Summary
Meta Inc. platforms’ Facebook experienced a data breach involving personal data and phone numbers of over 533 million users published in a low-level hacking forum on April 2, 2021 (Holmes, 2021). The leak contained Facebook user data from 106 countries, with over 32 million users from the US, over 11 million records from the UK, and over 6 million users from India. The data comprised Facebook bios, IDs, Phone numbers, locations, full names, birth dates, and in some instances, email addresses. Some insiders on Facebook reviewed the leak. It was verified with several records matching listed Facebook IDs to phone numbers using the password reset feature that could partially reveal users’ phone numbers. As per Facebook’s spokesperson, the data scrap was possible because of a system vulnerability, which the company claimed to have patched in 2019 (Holmes, 2021). Data scraping (web scraping) involves importing data from a website into a local file or a spreadsheet based on a local machine.
A Facebook spokesperson said the attacker had scraped the data of its site by exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in a feature that allowed Facebook users to find their friends using their phone numbers. In addition, the information found on the leak contained data available publicly on the user accounts; therefore, Facebook chose not to notify affected users.
Type of Data Breach
In this case, the type of data breach involved personally identifiable information (PII). PII is any data that can potentially identify specific individuals. This data category comprises home addresses, date of birth, phone numbers and can be used as an identifier. In addition, PII can be defined as i) any information that directly identifies an individual, such as email address, telephone numbers, social security numbers, name, and addresses. (ii) any information that an agency may identify an individual combined with other information such as geographic indicator, birth date, race, gender, and other descriptors. Moreover, any information online or physical that may aid in contacting a specific person is categorized as PII. In this case, an attacker could obtain user names, phone numbers, birthdates, and email addresses of Facebook users. Contractors are remended by the department of labor (DOL) to save guard sensitive data.
The other type of data breach is the loss of intellectual property. The company discovered a flaw in June 2020 that allowed third parties to access personal data rather than their level of access. The issue was patched on July 1, 1 same year. Intellectual Property theft (IP theft) refers to robbing people or companies’ Generally, and there are four types of IP theft, patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets. Facebook had implemented a policy that allowed developers to access clients’ data for only 90 days After the Cambridge Analytica Saga in 2018. However, the company found out that third-party developers had access to user data of inactive users if they were friends with other active users.
Impact of the breach on the organization; legal, financial, and reputational
| Impact | Short-term | Long-term |
| Legal | – Legal penalties: for failing to secure user data.
– Government fines: failure to inform relevant government bodies about breaches will attract penalties. – In extreme circumstances, those involved will serve prison time |
– Legal Penalties
The legal team must deal with data breach repercussions in the post-breach era. They must ensure that users and the federal government is notified and all the regulations are followed. The company also faces another challenge of infractions of global data privacy compliance violation because it has a global consumer base. In 2019, Facebook reached a landmark settlement with FTC and paid a $5billion fine for failure in data privacy. |
| Financial | – Financial Impacts
The company lost more than 26% of its shares during the last quarter of 2021. In addition fell in market value to about $230 billion (Snider, 2022). |
According to (MetaCompliance Marketing Team, 2021), the company is expected to lose an estimated cost of $3.7 billion. This is because of exposing locations, date of birth, phone numbers, full names, and some email addresses. |
| Reputational | The network has been losing a significant number of its users. Its daily active users have declined. Comparing active users, in the last quarter of 2021, daily active users were capped at 1.929 billion compared to 1.93 in the past quarter (Snider, 2022). | – Less Attractive to New Employees
Further decline in user base will adversely influence the company’s ability to deliver on their ads and impression, thus affecting their financial performance. |
Security Issues Facebook was Facing Before the Breach
- Failed Access control
The company made the issue public through a blog post on July 1, 2020. The bug enabled third-party developers to have more excessive access to personal user data than they should (Heiligenstein, 2022). Developers were able to see user details of inactive users if they were friends with active users. The flaw was discovered and patched. Failure enables hackers to perform unauthorized information modification, disclosure, or destruction of all data. In addition, it allows hackers to perform business functions beyond their limits.
- Back doors and application vulnerabilities
In 2019, the company had backdoors and application vulnerabilities that led to breaches (Heiligenstein, 2022). A second server was discovered in 2020, containing 42 million more users, making about 310 million. These flaws expose the company to security breaches or exploitations. With the global outreach of the internet, web applications are vulnerable to these flaws and attacks coming from a range of attack vectors.
- Code Error
In September 2018, hackers accessed user data, allowing them full access to the entire profile (Heiligenstein, 2022). This was possible because of a flaw in the platform “view as” feature. This feature gives a user ability to view their profile from the perspective of other users. However, an error in the code allowed hackers to steal tokens and view information deemed private. According to Facebook, it took about a year for the flaw to be noticed and be patched.
- Poor credential management.
User data was stored in an encrypted format exposing them to workers of Facebook (Heiligenstein, 2022). Data was stored in plaintext. This can lead to severe damages when a data breach occurs.
CSC Suitable Control
Center for Internet Security (CIS) released a collection of 20 controls called Critical Security Controls (CSC) to help organizations protect themselves from identified threats and security attacks (CIS Critical Security Controls, nd). Facebook had faced several security breaches before the breach in the case study, as discussed in the previous question. Here we will recommend controls for the given breach to help mitigate the risk associated with the issue.
| Security Issue | Recommended control | Recommended sub controls | Recommended Tools | Risk Control Strategy |
| Failed Access Control | CSC:1- Inventory of /authorized and Unauthorized Devices | IA-3: Device Identification and Authentication
PM-5: Information System and Inventory |
– security information and event management (SIEM) | Mitigation |
| Back door and application vulnerability | CSC 3: Secure Configuration for Hardware and Software on Mobile Devices, Laptops, Workstations, and services | CA-7: Continuous Monitoring.
SI-4: Information System Monitoring |
– Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
– Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) |
Defense |
| Code Error | CSC 18: Application Software Security | SA-15: Deployment process, standard, and Tools
SA-17: Developer Security Architecture and Design. |
– Dynamic Application Testing (DAST) tool.
– Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tool. |
Mitigation |
| Poor credential Management | CSC 4: Continuous Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation | CA-2: Security Assessment.
SI-7: Software, Firmware, and Information Integrity |
– IBM Guardium for File and Database Encryption
– BitLocker |
Mitigation |
It was added to the previous table.
Open-Source Tools vs. Commercial Tools.
| Tools | Open Source | Commercial Tools |
| Advantages | SIEM Tools
– Improves Cybersecurity Performance—it shortens the time to detect and identify threats allowing the company to react fast. – Helps with regulatory Compliance – Provides Details Forensic Analysis – Offer a wide range of uses |
Access Rights Manager
– It helps IT and security specialists to automate their work. – In addition, it will help the company to improve on compliance issues and avoid violations of set guidelines. – It will help the company better visualize its resources and control its data. – It will help Facebook prevent unauthorized parties from accessing the company’s data. – It will also prevent data loss and data breaches. – It is effective with both outsider and insider threat detection. – It uses Machine-learning algorithms to identify new sensitive data. |
| Disadvantages | – Requires Technical expertise- its effectiveness will be entirely based on its implementation. In addition integrating, configuring, and analyzing SIEM reports require technical expertise.
– It takes a long time to implement- it can take up to 90 days, depending on the firm’s size. – Generates Large amounts of False-positive- when it is misconfigured, it creates large amounts of false positives in a day. |
– Before implementing any DLP Software, one must study the pros and cons of every software.
– The company will need to define and develop core data protection strategies for business and technical requirements. Otherwise, it will not be effective. This is because implementing a data leak prevention policy takes time to develop. – DLP assigns network access based on privileges. All accounts need to be audited to ensure that they can distinguish between regular and privileged ones. – It is challenging to implement DLP; thus, the company must have a comprehensive overview of data flow within the company. |
Security Architecture
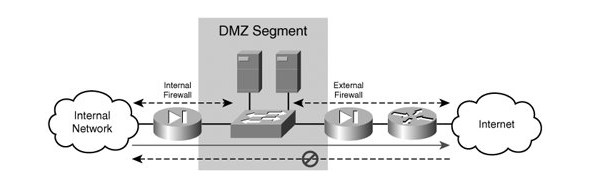
I will deploy an Enterprise Security Architecture to secure the company’s information system. This will be possible by determining Facebook Inc.’s security requirements, such as planning, implementing, and testing security systems. In addition, it will work in preparation of security standards, procedures, policies, and mentoring team members. The Enterprise Security Architecture will utilize a dual-firewall. A dual firewall is more complex than a single firewall implementation. However, it is overly secure, providing granular control over internet traffic flowing through the firewalls. Ideally, the firewalls should have different models and vendors acting as interior and external firewalls, offering a DMZ segment between the internal and external firewalls. Like in a single firewall model, the DMZ will allow internal to external firewall traffic. However, no traffic will be permitted from the external network directly to the internal network.
Reflection and Lesson Learned from the Incident
After going through the case study, I have learned that even giant firms like Facebook can be faced with data breaches and are vulnerable to data breaches. For a firm to be secure, it has to take proactive measures in data security and pay the cost of implementing the associated standard. When a company is involved in a data breach, customers lose their trust in the company, and it is faced with a high attrition rate of both customers and employees. The consequence of the high attrition rate has more significant impacts on the company’s investors.
I have learned the following after studying the case study:
- Companies should monitor systems, hosts, and their networks in real-time.
- The development of new software leads to unique security gaps; therefore, there is a need for proper testing.
- There is a need for log and alerts on changes to administrative group membership,
- There is a need to have a red and blue team perform incidence response and find errors in the web application.
- When a company is faced with a data breach, the brand is also harmed.
- User data should be secured with proper and updated tools.
- Companies should perform data audits and control all logs.
References
Avery, A. (2021). After the disclosure: measuring the short-term and long-term impacts of data breach disclosures on the financial performance of organizations. Information & Computer Security, 29(3), 500–525. https://doi.org/10.1108/ics-10-2020-0161
Choi, Y. B. (2021). Organizational Cyber Data Breach Analysis of Facebook, Equifax, and Uber Cases. International Journal of Cyber Research and Education (IJCRE), 3(1), 58-64.
Downing, A., & Perakslis, E. (2022). Health Advertising on Facebook: Privacy & Policy Considerations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.07263.
Foecking, N., Wang, M., & Huynh, T. L. D. (2021). How do investors react to the data breaches news? Empirical evidence from Facebook Inc. during the years 2016–2019. Technology in Society, 67, 101717.
Holmes, A. (2021, April 21). 533 million Facebook users’ phone numbers and personal data have been leaked online. Business Insider. Retrieved March 20, 2022, from https://www.businessinsider.com/stolen-data-of-533-million-facebook-users-leaked-online-2021-4?r=US&IR=T
Snider, M. U. T. (2022, February 4). $230 billion? Facebook’s stock plunge brings big losses for Mark Zuckerberg, Meta – and maybe you. USA TODAY. https://eu.usatoday.com/story/money/2022/02/03/facebook-zuckerberg-retirement-funds/6654000001/
Strawbridge, G. (2020, February 28). 5 Damaging Consequences Of A Data Breach. MetaCompliance. https://www.metacompliance.com/blog/5-damaging-consequences-of-a-data-breach/
 write
write