Macroeconomic forecast is a crucial aspect in making investment decisions. For a practical macroeconomic analysis, it is essential to analyze the crucial factors contributing to the economy. For instance, economic factors must be considered to ensure an effective analysis of the economy’s performance. Some of the economic factors that can be used for the analysis are gross domestic product and unemployment rate. Also, it is essential to analyze the fiscal factors of the economy. Furthermore, monetary policy is also a vital determinant of the economy’s performance. This will be used to make informed decisions during the forecast. Delving into the economy’s performance by analyzing the various factors influencing the economy will lead to effective decision-making. This report analyses the three major economic determinants that can help make an informed decision about the economy’s performance and ensure an effective decision-making process.
Economic Factors
Understanding the historical trends in the key economic indicators is essential to assess the present situation and make accurate forecasts. Various economic factors can be used to make effective forecasts of the economy. In this subsection, we will inspect the tendencies in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate and unemployment rate from 2018 to the present, explaining the factors implying the changes in each indicator. Delving into these factors will identify the trends in the market, enabling an effective and informed decision-making process.
Gross Domestic Product
The GDP growth rate is a fundamental indicator of economic performance, representing the general development or contraction of the economy. US GDP growth rate had a diverse movement from 2018 to 2021. Growth in the GDP was robust in 2018 and 2019, with a growth of 2.9% in 2018, followed by a 2.3% growth in 2019. This is likely to be influenced by high consumer spending, business investment, and favorable global economic conditions. Nevertheless, the COVID-19 pandemic 2020 resulted in a recession, with the real GDP growth rate falling to -2.8%. This has contributed to the lowest GDP in the history of the U.SU.S. The decline in the GDP could have resulted from the measures taken by the government to fight the pandemic, such as lockdowns and restrictions which crippled economic activity (Sheiner et al., 2021). The following is a summary of the GDP changes since 2018.
![]()
The recovery of 2021 was characterized by rapid GDP growth, reaching 5.9% in the previous year. Primary fiscal measures, resumption of business operations, and accelerated vaccinations stimulated this. Furthermore, there was an increase in 2022 to 2.1%, followed by the recent measure in the last quarter of 2023, which had an increase of 3.3%. The comparison of the real GDP in 2022 and 2023 is indicated in the graph below.
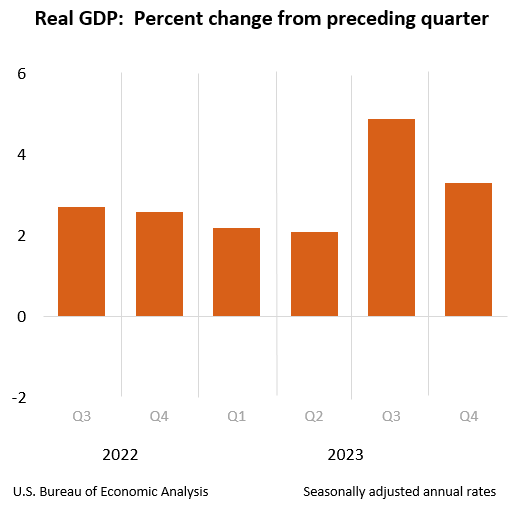
Unemployment Rates
The unemployment rate is a critical indicator of the labor market performance and the economy’s health, as it shows the percentage of the unemployed labor force that is still looking for work. Before the pandemic struck, the American labor market was in great shape, with the unemployment rate fluctuating between 3.5-4%, which was at historically low levels in 2018 and 2019 and reflected strong job growth and a decline in joblessness among various groups. At the end of 2018 and 2019, the rate was 3.9%.
In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic came out of the blue, and hence, an unprecedented rise in the unemployment rate occurred, reaching 14.8% in April 2020, the highest since the Great Depression. The rate began to decrease in the following months, decreasing to 13.2% and 11% in June. By the end of 2021, the unemployment rate had recovered from about 3.9%, which indicated a significant improvement in employment levels but also underscored some challenges like labor force participation problems and misalignments.
Fiscal Factors
The fiscal policy scenery has been drastically changed with the implementation of the 2021 Infrastructure and Investment Jobs Act (IIJA) and the 2021 Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). These legislative acts reveal a huge investment of resources in building infrastructure and eradicating inflationary pressures, which can lead to diverse impacts on the economy of the U.S.
2021 Infrastructure and Investment Jobs Act (IIJA)
The IIJA is a major legislation that modernizes U.S.U.S. infrastructure and creates economic opportunities. The program enables over $1 trillion to be spent over the next ten years. The expenditure focused on the most essential areas of transportation, broadband, water systems, and clean energy. This funding will be distributed to critical sectors to upgrade the infrastructure, create jobs, and, thus, increase the country’s competitiveness on a global scale. The government allocates a specific amount of money to such investments to ensure an increased investment in them. The investment further creates jobs for other individuals.
Within alternative energy investments, the IIJA has important possibilities. Much of the funds are directed into renewable energy projects such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. This influx of capital serves to quicken the world’s transition to a greener energy paradigm and generates innovation and investment in green energy technologies. Additionally, the fact that the IIJA prioritizes the modernization of the nation’s electric grid and increase in renewable energy resonates with the objectives of the alternative energy businesses, which can create synergies and partnership opportunities (Brookings n.d.) Furthermore, there has been an increase in the allocation of funds for electric buses. This increases the preservation of the environment.
2021 Inflation Reduction Act (IRA)
The IRA was created to deal with the mounting inflation pressures by controlling rising consumer prices and preserving economic stability. This act comprises steps to mitigate inflation, including but not limited to targeted spending cuts, tax incentives, and regulation reforms. These measures are implemented to invest in clean energy and reduce carbon emissions (Justin et al., 2022). Through curbing inflation, the IRA aims to protect the purchasing capacity of consumers, boost business prestige, and ensure stable economic growth.
The IRA has a dual influence from the angle of alternative energy investments. One of the main ways the IRA achieves this is by controlling inflation, thus maintaining the right macroeconomic environment for investments and reducing uncertainty and risk. Price stability and positive predictability of inflation are key to long-term planning and finance allocation in the alternative energy sector. The second aspect is that IRA can indirectly assist alternative energy ventures by increasing consumer demand and overall economic activity. When inflationary pressures subside, households have more money to allocate to energy costs, thus potentially increasing demand for renewable energy solutions.
Evaluation of Keynesian-Based Infrastructure Investments
The Keynesian-based infrastructure investments that the IIJA provides are key drivers for economic growth and the availability of alternative energy. The government can increase aggregate demand and create new jobs by financing infrastructure development. Therefore, this leads to positive reciprocal effects within the economy because the higher consumer spending and the increased investment activity cause the economic activity to grow.
In the area of alternative energy, Keynesian infrastructural investments have a number of advantages. They are the key source of financing for renewable energy projects, especially at the early investment stage, where capital-intensive investment is needed. Moreover, infrastructural advancements, including the upgrade of power networks and the construction of charging stations for electric cars, directly support the deployment of alternative energy technologies. Finally, by developing a favorable investment environment and promoting sustainable economic growth, Keynesian policies improve the long-term viability and market appeal attractiveness of alternative energy ventures to investors.
Generally, the fiscal policy tools implemented by the IIJA and the IRA will considerably affect investments in alternative energy. Through the focus on infrastructure development, inflation control, and economic promotion, those policies create an environment favorable to expanding alternative energy enterprises, supporting innovation, employment, and sustainable development.
Monetary Policy Review
The Federal Reserve controls the monetary policies in the U.SU.S. As a reaction to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federal Reserve has implemented significant changes in monetary policy, moving from an expansionary to a contractionary policy stance starting in early 2022. This change was fueled by mounting worry about the inflationary pressures that reached 40-year highs and called for adequate measures to prevent the economy from overheating.
Response to COVID-19 Crisis
At the outset, the Fed rolled out expansive monetary policies in March 2020 to provide support in the face of a pandemic-induced recession. These measures ranged from lowering the federal funds by 1.5% to a rate between 0% and 0.25%. Implementing quantitative easing programs to stabilize the financial system to provide liquidity support ensures that credit markets continue operating without disruption (Clarida et al., 2021). The Federal Reserve moderated its stance to a contractionary monetary policy as the economy recovered from recession and the inflationary pressures became severe. The transition process included communications signaling the intentions to raise interest rates, gradually scaling up the asset purchases, and using more hawkish tones regarding future policy actions.
Factors Contributing to Inflationary Pressures
The increase in the prices of commodities without the increase in wages was the major contributing factor to inflationary pressures. During the pandemic, the prices increased significantly. However, there was no consumer wage increase (Bernanke, 2023). As a result, there was pressure on the consumers,
Future of Inflation
The article by the IMF on the future of inflation identifies important issues at the root of today’s unique inflation challenge. The available measures include supply bottlenecks, accommodative fiscal policies, shifts in consumer behavior, and inflation expectations (Bernanke, 2023). The Federal Reserve’s determination to reduce inflation to 2% requires effective measures such as reducing the supply kinks and unemployment rate.
Macroeconomic Forecast
The economic forecast by the Congressional Budget Office is crucial in predicting what is expected of the economy in the future. It is essential to delve into various analyses to understand future performance better. Over two to three years, it provides projections for GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates while incorporating information from authoritative sources such as the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) and the Federal Reserve Board.
The path of GDP growth rate over the next 2 to 3 years is determined by a wide range of factors such as the phasing out of fiscal stimulus, business investment, consumer spending, and global economic conditions. According to the CBO’s Economic Outlook and other economic assessments, GDP growth will maintain its pace in the short run, driven by additional fiscal measures focusing on infrastructure investments and stimulus programs.
Inflation has risen to multi-year highs recently, partly due to factors like supply shortages, increased demand, and rising fuel prices. The predicted average for the inflation rate is at 2%. This aligns with the Fed’s target of 25 in the future.
Unemployment Rate Forecast
The unemployment forecast allows for incorporating labor market dynamics, demographic trends, and the speed of economic recovery. The inflation rate prediction is slightly low, and there is an increase in GDP growth. However, according to CBO, the employment rate is determined by other factors and non-monetary policies. Investigating the various adverse outcomes that might influence the employment rate is essential. However, the FOMC predicts the unemployment rate will grow between 5.2% and 6%. This is a high chance that the economy will operate. There is no constant prediction factor for the evaluation of the unemployment rate in the future since due to the many factors affecting the economy performance.
The interplay between the various economic factors determines the measure and prediction of the economy’s future performance. The significant factors to consider in determining the growth rate are GDP, inflation, and unemployment. There is a prediction of an increase in the GDP growth rate and a 2% inflation rate. However, there is a challenge in predicting the future unemployment rate due to the factors affecting its performance. With this combination, there will be an increase in economic growth, which predicts a decrease in the unemployment rate.
References
Clarida, R. H., Duygan-Bump, B., & Scotti, C. (2021). The COVID-19 Crisis and the Federal Reserve’s Policy Response. Finance and Economics Discussion Series, 2021(034), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.17016/feds.2021.035
What did the Fed do in response to the COVID-19 crisis? (n.d.). Brookings. https://www.brookings.edu/articles/fed-response-to-covid19/#:~:text=Temporarily%20relaxing%20regulatory%20requirements%3A%20The
Brookings (n.d.) Unlocking new federal infrastructure funding to drive green workforce development. Retrieved February 21, 2024, from https://www.brookings.edu/articles/unlocking-new-federal-infrastructure-funding-to-drive-green-workforce-development/#:~:text=The%20Brookings%20Federal%20Infrastructure%20Hub
Sheiner, L. E., Campbell, S., Alcalá Kovalski, M., & Eric , E. (2021). How pandemic-era fiscal policy affects the level of GDP. Brookings. https://www.brookings.edu/articles/how-pandemic-era-fiscal-policy-affects-the-level-of-gdp/#:~:text=The%20largest%20boost%20to%20GDP
Justin, B., Jared, C., Adi, K., Nehal, M., Sara, O., & Julia, S., (2022). What’s in the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) 2022 | McKinsey. Www.mckinsey.com. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-sector/our-insights/the-inflation-reduction-act-heres-whats-in-it#:~:text=The%20Inflation%20Reduction%20Act%3A%20Here
FRB: Monetary Policy Report, February 29, 2012 – Part 3: Recent Developments and Outlook. (n.d.). Www.federalreserve.gov. https://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/mpr_20120229_part3.htm
The White House. (2021, August 3). UPDATED FACT SHEET: Bipartisan Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. The White House. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2021/08/02/updated-fact-sheet-bipartisan-infrastructure-investment-and-jobs-act/
The White House. (2022, August 16). Inflation Reduction Act Guidebook. The White House. https://www.whitehouse.gov/cleanenergy/inflation-reduction-act-guidebook/
Bernanke, B. (2023, June 13). What caused the U.S.U.S. pandemic-era inflation? Brookings. https://www.brookings.edu/articles/what-caused-the-u-s-pandemic-era-inflation/
 write
write