A study conducted by Twenge and Campbell showed that high screen time usage among adolescents increased the risk of anxiety and depression. Due to the increased vulnerability, adolescents are more likely to have seen or need a mental health profession. The study helped me understand more about the psychological impacts of screen time on adolescents. The final source that I used for my essay was Lopez’s study on changes in mood due to too much screen time. In her research, Lopez investigated the effects of screen time on mood changes in children, and the results of the study showed that screen time had negative impacts on the behavioral changes in children who spend too much time in front of the screen. The study by Lopez compliments the other two sources that I chose for the essay.
Part Two: Image Explanation
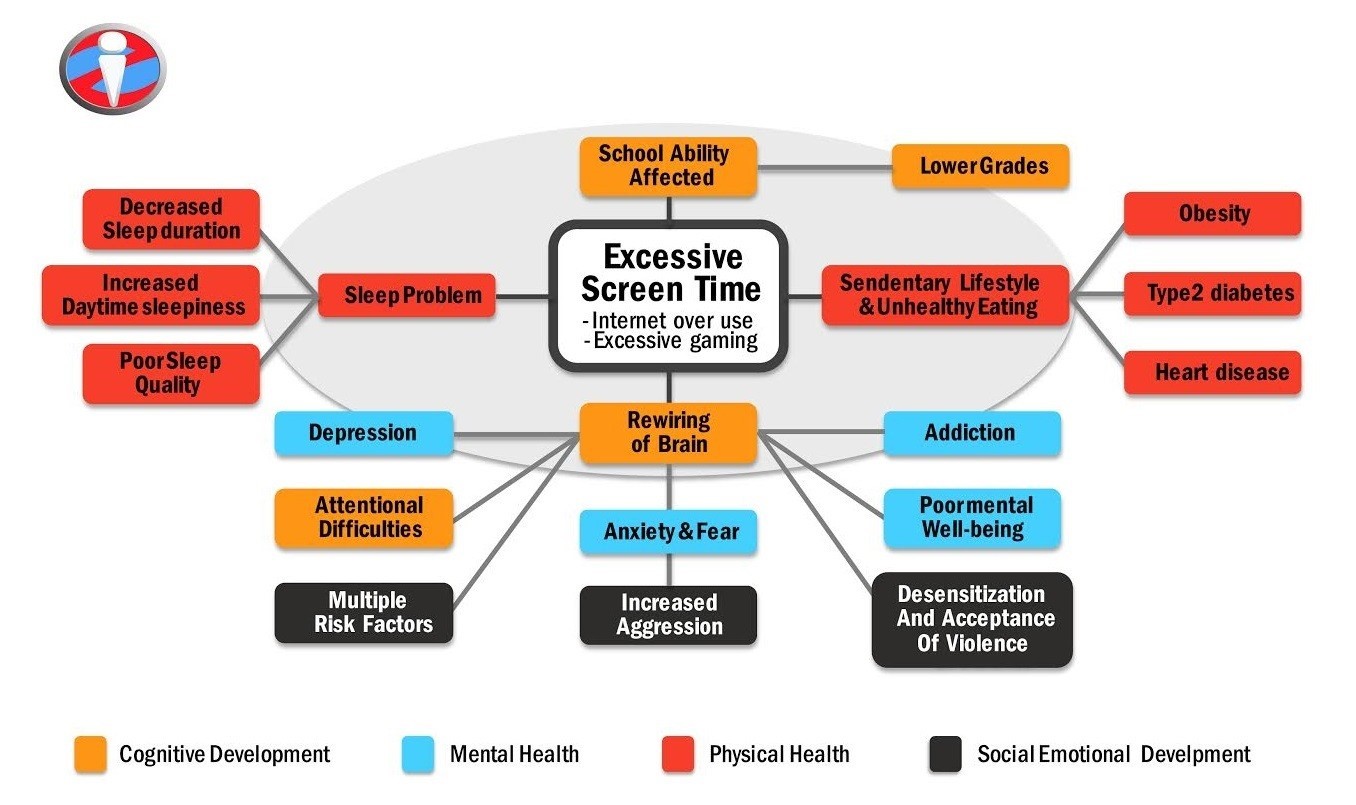
The image above presents valuable information on how excessive screen time affects children. The image represents the effects of excessive screen time on cognitive development, mental health, physical health, and children’s social-emotional development. When children spend too much time in front of the screen, their cognitive development is affected. This image complements the study by Jay (2018), which showed that children who spend a significant amount of time on their screen had a poor academic performance. Their school ability was affected as they spent time watching cartoons and playing video games.
The image addresses the effects of excessive screen time on children. It addresses the various effects by providing the different impacts of too much screen time on children’s mental, and physical well-being. The image complements the other three sources that have been selected for the study. Children learn by exploring their surroundings, and spending too much time on the screen impacts their brain development. Too much screen time can lead to addiction, thus affecting the mental and emotional well-being of children. Behavioral problems such as aggression are rampant in children as children who spend too much time on the screen are likely to have outbursts or be irritable when not using these devices (Twenge and Campbell, 2018). When children spend too much time in front of the screen, they might develop social interaction problems. This could later affect their social and relationships with others later in their lives. This image shows the results of the different effects of excessive screen time, and these effects are also evident for other audiences who might view the image.
The image could be used to educate parents about the adverse effects of allowing their children to spend too much time on screen. Even though parents have little to no control over what is accessible in the media, they can regulate what their children are exposed to and the amount of time they spend in this media. When children spend a considerable amount of time away from the screen, it promotes their physical and social development. The image helped me comprehend that excessive screen time also had negative effects on the weight of children as it affected their eating habits. This strengthened my perspective of the adverse effects that too much screen time had on children’s health. I hope the image will educate parents on the negative effects of excessive screen time, and they will take the issue more seriously, seeing its potential effects on their children. When selecting the image to be used, I chose an image highlighting the effects of excessive screen time so that my target audience can easily understand the contents of the image easily.
Part Three: Blog Entry
Children using screen devices for more than the recommended time are at an increased risk of developing severe conditions, thus affecting their cognitive development. Children need time to interact with other people, and when they spend unmonitored time on their smartphones, television, or tables, this affects their cognitive learning process (Lopez, 2017). Too much screen time is associated with abnormal sleeping patterns among children. Sleep is vital for the healthy development of children, and when a child is exposed to screen light, this might affect their sleeping pattern as the brain might signal the body to stay awake even at night. This leads to imbalances in the sleeping patterns, further affecting the development of the child.
In addition, excessive screen time also affects the eating habits and the weight of children. Children don’t have as much conscious control over what or how much they eat when spending too much time on-screen. They are likely to engage in unhealthy eating habits, thus affecting their weight and can lead to severe health problems. Children who have a habit of spending too much time on screen are likely to become overweight, leading to severe health problems such as diabetes. The adverse effects of excessive screen time have been clearly outlined thus, parents have a responsibility to monitor how much time their children have access to the screen. According to Twenge and Campbell (2018), children exposed to excessive screen time are much likely to lose their temper and have issues controlling their feelings. Parents should establish screen time rules for their children to reduce these risks. The government should enforce strict measures to ensure that children are not exposed to excessive screen time. They can do this by levying fines on parents and banning all digital media from children under three years. There’s no productive role that digital technology can have on children under two years; thus, parents are responsible for protecting their children from digital technology (Jay, 2018).
References
Jary, S. (2018). How much screen time is healthy for children. Expert tips on-screen safety, education, mental development, and sleep ‘. PC Advisor. URL: http://www. pcadvisor.co.uk/feature/digital-home/how-much-screen-time-is healthy-for-children-benefits-3520917/(аccessed: 22.02. 16).
Lopez, R. (2017). Changes in Mood Due to Too Much Screen Time.
Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2018). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 12, 271-283.
 write
write