Executive Summary
In this business consultancy report a brief discussion and analysis of the existing business models of Virgin group has been taken place. The business report included the discussion about the required changes in the business models that have been advised to be incorporated. In this business consultancy report the virgin group has been advised to do a few changes in the existing business models aligned with the resources and limitations of the organization. A clear rationale along with a proper justification of the changes has been presented in the report with having the industrial analysis done for a better understanding of the characteristics of the models.
Introduction
In order to succeed in the business world, every entrepreneurial organization needs to integrate an effective business model in the operation management system. This describes the business model of the Virgin group of the UK and will also state the need for the changes in the business model utilizing industry analysis. Apart from that, the needed changes would be recommended for the company in the context of the Business model canvas framework.
A clear justification for the recommended changes would be provided for the organization. Richard Branson, the CEO of the Virgin group is a well-known person in the communication and hotels, radio, and financial service industry and the company has introduced an efficient model named ‘Premium model’ which offers value for the money. Apart from that, the company has adopted superior customer service and innovation in the operational management of the organization. In this consultancy report, the need for the changes of this premium business model will be described and a clear rationale will be inflicted hereafter. Apart from that, the recommended changes that need to be adopted by the organization will be discussed with justification (Hearts, Oleshko and Leshchinsky, 2021).
The current business model of Virgin group
The current business model of the virgin group is the ‘Premium business model’. Apart from that, the organization has relied on innovation and strong customer care services which are known as one of the most superior business models in the world. The organization operates in the communication and the wireless industry, hotel and hospitality industry, radio stations, health clubs, renewable technologies, and financial services. The virgin brand is built offering value for the money which is referred to as the premium business model. The premium business model is based on the offering of high-end goods and services appealing to the discriminating customers. The brand image of any company is very important in this business model as the quality of the products of the company is often regarded as a subjective matter. This premium ‘business model’ seeks a high margin of profit on the lower volume of sales (Baxter, 2019).
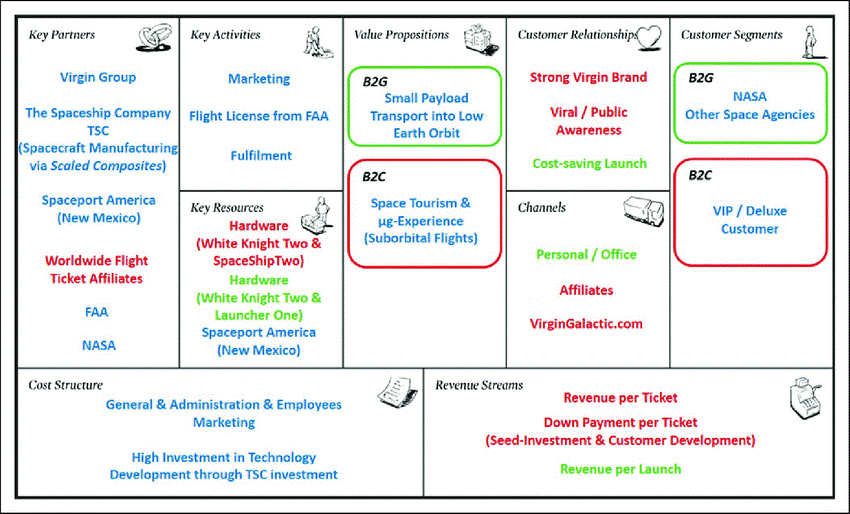
Figure 1: Business Model Canvas of virgin group
(Source: Kerr, 2021).
As the virgin group is still outreaching to the communication, radio, hospitality, and financial service furthermore, the company is still relying on the premium business model as it can entail them to profit a higher margin based on the lower volume of the sales of the company. The virgin group is a global investor and this UK-based organization has relied on the knowledge of the institutional markets in the context of achieving value based on the premium business model and innovation (Stål and Corvellec, 2018).
The capability to leverage this strong brand and on the other hand the extreme diversification in the context of both the industry sector and geography are the premier strengths of the organization. From this aspect, this business model is unique and successful. Apart from that, the organization has been found to have a Freemium ‘business model’ to some extent which offers its customers the products of it for free. This business model is very effective on internet marketing as the acquisition cost is very slow on the internet. Even If the product is not sold the mouth-to-mouth publicity will take place with the news of their great acquaintance. To some extent, the organization has been seen adopting the freemium business model (Kerr, 2021).
The rationale of the changes needed in the business model
The premium business model on which the virgin group has been dependent is lacking to appeal and pitch the people to form a low economic structure. The high-end products that the company is offering based on the premium business model have not been able to attract consumers from a low ergonomic background. The organization is relying on the offering of the value of the money that is not all the time benefiting the company. The premium business model is most likely to have a loyal but smaller customer base. The smaller customer base has occurred due to the con fineness of the target audience. The organization once approached the market of India in the smartphone sector but due to the offering only high-end products, that too in the not so high economic structural country, the organization could not succeed in the Indian market (Mac, Ever and Gliga, 2021).
The freemium business model has not been proved to be beneficial as despite the mouth to mouth publicity the sales volume could not increase.
The PESTEL analysis of the virgin group can be drawn for a better understanding of its industry analysis which is as follows.
Political factors
- Virgin is operating under a single brand and collaborated with Stagecoach with a simple majority (51%) in the share of share in hand (Vandenberghe, 2021).
- The political interventions in the business of the virgin group regarding financial issues are not clear due to the partnership of the organization with numerous companies which shows the need for changes in the business model.
Economic factors
- Most of the companies partnered with Virgin Group are putting a large amount of money into extending their business to the high-end market where all profit is most likely to go to those companies (Coline, 2021).
- Global recession amidst the pandemic situation has had a formidable effect on the high-end customers and offering of value for the money.
- Fluctuation in the local and international communication and hospitality industry has a direct impact on the business.
Social factors
- As the premium business model does not focus much on CSR, amidst the Covid 19 pandemic the brand image has been affected (Bao et al., 2019).
- Virgin group has low service in punctuality.
- Virgin mobile offers distinguished offers according to their social condition.
Technological factors
- Virgin group always enhances its technological; base for improved service.
- Technological policies of the organization are changing, aligning with the interest of their stakeholders (Gasde et al., 2021).
Environmental factors
- The company has not taken many CSR initiatives for improving profit margin based on low volume of sales.
Legal factors
- Virgin group’s business has been interrupted and intervened by the UK government regarding legal lawsuits (Frost et al., 2020).
Outline of recommended changes in business model
The premium business model needs to be changed to some extent for increasing the business volume and profit margin that would not rely on the low volume of sales only the businesses coming from high-end customers. The hospitality industry and the communication service must be the primary focus of the enhanced premium ‘business model’.
According to the “business model canvas framework, the premium business model is not making virgin group benefited in terms of the value proposition and increasing profit margin. Lower research and development cost and low cost through the efficiency of the operational management would be best for the organization’s businesses. The organization can incorporate more characteristics of the freemium business model for the country of India for the low economic structure of the country (Leavy, 2018).
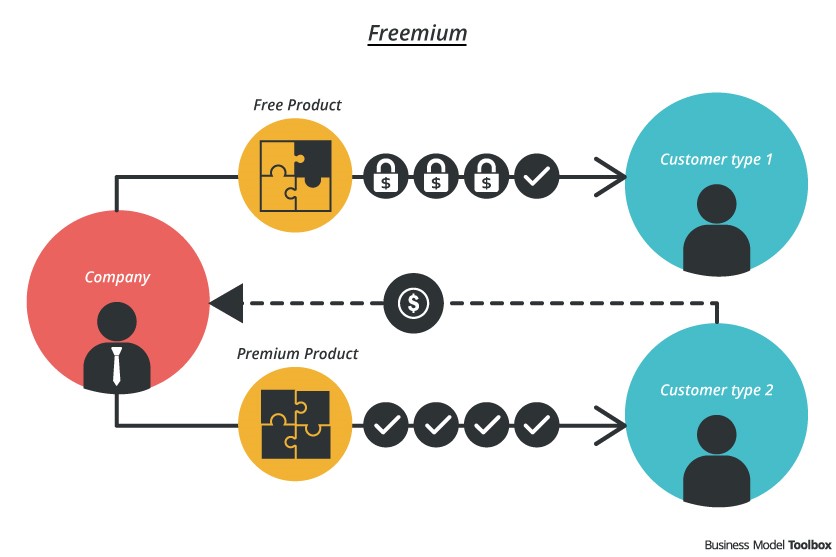
Figure 2: Freemium Business Model
(Source: Namboodiri, Banerjee and Dasgupta, 2019).
The right-hand side of the BMC focuses on the target consumers whereas the left-hand side concentrates on the business. As per the value proposition, customer segmentation, custom ere relationships, channels, key activities, key resources, and key partners a few changes would be needed for the virgin group. A strong value proposition and customer segmentation would be the best fit for the organization. The organization should approach customers from lower economic backgrounds in countries like India and China for their potential market. This should approach the young consumers (Namboodiri, Banerjee and Dasgupta, 2019).
Not wholly going through the premium and freemium business model the organization should rely on the characteristics of the blue ‘ocean strategy and the Aikido business model. In the blue ‘ocean strategy’ the limit and industry structure are not predetermined and changed according to the actions of the participants of the industry. From the Aikido business model, the Virgin group can gather the knowledge of the strengths of its adversaries for getting a competitive advantage. Upgradation of existing technology, software, and infrastructure apart from enhancing the logistic support facilities should be undertaken by the organization that would help in bringing more added values and high volume of sales resulting in high profit (Yunus and Sijabat, 2021).
Justification of recommended changes
The premium business model and the wrong implementation of the freemium business model have not been able to make a high profit for Virgin Group despite having business in various sectors. The premium business model of the organization offers value for the money but the main drawback of the premium business model is that it focuses on high-end goods often which are not affordable for the consumers from a low economic background. The organization has been found to give free products initially on the internet in countries like the Us and the UK. But the US and the UK do not have many low-end customers who would be attracted to the free services and products. The wrong implementation of the freemium business model has harmed the business profit margin. The profit growth of Virgin Group is 73% in the fiscal year of 2019-2020 (De, Decock and Van, 2021).
According to the Business ‘model canvas’ the value proposition, resources, customer segmentation, customer relationship of the virgin group are not high and these need to be enhanced depending on the high resources, and appealing effect to the target market. It has been seen that a high number of free consumers never convert to loyal customers. The limitation of the freemium business model lies in the wrong implementation of it by virgin group. Apart from that, the freemium business model which is used by virgin groups to some extent has a high churn rate where the consumers can easily integrate the throwaway mentality. The resources like fund, communication infrastructure, structural infrastructure, operational management policy, and financial stability have been present in the organization for the required changes in the existing business model. Often it has been found that to those consumers the virgin group is inflicting free goods on those who have the ability to purchase those goods easily (Rauhut, Votteler and Hiller, 2020).
Summary of Findings
The report has found the intrinsic understanding of the premium and freemium business models that are used by the virgin group, a UK-based organization. The organization has been seen adopting a freemium business model for the consumers of the UK and the US. Due to having high economic standards the consumers from these two countries and customers from Scandinavian countries have not availed the free service on the internet where the acquisition cost is very low. The organization’s business model has adopted the freemium business model for the countries like India and many south Asian countries gas built its business offering high value for the money according to the premier principle of this business model. The organization has tried to make a high profit depending on the low volume of sales by which the organization has lost its value which was more used more often resulting in brand dilution (Thomas, 2019).
The characteristics of the ‘blue ocean’ strategy business model along with the ‘Aikido ‘business model should be adopted if the business model canvas is taken into consideration. As the former business model focuses on the industry structure and market limit, those are not predetermined and the latter business model extracts the idea of knowing the strengths of the adversaries of any company to get a competitive edge over them. This is done by finding the weakness of the strategic position of an organization’s adversaries. Through enhancing technologies, increasing-price, up-gradation of software, improvement of logistic support facilities the elements of those two business models can be incorporated (Kane, 2021).
Conclusion
The Virgin Group, a UK-based organization predominantly operates in the communication, wireless, hospitality, and financial industry has a vulnerable approach in the context of its premium and freemium business model. The organization had a 73% profit growth in the fiscal year of 2019-2020. In the business consultancy report, the organization has been advised to integrate the characteristics and elements of the ‘Blue ocean’ strategy business model and Aikido business model according to the business model canvas framework through improved customer segmentation, value proposition, channels, resources, customer relationship. The virgin group had improved customer relationship management accomplished by a strong customer care service. Henceforth, in this consultancy report, a brief discussion of the Virgin group’s business model has been done followed by the discussion about the need for changes in it (HENLEY, 2019).
Reference
Bao, Z., Lu, W., Chi, B., Chin, C.S. and Hao, J., 2019, October. Construction waste cross-jurisdictional trade under PESTEL context. In Sustainable Buildings and Structures: Building a Sustainable Tomorrow: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference in Sutainable Buildings and Structures (ICSBS 2019) (p. 283).
Baxter, G., 2019. Capturing and Delivering Value in the Trans-Atlantic Air Travel Market: The Case of the Air France-KLM, Delta Air Lines, and Virgin Atlantic Airways Strategic Joint Venture. MAD-Magazine of Aviation Development, 7(1), pp.17-37.
Bereznoy, A., 2019. Changing competitive landscape through business model innovation: The new imperative for corporate market strategy. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 10(4), pp.1362-1383.
Coline, D., 2021. Analyse PESTEL-Virgin. Publications Études & Analyses.
De Baets, G., Decock, S. and Van Praet, E., 2021. Interviewing aikido experts: aikido as an embodied pedagogy for recipient design in intercultural business communication. In PLIN Linguistic Day 2021.
Frost, K., Jin, H., Olson, W., Schaffer, M., Spencer, G. and Handwerker, C., 2020. The use of decision support tools to accelerate the development of circular economic business models for hard disk drives and rare-earth magnets. MRS Energy & Sustainability, 7.
Gasde, J., Woidasky, J., Moesslein, J. and Lang-Koetz, C., 2021. Plastics recycling with tracer-based-sorting: challenges of a potential radical technology. Sustainability, 13(1), p.258.
Heiets, I., Oleshko, T. and Leshchinsky, O., 2021. Airline-within-Airline business model and strategy: case study of Qantas Group. Transportation Research Procedia, 56, pp.96-109.
HENLEY, A., 2019. No Mind in Community. Catalyzing the Field: Second-Person Approaches to Contemplative Learning and Inquiry, p.203.
Kane, B., 2021. Equine-imity: Stress Reduction and Emotional Self-Regulation in the Company of Horses. Dreamspark Press.
Kerr, A., 2021. The Media in Ireland: Concentration, Exclusion and Datafication.
Leavy, B., 2018. Value innovation and how to successfully incubate “blue ocean” initiatives. Strategy & Leadership.
Mac Cathmhaoil, B., Evers, N. and Gliga, G., 2021. Digital business model internationalisation: illustrative cases of born global digital companies. In Entrepreneurial Internationalization in an Increasingly Digitized and Networked World Economy. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Namboodiri, S., Banerjee, S. and Dasgupta, H., 2019. A coherent metasynthesis of blue ocean strategy (bos) using grounded theory approach. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 18(4), pp.1-18.
Rauhut, A., Votteler, J. and Hiller, S., 2020, September. Analysis and Evaluation of Business Model Patterns for the Craft Sector. In European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship (pp. 521-XXI). Academic Conferences International Limited.
Stål, H.I. and Corvellec, H., 2018. A decoupling perspective on circular business model implementation: Illustrations from Swedish apparel. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171, pp.630-643.
Thomas, L., 2019. Business models for open source hardware (Doctoral dissertation, Université Grenoble Alpes).
Vandenberghe, J., 2019. Defining and comparing business models for.
Young, D. and Reeves, M., 2020. The quest for sustainable business model innovation. Boston Consulting Group-Henderson Institute.
Yunus, M. and Sijabat, F.N., 2021. A Review on Blue Ocean Strategy Effect on Competitive Advantage and Firm Performance. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(1), pp.1-10.
Appendix
- I created a consultancy report for the virgin group.
- By doing industrial analysis and discussing the business model of Virgin group I created this consultancy report. I allocated roles between the members of the consultancy. I allocated the time accordingly to the priority of our consultancy and data that have been gathered from secondary sources.
- The members of the consultancy performed well in terms of identifying the business model of the virgin group and identifying the strengths and weaknesses of its adversaries and took almost 3 months.
- I developed high analytical skills and used my communication skill while working on them.
- As this report took a lot of analysis, I developed high analytical skills.
- I would make technological skills if I were to undertake a similar kind of report to understand technical aspects more effectively.
 write
write