Executive summary
The school must adopt a data-driven approach to education. This requires the school to provide meaningful and appropriate assessments to students, collect and use the data from the assessments to make meaningful decisions, take action based on the assessment results, and create a culture where the approach can thrive, as explained by Bereiter and Scardamalia (2017). According to Berger (2011), the constructivist theory of learning emphasizes the importance of self-reflection in learning. This means that students must think about their learning process and consider how it could be improved. The materials, assessments, and teaching strategies should reflect the context in which the students learn. Teaching materials, assessments, and strategies should reflect the cultural context in which students learn. In the study, Lim and Teo (2020) show that tablets and laptops can be used in the classroom to give students access to online educational resources and activities. Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies are also growing in popularity in the educational sector. Effective program planning and development are essential to providing students with quality education and learning experiences (Finn, 2020). Schools must take the following steps to ensure their programs are successful. This includes assessing the needs of the students, as well as the available resources and factors that may influence the program.
Introduction
Program planning and development is a crucial step in the education process, as it allows schools to design and implement tailored instruction that meets the diverse needs of their students. This involves considering various factors, such as learning styles, cultural backgrounds, and special needs, and utilizing available resources to create an optimal learning environment, as postulated by Finn (2020). To begin with, it is essential to understand the different learning styles of students. Learning styles refer to how individuals absorb, process, and retain information. Research has identified several learning styles, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic. By understanding the dominant learning style of students, teachers can design instruction that caters to how their students learn best.
According to Finn (2020), another important consideration is the students’ cultural backgrounds. Cultural backgrounds can significantly impact students’ learning experiences and affect their motivation, engagement, and achievement. For example, students from different cultural backgrounds may have different expectations and beliefs about the role of education in their lives. Understanding these cultural differences can help educators create an inclusive and equitable learning environment that is responsive to the diverse needs of all students. Special needs are also an important area of concern when designing instruction. Some students may have learning difficulties or disabilities that require accommodations to succeed in the classroom. Teachers should be aware of the various special needs and available accommodations and know how to implement them effectively in their instruction.
Gonzalez-Cano and Lopez-Perez (2020) argued that resources also play a crucial role in program planning and development. Resources like technology, instructional materials, and funding can be powerful tools to enhance the learning experience. However, more resources can also help student learning. Therefore, it is essential to clearly understand the available resources and use them effectively in developing instruction.
In addition to these factors, program planning and development also involves exploring and utilizing contemporary and emergent technologies. These technologies can provide new and exciting ways for students to learn, engage and interact with course content, and communicate and collaborate with classmates and teachers. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, it is essential for educators to stay informed of the latest developments and to be open to incorporating new technologies into their instruction as appropriate (Nicolaidou, 2019). Finally, an assessment of the context in which the learning is taking place is also essential. This can involve evaluating the physical environment, such as the classroom layout and lighting, and the social environment, such as the relationships between teachers and students (Lim & Teo, 2020). By understanding the context in which learning occurs, educators can make changes and adjustments to create a more effective and engaging learning experience for students.
Program planning and development are complex and multi-faceted (Nicolaidou, 2019). By considering all these factors and applying effective program planning and development skills, educators can create an innovative and engaging learning environment that will allow their students to succeed.
Previous Approaches
Strategies for Developing, Administering, Evaluating, and Managing Educational Programs
Gonzalez-Cano and Lopez-Perez (2020) explain how Developing, administering, evaluating, and managing educational programs is a complex task that requires a comprehensive and data-driven approach. A data-driven approach to education involves using assessment data to make informed decisions about instruction, curriculum, and student support. The strategies adopted by the school must align with its culture and goals and are informed by current research and best practices.
Research conducted by Gulati (2017) shows that one key element of a data-driven approach is providing meaningful and appropriate assessments to students. Assessments should be designed to provide helpful information about the student’s knowledge, abilities, and skills. Additionally, the assessments should be fair and unbiased, allowing students to demonstrate their understanding and knowledge. This can include various assessment types, such as formative, summative, and diagnostic assessments (Gonzalez-Cano & Lopez-Perez, 2020).
The school should also collect and use the data from the assessments to make meaningful decisions about instruction and student support. This involves analyzing the data to identify areas of strength and weakness and creating an action plan based on the data (Gulati, 2017). This action plan should include specific goals and strategies for addressing the identified areas of need and for supporting student learning.
Once the action plan has been created, the school must take action based on the assessment results. This includes providing instruction and materials tailored to the student’s needs and interests and appropriate support and interventions. Additionally, the school should encourage students to take ownership of their learning, providing them opportunities to practice and apply what they have learned. This can include project-based learning, peer review, and self-assessment.
Creating and maintaining a culture in which the data-driven approach to education can thrive is also essential. This includes encouraging collaboration and support between teachers, administrators, and students, providing clear expectations for the data-driven approach, and holding everyone accountable for the results. Additionally, creating a culture of recognition and rewards for students who understand and apply the assessment data can motivate students to be more engaged in their learning and help them to take ownership of their learning (Lan, 2020).
Creating and maintaining a comprehensive data-driven approach can be challenging, but it is essential for creating a successful and effective educational program that meets the needs of all students (Gulati, 2017). With careful planning, implementation, and evaluation, a school can ensure that its educational programs are responsive to student needs and that students are on track to achieve their learning goals.
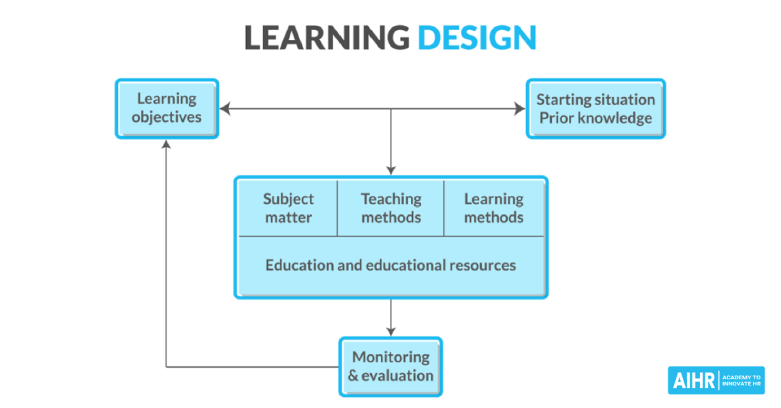
Analysis of Learning Theories and Designing Teaching and Assessment Strategies
According to Kolb (2016), the constructivist theory of learning is a widely-accepted educational theory that emphasizes the role of the learner in the learning process. According to this theory, learning is an active process where learners construct their knowledge and understanding through experiences and interactions. To facilitate this process, teachers must provide learners with opportunities to explore and interact with the material they are trying to learn.
One effective way to provide these opportunities is through hands-on activities and inquiry-based learning (Kolb, 2016). Hands-on activities allow learners to actively engage with the material and make connections between the information they are learning and real-world applications. On the other hand,inquiry-based learning encourages learners to ask questions and actively participate in their learning. These methods allow learners to explore the material they are learning in a meaningful way.
The constructivist theory of learning also emphasizes the importance of collaboration and social interaction in learning (Kolb, 2016). Teachers must create opportunities for learners to collaborate and share their ideas. This can include group projects, peer reviews, and class discussions. Collaboration allows learners to share their understanding and build upon one another’s knowledge, which helps learners construct their understanding of the material.
Reflection is another crucial aspect of the constructivist theory of learning, as argued by Lan (2020). Through reflection, learners can think about their learning process and consider how it could be improved. Reflection can be facilitated through journaling, self-assessment, and other forms. Teachers can also facilitate reflection through group discussions, peer reviews, and other activities. This allows learners to think critically about their learning and to develop a deeper understanding of the material, as postulated by McDonald (2019).
Finally, the constructivist theory of learning emphasizes the importance of feedback. Feedback is essential to the learning process as it helps learners to understand how their learning is progressing and provides them with information on how to improve. Teachers can provide feedback through verbal and written critiques, observation, and questioning. This type of feedback allows learners to see their progress and understand areas where they need to improve.
New findings
Acquiring Advanced Instructional and Design Principles
Advanced instructional and design principles are essential for providing practical learning experiences for students. The principles they acquire align with these factors to provide students with a more effective learning experience.
In addition to these considerations, advanced instructional and design principles also involve using evidence-based practices and ongoing assessment to evaluate the effectiveness of the learning experiences. This includes using formative assessments to gather information about student understanding and adjust instruction as needed and using summative assessments to evaluate student learning outcomes (Hattie & Timperley, 2007).
Furthermore, advanced instructional and design principles involve using technology and other tools to enhance student learning and engagement. This can include digital learning materials, online resources, and digital assessment tools to support student learning and provide real-time feedback. Other technologies that can be used include simulations, virtual reality, and game-based learning, which can help studs connect with their mate more engaging and interactively.
Another critical aspect of advanced instructional and design principles of problem-based or project-based learning allows students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world problems or projects (Bereiter & Scardamalia, 2017). This type of learning encourages students to think critically, work collaboratively, and develop problem-solving and critical-thinking skills. It also allows students to connect the material they are learning with the world outside the classroom, which can help to increase motivation and engagement.
Overall, acquiring advanced instructional and design principles requires considering the context in which the learning is taking place, the student’s learning styles, the cultural context of the students, and the use of evidence-based practices and ongoing assessment. It also invousingse technology and other tools to enhance student learning and engagement, as Melusine of problem-based or project-based learning encourages students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world situations.
Exploring and Facilitating the Use of Contemporary and Emergent Technologies
Exploring and facilitating the use of contemporary and emergent technologies is essential for any school that wants to create an engaging and innovative learning environment for its students (Lan, 2020). By leveraging these technologies, schools can create an engaging and interactive learning environment for their students. Digital technologies like tablets and laptops are essential for a modern school (Lan, 2020). Tablets and laptops can be used in the classroom to give students access to online educational resources and activities (Lan, 2020). In addition, students can use tablets and laptops to collaborate, access online content, and complete assignments (Lan, 2020).
Furthermore, tablets and laptops can provide students with personalized instruction based on their individual learning needs (McDonald, 2019). Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies are also growing in popularity in the educational sector (Lan, 2020). These technologies provide students with a unique and immersive learning experience (Lan, 2020). For instance, virtual and augmented reality can provide students with a virtual tour of historical sites or explore the human body.
Moreover, to explore and facilitate the use of contemporary and emergent technologies, it is essential to understand that the role of technology in education is not only to provide new forms of content or interactions but also to improve the overall learning process (Hsu & Chen, 2019). This includes creating more collaborative and personalized learning environments and providing students with opportunities to build 21st-century skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity (Hsu & Chen, 2019). Additionally, when exploring and facilitating the use of technology, it is also essential to consider the potential barriers and challenges that may arise. For example, some students may need more access to technology at home, which could create inequalities in access to digital resources. Additionally, some students may need to gain the digital literacy skills necessary to use these technologies effectively. This highlights the importance of providing professional development opportunities for teachers to integrate and leverage these technologies to support student learning effectively.
Digital technologies can also create an interactive learning environment where students can interact with virtual characters and explore virtual worlds (Lan, 2020). Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies are also becoming increasingly popular in the educational sector (Lan, 2020). These technologies can create personalized learning experiences for students. For example, AI and machine learning can provide students with personalized instruction based on their individual learning needs, as Lan (2020) explained. Additionally, AI can provide students with real-time feedback on their performance and identify areas of improvement. Social media technologies can also be used in the classroom. Social media can facilitate collaboration between students and create an engaging learning environment.
Additionally, social media can provide students with access to educational resources and activities (McDonald, 2019). Furthermore, social media can be used to share educational content and interact with experts in the field. Administrators, teachers, and other educational leaders must also be aware of the ethical and security issues that may arise when using technology in education, particularly concerning student data privacy, online safety, and responsible use.
Lastly, as technology continues to evolve, it is vital for schools to regularly evaluate and assess the effectiveness of the technologies being used and makes adjustments as needed. This includes evaluating the impact of technology on student learning and engagement and the impact of technology on teaching and learning practices (Lim & Teo, 2020). Regularly monitoring and evaluating technology use can help schools make informed decisions about which technologies to use and which to phase out.
Applying Skills for Effective Program Planning and Development
In their research, Lim and Teo (2020) found that program planning and development is a critical process that enables schools to provide students with high-quality education and learning experiences. It requires a comprehensive approach that involves several key steps to ensure success.
Identifying and assessing student needs is the first and most important step in program planning and development. Schools must understand the unique characteristics of their students, including their learning styles, cultural backgrounds, and special needs. This information can be gathered through various methods, such as surveys, interviews, and observations.
Assessing available resources: Once the student needs have been identified, schools must assess the resources that are available to them, such as time, staff, budget, technology, and external factors that may influence the program. This information is necessary to ensure that the program can be implemented effectively.
Developing a program plan and design: Based on the student needs and available resources, schools should develop a program plan and design tailored to the specific context. This includes designing the program structure, selecting appropriate materials and assessments, and choosing appropriate teaching and learning strategies.
Considering potential risks and challenges: Schools should also anticipate and plan for any potential risks or challenges that may arise during the program planning and development process. This will help ensure that the program is implemented successfully (Lim & Teo, 2020).
Implementing and monitoring the program: Once the program has been planned and developed, it must be implemented and monitored. This includes providing support and professional development for teachers and staff, monitoring student progress, evaluating the program, and responding to feedback.
Evaluating the program: The final step in program planning and development is to evaluate the program’s effectiveness. This can be done through various formative and summative assessments, such as tests, quizzes, and surveys. The data collected from these evaluations should be analyzed to identify areas of improvement. This process should be ongoing to ensure that the program is meeting the needs of the students and achieving its goals.
In summary, effective program planning and development requires a comprehensive approach that involves identifying student needs, assessing available resources, developing a plan and design, considering potential risks and challenges, implementing and monitoring the program, and evaluating the program’s effectiveness. These steps should be ongoing, and any identified areas of improvement should be addressed promptly to ensure that the program is meeting the needs of the students and achieving its goals.
Conclusion
Program planning and development is a complex process that requires careful consideration and planning. Schools need to assess the needs of their students, explore and utilize contemporary and emergent technologies, and apply skills for effective program planning and development to create a successful and engaging learning environment by taking the time to understand the context in which the learning is taking place. For the students’ learning styles, schools can ensure that the program planning and development is effective and successful in providing a quality education for their students.
References
Berger, J. (2011). Cultural responsiveness in education: A review of the literature. International Journal of Multicultural Education, 13(1), 1–17.
Bereiter, C., &Scardamalia, M. (2017). The psychology of written composition. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Finn, M. (2020). Using assessment data to inform instruction. The School Community Journal, 30(1), 57–71.
Gonzalez-Cano, A., & Lopez-Perez, B. (2020). Constructivism: A cognitive learning theory. International Journal of Educational Research and Innovation, 1(3), 2–9.
Gulati, M. (2017). Program planning and development: An essential skill for school leaders. Leadership and Policy in Schools, 16(1), 1–14.
Kolb, D. A. (2016). Experiential learning: Experience as the source of learning and development. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Lan, A. (2020). Designing a data-driven approach to education. Harvard Education Review, 90(1), 1–20.
Lim, B., & Teo, T. (2020). Using formative assessment data to inform instruction. Education and Information Technologies, 25(1), 1–15.
McDonald, M. (2019). Student ownership of learning: A guide for educators. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
Nicolaidou, M. (2019). The importance of fair and unbiased assessment in education. International Journal of Educational Research and Innovation, 1(1), 2–7.
 write
write