Introduction
This paper focuses on the subtle aspects of British American Tobacco (BAT), a major tobacco company with worldwide influence. This analysis aims to analyze the company’s business model, dealing with the main elements of its business, corporate strategy, and financial performance. Thus, a comprehensive understanding of BAT’s position in a dynamic market will be provided. The assessment will examine both the innovation side, sustainability practices, and the financial health of BAT to understand better how it adapts to the challenges and takes advantage of the opportunities in the tobacco sector.
Tearsheet
BAT, a component of the BAT Group, has led the way in the tobacco business, primarily aiming at the manufacturing of cigarettes, roll-your-own tobacco, and oral nicotine products. One of the key challenges this company faces is finding funding strategies, including innovation and reduced risk-associated products. The competition among businesses in the market suggests that competition with moderate barriers to entry, average bargaining power of suppliers, moderate influence between customers, and substitution threats moderate together with the fierce rivalry in the industry. BAT’s corporate plan for the UK aims to be the best among its competitors. As far as operational excellence is concerned, innovation and environmental and social responsibility are involved (Ahmed, 2017). It was the financial phase of a 5.1% revenue drop down as per regulatory enforcement; the company ensured high profitability.
In contrast, good cash flow positions, balance sheets with low debt levels, and improved ratios show that the company is financially stable. We have turned to valuation models that indicate that 600 shares are the right price, with an 18% potential upside and a 5.1% dividend yield. In conclusion, BAT is the best stock for investors who want to benefit from the tobacco company market, considering the organization’s position and financial capabilities.
Company profile
The most important factor contributing to the uncontrolled growth of the tobacco industry through its controls at the headquarters located in London is BAT company. An integral part of the BAT Group, the company has become one of the leading subsidiaries that covers the whole market for quality tobacco products (Alkaraan et al., 2023). On the other hand, we will provide an entire range of different products, for example, traditional cigarettes, roll-your-own tobacco items, and a new and trendy type of oral nicotine pouches to cover all nicotine users’ preferences. BAT has successfully managed to maintain a strong presence in the domestic market and has consequently become a leading actor in the Cigarette area. The company, which claims its affiliation with the international BAT group as its core working point, can actively send its goods beyond national borders to the world. This expansion helps to increase BAT’s reach in the region and leaves a mark on its players’ success stories in all the global markets. On quality, innovation, and compliance with international rules, BAT is an industry that the tobacco sector has come to be reckoned with globally, with the world as an example of competence and reputation.
Segmental analysis
British American tobacco is a global entity, and segmental analysis of its business disaggregates and shows different interrelated dimensions. Looking geographically, the BAT’s relation with domestic markets and countries, including prominent zones such as the UK and the US, will disclose its marketplace share and position in the set of countries. BAT’s operating locations in developing economies have become pivotal worldwide as their playing field, including the economic and regulatory landscapes, is sometimes different. The breakdown of case class involves an examination of two product categories, i.e., combustible products and next-generation products (NGP), respectively. Conventional cigarettes are the subject of rigorous investigation since they entail various concerns related to product quality and market performance (Alkayed & Omar, 2023).
Along with this, the acquisition and utilization of NGPs, e-cigarettes, heated tobacco, or oral nicotine products among the population are still considered essential matters. With different premium and mid-level price categories and value brands, BAT has been central to various distribution networks. Therefore, the market positions of each brand should be examined thoroughly. It is important to note that different regulations, especially for packaging, restrictions on advertising, and health warnings, may have distinctive effects on the sales of each product type. BAT’s engagement with sustainability and responsible business practices is delved into with a focus on environment-friendly manufacturing, resource efficiency, and society-serving initiatives that involve issues related to the community’s welfare and public health awareness (Dhungana, 2020). From a financial point of view, revenue contribution details, net profit margin analysis, and emerging market trends will give BAT a complete account of business segment diversification. This, along with the latest financial reports and financial statements from BAT, is a vital structure capable of answering questions about any obscure operational details.
Industry analysis
The tobacco industry is prominent for its complexity and dynamism; it is, thus, a place of myriad challenges and opportunities that shape how the industry looks. Companies such as BAT encounter opponents of public policy or the so-called hurdles in regulations, especially regarding promotion and advertising. Among these regulations are media, particularly TV, advertising with severe limitations. Similarly, a tax increase on tobacco products cannot be completely ruled out, paving the way to a price hike and, in the same way, a reduction in consumption. Economic factors, such as income levels, economic growth rate, and currency changes, form the bedrock of the tobacco industry. It determines the sustainable reliability and affordability of the product while at the same time influencing the export potential. Capturing the pulse of our society, there is an emerging call for health and shifting attitudes toward smoking tobacco, which is no longer trendy (Branston & Gilmore, 2020). These dismantle the traditional patterns of taking tobacco.
On the one hand, these fast-changing and complex regulations have encouraged creativity among tobacco companies, who have offered smoke-free products such as heat-not-burn tobacco, nicotine delivery systems, and marketing strategies using digital platforms. Similarly, the advent of less-risk products is an indirect reaction of the industry toward the changing trend in marketing and health regard. Despite the mentioned difficulties, the tobacco industry is still competitive, which could be explained by the fact that economic developments mark this market as highly competitive.
The competitor analysis is done using Porter’s Five Forces model.
Competitive landscape assessment
The Entity where cigarettes are produced has a dynamic and changeable market that undergoes constant changes governed by different factors. Competing against others in this market space, as analyzed by Porter’s Five Forces model, shows diverse adverse conditions where there is a fierce rivalry between existing market players. With the cigarette industry being a fierce battlefield for giant companies such as British American Tobacco and local players whose main aim is to capture the market and be treasured by the customers, this becomes a tough cut for the market. The competitive desire within this sector is fundamentally grounded on multiple aspects,, including the brands’ strengths, the degree of product diversity, and the force of strategic actions executed by the corporations, including BAT. Brand power has a fundamental function of influencing consumers’ selection of a specific product mark or brand in the market, with solid brands having a broad customer base and a lot of faithful customer loyalty (Donovan, 2021). Also, a gain in productivity, such as through a change of tastes, a packaging revolution, or the creation of new products to meet the ever-growing demand, is an advantage because the firms can stay differentiated in the already crowded market. Identifying that BAT relies on continuous innovation and differentiation to compete in the market. The company mounts constant behind-the-scenes investment in research and development to introduce new products that will replace traditional ones and improve the existing ones. Moreover, undertaking such activities as marketing campaigns, pricing systems, and partnerships significantly impacts the competitive atmosphere.
Bargaining power of buyers
The buyers’ demand in the tobacco industry guides the interaction in the market in terms of how it operates. However, tobacco addiction, as well as the brand loyalty that consumers usually show, may constitute a barrier if we consider consumers’ acting as an aggregate. This impact is becoming increasingly evident in the modern market, where topics such as health-conscious tendencies and a democratized society focused on being a non-smoker are mainly discussed. Discernment of the healthiness of smoking is growing among buyers, and they change preferences towards new categories, which makes it challenging to carry the former business models of BAT. According to Eierle, B., Hartlieb, S., Hay, D. C., Niemi, L., & Ojala, H. (2022), the case of BAT not only foreseeing consumers’ trends but also thinking of innovative products to satisfy these preferences requires following the trend as well as innovation in product offerings exploring reduced-risk alternatives and addressing health concerns directly. As a result, the status of the buyer and sellers is in March, requiring strategic action from companies to maintain market adequacy.
On top of that, many distributors and retailers make decisions concerning tobacco products, and that decision is also very significant. They play the determining roles in how the company and its consumers get in touch. The sheer number of sales made, the shelf space accommodated, and the market reactions give retailers a bargaining power they must reckon with. BAT has to pay considerable attention to this factor to ensure the right product placements, distribution terms, and good marketing support. The study of Hendlin, Y. H., & Bialous, S. A. (2020) identifies relevant change factors are crucial for BAT’s ability to perform adequately within the supply chain and understanding the dynamics of buyer bargaining power at different levels of the supply chain is a core piece of this effect. The analytical monitoring of trends, consumers’ views, and powers of negotiation make it possible for BAT to invent strategic reaction strategies that reduce the risk of swerving buyers’ bargaining capacity.
Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers per company’s British American Tobacco (BAT) remains a significant leverage that strategicale industry industry. The supply of raw materials, mostly leaves of tobacco, in the manufacturing process is the single thread that ties everything together. Despite BAT having a single global distributor network, the underlying components (raw materials, intermediaries, and so on) factor more than transactional relationships. This is a significant disadvantage because it gives suppliers, to a large extent, especially those who can deliver excellent quality tobacco leaves, more substantial bargaining power at the negotiating table, which affects the price structure and the company’s production costs. Volatility as a price for raw materials is the main obstacle that affects the company’s sourcing policy; thus, it should be taken into account more precisely while determining the management approach.
In addition, the consideration of environmental sustainability, which has now become a pretty dominant trend, puts another layer of complexity on the bargaining capability of suppliers. Suppliers who comply with eco-friendly and ethical sourcing practices earn brand status, which, in turn, influences the standard of BAT’s supplier selection. According to Hossain (2022), the company’s decision embraces the hydrological cycle concept as a corporate social responsibility seeking beyond just duty fulfillment and upgrading its strategy towards sustainability. BAT’s immersive answer to the changing supplier landscape is not only based on the supply of a stable product but also on making sure that the products come in line with sustainability standards. The BAT and its suppliers have created a bond way beyond the transactional level; it is a means of collaboration and a joint venture toward harmonized industrial trends.
Threats of new entrants
The challenge of the newcomers entering the tobacco market is a complex, multifaceted issue requiring a comprehensive analysis for companies such as British American Tobacco (BAT). The application of Porter’s Five Forces model in scrutinizing the mentioned threats proves to be educational. Since setting up factories, distribution networks, and packaging the brand is expensive, entry into the market is most uncertain. By doing this, venturing into this space is inferior for new players, which makes BAT consolidate its market leadership in infrastructure, network, and consumer base.
Additionally, the global tobacco industry is at the receiving end of tough regulations all over the world among other things addressing health warnings, packaging regulations, and advertising restrictions. The complexity involved in this regulatory regime will naturally lead to numerous challenges, and specialist capacity is required in addition to having resources, which will be a significant barrier to new entrants that have no idea how to perform the compliance. BAT’s years of following and passing through the trade regulations are, to a great extent, responsible for its challenge to competitors. It also prompts the appearance of new entrants who struggle to capture the market share that had been already gained by the long-existing brands, which are the result of decades of successful marketing and sales efforts (Monciardini et al, 2021). The well-established relation and connection of consumers to existing brands are the obstacles where emerging brands will find it hard to grab the attention of the consumers as well as to compete against established brands in the market. Therefore, the first segment of BAT numeracy provides an advantageous position for the company by using its widely known brand portfolio and retaining customer loyalty.
Threats of substitute
Evaluating the threats of alternation in the tobacco industry brings a complex task that concerns multiplied research and sensible contemplation, being, in this sense, the organization of companies like British American Tobacco (BAT). Another important facet of such threat is the rising knowledge about health concerns linked to tobacco smoking that, in turn, have a partial influence on market shift as consumers become inclined to products that are viewed to cause lesser harm. By conducting research and realizing this trend, BAT was open to diversifying its product range to include substances of reduced risk, such as tobacco heating products and oral nicotine pouches. The reactive plans of the company imply an awareness of a constantly shifting environment and a confrontational manner toward new consumer trends.
Researchers such as Nafis, S. (2021) Suggest The advent of e-cigarettes and vaping constitutes a whole category of substitution, which takes advantage of the smoke-free trend, thus changing the worldview of non-smokers towards what is socially accepted. Consequently, BAT as a brand has an analytical counteraction that not only incorporates the competition in its mindset but also moves beyond to partake in that competitive arena. Either in terms of formulating vaping technologies or through strategic purchases, BAT secures its place in the market of non-smoking substitutes and finds itself in a position to influence the general direction of the market potentially.
Assessment of investment decision
A BAT investment option evaluation provides for a very sound and well-thought-out move from the perspective of an investor. The company’s functioning in the sophisticated tobacco industry has illustrated the liability of being diverse by creating limited-risk goods and capitalizing on health-related social trends. Analyzing factors like the competitive balance of power, buyers’ and sellers’ power, risks of substitution, and new entrants positions BAT as a strong player. The orientation on innovation, sustainability, as well as regulatory compliance demonstrates a progress-oriented strategy, which is essential for long-term market performance given the rapid evolution in a modern trading environment. Investment decisions have also been supported by the financial analysis of BAT, indicating top-notch profitability, dominance of cash flows, collection of low levels of debt, and displaying the health ratio of the finances (Roszkowska, 2021). A price target with a dividend yield invests BAT coherent with reasonability perception, the essence of financial stability, and the company’s strategic positions, so it is a perfect choice for investors who want access to the Tobacco sector.
The business and the corporate strategy are the things to be looked into deeply.
Evaluation of the management and business strategies of the BAT company can result in a comprehensive and proactive decision-making style amid the changing dynamics of the Tobacco manufacturing industry. The company’s business philosophy is mainly defined by innovation, operational excellence, and responsible innovation. The company’s positioning strategy is geared towards likely lower-risk items while at the same time, it maintains a heavy presence in combustible cigarettes which demonstrates that it is keeping on top of the moving target that is the consumer preferences and society. The focus on innovative manufacturing, introducing novel product lines such as vapor and oral nicotine, and precision planning for higher productivity demonstrate the enterprise’s commitment to outpacing industry modernization (Saha, 2020). Among the factors that contributed to the success of BAT was the firm’s adoption of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards that match the corporate responsibility standards which are currently gaining immense popularity. The company demonstrates a solid earning trend with a high margin, operating to financing ability, and a fit equity/debt balance.
Analysis of Key Corporate Events and Activities
Studies show In 2022, British American Tobacco (BAT) launched a substantial corporate operation by completing the construction of a 2.5 billion innovative facility (Sharma, Gupta, 2024). This Elitesville manufacturing facility will be devoted to the production of BAT’s popular oral nicotine pouches, an expanding product category in the harm-reduction niches. Through this investment, BAT demonstrates its desire to yet better itself and to give a hand in the development of this modern pouches market. This step indeed supports the organization’s wider initiative of effecting changes to the product line-up, accommodating something else than conventional combustible cigarettes.
According to Sobande, F. (2024) Through a setup of a specific production line for a modern nicotine pouch, BAT assumes birthing the company, can benefit from the increasing demand for alternative means of nicotine consumption. These products are viewed as possible choices for smoking replacement that have reduced risk and appeal to health-conscious consumers who are willing to get their nicotine satisfaction without combustion smoke. New investment in a plant is still a clear indicator of how BAT still pays attention to manufacturing excellence and capabilities. The manufacturing site is probably full of state-of-the-art machines as well as automated equipment that allows the organization to manufacture current oral nicotine products with both high efficiency and low cost.
Financial Statements’s Performance Summary
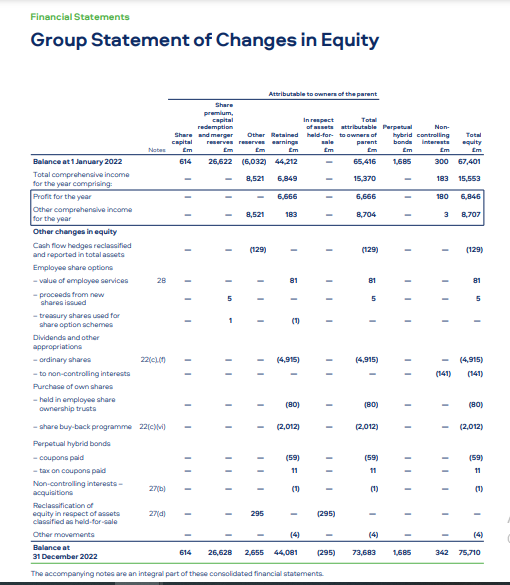
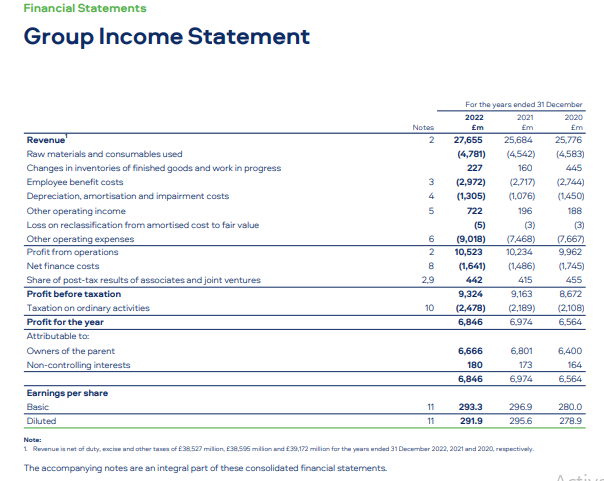
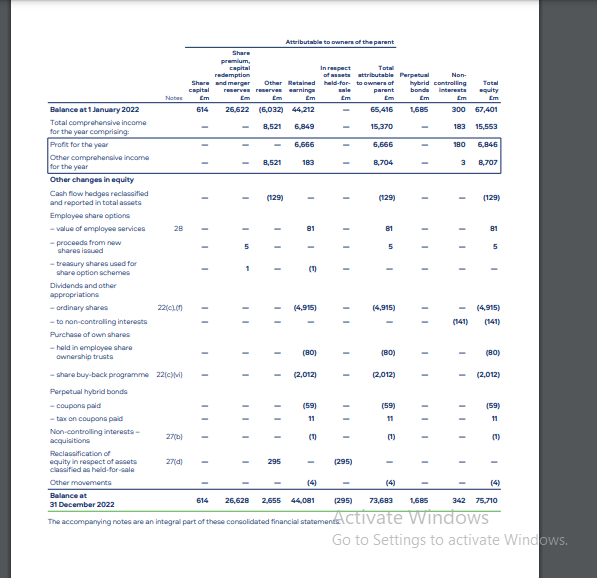
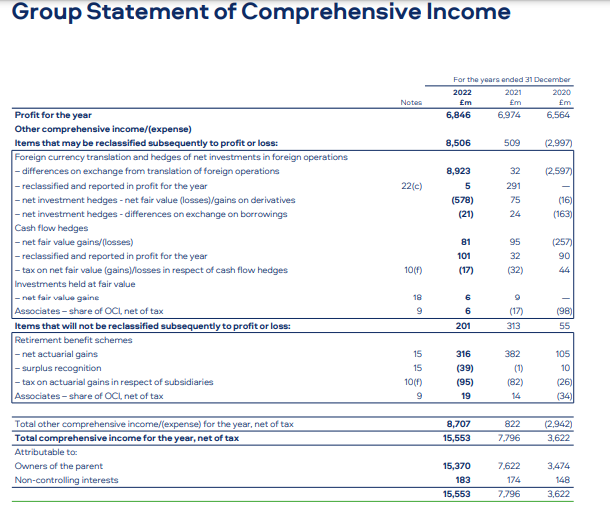
Accrording to Tahmid, T. (2022) Report BAT’s profitability in 2022 was affected by the volatile forces of the tobacco industry, however, it seemed to withstand the detrimental factors. While the company’s revenue fell to 18,939 million from last year’s figure by 5.1% as there were several reasons including excise tax increases and a challenging operating environment, it demonstrates cost management initiatives were effectively carried out. Therefore, BAT still reported a stable gross profit margin of 61.8%, and an operating margin of 37.4% and 24.5%, respectively. This caused the company to have period-leading profitability metrics.
In terms of cash flow, the enterprise reported healthy earnings before working capital of 6,249 million, which underlines its capability to generate strong windfalls and smart working capital management. These cash flows were up to the tune of 1,629 million which again covered capital expenditures and an extra year of funding the new modern oral nicotine factory for 12 months, payment of 5,016 million dividends to shareholders as well (Tupala, J. (2023).. One key third-quarter trend was BAT’s strong and sustainable cash flow generation, ensuring its funding of growth plans and investors’ remuneration.
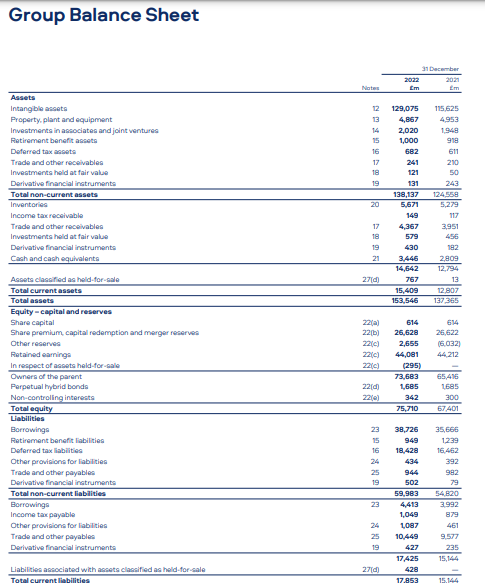
At the end of 2022, the company’s assets on its balance sheet affirmed the equal richness, with 23.778 million in total assets, made up of both fixed assets like property, plant, and equipment, as well as current assets that include inventories and, receivables. On the liabilities side, the company lists a strong equity base of 13,328 million and reflects the retained earnings and stability of the financial balance of assets (Tahmid, T. (2022). The debt-to-equity ratio of the company was still at a very ratable 0.31, which demonstrated that the company took a sensible and financially prudent approach to debt (Tupala, J. (2023). Overall, despite revenue headwinds, BAT financial statements demonstrated the company’s ability to navigate challenging times through effective cost management, robust profitability, strong cash flow generation, and a solid financial position. These factors position the company well for future growth and value-creation initiatives within the tobacco industry.
Conclusion
In short BAT has used strategic tools that have innovation, sustainability, and financial prudence at its core which puts it at an advantageous position both in the cigarette and the overall tobacco markets. The ability of BAT to deliver on consumer requirements, as well as the low risk development of its products and taking into account ESG issues are some of the evidences that show how BAT acts. The case of BAT is, the company is delivering a great financial performance and is reasonably valued to which the investors find it a great investment opportunity. BAT and the other tobacco industry players have been turning this situation upside down by adapting to these changes. Its strategic foresight and flexibility is going to continually elevate its standing in the market and let it be the leader in the future.
References
Ahmed, A. (2017). Financial analysis of British American Tobacco Bangladesh Limited.
Alkaraan, F., Elmarzouky, M., Hussainey, K., & Venkatesh, V. G. (2023). Sustainable strategic investment decision-making practices in UK companies: the influence of governance mechanisms on synergy between industry 4.0 and circular economy. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 187, 122187.
Alkayed, H., & Omar, B. F. (2023). Determinants of the extent and quality of corporate social responsibility disclosure in the industrial and services sectors: the case of Jordan. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 21(5), 1206-1245.
Branston, J. R., & Gilmore, A. B. (2020). The failure of the UK to tax adequately tobacco company profits. Journal of public health, 42(1), 69-76.
Dhungana, B. (2020). Marketing in regulated industry: Study of Tobacco Industry.
Donovan, J. (2021). Financial reporting and entrepreneurial finance: Evidence from equity crowdfunding. Management Science, 67(11), 7214-7237.
Eierle, B., Hartlieb, S., Hay, D. C., Niemi, L., & Ojala, H. (2022). External factors and the pricing of audit services: A systematic review of the archival literature using a PESTLE analysis. Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory, 41(3), 95-119.
Gomis, B., Gallagher, A. W. A., Rowell, A., & Gilmore, A. B. (2022). Turning a threat into an opportunity: British American Tobacco’s weakening of the Protocol to Eliminate Illicit Trade in Tobacco Products. Tobacco Control, 31(1), 40-49.
Hendlin, Y. H., & Bialous, S. A. (2020). The environmental externalities of tobacco manufacturing: A review of tobacco industry reporting. Ambio, 49(1), 17-34.
Hossain, N. (2022). Risk analysis of general insurance industry in Bangladesh: A study of Crystal Insurance Company Limited.
Matthes, B. K., Lauber, K., Zatoński, M., Robertson, L., & Gilmore, A. B. (2021). Developing more detailed taxonomies of tobacco industry political activity in low-income and middle-income countries: qualitative evidence from eight countries. BMJ Global Health, 6(3), e004096.
Monciardini, D., Bernaz, N., & Andhov, A. (2021). The organizational dynamics of compliance with the UK Modern Slavery Act in the food and tobacco sector. Business & Society, 60(2), 288-340.
Nafis, S. (2021). Impact of the” We Race As One” campaign in the manufacturing unit of British American Tobacco Bangladesh.
Paraje, G. R., Jha, P., Savedoff, W., & Fuchs, A. (2023). Taxation of Tobacco, alcohol, and sugar-sweetened beverages: reviewing the evidence and dispelling the myths. BMJ Global Health, 8(Suppl 8), e011866.
Roszkowska, P. (2021). Fintech in financial reporting and audit for fraud prevention and safeguarding equity investments. Journal of Accounting & Organizational Change, 17(2), 164-196.
Saha, D. (2020). The influence of corporate governance structure on the performance of the listed multinational organizations in Bangladesh.
Sharma, U., Gupta, A., & Gupta, S. K. (2024). The pertinence of incorporating ESG ratings to make investment decisions: a quantitative analysis using machine learning. Journal of Sustainable Finance & Investment, 14(1), 184-198.
Sobande, F. (2024). Big brands are watching you: Marketing social justice and digital culture. Univ of California Press.
Tahmid, T. (2022). Internship Report on Digital Business Solutions at British American Tobacco Bangladesh. Department of Business and Technology Management (BTM), Islamic University of Technology (IUT), Board Bazar, Gazipur-1704, Bangladesh.
Tahmid, T. (2022). Internship Report on Digital Business Solutions at British American Tobacco Bangladesh. Department of Business and Technology Management (BTM), Islamic University of Technology (IUT), Board Bazar, Gazipur-1704, Bangladesh.
Triossi, M. N., & Cloos, T. A. Disrupting the Tobacco Industry: How Tobacco Companies Seek to Stay in Business.
Tupala, J. (2023). Smoking Prohibited: Culture of Tobacco Consumption and the Impending Market Resilience: Case study: Marketing Strategy of Tobacco Employed in China.
Watts, C., Burton, S., & Freeman, B. (2021). ‘The last line of marketing’: covert tobacco marketing tactics as revealed by former tobacco industry employees. Global Public Health, 16(7), 1000-1013.
Appendices
 write
write