Measuring and Managing Interest Rate Risk
The danger of adverse financial consequences as a result of fluctuations in interest rates of a market is called interest rate jeopardy. Variations in interest rates influence the result of a bank and whole economic steadiness. From a financial viewpoint, jeopardy might be determined by regulating either net Rates of Interest or the net Interest Revenue. Like various enterprises, a bank must maximize profits to survive. On the other side, maximizing benefits requires accepting some risk. Cost and benefit go hand in hand. If the likelihood of loss is high, then a larger projected profit is necessary to offset this risk; conversely, if the risk exposure is low, a smaller projected profit margin is necessary, and vice versa. The firm’s top management sets the ideal risk-return trade-off for a given financial institution and will likely differ from one institution to the next. The risk of fluctuating interest rates is only one of several that a bank must bear. Managing risks such as forex trade rate, credit risk, or liquidity risk is all considered part of the larger risk management framework. This paper discusses the roles of ALCO and a detailed fraud risk assessment framework for Barclays.
1.0 Roles of ALCO
The Asset Liability Committee (ALCO) can mitigate interest rate risk by taking the following steps. As not all banks are adopting a rate shock of 400 to evaluate its influence on proceeds, these organizations have to adopt an in-series rate move to evaluate its profits’ impact in a variety of contexts (Carey, 2019). ALCO should analyze the assumptions used to create the balance sheet, including advance payment rates of credit plus payment accounts betas, to determine if any adjustments are necessary (Serafeim & Trinh, 2020). Banks consider the danger of interest rates and fluidity contemplations in managing their liability or asset. Keeping the bank liquid by minimizing the difference between interest income and interest expenses is one of the statutory duties of the ALCO. Investments and operational risk are two major considerations. The responsibilities of an ALCO typically consist of keeping tabs on market risk tolerances, establishing sufficient Market risk tolerances (MRI), updating and authorizing the liquidity and funds management strategy regularly, establishing and enforcing a contingency funding plan, and evaluating urgent funding needs and sources. In addition, ALCO is responsible for evaluating the potential impact on the liquidity of a wide range of bad situations. Any ALCOs will hire independent third parties with superior subject matter knowledge to double-check the findings and data in management reports, whether publicly or privately generated.
1.1 Risk Tolerances and MIS
It is essential to develop and review reports on activities such as those listed below for ALCO to effectively manage business risk tolerances and define suitable MIS. Information about expected and actual sources of revenue, Guidelines for a contingency financing strategy are essential for large deposits and catastrophic scenario reports.
Roles
- a) It should formulate plans detailing the bank’s commitment to risk management limitations.
- b) It should formulate plans detailing the bank’s commitment to risk management limitations.
1.2 Measuring Interest Rate Risk
A portion of our duties funds the interest rate risk reserves. Once more, the balance sheet is split into vintage to indicate increased possessions or duties. Assets and liabilities may be repriced at maturity or when variable costs rise as a result of contract terms. Improvements in the accuracy of both short-term and long-term risk assessments have been made possible by the increasing complexity and precision of the many financial methodologies accessible. To further alleviate the jeopardy of interest rates, economic organizations ought to rebalance their asset and duties selections (Feyen et al., 2020). Then, to mitigate some of their exposure to fluctuations in interest rates, certain financial institutions may enter into contracts with others. The federal government still has a substantial obligation to handle risk in the financial industry. Banks are being evaluated on how well they can analyze IRR while staying out of trouble. Some tools applied in approximating jeopardies of Interest Rates include; Net Economic Value (NEV) Models, Income Simulation Models, and Gap Analysis.
1.2.1 Gap Analysis
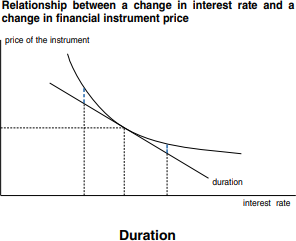
The risk may be evaluated using gap analysis, a useful supplementary method. This is classically controlled by applying the period gap method, which is based on the tenancy of tools of the balance sheet. To compute the formula for approximating the duration, we have to establish the net worth of a tool with n fiscal flows2.
1.2.2 Income simulation modeling
This model foresees forthcoming remaining interest revenue plus its growth regarding differences in interest rate. Jeopardy extent is relative to the extent amid the current price in the market in addition to higher and lesser rates profitable.
1.3 Measuring and Managing Liquidity Risk
The incapability of an organization to achieve its goals when they become unpaid minus experiencing large expenses or losses depiction its profits or capital to liquidity risk. A commercial bank’s on- and off-balance-sheet positions are analyzed by liquidity jeopardy control activities to estimate liquidity and how they shall be fulfilled. Accessing and understanding the financing markets available to the bank, assessing the present and coming utilization of those markets by the bank, and keeping a watch for indicators of interest lessening every fall under the above-mentioned “overview.”
To evaluate the likelihood of future shortages in net financing, organizations approximate their cash flow by likening their assets and liabilities plus the cash flow evaluation of their assets. Institutions should be able to measure and anticipate their future cash flows for in-flows, outflows, obligations of an off-balance sheet, and safeties over numerous durations in usual and unusual stress scenarios.
Functions of ALCO for operational liquidity risk management include:
- The way it handles and keeps tabs on the firm’s net liquidity.
- If it is an external-unified bank, it must give information to the state’s uppermost political system.
- Promoting, organizing, collaborating, and monitoring balance sheet planning can help ALCO deal with the unknowns of regulating liquidity and interest rate convergences.
- Banks have ALCOs whose job is to ensure they follow the rules set forth by the board. Therefore, the ALCO is not responsible for designing an internal in-flow jeopardy management program.
An operational assessing and checking system is vital for successful liquidity jeopardy management. Thus, the enterprise ought to implement techniques for early detection of liquidity risk so that appropriate remedial action may be done to avert disastrous losses. Along with serving cash flow management during recessions, a healthy method for determining and managing cash flow jeopardy may increase returns by creating the utmost accessible means. Essential elements of an efficacious jeopardy management operation include a strong MIS and methods to analyze, track, and control jeopardies.
Treasury tasks like trade, treasury operations, and risk management to run smoothly, the Management Information System of an organization must be connected to the institution’s general management information systems.
The liquidity position of the bank’s measurement includes;
- Minimum liquidity ratio – ‘As stated by the Banking Act, “a company should have such minimal allotment assets as the Central Bank might from over a period suggest.” Companies have historically been required by law to have a minimum amount of cash on hand equal to twenty percent of their particular credit liabilities, matured and temporary obligations. The institution shall, however, establish its particular sophisticated least cash flows ratio centered on its dimensions, plus risk hunger.
- Loan to Deposit Ratio – it can be determined every month. The ratio between a bank’s illiquid assets and its controllable liabilities may be calculated using this metric. Cash flow risk management can be reinforced when the proportion of credits and payments upsurges over a specific level.
- Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) – This is set at 30 days to foster resilience against potential liquidity disruptions. Regarding a temporary strain condition, the proportion guarantees financial organizations have adequate unfettered, great-value cash flow assets to balance net liabilities.
For the given strain situation, the net cash flow is the increasing predicted cash outflows minus the increasing predictable cash assets during the duration.
1.4 Measurement of Liquidity Risk
Basel III, BSA, and MM, calling for both NSFR plus LCR, are among the scarce means by which cash flow risk may be evaluated NSFR.
Liquidity and consistency of financing are factors considered when analyzing the balance sheet in obtaining the comparative implication of numerous inflow and outflow modules.
Liquidity might be validated that the dimension of fairness’s flow table, duties surpasses the extent of Equity’s liquefiable resources. The incongruity might lead to a liquidity crisis in the equity market. This inconsistency may be explained as a responsibility in how Equity handles its finances.
Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR)
LCR = security of high-quality liquid assets / ≥ 100%
Overall net cash outflow of 30 days
| ($millions) | |
| Quarterly Average Weighted Amount of Dec 31, 2021 | |
| HQLA | 17, 424 |
| Net cash outflows (calculated at 85%) | 8,824 |
| LCR | 200%₂ |
The HQLA of Barclays for this quarter is $17,424 million, representing the value of assets that can be easily converted into cash in times of stress. On the other hand, the overall net cash outflows of the bank for the next 30 days are estimated to be $8,824 million (Barclays, n.d). This figure is calculated using a weighted average approach and assumes an 85% outflow rate for certain deposits and other liabilities.
The LCR of 200% suggests that Barclays is well-positioned to meet its short-term liquidity needs in the event of a significant stress scenario. This can assure regulators, investors, and other stakeholders that the bank effectively manages its liquidity risk.
Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR)
Financial institutions must keep their in-flow combines and off-balance sheet actions in line with their liquidity profile. A long-lasting cash-low context tries to limit the likelihood that blows to a bank’s representative pay sources will erode its liquidity position, raising the risk of bank deterioration and generating higher systemic stress. The NSFR promotes funding flexibility by advocating for a more thorough examination of funding risk across the on-balance and off-balance sheet goods and decreasing reliance on short-term wholesale finance.
2.0 Barclays Operational Risk Management Performance
2.1 Brief background on Barclays Bank
Barclays Bank, plc is a financial services and investment banking institution in London, United Kingdom. From its inception in 1690, this financial institution has expanded to become a global powerhouse, employing over 80,000 people across 40 countries (Barclays, n.d).
Barclays Bank’s retail banking, corporate and investment banking, wealth management, and credit card offerings serve personal, commercial, and institutional customers. The bank has a rich history of pioneering financial technology; it developed the first automated teller machine in 1967 and the first credit card in the United Kingdom. While it has been around for quite some time, Barclays Bank has been embroiled in several scandals, including accusations of unethical and illegal practices. In recent years, the bank has prioritized enhancing its public image by committing to more openness and accountability.
2.2 Risk Fraud Assessment Framework
| Identified Fraud Risks and schemes | Likelihood and impact | Personnel/Departments involved | Effectiveness of control | Residual Fraud risks | Fraud Risk Responses |
| Operational fraud: This type of fraud involves manipulating operational processes or procedures, such as misappropriating assets, theft of confidential information, or false documentation.
Financial fraud: This type of fraud involves the manipulation of financial statements, such as misrepresenting financial performance or fraudulent trading activities. Cyber fraud: This type of fraud involves using technology to perpetrate fraud, such as phishing scams, identity theft, or hacking. Insider fraud involves employees or contractors who abuse their access to company resources or information for personal gains, such as embezzlement or insider trading. Vendor fraud: This type of fraud involves third-party vendors who exploit their relationship with the bank for personal gains, such as kickbacks or collusion. |
The likelihood and potential impact of each fraud risk occurring will depend on several factors, including the strength of the bank’s internal controls, the level of employee awareness and training, and the effectiveness of the bank’s fraud detection and prevention measures.
For example, the likelihood of cyber fraud may be higher if the bank has weak cybersecurity controls or employees are not adequately trained on cybersecurity best practices. The potential impact of cyber fraud could be significant, as it could result in the loss of sensitive customer data or financial losses. Similarly, the likelihood of insider fraud occurring may be higher if the bank does not have strong controls in place to monitor employee access to confidential information or if employees are not adequately trained on ethical conduct. The potential impact of insider fraud could be significant, as it could result in reputational damage, financial losses, and regulatory sanctions. Therefore, it is important for Barclays Bank to regularly assess its fraud risks and implement appropriate measures to mitigate those risks. |
The personnel and departments that are most vulnerable to fraud risks in Barclays Bank may include:
Accounting and finance personnel: These employees can access financial records and potentially manipulate financial data. Operations personnel: These employees can access operational processes and systems, which could be manipulated for personal gain. IT personnel: These employees have access to sensitive information and technology systems, which could be exploited for personal gain or to perpetrate cyber fraud. Senior management: These individuals may have a higher level of authority and access to sensitive information, making them more susceptible to insider fraud |
The effectiveness of the existing control measures to mitigate fraud risks in Barclays Bank will depend on several factors, including the strength of the control measures, the level of employee awareness and training, and the effectiveness of the bank’s fraud detection and prevention measures.
The bank has implemented various control measures to mitigate fraud risks, including regular risk assessments, segregation of duties, training and awareness programs, monitoring and surveillance, a code of conduct and ethics, and a whistleblower hotline. These measures are designed to prevent and detect fraud across all departments and personnel in the bank. However, the effectiveness of these control measures can be evaluated through monitoring and testing of the control environment, including assessments of control design and operating effectiveness. The bank can also track the incidence and frequency of fraud events and investigate any incidents to identify areas where control measures may be improved. b. Any gaps or weaknesses in the control measures identified through monitoring and testing should be addressed promptly by the bank. For example, if the bank identifies that certain employees lack awareness of the bank’s code of conduct and ethics, it may be necessary to provide additional training and communication. Other gaps or weaknesses may require changes to control design or the implementation of additional controls. For example, suppose the bank identifies that the segregation of duties is ineffective in preventing fraud in a particular area. In that case, revising the process or implementing additional controls, such as monitoring or review processes, may be necessary. Barclays Bank must ensure a robust and effective control environment to prevent and detect fraud. The bank should regularly assess its control measures and take appropriate actions to address gaps or weaknesses identified through monitoring and testing. |
After implementing control measures, there may still be residual fraud risks that the bank needs to consider. These residual risks are the risks that remain even after control measures have been implemented.
To assess residual fraud risks, the bank should evaluate the effectiveness of its control measures and the potential impact of any remaining fraud risks. This can be done through ongoing monitoring, testing, and risk assessments. The residual fraud risks that need to be further mitigated or addressed in Barclays Bank may include the following: Insider fraud: Even with strong control measures in place, insider fraud is still risky, where an employee or contractor may exploit their position to commit fraud. The bank may need to implement additional measures to detect and prevent insider fraud, such as regular background checks or employee surveillance. Cyber fraud: As cyber threats continue to evolve, the bank may need to review and update its cyber security controls to ensure they effectively mitigate the risk of cyber fraud. This may include regular testing of systems and processes, as well as ongoing employee training and awareness programs. Third-party fraud: The bank may also need to consider the risk of fraud from third-party vendors and suppliers, particularly those with access to sensitive information or systems. The bank should assess the risk associated with these third-party relationships and implement appropriate control measures to manage the risk. Internal control weaknesses: Weaknesses in internal controls, such as inadequate segregation of duties or lack of oversight, could result in fraud. The bank should continue to monitor and test its internal controls to identify and address any weaknesses. |
Barclays Bank should develop and implement a fraud risk response plan that outlines the bank’s approach to preventing and detecting fraudulent activities. This plan should include a compliance policy outlining the bank’s ethical behavior standards and setting out the consequences for non-compliance.
The fraud risk response plan should also identify the bank’s risk appetite for fraud and establish a clear reporting process for suspected fraud events. The plan should outline the steps during a suspected fraud event, including investigation and remediation measures. b. The compliance policy should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it effectively prevents and detects fraudulent activities. This review should include an assessment of the policy’s alignment with current regulatory requirements and industry best practices. The review should also consider the effectiveness of the policy in addressing emerging fraud risks and any changes in the bank’s risk appetite. Any necessary updates to the policy should be made promptly and communicated to all employees to ensure that they are aware of the changes and the expected standards of behavior. In addition to reviewing the compliance policy, the bank should regularly assess its fraud risk response plan to ensure that it effectively prevents and detects fraudulent activities. This assessment should include an evaluation of the bank’s control environment, employee training, awareness programs, and fraud detection and prevention measures. |
2.3 Barclays Bank Operational Framework
Risk and control self-examination: Rules and dangers of the hazards inherent to Barclays Bank’s operations are identified and assessed using self-assessments.
Risk event: Every instance where Barclays Bank has lost or stands to lose money owing to the absence of or failure of control is considered an operating risk case.
Operational Risk Appetite: The Board of Directors of Barclays Bank reviews and approves an annual Operational Risk Appetite Statement detailing the acceptable operational risk level required to advance the bank’s strategic objectives.
Key indicators: Key metrics may be used to compare the Operational Risk Profile to the level of risk that management is willing to accept.
Risk scenarios: The risk events identified for Barclays Bank include the complete gamut of threats to the financial institution.
Reporting: Continuous monitoring and reporting of operational risk.
Operational risk measurement: Barclays Bank calculates its requirement for Operational Risk Capital using the Standardized Measurement Method (SMA)
Insurance: Barclays Bank uses insurance to mitigate the financial impact of some operational concerns.
References
Barclays. (n.d). Barclays plc our readiness for resolution. https://home.barclays/content/dam/home-barclays/documents/investor-relations/reports-and-events/annual-reports/2021/20220610-Barclays-RAF.pdf
Carey, P. (2019). A Consistent Earnings and Value Model of the Interest Rate Risks Arising from Banks’ Non-Maturity Deposits.
Feyen, E. H., Utz, R. J., Zuccardi Huertas, I. E., Bogdan, O., & Moon, J. (2020). Macro-financial aspects of climate change. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper, (9109).
Serafeim, G., & Trinh, K. (2020). A framework for product impact-weighted accounts. Harvard Business School Accounting & Management Unit Working Paper, (20-076).
 write
write