needed for astronaut survival on the Moon. This strategy uses scientific knowledge, experiences from past space missions, and the newest technical advances to support human life in severe environments. This research seeks to create a safe, well-rounded lunar tourist mission plan that prioritizes participant pleasure. It addresses lunar difficulties via ship design, habitat building, life support systems, spacesuit technologies, and resource management.
Research by Mueller (2022) is an excellent example of scientific rigor combined with practical solutions. In other words, the physical and emotional preparations of astronauts for space travel, which should be addressed through Mueller’s work, are the dual challenges of space travel. This study creates strong astronauts who can overcome the unusual challenges associated with lunar missions. The research centers on offering an unforgettable lunar service for guests while supporting the increasing demand for business space exploration. Additionally, Mueller’s results indicate that such a dual-focus approach improves the astronaut’s health and promotes larger purposes beyond NASA. Thus, the project is an essential basis for developing tourism to the Moon and the progress in this field, considering the mutuality of scientific advancement and the realities of space missions.
Figure 1 above shows the NASA Lunar and Mars space mission architecture studies (Mueller, 2022).
History, Perspective, Context, and Enabling Technological Advances
The scientific endeavor, “Optimizing Habitation and Life Support Systems for Lunar Tourism Missions: A one-week Lunar Sojourn,” arises amid a captivating historical backdrop of space exploration and lunar voyages. In recent years, there has been a noticeable increase in human interest regarding moon tourism and space travel, leading to its emergence as a significant focus point in space exploration breakthroughs. This study adopts a novel methodology to tackle the peculiar and arduous situation of a seven-day lunar tourism expedition, providing a fresh standpoint. The project incorporates a comprehensive range of scientific discoveries, collected experience from prior space missions, and recent technological advancements in the maintenance of human life in challenging conditions. This approach aligns with the ethos of ongoing progress in space exploration (Jawin et al., 2018). This topic exists at the intersection of the historical milestone strides in space exploration, the evolution of lunar tourism, and the scientific quest into whether the Moon can support life. Therefore, space tourism has shown a tremendous shift. The estimated worth of the global space tourism industry in 2022 was USD 869.20 million, and it is anticipated to surpass USD 3,884.18 million by 2032 with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately16.20% between the years 2023 and 2032 inclusive(Research, 2022).
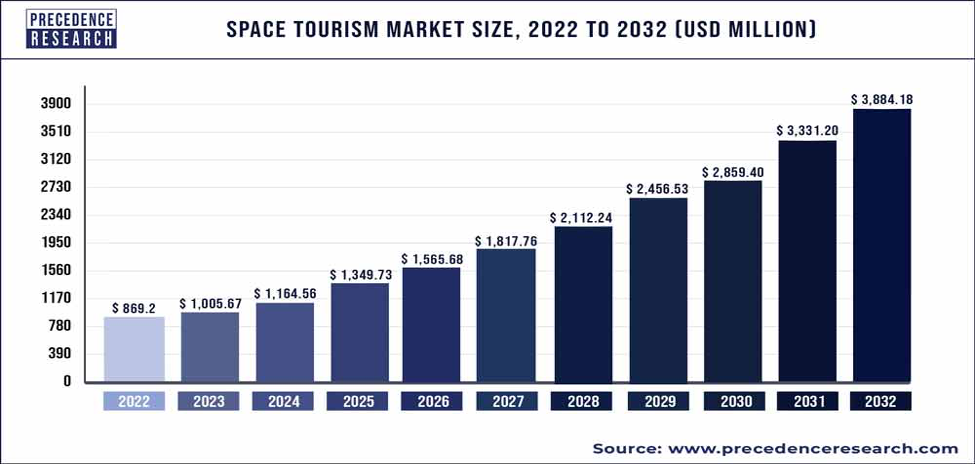
Figure 2 shows the space tourism market size, trends, growth, and report (Research, 2022)
Lunar science has improved after deploying numerous successful lunar missions, including the renowned Apollo project by NASA. In addition, current robotic expeditions are a preliminary to the actual lunar activity. The Artemis program, led by NASA, represents the renewed interest in lunar exploration as humans return to the Moon and create habitable settlements (Casalino et al., 2022). Also, private companies such as Space X are involved in developing lunar tourism infrastructure. Such scientific efforts in discovering mysteries on this celestial body pave the way for business ventures there. However, they also symbolize the ever-growing human spirit that never stops exploring and innovating as we move into the new era of moon tourism and beyond.
Literature Survey
For the study to be successful, it is crucial to conduct a thorough literature review of the existing literature on the topic of lunar tourism and space exploration. The complete analysis will provide the basis for the planned study and drive the project’s quest for creative solutions and forward development. The proposed study will examine the scientific literature on lunar exploration, previous space missions, and recent technological advances that might improve habitat and life support systems for lunar missions. Space travels have seen scientific and technical evolution from lunar exploration, such as the Apollo missions and the current Artemis program. It was through these Apollo missions that the moon landings, which are considered iconic of human lunar exploration, began. The Artemis program embodies a modern sustainability approach and boasts an international crew of astronauts. Concurrently, lunar tourism facilitated by SpaceX and Blue Origin is anticipated to transition from government-driven to privately-run. It necessitates ongoing research into spacecraft technology, moon domiciles, and the business aspect of lunar touring enterprises.
In order to make lunar tourism possible, it is imperative to focus on the health and security of the tourists. The research must thus encompass effects that have physical and psychological implications on the person for a long period of staying in space. Strict safety protocols, including spacecraft design, landing procedures, and maintenance operations, must be established for a successful lunar trip that meets guests’ expectations regarding entertainment hotel service. Service providers must tailor their offerings accordingly while considering potential challenges associated with space travel. Creating a practical framework requires amalgamating historical perspectives with current scientific efforts alongside human factors considerations. Overall, it is essential to prioritize guest satisfaction and ensure individual health before embarking upon any such initiative; this will ensure that travelers are safe without sacrificing fun or memorable experiences during what could prove an adventure fraught with unforeseen difficulties.
The intricacies involved in creating paths for smooth and safe landers are highlighted by Casalino et al. (2022): Optimization of lunar Descent Trajectories. Their work provides significant information about the technicalities of lunar missions and paves the way for greater achievements in space exploration. Through this, the research prepares for future lunar undertakings, setting an exemplary pace in lunar landings directed toward the desired destinations. De Micco et al. (2022) explored the radiation atmosphere in exploration-type space voyages, looking at its effects on plants that could be incorporated into Bioregenerative Life Support Systems (BLSS). It is crucial in developing long-term lunar missions because it addresses how plants grow under radiation conditions, which is vital in sustaining life. Thus, the study is relevant for future understanding of plant-radiation interactions that will determine the success of regenerative life support in moon colonies.
Dewan et al. 2022 turn their attention to the earth and study the resilient post-covid world of work. The study is especially important from the point of view of global problems and discusses how to be flexible in different fields, such as space research. This shows that the socio-economic implications outlined show the link between various social and economic issues and how such development changes the trajectory of sciences and technologies and, hence, the strategic response to constantly shifting dynamics in the new environment. Dupeyras and MacCallum (2023) discuss the indicators for competitiveness measurement in tourism. This source does not directly connect to lunar exploration but highlights the significance of measuring competitiveness in different situations. Such indicators can be adapted to evaluate the efficacy of lunar missions by including technology development, international collaboration, and mission success rate, thus forming a crucial evaluation framework for lunar missions’ effectiveness.
The Lunar Science for Landed Missions workshop of 2018 by Jawin et al. (2018) describes the lunar mission’s scientific intentions. The findings form the basis upon which future research efforts are guided, directing the scientific community on the priorities and objectives of the lunar survey. The workshop’s outcomes inform how lunar research will be shaped to ensure scientific objectives inform it and contribute meaningfully to what we know of the Moon.
Mane (2022) thoroughly surveys fuel-optimal mission design for lunar soft-landings by highlighting the technical issues involved in lunar missions. Soft landing is among the vital aspects of lunar expeditions. In this regard, the optimization of fuel use is of the essence in order to make the idea viable and workable. Mane’s paper is a technical literature with very important information to help mission planners and engineers save on fuel during lunar missions.
Mueller (2022) reviews lunar base construction, including the difficulties and procedures involved in humanizing the moon. This source concerns the practice aspect of lunar exploration and tackles issues such as engineering and construction contributing to the moon’s habitability. Mueller’s work addresses lunar base development by exposing its complexities and offering lessons to future researchers and engineers interested in lunar bases or colonies. Sharma et al. (2022) study the feasibility of regenerative medicine via biomanufacturing in low Earth orbit. This work has significance for lunar exploration as it concerns the manufacture of in-space medical supplies and materials for the sustainment of lunar missions.
Wilmer and Bettinger (2022) investigate earth-moon logistic operations with cislunar periodic orbits and their difficulties in lunar exploration. Optimized mission profiles with improved transportation and orbital maneuvers are vital in successful lunar exploration missions. Efficient logistical strategies are developed for lunar missions that improve the feasibility and the success rate of Earth-moon traveling and exploration. Xue et al. 2020) discuss various techniques used in assembling structures and systems in space. However, this research does not deal directly with Lunar exploration but introduces technologies that can be adopted to make the development of habitats or massive infrastructure possible on the Moon. The research adds to the existing inventory of lunar exploration tools by shedding light on new assembly strategies supporting expeditious lunar missions.
Optimizing Lunar Mission Concepts: Approaches and Technologies
Researchers and engineers should employ a multi-dimensional approach that combines technical precision, logistics efficiency, and innovations for successful conceptual design optimization for lunar missions. Mane (2022) has undertaken a careful investigation into fuel-optimal mission design, underscoring the importance of appreciating spacecraft dynamics and propulsion systems. This approach helps mission planners overcome the challenges of landings on the moon and save fuel while achieving success. Mueller (2022) explores the design of a lunar base that provides a framework for improving engineering, construction techniques, and long-term lunar habitat sustainability. The above lessons help create conceptual designs adaptable to the lunar environment, have good radiation protection, and are long-lived. The multifunctional approach makes Moon habitation structures durable and able to accommodate diverse human needs over a relatively long period.
Emergency Preparedness
To ensure safety and security during their one-week stay on the Moon, lunar tourists must undergo an emergency preparedness training program. This training includes simulated emergency drills exposing tourists’ to the possibility of oxygen system failure, habitat failure, and unexpected lunar surface challenges. These exercises, conducted under the watchful eye of an Emergency Response Team (ERT) staffed by highly qualified astronauts and professional team members, are designed to teach astronauts critical skills like making timely decisions, developing muscle memory, and maintaining composure under duress (Casalino et al., 2022). it encourages a partnership between the emergency response team and tourists in effective crisis communication. Also, given the psychological effects of crises, stress management and coping techniques are emphasized to focus on the lunar guests’ condition. Additionally, the training program involves ongoing assessment and growth by leveraging simulated drills, technological advances, and practical scenarios. This dynamic approach should keep the curriculum reactive to the growing difficulties during lunar tourism. The training program emphasizes psychological preparedness and constant improvement, and it equips lunar tourists with strength and flexibility towards coping with emergencies and achieving success in lunar tourism missions.
Mission Scenario
The mission scenario at the center of the study mission embarks on an in-depth examination of lunar tourism, concentrating on a one-week lunar vacation. Spacecraft optimized for lunar missions, lunar habitat construction, cutting-edge life support systems, spacesuit technology to ensure astronaut safety in the lunar environment, and efficient management of essential resources for lunar tourists: all are under scrutiny in this immersive scenario (Dupeyras & MacCallum, 2023). With the primary goal of ensuring safety, fostering profound satisfaction, and nurturing the well-being of lunar tourists, this all-encompassing mission scenario is intricately designed to catalyze enhancing their overall experience (De Micco et al., 2022).
Analysis and Findings
The study mission’s findings and analysis are focused on laying out a detailed plan for a weeklong tourist journey to the Moon that prioritizes the safety, well-being, and enjoyment of all participants. This in-depth analysis considers many factors crucial to improving the entire visitor experience on the Moon, such as ship design, lunar habitat building, life support systems, spacesuit technology, and resource management. The results of this study are meant to provide a solid foundation for astronaut training and the satisfaction of visitors interested in visiting the Moon. These discoveries will be founded on solid scientific principles without using science fiction or speculation. They will use cutting-edge technologies to address the specific difficulties of the Moon’s terrain. The results of this study will be used to provide comprehensive guidelines and suggestions for the safe and enjoyable completion of lunar tourist missions for the benefit of everyone involved. This effort is a giant leap forward for human space exploration and the quality of lunar tourism.
Phase 1 – Pre-launch
The pre-launch phase for a lunar tourist is very important since individuals should ensure their safety, well-being, and success of the mission in general. For example, the health of the tourists, as well as optimizing the spacecraft for the journey, must be taken into account. This is emphasized in the literature that a complete health assessment prior to the launch is mandatory. Instead of relying on normal medical examinations, one can emphasize psychological evaluations and prepare tourists for the stress associated with space flights. During this stage, psychological counseling and mental health resources should be provided in order to make the crew more resilient and adaptable. More importantly, VR simulations should be included in pre-launch training. They will help make tourists more comfortable and ease possible stress and anxieties associated with the upcoming journey. It exposes people to a simulated environment involving confined spaces and deprived gravity.
Phase 2 – Launch to LEO
The tourist’s health during the launch to LEO is paramount as the spacecraft undergoes great stress. More recent research has noted ergonomic designs and the impact of seat acceleration on the human body. However, biofeedback systems to help tours and ground control monitor physiological parameters and provide real-time data would also improve health care in this period. This data provides the basis for adaptive seating arrangements that change as per individual needs. Such seating arrangements help reduce discomfort and avoid health risks.
Phase 3–LEO Launch to destination orbit.
When transitioning from LEO to destination orbit, the spacecraft navigation and safety of the crew must be optimized. Recent literature indicates the inclusion of more effective life support systems that save on resources and reduce waste. For instance, closed-loop systems that purify air and water decrease the need for resupply, thus ensuring sustainable space travel. The phase necessitates continued psychological support in which recent studies recommend adopting interactive AI systems that offer companionship and cognitive stimulation. The well-being of the tourists depends on their good psychological state, especially during the long journey.
Stage 4 – Destination Orbit Down to Surface phase.
Ensuring a smooth transition as the spacecraft descends from the destination orbit to the lunar surface becomes critical. The studies highlight the importance of having better guidance and navigation systems for the difficult lunar terrain. The literature proposes customized environmental control within the spacecraft regarding hab-life support. With the technology, tourists can adjust the lighting and temperature to make them comfortable in their new environment, thus alleviating most of the stress that comes with starting to live on another planet.
Phase 5 – Surface Stay
Lunar surface stay is an exciting experience that tourists should have. Recent studies have emphasized that psychological well-being includes more than just the basic hab-life support system; it also requires leisure time and entertainment. Creating an enclave of recreational space within the lunar facility, with virtual reality entertainment, provides a refuge of escape and relief from the realities beyond. Furthermore, integrating communication technologies that enable tourists to link up with their family members and peers on Earth can ease isolation. Psychological resilience during the extended stay requires maintaining a sense of connectedness with the home planet.
Phase 6 – Surface to Orbit
It is important to plan properly for the return trip from the lunar surface to the orbit as this would be vital in maintaining the health of the tourists. Modern research encourages the use of up-to-date medical diagnostic units that will assist in tracking physiological markers and diagnosing problems at their onset. Moreover, formulating tailor-made dietary regimes based on personal health indices could be prudent in promoting tourism-related nutrition for this period. Nutrition is vital for health and well-being in the space microgravity condition.
Phase 7 – Orbit to LEO
Propulsion systems should be used efficiently while ensuring continued good health to transition back to Low Earth Orbit from lunar orbit. Modern research shows that installing artificial gravity devices inside the ship is necessary to prevent long-term health problems. Secondly, high-tech exercise equipment and tailor-made tourism fitness programs can also benefit a tourist in this phase by enhancing his or her well-being. Space travel is associated with muscle atrophy and bone density loss, which can be mitigated by regular exercise.
Phase 8 – LEO to Earth
The final leg of the lunar tour is the trip from Low Earth Orbit to Earth. The most recent findings stress the importance of thorough post-mission health tests and their significance in revealing the consequences of spaceflight on human health. This involves measuring bone mineral density, body composition, and cardiac output. With respect to hab-life support, some relaxation and mindfulness programs could be included in this phase to assist in the psychological acclimatization to Earth’s gravity. These practices include meditation and virtual nature experiences, which help readjust astronauts back to earth.
Phase 9-Post-mission on Earth.
To promote the welfare of tourists, the post-mission phase is equally important. The post-mission medical and psychological evaluation has recently been emphasized for re-integration into work or civil life. Additionally, integrating customized health and fitness regimens designed for each visitor to improve their general wellness after the mission completion. Such rehabilitation programs, which may include physical therapy and mental health support, may help with acclimatizing to everyday life and adapting to the gravity of Earth.
Synthesis and Interpretation
Synthesis of literature findings supports integrated approach in lunar tourist moon mission design. The overall success of lunar tourism depends on integrating advanced medical, psychic, and environmental support systems throughout all phases of this mission. However, the psychological issues that occur in space travel are highlighted, which are crucial to tourists’ emotions and thoughts. Hence, ongoing actions should be made to facilitate individualized experiences, viable communication channels with Earth, and leisure options for keeping an upbeat psyche during the entire expedition. Synthesis proposes using advanced closed-loop environmental systems, adaptive seating arrangement, and personalized controls in hab-life support. These improvements greatly contribute to the convenience and pleasure of moon visitors. Furthermore, sustainability, as a significant consideration, should integrate lifeline supporting systems that minimize the need for resupply missions, guaranteeing the economic viability of lunar tourism. Additionally, the combination of AI friendship systems, virtual reality simulations, and interactive technologies is stressed. Psychological well-being is not the only perceived significance of these technologies, as they are also used for training, entertainment, and communication.
The synthesis stresses the need for an all-inclusive and inclusive approach to designing lunar tourism. Continuous technological innovations and development will be necessary for such missions to succeed. This forward-looking view will help shape tomorrow for space tourism, ensuring lunar space is safe for tourists to explore. The interpretation of the following research mission provides a comprehensive nine-step plan vital to the success of lunar tourist missions. Pre-launch has been identified as a planning stage that incorporates attention to life support, habitation, safety, health, and satisfaction (Sharma et al., 2022). The first stage serves as a foundation for other stages by reinforcing the importance of a good map for the journey. Phases 2 to 4 encompass the launch into Low Earth Orbit (LEO), the journey towards the moon’s orbit, and the preparations for touchdown on the moon’s surface.
The most crucial phase, Phase 5, “Surface Stay,” is focused on ensuring housing, life support systems, and safety are optimized and satisfaction is achieved. The trip back home consists of phases six to eight, demonstrating the fully-fledged nature of the expedition and the need for lunar visitors to enjoy a complete journey. The last phase, Post-mission on Earth, is concerned with protecting the bodily and psychological well-being of astronauts and visitors after their return to earth and assessing the general efficiency of the mission. This indicates the importance of the scientifically sound approach to lunar tourism, implying that lunar tourism requires a methodical methodology involving scientific expertise, careful planning, and technical progress as fundamentals (Wilmera & Bettingerb, 2022). Every stage represents a key point in realizing the big targets of the mission, stressing the importance of implementing every stage so that the lunar tourist experience can be successful.
Summary and Conclusion
Summary
The research project’s summary is meant to provide a concise but valuable synopsis of the study’s most important results and insightful takeaways. It condenses the extensive research and stresses how critical it is to fine-tune lunar tourism missions. A comprehension of the mission’s goals and the revolutionary possibilities they represent for the future of lunar exploration and space tourism may be launched from this overview, which serves as a fulcrum.
Conclusion
The study mission might improve tourists’ and astronauts’ safety, well-being, and happiness during their week on the Moon and increase our understanding of lunar tourism. If mission suggestions are followed, lunar tourist missions will succeed. These include a focus on scientific knowledge, cutting-edge life support systems, lunar-specific ships and habitats, spacesuit technological advances, and novel resource management methods. This paper emphasizes the importance of scientific discoveries, space mission experience, and technological advances for lunar tourism. Overcoming lunar tourism’s unique challenges requires a commitment to scientifically sound, practical solutions. As humanity explores space, this project is essential to increasing lunar visitor safety, scientific knowledge, and sustainability. This investigation might lead to new scientific understanding and lunar tourism, making it crucial for space exploration. These aims will usher in a new age of space exploration and allow future generations to see the Moon’s aesthetics.
Recommendations
The research mission has significant consequences and requires proposals for future lunar tourism trips. The mission scenario requires drawing on study and experience to ensure lunar visitors’ well-being, safety, and happiness throughout their one-week stay on the Moon (Xue et al., 2020). The first suggestion is to create a solid scientific knowledge library to educate lunar tourism by analyzing scientific data from past missions and continuing research. It would make future lunar missions scientifically sound, minimizing speculation and prioritizing real solutions. Another important proposal is the development of enhanced life support systems for space flight. These devices should effectively solve lunar problems to protect astronauts and visitors throughout their one-week lunar stay.
Research and development must also focus on lunar terrain-specific spacecraft and habitats. Lunar homes should be constructed to improve visitor safety and satisfaction based on lunar surface characteristics. Upgrades to spacesuit technology are crucial to solving lunar problems. Upgrades must ensure astronaut and visitor comfort, safety, and effectiveness on the Moon. Lunar excursions need efficient resource management. It suggests researching novel resource management systems, considering the lunar surroundings, and assuring lunar visitor satisfaction and sustainability. Finally, astronaut training programmers should give visitors a memorable experience while preparing them for the Moon (Dewan et al., 2022). By following these guidelines, lunar tourist missions may maximize participant well-being, safety, and happiness and assure future success.
References
Casalino, L., D’Ottavio, E. A., & Fasano, G. (2022). Optimization of Lunar descent trajectories with Direct Methods. https://webthesis.biblio.polito.it/23344/1/tesi.pdf
De Micco, V., Arena, C., Di Fino, L., & Narici, L. (2022). Radiation environment in exploration-class space missions and plants’ responses relevant for cultivation in Bioregenerative Life Support Systems. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 1001158. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2022.1001158/full
Dewan, S., Ernst, E., & Kühn, S. (2022). 1 Rebuilding a resilient world of work after the COVID‐19 pandemic. World Employment and Social Outlook, 2022(1), 17–37. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/wow3.178
Dupeyras, A., & MacCallum, N. (2023). Indicators for Measuring Competitiveness in Tourism. In OECD Tourism Papers. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/industry-and-services/indicators-for-measuring-competitiveness-in-tourism_5k47t9q2t923-en
Jawin, E. R., Valencia, S. N., Watkins, R. N., Crowell, J. M., Neal, C. R., & Schmidt, G. (2018). Lunar Science for Landed Missions Workshop Findings Report. Earth and Space Science. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2018EA000490
Mane, S. (2022). Fuel Optimum Mission Design for Lunar Soft Landing at a Specified Location: Comprehensive Review. Fuel, 10(11). https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Shreya-Mane2/publication/365870186_Fuel_Optimum_Mission_Design_for_Lunar_Soft_Landing_at_a_Specified_Location_Comprehensive_Review/links/63875aa3bbdef30dc9876dd9/Fuel-Optimum-Mission-Design-for-Lunar-Soft-Landing-at-a-Specified-Location-Comprehensive-Review.pdf
Mueller, R. (2022). Lunar Base Construction Overview. Retrieved from https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20220000418/downloads/Lunar%20Construction%20Overview%20v1%20RPM.pdf
Sharma, A., Clemens, R. A., Garcia, O., Taylor, D. L., Wagner, N. L., Shepard, K. A., … & Wagner, W. R. (2022). Biomanufacturing in low Earth orbit for regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Reports, 17(1), 1–13. https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/pdf/S2213-6711(21)00598-1.pdf
Wilmera, A. P., & Bettingerb, R. A. (2022). Earth-Moon Logistical Operations Utilizing Cislunar Periodic Orbits. Space exploration, 4, 5. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Adam-Wilmer/publication/363819066_Earth Moon_Logistical_Operations_Utilizing_Cislunar_Periodic_Orbits/links/632f573f165ca227876bd3bc/Earth-Moon-Logistical-Operations-Utilizing-Cislunar-Periodic-Orbits.pdf
XUE, Z., LIU, J., WU, C., & TONG, Y. (2020). Review of in-space assembly technologies. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1000936120304854
 write
write