Introduction
The term “blockchain” is quickly becoming one of the most popular buzzwords in the world of medical technology. There is a valid explanation for this. In simple terms, blockchain technology can completely transform the healthcare industry. Patients will be able to take their rightful place at the heart of all procedures once it is fully implemented; as a result, those operations will be completely rethought to provide improved safety, confidentiality, and ease of access (Haleem et al. 2021). The report aims to identify and thoroughly analyse the necessity of blockchain solutions within the healthcare industry. As a result, it will suggest a blockchain solution model for the healthcare industry, provide a design proposal, and explain the essential governance mechanisms.
The Need for Blockchain Technology in the Healthcare Industry
In healthcare, the necessity and development are increasing at a faster rate. There is a demand for high-quality healthcare facilities supported by enhanced and cutting-edge technology. Blockchain will indeed play an essential role in reshaping the healthcare industry in this case. Furthermore, the healthcare landscape is shifting toward a patient-centered approach emphasizing two key aspects: always-accessible services and appropriate healthcare resources. Blockchain improves the ability of healthcare organizations to offer satisfactory patient care and high-quality healthcare facilities. Another time-consuming and repetitive process that contributes to high healthcare costs can be resolved quickly with this technology. Residents can participate in health research programs using Blockchain technology (Haleem et al. 2021). Furthermore, improved research and data sharing on public well-being will improve treatment for various societies. A centralized database should be applied to handle the entire healthcare system and organization.
The Role of Trust in the Healthcare Industry
Trust is important in healthcare environments since many people perform several jobs within the system, and arrangements are primarily relational. Patients, clinicians, insurers, suppliers, regulators, and other health system actors interact differently in healthcare settings. Because interactions between these persons shape the healthcare experience, trust is crucial in this situation. As Gilson points out, “trust is vital to health systems because it sustains the system-wide collaboration necessary for health production.” Lack of trust among healthcare personnel may lead to misunderstanding, inefficiency, growing expenses, and medical blunders, the consequences of which can mean the difference between life and death for certain patients. Establishing reliable connections among different partners within the health system is critical to ensuring the quality of treatment provided to patients (Gilson 2020).
Trust is also essential in healthcare settings with a principal-agent relationship. The principal-agent relationship is described as a “contract under which one or more individuals (the principals) employ another person (the agent) to execute some service on their behalf, which includes transferring some decision-making power to the agent.” This connection underpins interactions in healthcare environments where patients (the principals) seek treatment from physicians, nurses, and other healthcare personnel (the agents). Patients depend on agents to offer the treatment they need since they cannot address their conditions. Due to this connection, patients bear the danger that the agent may not behave in their best interests when making choices on their behalf. Patients must decide if they trust the practitioner to make the best treatment choices.
Role of Trust in Blockchain
Blockchain technology is often seen as the tool that will restore customers’ faith in businesses. Blockchain technology alone will not build trust, but blockchain components will contribute to the process. Immutability, decentralization, and transparency are the three pillars around which blockchain technology is founded. While these qualities will help build confidence, blockchain is still a relatively new technology; therefore, it has not yet proven its trustworthiness (Bianco et al. 2020). One of the most important aspects of creating trust is knowing how the data provided by the user is being utilized (Bianco et al. 2020). This is a common problem within the realm of big data.
The consortium network business model would be ideal for this suggested blockchain solution since it is sector-specific. Multiple organizations, each with their own set of adjustable contractual conditions, would administer the blockchain, resulting in increased value and visibility thanks to collaborative efforts (Tan & Saraniemi 2022). It will be helpful to form a consortium to investigate and produce a single industry standard, ultimately improving the industry’s overall efficiency (Malhotra & Elnakib 2021). In addition, the blockchain will have improved speed and experience, and permissioned and scalability concerns will not be an issue. Even though this will not be a private blockchain, it will nonetheless enable decentralization which will solve the critical problem of maintaining users’ and healthcare providers’ respective privacy regarding data collection and utilization (Tan & Saraniemi 2022). By having several contributors, the blockchain will incorporate various elements relevant to each organization, producing a more finely tuned system that will embrace more than just the aim of one organization.
Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain technology offers various applications and functions within the healthcare industry. The ledger technology assists researchers in the healthcare industry in deciphering genetic code by controlling the medication supply chain, supporting the safe transfer of patient medical records, and facilitating the secure transfer of patient medical data. The figure below illustrates the myriad of qualities and crucial enablers of the Blockchain concept in various healthcare sectors and its linked fields. Some of the technically derived and impressive features employed in the development and practice of Blockchain technology include the protection of healthcare data, various genomics management, electronic data management, medical records, interoperability, digitalized tracking and issues outbreak, and other similar features. Blockchain technology is used to develop and practice. The fully digitized qualities of Blockchain technology and the fact that it may be used in applications linked to healthcare are the primary reasons for its widespread acceptance.

Proposed Patient-Centered Blockchain System
Using blockchain technology, there is a proposal for a medical data management system that is safe and enables patients to maintain control over their data while providing healthcare providers with quick access to the patient’s medical information. The service is a decentralized platform that enables designers to run apps on a blockchain they have constructed themselves and serves as the foundation of our system (Ethereum Foundation 2018). It stores accurate medical records on decentralized cloud storage. In many cases, blockchains do not inherently provide adequate capacity. The service is created by combining the decryption key with the one-of-a-kind swarm hash associated with each medical record. Access to the material is restricted to only those who know the reference to the root chunk. Therefore, the root pieces are safely held in the form of smart contracts on the blockchain, and they are only made available after specific criteria have been met.
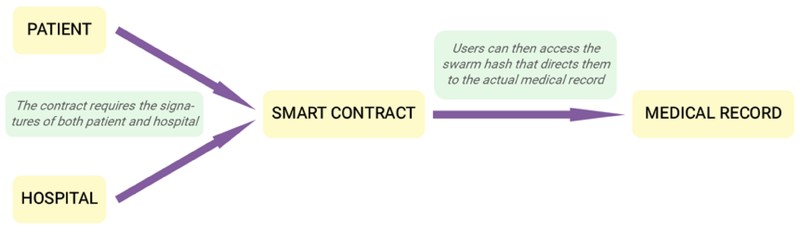
Figure 1 Overview of the Proposed Blockchain Model
It uses a multi-signature contract, also known as multisigs, in order to overcome the issue of data ownership and control. In order to authenticate a transaction using multisig, several customers, in this example, the patient and the healthcare provider, are required to utilize their respective confidential keys to sign the transaction. In this manner, the patient will not be able to make any changes to the record without the authorization of the hospital, but he/she will continue to have control over who has access to his information. Because the previous swarm hash is now public knowledge, it is necessary to construct a new swarm hash each time after the data has been read. Because of this, we include a timestamp that indicates when the data was most recently accessed. Any modification to the data will result in an immediate update to the swarm hash, which may then be protected once again until it has the necessary access permissions. This architecture not only delivers the immutability and security that blockchain technology provides, but it also gives a multisig answer to the problem of who owns the data and who has access to it.
Governance Mechanism for Blockchain
Governance on a blockchain is a necessary component in order to facilitate collaboration throughout the network. Governance in the blockchain is the complete set of rules that the participants agree upon to guarantee that the essential requirements of trust, control, transparency, and coordination are satisfied (Lumineau, Wang & Schilke 2020). The administration of a blockchain often falls into one of two categories: a permissionless network or a network that requires user authentication. The permissioned blockchain will be used for marketing purposes so that the company may maintain control over the information and protect the confidentiality of user data. The three main governance mechanism for blockchain include Business Network Governance, Technology Infrastructure Governance, and Network Membership Governance.
Network Membership Governance is a discipline that helps assure fast effectiveness in network processes, including support services, permissions, hazards, and a cost structure that is divided evenly depending on the actions of each member. Contributes to developing an interactive environment for healthcare workers, allowing them to fulfill business goals via a decentralized ledger, resulting in increased operational efficiency. In order to more effectively enforce equitable and healthy behavior inside the workplace, there is a need for rules and contracts (Lumineau, Wang & Schilke 2020).
Business Network Governance” refers to an external ecosystem that includes supplementary business networks and government regulatory organizations. These would include the structure of how the firm operates, the standards that are particular to the industry, and compliance with the law and regulations.
The third component is technology infrastructure, which focuses primarily on the information technology (IT) infrastructure, its resources, performance, security, and related risks. In most cases, this entails the process of establishing tools and procedures in order to guarantee that the business strategy of the organization is aligned with the technological infrastructure that is given in order to carry out everyday activities.
Risk and Challenges
Blockchain technology is unlike any previous technology, leading to reluctance to alterations and a lack of acceptance. The main challenge with blockchain implementation is the lack of understanding clients, and users have about the technology. As this blockchain is constructed around clients’ data, users will require a broader awareness of the system to simplify its usage and win confidence. Via the use of the consortium network business model, there will be better contact with patients via an extensive reach of each partner. A clear set of goals and standards must be projected to prospective customers to increase their understanding of why the system would assist them (Das et al. 2022). In addition, this blockchain will need particular guarantees to customers that although the model will attempt to keep clients’ data safe, they will be informed of any threats involved with safety, removing any possible ethical difficulties that may develop in the coming years.
The governance issues are size and complications, standards, and state restrictions. As blockchain constantly transforms, there is a lack of governance, laws, and standards for the systems. Standardisation across blockchain systems would be helpful in the continuing development of the technology, providing a sustainable structure and decreasing costs and hazards. As there is a lack of uniformity within the technology, the growth of trust and acceptance is decreased (Das et al. 2022).
Future Trends
Blockchain is expected to penetrate and revolutionize hospital operations in the coming years. As more healthcare providers use the technology, there should be more accessibility and quality to data with a higher possibility of standardizing. Using technologies based on Blockchain, transactions will be able to be validated and recorded in the following days, provided that all members of the network give their approval (Morey 2020). As the basis for the next generation of health information exchange, blockchain will bring the numerical security afforded by public and private key encryption down to the level of the individual patient. This technology has the potential to treat patient data, avoid intellectual property infringement, increase interoperability, rationalize processes, regulate medicines and prescriptions, and monitor medical supply chains. The use of blockchain technology in healthcare is anticipated to see phenomenal growth in the years to come (Das et al., 2022).
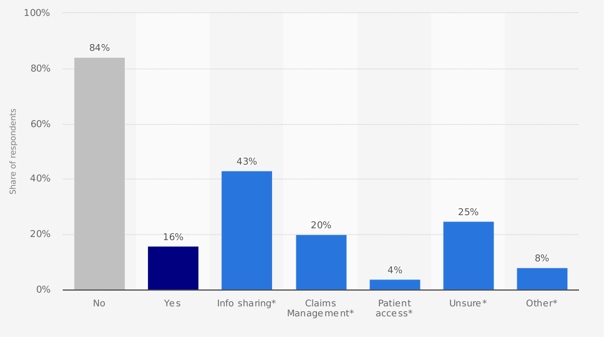
Figure 2 Awareness of Blockchain in Healthcare (Source: Statista 2018)
Conclusion
Blockchain technology can be applied to many different aspects of the healthcare system since it significantly increases security and accessibility. It can store and share insurance and medical records in healthcare facilities, mobile devices, remote monitoring systems, and clinical trials. There is little study on blockchain’s applicability in healthcare, but that research is growing daily. Blockchain is one of the most active areas of software development right now, and it has the potential to alter the hierarchy of healthcare by giving patients back control over their medical records and personal health information. Given that the blockchain movement for patients is only getting started, this power transfer may result in a general shift toward patient-centered treatment.
Reference list
Bianco, W, Gaddie, K, Rice, J, Shin, D, Stahl, H, Winecoff, R & Winecoff, WK 2020, ‘Incentivizing Innovation in a Knowledge Society, Social Science Quarterly, vol. 101, no. 7, pp. 2389–2397.
Das, L, Sharma, S, Yadav, SA & Dadhich, K 2022, Application of Blockchain Technology in an IoT-Integrated Framework, Information Security Practices for the Internet of Things, 5G, and Next-Generation Wireless Networks, viewed 14 October 2022, <https://www.igi-global.com/chapter/application-of-blockchain-technology-in-an-iot-integrated-framework/306840>. Ethereum Foundation 2018, ethereum.org.
Gilson, L 2020, ‘Trust and the development of health care as a social institution,’ Social Science & Medicine, vol. 56, no. 7, pp. 1453–1468.
Haleem, A, Javaid, M, Singh, RP, Suman, R & Rab, S 2021, ‘Blockchain technology applications in healthcare: An overview, International Journal of Intelligent Networks, vol. 2, pp. 130–139.
Lumine, F, Wang, W & Schilke, O 2020, ‘Blockchain Governance—A New Way of Organizing Collaborations?’, Organization Science.
Malhotra, A & Elnakib, S 2021, ’20 Years of the Evidence Base on What Works to Prevent Child Marriage: A Systematic Review, Journal of Adolescent Health.
Morey, J 2020, Council Post: The Future Of Blockchain In Healthcare, Forbes.
Tan, TM & Saraniemi, S 2022, ‘Trust in blockchain-enabled exchanges: Future directions in blockchain marketing,’ Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science.
 write
write