Introduction
Microsoft Corporation is a multinational technology company originally from America and is considered a guru tech in the computer industry. Microsoft began in 1975, with its headquarters in Redmond, Washington (Bhanji, 2012). Microsoft dominated the operating systems market during the 80s and 90s with its MS-DOS and Windows. Microsoft remains in a significant position in the market with diverse and wide-ranging products, from personal computing to cloud computing and artificial intelligence. Microsoft’s strategic plan focuses on diversifying its product portfolio, which includes hardware, software, and cloud services. Microsoft’s plan mainly emphasizes artificial intelligence, integration, and partnerships. This report aims at highlighting its opportunities by selecting a roadmap for its sustainable growth and new ventures.
Task 1: Report
Relationship Between Corporate, Business, and Operational Strategies
Corporate Strategy
Microsoft’s corporate strategy focuses on its vision and goal to be the world’s number one provider of various innovative technological solutions that aid in realizing the satisfaction of its customers. Microsoft’s critical corporate strategy entails inclusion, representation, and innovation that it aims to achieve during its expansion, such that all talent across all races is chosen to represent most of the successful corporations in the world (Bhanji, 2012). The strategy is to create an ideal workplace environment that will become a communication and interaction center with all the activities developed.
Microsoft is a corporate giant that became a divisional organization focusing on specific goods or services. The division group entails Windows and live Windows, server software, online services, entertainment and devices, and Microsoft business that includes research and development, sales, and customer service staff as part of each group. Therefore, to allow efficient communication within the group, all employees are usually located in one area, directly affecting the product and service quality. Lastly, investment and global expansion remain among its core strategies within the corporate realm by considering the enormous population arising from countries like India and China that would eventually provide a vast market.
Business Level Strategy
Microsoft’s business strategy focuses on a diversified product portfolio that includes software, hardware, and cloud services. It has since shown its dominance from operating system dominance to cloud computing and artificial intelligence by showcasing its strategic evolution, characterized by the capacity to adapt to new technologies (Abhari & McGuckin, 2023). Microsoft’s business-level strategy entails involving and pushing for innovation expansion to achieve market excellence. Microsoft’s primary aim to achieve this strategy is to diversify its workforce into its product. Microsoft attracts highly skilled talents, including women, minorities, veterans, and businesses owned by disabled and small-scale enterprises aiming to purchase its products competitively from Microsoft. In 2009, Microsoft spent over a billion working with over 1200 suppliers in all categories, an increase of more than 250% in the last few years, contributing to its growth (Abhari & McGuckin, 2023).
Microsoft’s general focus is providing a platform to computer tech giants and beginners in the technology world to find a place in the Microsoft world and be able to assist in their accomplishments and success throughout their lifetime. Microsoft’s current and in-depth competitive strategy pushed Windows 8 and Surface against its industry rivals in 2013. Consequently, it has developed various products to fit users’ changing wants and needs. Microsoft’s 1 billion investment in 2019 marked the beginning of a strategic partnership with an institution that would reshape the entire technological landscape upon its 2023 release of ChatGPT.
Operating Strategy
Microsoft operates under its products, including cross-device, operating system and collaboration applications, server and collaboration applications. The Microsoft corporation’s operations management relies on various strategic decisions that address the productivity needs of the information technology online services business. Hill et al. (2020) describe how Microsoft depends on its design of services and goods, the operations management decision aspects dealing with the needed strategies and tactics meant to develop profitable products. In public knowledge, Microsoft began its operation by focusing on designing software; despite its continuous expansion on product diversification, the broad strategic decisions are always on the manager’s knowledge of the business.
Another aspect of Microsoft’s operating strategy is the focus on quality management, where operation managers’ tasks ensure customer satisfaction and expectations are in order, considering quality. Continuous improvement and innovation remain among the key Microsoft operational objectives and approaches. Another strategy focuses on process and capacity design, whereas optimization and automation of process and capacity are the company operation management focus (Henry, 2021). Microsoft also focuses on its strategic approach based on supply chain management by maintaining the streamlined supply chain integration with other business activities. The plan aims to monitor its global supply chain through computer networks based on real-time data, distribution networks, and other business areas.
Applications of Strategic Models and Tools to Microsoft
Strengths
Microsoft enjoys strong brand loyalty in the industry with approximately more than 90%of the market share, besides being the leading software and OS provider over the years. Lohrke (2022) recognizes that Microsoft also enjoys a good brand reputation that largely contributes to the corporation’s higher sales and market share and is ranked as the 5th globally with the utmost valuable brand with its value standing at $57.8 billion by the Interbrand, and the seventh most world reputable business as listed by Forbes. Microsoft’s strengths include its easy-to-use software, robust financial performance, and strong distribution.
Weaknesses
Despite the highs of the Microsoft corporation, it also experiences a couple of weaknesses that might interfere with organization operations performance and output. Microsoft experienced poor acquisition and investment, leading to massive link exchange and danger and multiple shutdowns of the acquisitions. Others include criticism over security flaws and slow innovation.
Opportunities
Microsoft’s exposure to various opportunities, such as cloud-based services, allows it to expand its range of cloud services and software as demand for cloud-based services increases. Microsoft also has an excellent opportunity to tap into markets with its mobile OS based on the expected mobile advertising market growth and introduce one of its own Microsoft portable devices, such as tablets and mobile phones.
Threats
Microsoft faces various threats, such as competition in software products, with Microsoft bowing to the pressure of introducing new products such as OS to both the mobile market and PC. The company experiences stiff competition from the already established market, with each company securing a niche in the market. Another threat is the changing consumer habits and needs from laptops to smartphones. Other threats include free entry into the industry, such as open-source projects like new Linux OS, and potential lawsuits.
PESTLE Analysis
Political Factors
Microsoft experiences broader political influences, such as government regulation, taxation, import-export policies, data privacy, and intellectual property. Hence, Microsoft must adhere to different countries’ laws to penetrate these markets. Political stability in a region directly influences Microsoft’s strategic decisions, such as which places to establish offices, data centers, and support centers to ensure business security and continuity. Government digital transformation provides a company with an opportunity and informs Microsoft’s decision to provide solutions based on regulations.
Economic Factors
Microsoft Corporation’s decisions are affected mainly by the global economic condition that directly influences its sales. Moreover, during economic downturns, employees and consumers may reduce their spending on technology services and products, which could decrease Microsoft’s revenue (Barrantes et al., 2021). Other financial aspects that Microsoft needs to consider are the exchange rates in various countries, market demand, taxation policies, and inflation to deal with the economic conditions affecting the organization’s growth, profitability, and operations.
Sociocultural Factors
Some sociocultural factors influence organization operations, such as changes in consumer habits and prospects, increased demand for mobiles, and cloud-based services arising from the customers’ changing needs. Other factors are the digital literacy and technology adoption rate, where the level of society literacy influences demand for Microsoft products and services. Other factors include demographic shifts and work culture shifts.
Technological Factors
Technological factors such as innovation and R&D, digital transformation, and cloud computing refer to integrating digital technology into its business areas, influencing business operations, and delivering value to its customers. As a global tech provider, Microsoft benefits from technological advancements in its digital transformation efforts.
Environmental Factors
There are various environmental factors that Microsoft needs to consider, such as climate change, which has since been a worrying factor globally, and corporations such as Microsoft that need to take part in its mitigation. Microsoft commits itself to be carbon negative by 2030, limiting its energy use and encouraging efficient energy use, especially in its data centers. Another factor is waste management, which requires Microsoft to act responsibly in the management of electronic waste as a producer of hardware like surface devices and Xbox. Microsoft needs to consider its product lifecycle and the know-how on recycling in an environmentally friendly manner.
Legal Factors
Compliance remains a fundamental legal factor in each organization, with factors such as taxation, health standards, and employee well-being within the international markets. Intellectual property laws protect Microsoft inventions, trademarks, and designs. The cyber security regulations require Microsoft to comply with the numerous cyber security laws that typically injure data protection and amicable responses to cyber security incidents.
Strategic Options and Critical Success Factors
Microsoft’s success strategies have been informed by multiple challenges and failures that have, due to long perseverance con, contributed to its growth. Among its primary strategy is focusing on cloud computing and prioritizing Azure. That has, however, taken the space of becoming a leading cloud computing platform contributing to Microsoft’s revenue growth.
Another success factor associated with Microsoft is its association with new technology that has since shown its adoption of Kubernetes, which helped the organization stay ahead of the curve despite being developed by its competitors. (Cusumano, 2016) another critical success factor is investment in artificial intelligence and machine learning, embracing open-source technology such as Linux and AZURE, and collaboration and expansion into new markets.
Recommendation and Business Objectives
Microsoft needs to be specific in its objectives as an organization to ensure successful sustainability and Diversification. Microsoft is known to have a monopoly on the operating system market with Windows and Office Suite in the early days of the tech industry. Later, Microsoft lost its monopoly over new entrants Apple and Google, creating a market share. Therefore, Microsoft needs to tap into its lost strategic areas, such as mobile phones dominated over the years by its competitors, such as Google’s Android operating system OS, iPad, and Apple iPhone (Abhari & McGuckin, 2023).
Microsoft needs to be quick in diversifying and shifting to new technology advancements and trends, such as search and advertising and social media, by innovating different services to counter Google’s dominance in the search and advertising space. Microsoft needs to diversify into new markets and develop new products apart from gaming to ensure its survival in the industry.
Force Field Analysis
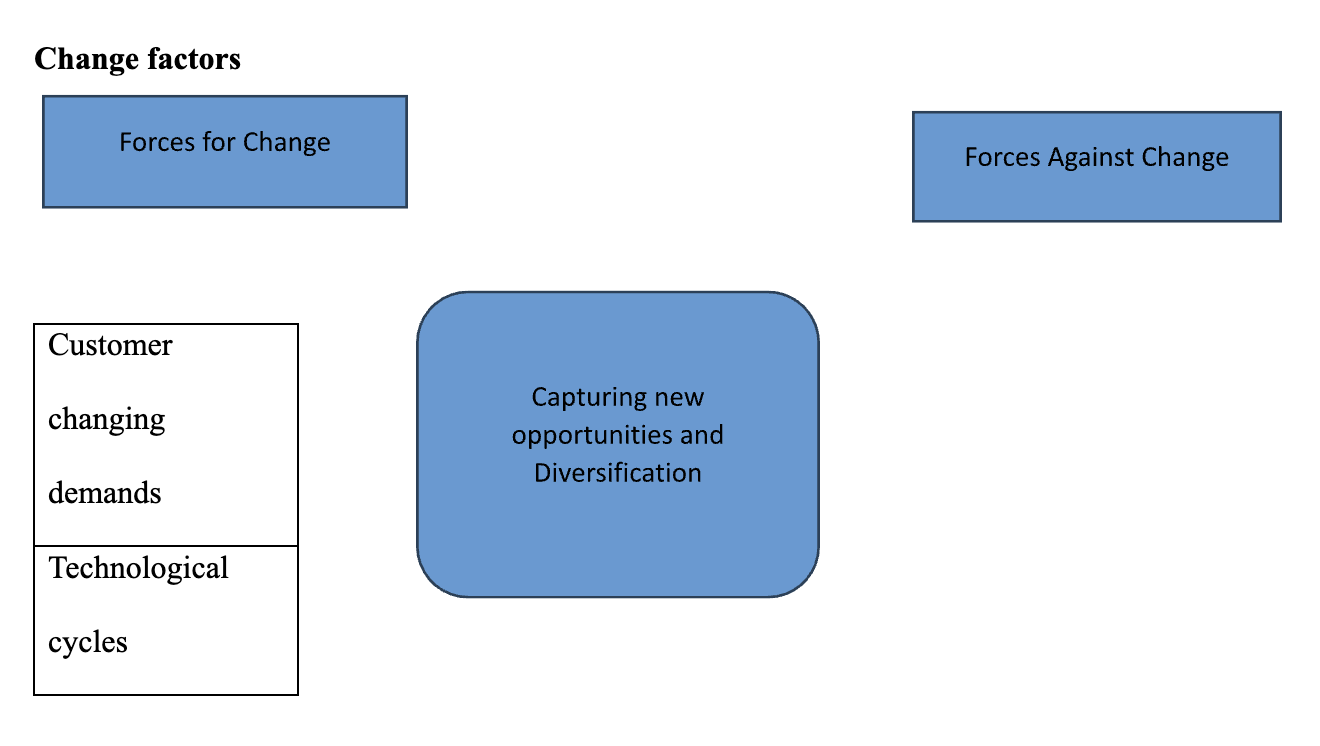
| Customer changing demands |
| Technological cycles |
| Competition |
| Organization culture |
| Focus on Divisions |
| Slow Adaptation |
Force Field Analysis
The introduction of new technological gadgets such as smartphones and tablets changed consumer preference, hence leading to the creation of broadband, contributing to the profound performance of Microsoft. According to the force field analysis, models reveal the major driving forces as the customers’ changing needs, technological cycles, and competition (Nengsih et al., 2022). However, the study also described the forces against change, focusing on division, organizational culture, and slow adaptation to new technology trends. However, restraining factors, such as financial constraints, would have hindered change within Microsoft (Cusumano, 2016).
Resource Implementation Plan
| No | Name | Duration | Start | Finish | Predecessor |
| 1. | Milestone1: Planning and Research
–In-depth market research |
3Months | 1/2/2024 8.00 AM | 31/3/2024 5.00 PM | |
| 2. | Milestone 2: Product Development and Training | 6 Months | 1/4/2024 8.00 AM | 30/9/2024
5.00 PM |
I |
| 3. | Milestone3: Marketing and Promotion | 3Months | 1/10/2024 8.00 AM | 31/12/2024 5.00 PM | 2 |
| 4. | Rollout &Integration | 5Months | 1/1/2025
8.00 AM |
31/5/2025 | 1 |
Monitoring and Control System
A foundational mechanism must entail monthly distribution and sale tracking by analyzing the company production and supply chain data. The tracking evaluation would enable the rate of demand and supply to be evaluated and get consumer feedback.
Risk Assessment
| Risk | Likelihood
(Medium, High, Low) |
Impact
(High, Medium) |
Mitigation Strategy |
| Market Rejection | Low | High | Comprehensive Market research |
| Supply Chain Distribution | Medium | medium | Diversification of suppliers |
| Regulation Hurdles | low | medium | Compliance with specific countries’ regulations and rules. |
Task 2
Reflective Essay
By looking into Microsoft’s strategy for change, which includes Diversification, its venture into cloud computing and open-source software such as Azure contributes to its success. However, the underlying change aspects of Microsoft entail its operating strategy that focuses on quality management where operation managers must ensure customer satisfaction and expectation is met considering quality. Therefore, Microsoft uses unique methods in its operation management by prioritizing the company’s objective by constantly improving and innovating (Abhari & McGuckin, 2023).
Another agent for change focuses on the process and capacity design, whereas Microsoft operations management focuses on extensive automation that optimizes the processes and capacity. Microsoft also focuses on its strategic strategy based on supply chain management by maintaining the streamlined supply chain integration with other business activities. The change strategy aims to monitor its global supply chain through computer networks based on real-time data, distribution networks, and other business areas.
Analysis of Change Management Model
Change management is intriguing since it is a universal agent that beholds everyone at a particular time. Kotter’s and Lewin’s change model reflects on two prominent models that have since dominated the change management discourse. Kotter’s Model establishes its urgent need for change. Microsoft saw its competitors taking over the industry based on technology trends and innovation to meet the customers’ changing demands, creating the need for change in Microsoft Corporation to cope with the surrounding competitive market. Kotter’s eight-step approach change model remains the best when implementing organizational change to remain relevant in the software industry. However, introducing change is not always accessible, regardless of whether the change is small or large.
However, Lewin’s change management model simplifies the change process into three steps: Unfreeze, Change, and Refreeze. The unfreeze phase is the initial step of recognizing the need for change, where Microsoft as a company can actually look at its sales and market share and indeed allude to the fact that there is a need for change. The second phase is the change itself, such as Microsoft increasing its global expansion or introducing new products or services required to boost or position Microsoft in the competitive industry to foster its growth. Lastly, refreezing represents the last stage of implementing Microsoft change elements intended for long-term gain.
As a change agent, I prefer using Kotter’s change strategy by first ensuring that there is a sense of urgency created by providing that all the organization’s stakeholders urgently need change for better results. Urgency creation takes place when leaders take the crucial initiative of honest discussions with everyone on the threats and opportunities the company might be experiencing. I concur with Kotter’s further explanation that 75% of a company’s top leadership should agree with the concept of organizational change to succeed. A company must prepare well for the change process to avoid further shortcomings. Considering Microsoft’s state, it requires urgent change following the takeover by other competitors such as Google. Its leaders must show some urgency to change some aspects of the organization.
Kotter’s Model entails forming a coalition of change within the organization. An organization’s key staff must participate in the change process based on robust and sober leadership. There is a need to incorporate influential leaders within the organization to continue creating and spreading the urgency of the need for change. Team building is one of the tactics to ease tension and find a more peaceful way of introducing change to its staff. Working as a team considers starting change by the leaders typically leading to success. (Gupta, 2021). The change coalition should collaborate with other staff from the different organizational departments for inclusivity. Nonetheless, the phase for change requires identifying weak areas during the change process to be corrected as soon as possible before the implementation process begins.
Various approaches to change implementation strategies include encouraging leaders to develop a clear vision for change. In this stage, all the ideas the change team members generate are later harmonized to create an inclusive vision that all stakeholders understand. As a change agent, there is a need to ensure that all the people involved in implementing change are clear on the company’s vision and objective. The organizational change must be in line with explicit values representing the company’s intention.
In line with Kotter’s Model of change, a change leader needs to communicate their vision for change to the other members of the organization. The organization’s success depends on the change leader’s commitment (Grenway, 2021). The change leaders must regularly and intentionally dispense the message to drive the change. There is a need to remind every person within the organization of its discourse to change and to be familiar with the company vision. As a change agent, it is essential to address the employee’s concerns and fears brought about by the change. The company’s vision for change should be communicado to all the departments, and training should be readily available for the staff.
As a change agent, I need to consider Kotter’s model approach, which includes dealing away with change obstacles to avoid causing further inconveniences that escalate the resistance rate. The change leaders need to put new processes and policies that guide the staff on change processes and eliminate barriers. There is a need for constant encouragement from the management to the employees to voluntarily participate in the change process by issuing rewards to the exemplary performers in the change process within the organization.
Also, it is necessary to include people or professionals who can foster change. Furthermore, there is a need for leaders to encourage others who resist change for its benefit.
According to Kotter (1996), implementing change requires the creation of short-term wins that tend to motivate the staff to accept and appreciate change. The staff needs to recognize the immediate results of change by erasing the negative thoughts in their minds. All the stakeholders need to experience the fruits of change as soon as possible, where change critics can only be silenced in a scenario where the company enjoys its taste of victory. The victory can only be reached following the creation of achievable short-term goals. It is essential to critically analyze targets to determine whether they are attainable to avoid messing with the changing process. There is also a need to reward and recognize the people driving change to feel motivated and stay on the course.
Recommendation of a Change Model
Based on my observation, Kotter’s model change would be the most appropriate tool with a comprehensive roadmap to deliver an efficient and successful change strategy considering Microsoft’s poor performance despite its impressive rich history. Change is regarded as a long-term process that requires determination and patience. Change is a gradual process, and a win in the process should be considered as a learning experience for the people involved in the change process (Grenway, 2021).
Lastly, as a change agent, there is a need to encourage and instill in the leaders the desire to anchor the changes in the corporate culture. All the aspects of the organization need to reflect on the values that brought about change. Change should be part of organizational culture and remain sustainable even if the change leaders leave the company. It is, therefore, clear that an organization such as Microsoft with unimpressive performance requires the urgent need for change as a means of revival.
Therefore, an organization must choose which change process to adopt. Microsoft needs a radical change to compete with its competitors, such as Google and Apple. Microsoft needs to consider changes in innovation and marketing to regain its initial glory. Based on the change models, Kotter’s Model remains suitable for implementing change in Microsoft Corporation.
As a change agent, I oversee Microsoft’s transition into an all-around innovation hub that adjusts to customer demand and technology trends to remain on the industry’s competitive edge. My role would drive the organization’s change by managing and navigating around the stakeholder’s expectations to ensure its success after that. My initial step would be to recognize the organization’s problem, identify the correct change strategy with the help of the top managers, and create a brainstorming session to derive a shared vision for driving the change. I intend to teach various strategies to leaders to introduce changes within their departments through team buildings, interdepartmental meetings, and personal coaching to ensure employees are well familiar with the changes and their concerns are attended to by their leaders. I intended to use various tools, such as monitoring and evaluation tools, to capture and allocate quality time for the change process.
Conclusion
Therefore, an organization’s significant staff must participate in the change process grounded on strong and sober leadership. There is a need to incorporate significant figures within the organization to create awareness constantly and spread the urgency for change. Over the years, team building has been effectively used as a tactic to ease tension and find a more peaceful way of introducing change to its staff. It is significant that in all scenarios for change, leaders need to act and lead by example to try to preach the same gospel to other staff and by working as a team. The team for change coalition should involve staff from different departments in order to demonstrate the spirit of inclusiveness.
Reference
Books
Bhanji, Z. (2022). Microsoft Corporation: A case study of corporate-led PPPs in education. Public-private partnerships in education: New actors and modes of governance in a globalizing world, pp. 182–198.
Burke, W. W. (2023). Organization change: Theory and practice. Sage publications.
Henry, A. (2021). Understanding strategic management. Oxford University Press.
Hill, C. W., Schilling, M. A., & Jones, G. R. (2020). Strategic management: an integrated approach: theory and cases. Cengage Learning.
Journals
Abhari, K., & McGuckin, S. (2023). Limiting factors of open innovation organizations: A case of social product development and research agenda. Technovation, p. 119, 102526.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2022.102526
Barrantes, R., & Leach, T. (2021). The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on One of The Biggest Technology Giant Shares: A Financial Analysis on Microsoft Corporation. Journal of Student Research, 10(3).
https://doi.org/10.47611/jsrhs.v10i3.1689
Cusumano, M. A., & Selby, R. W. (2016). New Edition How Microsoft competes. Research-Technology Management, 39(1), 26-30.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08956308.1996.11671033
Courtois, J. P. Microsoft: Help shaping a new era—activating Microsoft’s strategic core worldwide. In Strategy Activation Canvas (pp. 259–271). Routledge.
https://www.taylorfrancis.com10.4324/9781003388791
Gupta, B., Mittal, P., & Mufti, T. (2021, March). A review of Amazon web service (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on ICT for Digital, Smart, and Sustainable Development, ICIDSSD 2020, p. 27-28 February 2020, Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi, India.
http://dx.doi.org/10.4108/eai.27-2-2020.2303255
Greenway, B. (2021). A Review and Application of John Kotter’s” Leading Change .”Journal of Sociology and Christianity, 11(2), 91–95.
https://sociologyandchristianity.org/index.php/jsc/article/view/218/200
Hou, J., Hübner, P., Schmidt, J., & Iwaszczuk, D. (2024). Indoor Mapping with Entertainment Devices: Evaluating the Impact of Different Mapping Strategies for Microsoft HoloLens 2 and Apple iPhone 14 Pro. Sensors, 24(4), 1062.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041062
Kotter, J. P. (1996). Leadership change. Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA.
Lessambo, F. I. (2022). Apple and Microsoft. Financial Statements: Analysis, Reporting and Valuation (pp. 369–399). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15663-2_23
Lohrke, F. T., Mazzei, M. J., & Frownfelter-Lohrke, C. (2022). Should it stay, or should it go? Developing an enhanced SWOT framework for teaching strategy formulation. Journal of Management Education, 46(2), 345-382.
https://doi.org/10.1177/10525629211021143
Nengsih, M. K., Gayatri, I. A. M. E. M., Wagini, K. C. S., & Indriasari, N. (2021, May). Strategy of Developing: Five Competitive Force Model Case Study: SMEs Fajarwonk. In BISIC 2020: Proceedings of the 3rd Beehive International Social Innovation Conference, BISIC 2020, 3-4 October 2020, Bengkulu, Indonesia (p. 180). European Alliance for Innovation.
https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=Lx0J9NQAAAAJ&hl=en&oi=sra
 write
write