Introduction
For the past weeks, we have been using an InCell Analyzer to locate the half-of-maximal effective awareness (EC50) for mobile viability as part of our challenge. The primary aim of this experiment is to discover the attention of a particular drug or molecule at which half of the cells examined show a cytotoxic reaction. This EC50 quantity is an essential part of toxicological research and the development of new medicines. As a part of the take-a-look, one-of-a-kind quantities of a chemical or medicine option that would be harmful have been added to grown cells. The high-throughput imaging device known as the InCell Analyzer was utilized by Riss et al. (2016) to take pictures of the treated cells, after which they examined them. This lets them use structural and fluorescent measurements to determine the cells’ viability.
The EC50, the amount at which 1/2 of the cells are affected, is critical as it suggests whether or not the chemical is good or bad. This project is exciting because it could assist many unique regions of technological know-how. Researchers in the pharmaceutical industry use the EC50 to locate exceptional treatments with the fewest facet results. An essential step in environmental toxicology is measuring a pollutant’s cytotoxicity, allowing us to understand how it influences dwelling things. Overall, this takes a look at is very critical for many motives, together with supporting us in learning how chemicals affect residing matters, guiding medical examiners, and ensuring chemical compounds are safe in diverse settings.
Procedure
- The cell viability test on the InCell Analyzer is a quick and accurate way to check the state of a cell’s membrane to see if it is alive or dead.
- Two DNA-intercalating dyes, Propidium Iodide (PI) and Hoechst, can be used with a laser-based high-content imaging device to find cells. This tech can be used for imaging, flow cytometry, or microplate tests (Feoktistova et al., 2016).
- To start the test, cell culture is exposed to different amounts of the thing being looked at, whether it is a possible drug or a chemical in the environment. After the cells have been exposed, they are stained with Hoechst and PI. Hoechst preferentially labels live cells by crossing intact cell membranes.
- The advanced optics and imaging capabilities of the InCell Analyzer make it feasible to take high-resolution photographs of the labelled cells. The laser-based technique, which helps you to depend on fluorescence alerts, may be used to get a precise photo of the sample’s live and useless cells.
- The first step is to install the InCell Analyzer to take photographs at wavelengths that match the fluorescence of Hoechst and PI. After taking the photograph, complex photograph analysis software is used to process and measure the data.
- This approach offers a whole and dependable evaluation of mobile viability, which facilitates us to apprehend the studied substance’s cytotoxic outcomes higher (Krause et al., 2019). The InCell Analyzer makes it possible for this assay to be quantitative, which is beneficial for drug discovery, toxicity, and the fashionable look of cellular biology.
- Before putting the drug on cells for twenty-four hours, you must dilute it in several instances. There are residing cells and useless cells in each well. The InCell Analyzer can inform you of this. Using the system C1V1 = C2V2, the InCell information may be used to locate the EC50, which is the quantity that kills 1/2 of the cells.
Results and Data Analysis
The Concentration That Has A Cytotoxic
- To use the formula C1V1 = C2V2 to find the EC50, you need to know the starting concentrations (C2) and volumes (V2) used in the experiment, as well as the concentrations (C1) and volumes (V1) for each column where 50% of the cells are influenced.
- This math is done with ColuColumns8.25 μM) and Colu 125 μM).
- The amount that damages 50% of the cells (about 8.25 μM to 4.125 μM) is known as C1.
- At 50% broken cells, the amount of medicine is unknown (V1).
- The concentration at the start (C2) is 8.25 µM or 4.125 ¼M.
- The original volume of this experiment, V2, has yet to be discovered.
- For the two columns given, use C1V1 = C2V2 to set up two equations and then solve for the unknowns:
- Column 4 (8.25 μM): 2C1V1=C2V2 (C1)V1=(8.25μM)×(V2)
- In Column 5 (4.125 µM), C1V1=C2V2 (C1)V1=(4.125µM) (V2)
- To find the quantity that affects half of the cells, you need to solve these equations for C1 and V1.
- Find your EC50 in C1. Column 4 has P4% affected cells, and Column 5 has P5%.
- It is (C4+C5)/2, where C4 is Column 4 and C5 is Column 5. This is the average quantity at 50% of damaged cells (C1).
Now, the equations become:
- For Column 4 (8.25 μM): (C1)×V1=(8.25μM)×V2
- 2(C4+C5)/2×V1=8.25×V2
- For Column 5 (4.125 μM):
- (C1)×V1=(4.125μM)×V2
- 2(C4+C5)/2×V1=4.125×V2
Two equations with two unknowns (V1 and V2) Replace C4 and C5, and solve the system of equations to determine V1 and V2. With these data, you may calculate the EC50 value, the concentration at which 50% of cells are damaged (C1).
- C4=8.25μM (concentration in Column 4)
- C5=4.125μM (concentration in Column 5)
- P4=63% (percentage of affected cells in Column 4)
- P5=1% (percentage of affected cells in Column 5)
The average concentration at 50% affected cells =(C4+C5)/2, and the equations become:
- For Column 4 (63% affected cells): (C1)×V1=(C4)×V2
- 2((C4+C5)/2)×V1=C4×V2
- For Column 5 (1% affected cells): 2(C1)×V1=(C5)×V2
- 2((C4+C5)/2)×V1=C5×V2
Now substitute the values:
- For Column 4: (V1)=(C4+C5)/2C4×V2
- (8.25+4.125)/2V1
- =(8.25+4.125)/28.25×V2
For Column 5: (V1)=(C4+C5)/2C5×V2 = 4.125
Total Cells
| Mean | 1778.8 |
| Standard Error | 78.79316644 |
| Median | 1784 |
| Standard Deviation | 498.33174 |
| Sample Variance | 248334.5231 |
| Kurtosis | 0.176588155 |
| Skewness | -0.294839757 |
| Confidence Level(95.0%) | 159.3742223 |
The average number of cells alive at the EC50 level is 1778.8, and the standard error is 78.79. This means that there is a modest amount of variation. The middle number in the data set is 1784, and the sample variation is 248334.52. The standard deviation is 498.33. This shows that there is an extensive range of data. The distribution is very close to normal, as shown by the kurtosis value of 0.18.
On the other hand, the negative skewness value of -0.29 shows a slight imbalance to the left. With a 95% chance of being right, the cell count will be between 1593.43 and 1964.17. These numbers tell us about the range and spread of cell survival data at the EC50 level…
Death Cells
| Mean | 810.25 |
| Standard Error | 78.67482 |
| Median | 780.5 |
| Mode | 1088 |
| Standard Deviation | 497.5833 |
| Sample Variance | 247589.1 |
| Kurtosis | 0.578214 |
| Skewness | 0.48229 |
| Confidence Level(95.0%) | 159.1349 |
Looking at how viable cells are at the EC50 level for dead cells shows an average count of 810.25 with a standard error of 78.67, showing moderate variation. A skewed distribution is shown by the median value of 780.5 and the mode value of 1088. The data has many variations, as shown by the standard deviation of 497.58 and the average variance of 247589.1. A superb skewness of 0.48 and a kurtosis of 0. Fifty-eight displays that the distribution has a tail that points to the right and a shape that may be peaky. With a 95% danger of being correct, the loss of life mobile counted is thought to be between 731.12 and 889.38. These numbers inform us loads approximately how the death cellular records are spread out and how one-of-a-kind it is far at the EC50 stage.
| Mean | 0.4716425 |
| Standard Error | 0.053599856 |
| Median | 0.45965 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.338995257 |
| Sample Variance | 0.114917785 |
| Kurtosis | -1.265102572 |
| Skewness | 0.038696197 |
| Confidence Level(95.0%) | 0.108415943 |
Live Cells
The check for viable cells on the EC50 indicates a mean viability of zero.4716 with fashionable mistakes of zero.0536, because of this, there is not always much variation. The facts have a reasonably slim range, as shown by the median cost of 0.45965 and the standard deviation of 0.339. A flattened curve has a kurtosis fee of -1.27, and a skewed curve with the aid of 0.0387 has a tail that points to the right. With a 95% self-assurance degree, the variety for stay mobile survival is notion to be among zero.363 and 0.580. These numbers inform us approximately how stable and unfold stay cell viability facts are on the EC50 degree, showing that this is a dependable and constant measure…
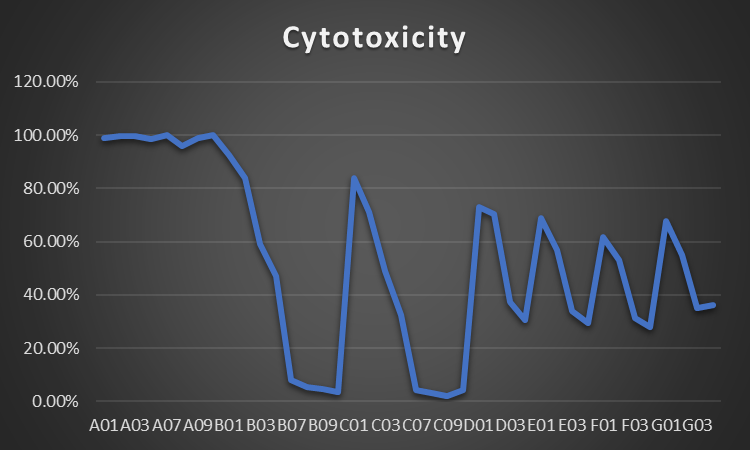
Cytotoxicity
| Cytotoxicity | |
| Mean | 0.5283575 |
| Standard Error | 0.053599856 |
| Median | 0.54035 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.338995257 |
| Sample Variance | 0.114917785 |
| Kurtosis | -1.265102572 |
| Skewness | -0.038696197 |
| Confidence Level(95.0%) | 0.108415943 |
The cytotoxicity test at the EC50 shows a median price of 0.5284 and a preferred mistake of 0.0536, which means there are not always many variants. The statistics unfold regularly, as shown using the median fee of zero.5404 and the usual deviation of zero.339. The skewness price of -zero.0387 shows a small leftward tail, and the kurtosis value of -1.27 shows that the curve is flattened. With a 95% chance of being right, the variety for cytotoxicity is between 0.419 and zero.637. As well-known, those numbers display that the EC50 cost for cytotoxicity is dependable and constant, with little trade from the suggested balanced variety.
Summary/Conclusions
Conclusively, an InCell Analyzer was used to measure cytotoxicity and cellular viability at the EC50 stage, a vital issue in toxicology and drug research. At the EC50 dose, the common range of cells became 1778.8. However, there have been a few variations. The standard range of loss of life cells turned into 810.25, indicating a lot of variation, and the distribution is not direct. The mean live cell viability becomes zero.4716, with little trade and distribution that becomes a bit flatter than every day. It looks as if the effects may be relied on because the cytotoxicity quantity became zero.5284. These consequences show how critical the EC50 is for finding first-rate doses of drug treatments and identifying how natural contaminants affect humans. A cautious procedure guarantees a methodical evaluation, and it is miles crucial to take protection measures. To sum up, this look, made viable using the InCell Analyzer, makes a large distinction inside the progress of technological know-how in many areas.
References
Duellman et al., S (2015). Real-time cell viability assay and use in inhibitor screening. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2015 Oct;13(8):456-65. doi: 10.1089/adt.2015.669.
Feoktistova M, Geserick P, & Leverkus M. (2016). Crystal violet assay is used to determine the viability of cultured cells—Cold Spring Harb Protoc.
Krause, R , Goldring, G & Dean, J (2019). “Crystal violet stains proteins in SDS-PAGE gels and zymograms”. Analytical Biochemistry. Elsevier BV. 566: 107–115. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2018.11.015
Riss TL, Moravec RA, & Niles AL, et al. (2016). Cell viability assays. Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144065/
 write
write