1. Introduction
Multinational companies (MNCs) establish businesses in their home countries but expand into global markets to increase their customer base and sales revenues. Entering a new market can be lucrative due to the two benefits, but critical barriers also characterize it. Organizations must evaluate the barriers and key influential factors before entering foreign markets. Walmart is a global retail company with headquarters in the USA but eyes emerging markets to expand its business. Therefore, this discussion evaluates influential factors to its global strategy implementation, barriers to international strategy implementation, and recommends solutions to prevent Failure of global strategy implementation.
2. Background to Walmart
Walmart is a leading discount store company and a global leader in the retail industry, with headquarters in Bentonville, USA. Sam Walton founded the company in 1962 but established it in rural areas to protect it from competition from established market players such as Kmart and Sears (O’Sullivan, 2019, p. 14). Walmart developed retail designs like Sam’s Club and Walmart Supercenters to expand business in foreign markets such as the U.K., Mexico, and China. Sam Walton’s death in 1992 did not mark the company’s end since its sales doubled in 1995and it acquired Moosejaw and Jet.com (Sims, 2018, p. 11). Currently, the company employs over 2 million people and operates over 10,000 international stores in 27 countries. Its key competitors include Amazon, Target, Costco, and Kroger.
Walmart’s mission is “to save people money so they can live better” (Yiannas, 2018, p. 56). It indicates how the company executes competent business strategies to influence consumer decisions. It aims at improving customer lives and reducing their financial burdens by surpassing expectations. Its vision is “to be the destination for customers to save money, no matter how they want to shop” (Wiggington, 2018, p. 20). It aligns with the company’s key reason for becoming a leader in the global retail market. Also, Walmart’s core values include honesty, inclusivity, fairness, accountability, and high performance (Weinstein et al., 2021, p. 1). It shows how the company places high customer value in its operations.
Statista (2022a) shows that Walmart acquired nearly 98% of its e-commerce sales from India in 2021. Canada contributed to the highest percentage of e-commerce sales in North America, followed by USA and Mexico, with 11.5% and 3%, respectively. The figure below shows Walmart’s global e-commerce market share.
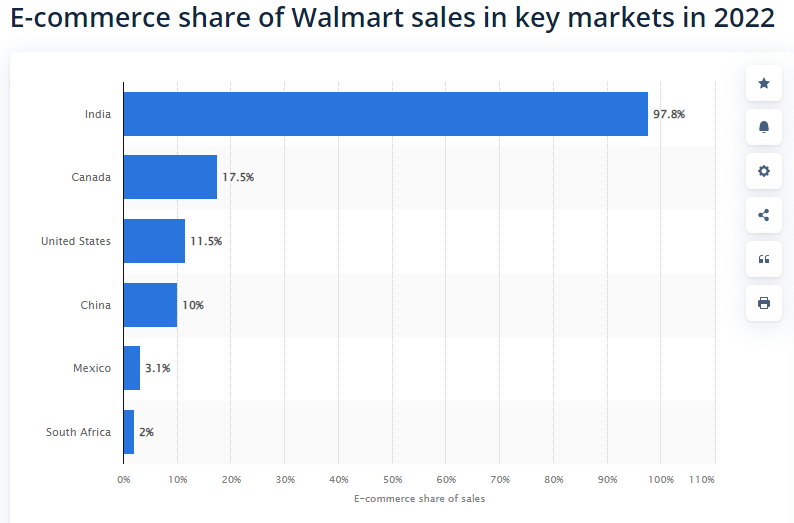
Source: Statista (2022a)
Fifteen key market players dominate the USA online retail. Amazon led the USA online retail with a market share of 37.8%, followed by Walmart, Apple Inc., and eBay with 6.3%, 3.9%, and 3.5%, respectively, as illustrated in the figure below.
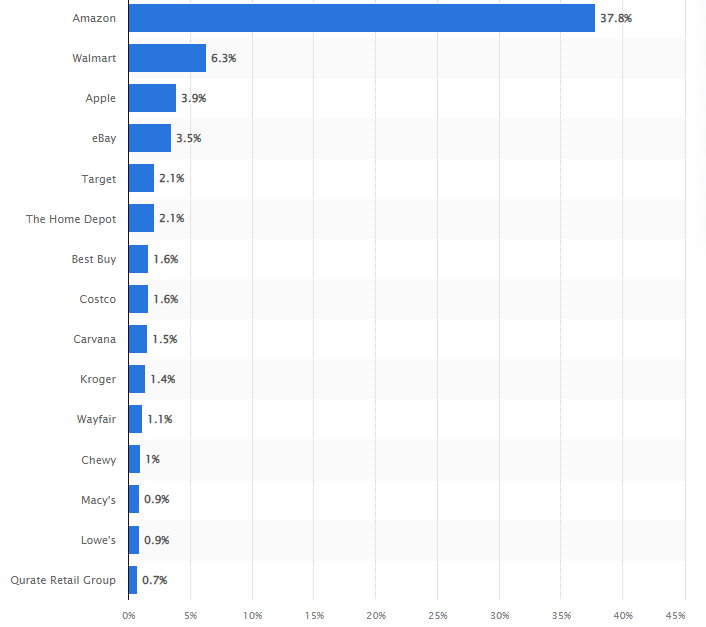
Source: Statista (2022a)
Walmart has recorded a sustained annual revenue increase over the past decade. It recorded $572.75 billion in revenue in 2021, about a 7% increase from the previous year. It is among the leading global retail brands based on revenue. The figure below shows its annual revenues over the past decade.
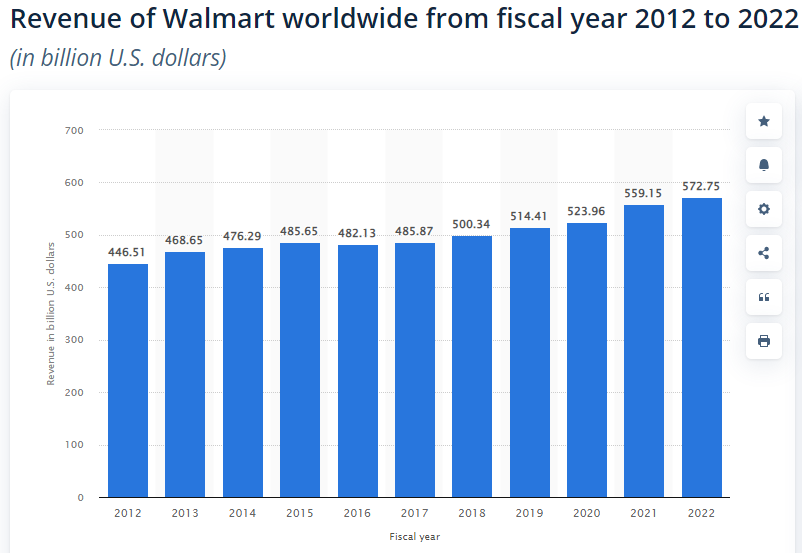
Source: Statista (2022c)
This study uses Walmart to evaluate the implementation of global strategies in the retail industry. The company is suitable for this discussion since it is a market leader in the ecommerce industry and operates physical stores. It provides the best scenario for a typical MNC that integrates traditional and online retail.
3. Major Influential Factors in the Implementation of Global Strategies in Walmart
Strategy implementation is the action phase of the strategic management process. It is the most challenging and dynamic stage since its execution involves the managers and the workers. It unites the entire organization behind the strategy and all company divisions. Grant (1991, p. 117) denotes that organizations invest more time, resources, and effort in strategy formulation than in its implementation. Failure of strategy implementation is a major challenge to many international organizations. Alharthy et al. (2017, p. 37) indicate that most strategies fail at the implementation stage. They further indicate that neglecting factors associated with strategy implementation is the key cause of ineffectiveness and strategy failure. Factors that affect the implementation of global strategies include communication, organizational leadership, organizational structure, organizational culture, and resource allocation.
3.1 Strategy Communication
Strategy communication influences strategy implementation and organizational success since it opens the way for the management and employees to discuss the underlying issues. Alharthy et al. (2017, p. 38) denote that most organizations need to give strategy implementation similar attention to strategy formulation. They may have excellent strategies but fail due to poor implementation; Failure to implement strong strategies adds no value to the company. In this respect, an organization needs to communicate the strategy to the employees. Dzimbiri (2008, p. 33) argues that strategy communication clarifies employees’ roles primarily by outlining what individual workers and teams are supposed to achieve; it measures performance against their targets, provides performance-based feedback, and rewards them based on the outcome. Failure to convey project status and plan to all employees creates knowledge gaps, thus leading to strategy failure. Effective corporate communication allows businesses to succeed by building brand image, reputation, and identity. It also helps to punctuate the right message to internal and external stakeholders. Walmart’s corporate communication strategy is integrated with its mission and identity to serve customers and communities where it operates. Its corporate communication strategy aligns with customer satisfaction, internal communication, and organizational strategies. The company’s internal and external communication aims to improve customer value by providing high-quality services.
3.2 Organizational Leadership
Organizational leadership influences global strategy implementation since the leaders initiate the implementation process. Oke et al. (2009, p. 66) describe leadership strategy as the style, skill, and process demonstrated by a leader who wants to influence the followers to achieve organizational objectives. Correspondingly, Advani (2015, p. 15) claims that the management sector is dominated by two critical leadership styles: transformational and transactional. Managers’ unique attributes influence employees and contribute to high organizational efficiency in the dynamic business environment. Maak et al. (2016, p. 472) argue that leadership approaches strategy implementation range from autocratic leadership to participatory leadership, requiring the active participation of various stakeholders. A superior leadership style is essential in the dynamic business environment since it enhances organizational innovativeness and responsiveness to emergent issues. Walmart’s management invests heavily in its human capital to motivate the workers. The management increases wages and promotes the workers through training to sustain a low-cost strategy (Xie & Cooke, 2019, p. 532). Also, the management uses its cost strategy to lead the global retail market; it spends on brand promotion, marketing, and offering discounts.
3.3 Organizational Structure
Organizational structure influences strategy implementation since it affects overall organizational operations. The organizational structure involves categorizing jobs and tasks into divisions and implementing them to achieve organizational objectives (Meyer & Rowan, 1977, p. 349; Joseph & Gaba, 2020, p. 300; Martela, F., 2019, p. 7). The relationship between various departments and units affects the outcomes of strategy execution. The strategy should precede organizational structure to allow the workers to interact and perform their roles quickly and effectively. Improper organizational structure results in reduced performance due to slacked service delivery. Walmart’s organizational structure allows the management to assign specialized roles to subordinate workers, thus helping the company to make quick and effective decisions. It has also invested in infrastructure like departmental and distribution centres to support physical and online retail. The firm’s infrastructure facilitates a smooth and efficient supply chain.
3.4 Organizational Culture
Organizational culture influences global strategy implementation since it facilitates and accelerates change. Organizational culture refers to the procedures, values, and beliefs that govern employees’ actions. Sanad (2019, p. 4) acclaims that the combination of organizational culture characteristics determines human duty, capacity, and sensitivity to internal and external business environments. Organizational culture often allows transition to maintain stable behavioural patterns and relationships. Meng and Berger (2019, p. 68) recommend that organizations take care to determine the consistency of the connection between strategy and organizational culture when implementing a global strategy. In this regard, an organization cannot implement an incompatible strategy with the existing organizational culture. Walmart wants to be different from other global retail companies by controlling employee turnover rates. It focuses on improving working conditions through increments of wages and training. Overall, employee retention helps the company retain key talents and enhance its brand image and reputation in the global market.
3.5 Resource Allocation
Resource allocation is a key influencing factor for strategy implementation. Organizations need financial, human, physical, and technological resources to achieve successful goals. Espinosa et al. (2015, p. 206) identify scarcity of organizational resources as a major challenge during strategy implementation. The ability to develop and maintain creative teams is an essential part of strategy implementation. Therefore, sufficient allocation of organizational resources is a key driver to successful strategy implementation. Walmart allocates key resources to increase its competitive advantage. It applies modern technology in supply chain management to increase efficiency. Other technological inputs include creating advanced e-commerce sites and apps to improve operational efficiency. Also, the company uses its procurement department to retain strategic agreements and sustain its business strategy. Load-building operations such as ORTEC help the company to increase operational efficiency (DiEugenio, 2018, p. 11). Therefore, resource allocation determines the effectiveness of strategy implementation.
4. Barriers to Implement Global Strategies in Walmart
Organizations experience internal and external barriers when implementing global strategies.
4.1 Internal Barriers
Lilo and Andrew (2013, p. 9) argue that internal sources form critical barriers to strategy implementation, especially when the employees exhibit complacency and resist strategic changes introduced by the company. They maintain the status quo and resist unknown changes introduced in the company.
4.1.1 Systemic Barriers
Systemic barriers arise when the company needs to support new strategies indirectly, thus causing the process of strategy implementation to lag. These barriers include insufficient financial resources to support the strategy, time limitations, and rigid and bureaucratic organizational structure. Strategy implementation in Walmart requires well-trained and qualified employees. The need for qualified workers to train can be a barrier to strategy implementation. Also, introducing strategies by ‘unfriendly’ managers prompts the workers to oppose them by resisting strategy implementation. Such resistance leads to delays, destabilizes the organizational change process, and leads to additional costs.
4.1.2 Behavioral Barriers
Behavioural barriers such as intolerance, misunderstanding, self-interest, and mistrust delay or prevent strategy implementation. Lack of direction from Walmart managers causes the employees not to know organizational expectations. Zahra et al. (2009, p. 524) argue that motivation issues can force workers to uphold their interests at the company’s expense. Walmart focuses on ecommerce more than physical outlets, thus lowering the motivation of employees in the latter. These workers can boycott strategy implementation to air their grievances. Also, the workers can boycott strategy implementation after comparing Walmart’s strategies to its competitors. Organizational culture is another behavioural barrier to strategy implementation. Utilization of inappropriate systems during institutionalization, operationalization, and control bars strategy implementation. Walmart’s leaders exhibit high leadership qualities and commit to strategy implementation. They involve subordinate employees in decision-making and strategy implementation. Fernandez et al. (2019, p. 158) indicate that strategy implementation produces the desired results by involving all key stakeholders. Participation and intervention of Walmart’s top management promote greater commitment levels in the implementation of its vision and strategies. Zerfass et al. (2018, p. 494) argue that senior management plays significant roles in strategy formulation and implementation, while Hoxha et al. (2022, p. 142) claim that leadership styles and tactics help in overcoming barriers in the lower levels that obstruct strategy implementation. Strategic decisions formulated by the top management may only succeed if they inform non-management and lower-level managers.
4.1.3 Communication Barrier
Communication barrier hinders the strategy implementation of global companies. Walmart’s organizational culture emphasizes effective communication; it enhances clear communication of employees’ duties and responsibilities in strategy implementation. Fischer et al. (2020, p. 124) indicate that firms that involve all workers in decision-making realize high success in strategy implementation. However, Mutuku and Mathooko (2014, p. 134) denote that organizational structure causes communication-related issues, which bars the implementation of strategic activities. Walmart’s management and employees understand that shared communication among human resources is essential in strategy implementation. For instance, vertical communication enhances shared understanding of key strategies, leading to improvements. The company’s culture allows workers from different levels to communicate organizational and individual issues to team leaders, peers, management, and other relevant personnel.
4.2 External Environment Barriers
External environment barriers to strategy implementation include social, political, and technological barriers.
4.2.1 Social Barriers
Social barriers such as communication deter the effective implementation of organizational strategies. It is easier to share information or address organizational changes with effective communication. Walmart emphasizes democratic communication structures since the staff share information in a well-structured manner. Walmart’s management inculcates risk mitigation methods to enhance effective strategy implementation since poor organizational structures and lack of risk management deter successful implementation of strategies. On the other hand, cultural differences cause mixed reactions at work; some employees prefer autocratic culture, while others favour democratic culture (Ihm & Kim, 2021, p. 683). It increases the difficulties of determining which cultural structure to adapt in the company. Cross-cultural differences are difficult to solve, but Walmart adopts organizational culture that aligns with the general culture in the society where it operates.
4.2.2 Political Barriers
Political barriers such as political instability and power struggles affect strategy implementation adversely. The management shifts attention from the main objective to solving the emergent issues. Some managers in Walmart apply personal ideologies at the expense of the organizational culture. Ihm and Kim (2021, p. 684) regard this phenomenon as political interference since individuals impose personal will in independent organizations; such individualization makes it difficult to correct the leaders when they err.
4.2.3 Technological Barriers
Technological barriers such as technological advancement and obsolesce bar strategy implementation. Sometimes technology fails to give the expected results, thus lowering its effectiveness (Alawamleh et al., 2020, p. 17). Also, the company needs to be able to install advanced technologies to tap into new digital markets. Walmart moves with technological advancement, as indicated by its emphasis on e-commerce.
5. Suggestion on how Walmart can Prevent Failure to implement its Global
Strategies
Most problems have solutions, and barriers to Walmart’s international strategy implementation have long-term solutions. This discussion suggests five strategies on how Walmart can prevent Failure to implement its global strategies.
5.1 Development of an Effective Communication Plan
Walmart should develop an asymmetric but effective communication strategy. This strategy will facilitate communication in a two-way approach where the managers, clients, employees, and shareholders present facts and ideologies for evaluation. Hu et al. (2021, p. 123) argue that an organization can recover from a crisis through team-building efforts. Also, the company should adopt a communication strategy that allows unrestricted communication that encourages communication between all levels of employees. It will facilitate problem identification and quick resolution.
5.2 Strategic Plans should Include Risk Management
Walmart’s strategic plan should include risk and crisis management plans to overcome the crises quickly and effectively. Shimizu and Hitt (2004, p. 48) acknowledge that companies should improve on their previous plans to prevent them from losing track of organizational activities and subsequent losses. Walmart can better achieve risk identification and management by involving all internal stakeholders in decision-making. It can achieve this premier goal by allowing all categories of workers to report organizational issues and suggest ideal solutions.
5.3 Setting Realistic Goals
Walmart needs to set realistic goals corresponding to its strategic plan to prevent it from interfering with resource allocation. It should also work on a realistic budget to avoid crises and conflicts. Ritchie (2004, p. 672) claims that catastrophes occur, and a company should develop a conclusive risk management plan to overcome future crises. Correspondingly, Coombs’s crisis management model states that firms should plan for crises to avoid negative publicity when the crisis occurs (Bundy et al., 2017, p. 1673). Therefore, Walmart should be prepared for all crises, including political issues.
5.4 Adherence to Core Principles
The managerial team should uphold the core values and principles since such disruptions amount to considerable losses. No one, including the top management, should defy company rules since the strategy aims to include all stakeholders’ views. In this regard, Walmart leaders must control the situation to ensure no one breaks organizational principles. Leigh (2009, p. 121) suggests that an organization needs to conduct a situation analysis to evaluate its strengths and weaknesses. It should maximize the strengths and overcome the weaknesses.
5.5 Maintaining Positive Government and Media Relations
Maintaining positive media and government relations enhances the success of international businesses. Lerbinger (2006, p. 113) indicates that government relations help create public goodwill and mutual agreements. Also, government relations help an organization maintain a political presence in a competitive market. It will help Walmart to overcome political barriers.
6. Conclusion
In summary, entering a new market can be lucrative due to the benefits, but critical barriers also characterize it. Walmart is a global retail company with headquarters in the USA but eyes emerging markets to expand its business. Influential factors for Walmart’s global strategy implementation include communication, organizational leadership, organizational structure, organizational culture, and resource allocation. On the other hand, barriers to strategy implementation include systemic, behavioural, communication, social, technological, and political barriers. This study recommends that Walmart develop an effective communication plan, including risk management in strategic plans, set realistic goals, adhere to core principles, and maintain positive government and media relations.
References
O’Sullivan, M., 2019. Economic fetishes of “modern” retail capitalism. Genève: Geneva School of Social Sciences, Department of History, Economics and Society, 2019, pp. 1-30.
Sims, S., 2018. Acquisitions: Walmart vs Amazon. Sam M. Walton College of Business University of Arkansas Fayetteville, Arkansas, pp. 1-19.
Yiannas, F., 2018. A new era of food transparency powered by blockchain. Innovations: Technology, Governance, Globalization, 12(1-2), pp.46-56.
Wiggington, D.K., 2018. Amazon: David becomes goliath. Integrated Studies, Center for Adult and Regional Education, Murray State University pp. 1-53.
Weinstein, A.T., Anti, K. and Ochoa, E., 2021. The world’s biggest retailer launches Walmart Plus, and customers have their say. Journal of Business Strategy, pp. 1-10.
Statista 2022a. Walmart: e-commerce share of sales by country 2022. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1192347/walmart-ecommerce-share-sales-by-country/ [Accessed November 26, 2022].
Statista, 2022b. Walmart: e-commerce share of sales by country 2022. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1192347/walmart-ecommerce-share-sales-by-country/ [Accessed November 26, 2022].
Statista, 2022c. Global revenue of Walmart 2022 | Statista. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/555334/total-revenue-of-walmart-worldwide/ [Accessed November 26, 2022].
Alharthy, A.H., Rashid, H., Pagliari, R. and Khan, F., 2017. Identification of strategy implementation influencing factors and their effects on the performance. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 8(1), pp.34-44.
Grant, R.M., 1991. The resource-based theory of competitive advantage: implications for strategy formulation. California management review, 33(3), pp.114-135.
Sanad, S. (2019). An Overview of the Factors Influencing Strategy Implementation Process. Researcher’s Forum, Institute of Management in Kerala, University of Kerala. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354321847_An_Overview_of_the_Factors_Influencing_Strategy_Implementation_Process [Accessed November 26, 2022].
Xie, Y. and Cooke, F.L., 2019. Quality and cost? The evolution of Walmart’s business strategy and human resource policies and practices in China and their impact (1996–2017). Human Resource Management, 58(5), pp.521-541.
DiEugenio, A. 2018. Walmart Supply Chain Driving Innovation. Available at: https://www.mwcog.org/file.aspx?&A=xJTaGBlSROHoJ6beArouU5o2%2BhUN%2FFCwdnmRMqnXltg%3D [Accessed November 26, 2022].
Lihalo, M.A. and Andrew, M., 2013. Barriers to strategy implementation by mid-sized companies in Kenya. Global Journal of Management and Business Research Administration and Management, 13(12), pp.8-14. Available at: https://globaljournals.org/GJMBR_Volume13/3-Barriers-to-Strategy-Implementation-by.pdf [Accessed November 26, 2022].
Joseph, J. and Gaba, V., 2020. Organizational structure, information processing, and decision-making: A retrospective and road map for research. Academy of Management Annals, 14(1), pp.267-302.
Martela, F., 2019. What makes self-managing organizations novel? Comparing how Weberian bureaucracy, Mintzberg’s adhocracy, and self-organizing solve six fundamental problems of organizing. Journal of Organization Design, 8(1), pp.1-23.
Dzimbiri, L.B., 2008. Experiences in new public management in Africa: the case of performance management systems in Botswana. Africa Development, 33(4).
Oke, A., Munshi, N. and Walumbwa, F.O., 2009. The influence of leadership on innovation processes and activities. Organizational Dynamics, 38(1), pp.64-72.
Advani, A., 2015. Impact of transformational and transactional leadership styles on employees’ performance in the banking sector in Pakistan. Global Journal of Management and Business Research: Administration and Management, 15(5).
Meyer, J.W. and Rowan, B., 1977. Institutionalized organizations: Formal structure as myth and ceremony. American journal of sociology, 83(2), pp.340-363.
Maak, T., Pless, N.M. and Voegtlin, C., 2016. Business statesman or shareholder advocate? CEO responsible leadership styles and the micro‐foundations of political CSR. Journal of Management Studies, 53(3), pp.463-493.
Meng, J. and Berger, B.K., 2019. The impact of organizational culture and leadership performance on P.R. professionals’ job satisfaction: Testing the joint mediating effects of engagement and trust. Public Relations Review, 45(1), pp.64-75.
Espinosa, A., Reficco, E., Martínez, A. and Guzmán, D., 2015. A methodology for supporting strategy implementation based on the VSM: A case study in a Latin-American multinational. European Journal of Operational Research, 240(1), pp.202-212.
Zahra, S.A., Gedajlovic, E., Neubaum, D.O. and Shulman, J.M., 2009. A typology of social entrepreneurs: Motives, search processes and ethical challenges. Journal of business venturing, 24(5), pp.519-532.
Hoxha, K., Hung, Y.W., Irwin, B.R. and Grepin, K.A., 2022. Understanding the challenges associated with using data from routine health information systems in low-and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Health Information Management Journal, 51(3), pp.135-148.
Zerfass, A., Verčič, D., Nothhaft, H. and Werder, K.P., 2018. Strategic communication: Defining the field and its contribution to research and practice. International Journal of Strategic Communication, 12(4), pp.487-505.
Fernandez, M.E., Ten Hoor, G.A., Van Lieshout, S., Rodriguez, S.A., Beidas, R.S., Parcel, G., Ruiter, R.A., Markham, C.M. and Kok, G., 2019. Implementation mapping: using intervention mapping to develop implementation strategies. Frontiers in public health, 7, p.158.
Fischer, M., Imgrund, F., Janiesch, C. and Winkelmann, A., 2020. Strategy archetypes for digital transformation: Defining meta objectives using business process management. Information & Management, 57(5), p.103-262.
Mutuku, C.K. and Mathooko, P., 2014. Effects of organizational communication on employee motivation: A case study of Nokia Siemens Networks Kenya. International Journal of Social Sciences and Project Planning Management, 1(3), pp.28-62.
Ihm, J. and Kim, E.M., 2021. When nonprofit organizations meet information and communication technologies: How organizational culture influences traditional, digital, and sharing media. VOLUNTAS: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations, 32(3), pp.678-694.
Alawamleh, M., Al-Twait, L.M. and Al-Saht, G.R., 2020. The effect of online learning on communication between instructors and students during the Covid-19 pandemic. Asian Education and Development Studies.
Hu, X., Yan, H., Casey, T. and Wu, C.H., 2021. Creating a haven during the crisis: How organizations can achieve deep compliance with COVID-19 safety measures in the hospitality industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 92, p.102-662.
Shimizu, K. and Hitt, M.A., 2004. Strategic flexibility: Organizational preparedness to reverse ineffective strategic decisions. Academy of Management Perspectives, 18(4), pp.44-59.
Ritchie, B.W., 2004. Chaos, crises and disasters: a strategic approach to crisis management in the tourism industry. Tourism Management, 25(6), pp.669-683.
Bundy, J., Pfarrer, M.D., Short, C.E. and Coombs, W.T., 2017. Crises and crisis management: Integration, interpretation, and research development. Journal of Management, 43(6), pp.1661-1692.
Leigh, D., 2009. SWOT analysis. Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace: Volumes 1‐3, pp.115-140.
Lerbinger, O., 2006. Corporate public affairs: Interacting with interest groups, media, and government. Routledge.
 write
write