Introduction.
As public awareness of climate change matters continues to grow, companies manufacturing electric vehicles (EVs) have seen an increase in sales. Jiang et al. (2024) state that EV adoption is widely considered an effective strategy in the fight against climate change as it seeks to replace the widespread use of gas-powered vehicles. With the increased adoption of EVs, as shown in Figure 1, entrepreneurs have invested in various sectors with opportunities. Jarrad Morris is one of these investors who have invested in the numerous opportunities presented with EV adoption. Morris’s company, Fleet-e & PLUG Charging, provides a variety of solutions to EV adoption, such as leasing and charging. Considering that EV adoption around the globe is still in its infancy, entrepreneurs like Morris have had to navigate the various challenges brought with it. One of these major issues that directly affect Fleet-e & PLUG Charging operations is the data privacy issues associated with the charging stations (Featherman et al., 2021). This paper seeks to critically explore the data privacy issues relating to EV adoption and how they have affected entrepreneurs around the globe like Jarrad. With data privacy concerns intensifying in recent years, this paper also looks to present the future implications of the privacy issues linked to EV charging systems.
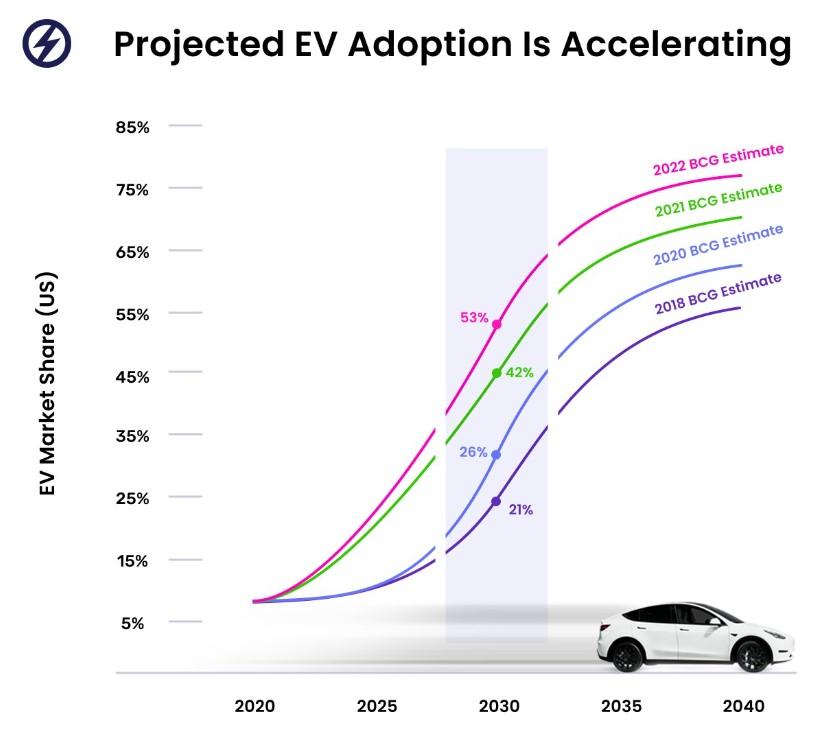
Featherman et al. (2021).
Critical Discussion of International Entrepreneurship.
International entrepreneurship refers to the launch of businesses by entrepreneurs in foreign countries. This period of globalisation has seen an increase in international entrepreneurship as countries look to be more independent of one another (Broadbent et al., 2018). International entrepreneurship has been associated with both benefits and drawbacks. According to Vadana et al. (2020, p. 474), one of the major benefits of international entrepreneurship is that it has allowed entrepreneurs to enter new markets. With various restrictions removed across different countries, entrepreneurs today experience fewer challenges launching their businesses in foreign countries (Nuhu et al., 2021, p. 454). This increased access to new markets has allowed entrepreneurs to increase their revenue as they expand their customer base.
In addition, increased international entrepreneurship has reduced the reliance on domestic markets. According to Raats and Krakauer (2020), companies today can sell their products in international markets when the demand for these products is low in their domestic markets. The reduction in reliance on domestic markets has also contributed to a reduction in expenses. Reliance on domestic markets has often been linked to increased expenses as businesses have to store products in warehouses during periods when demand is low (Vadana et al., 2020). With increased international business, entrepreneurs do not have to store their products in their warehouses as demand varies depending on different markets.
Businesses that engage in quality ventures have managed to enhance their reputation in the international markets. As companies penetrate international markets, quality expectations have risen with customers’ changing customer preferences. As a result, international entrepreneurs have been compelled to invest heavily in quality products. An example of these investments that international entrepreneurs have made is hiring quality employees from around the globe (Raats and Krakauer, 2020). Quality employees have the ability to enhance the reputation of an organisation while also reducing costs. Increased globalisation has enabled businesses to access quality employees as countries are interconnected thanks to technological innovations.
However, despite the many strengths linked to international entrepreneurship, critics have highlighted its limitations. An example of a challenge that international entrepreneurs have had to navigate is increased regulations across different countries. Nuhu et al. (2021) state that regulations in sectors such as the environment have increased, with countries requiring companies to lower their carbon emissions. Businesses found to violate these regulations have been fined heavily, leaving them in financial turmoil. Complying with these regulations has been a major challenge for most businesses as some negatively affect organisational processes (Broadbent et al., 2018). For instance, converting from non-renewable energy sources to renewable has been linked to high energy costs as companies highlight the high initial cost required.
In addition to increased regulations, increased competition is also another challenge that international entrepreneurs have had to navigate. As companies penetrate new markets, they have had to face stiff competition from other domestic and international companies. Competition in the international market is stiffer as it involves companies with huge financial capabilities as well as well-positioned brands (Vadana et al., 2020). In an effort to remain competitive, companies have had to constantly adapt to changing market conditions. Adaptability has been an increasingly valuable aspect of international entrepreneurship as it ensures adaptability, especially in periods of difficulty.
Critical Appraisal of Data Privacy Issues Linked to EV Charging Systems.
The increased adoption of EVs around the globe has highlighted its key limitations as countries look to transition from gas-powered vehicles by 2030. Jiang et al. (2024) state that data privacy concerns are one of the major concerns linked to EV adoption that entrepreneurs are yet to find a solution to address. EV entrepreneurs around the world have been criticised for failing to provide more detailed standards or record-keeping and reporting. Smart charging systems provided by these companies have been found to collect an extensive amount of data without the customers’ knowledge.
Due to the collection of customer information without their knowledge, EV companies around the world have been questioned about unauthorised access to specific user information through aggregated data. Privacy regulations governing data access require that companies lawfully obtain customer information for a specific purpose and not use it for any purpose other than what has been agreed upon by the client. States in North America and Europe are already imposing regulations to restrict businesses’ unauthorised access to customer data. According to Jiang et al. (2024), an example of these regulations is the bill passed in 2022 by California regulators that requires all EV charging operators to provide more detailed standards for record-keeping and reporting.
While some countries have already imposed regulations to address the privacy concerns associated with EV charging systems, the majority have yet to implement this much-needed policy. The UK’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was last amended in 2018 (Babu et al., 2022). Due to the lengthy period spent without amendments being made to the policies, technological innovations have outpaced policy implementation in the UK. An example of a limitation of the UK GDPR is that it does not set the limits of different types of data (Flammini et al., 2019). As a result, EV charging systems can collect vast amounts of data from their customers without facing any consequences. Collecting vast amounts of data exposes these companies to breaching attempts as cyber attackers often exploit the complex data systems in big data to disrupt operations.
In addition, organisations around the world have highlighted the nuances in regulatory laws across countries and regions. International businesses have been the main victims of the nuances in regulatory laws across regions. For instance, compliance with the GDPR does not automatically guarantee compliance with other regulations, such as Canada’s Anti-Spam Legislation (CASL) (Unterweger et al., 2022). Most international businesses have highlighted the need for expanded international cybersecurity laws, citing that it would enhance compliance. Most international businesses have mainly struggled to comply with various data privacy rules due to their complexity as companies move across borders.
Some regions, such as the EU, have a harmonised cybersecurity regulation known as the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA). While this regulation is linked to a number of benefits, one of its major drawbacks is that it is mainly aimed at improving operations for the biggest financial entities (Van Aubel and Poll, 2022). Critics of the DORA have highlighted that it fails to cater for the needs of micro-entities and small or mid-sized companies.
In an effort to address the data privacy issues associated with EV charging systems, organisations such as Cyber Risk Institute’s Financial Services Cybersecurity have consolidated approximately 2,300 regulations into about 280 diagnostic statements (Metere et al., 2022). Although not internationally recognised, these regulations have helped incentivise cybersecurity best practices by giving organisations a single framework to rely on and create economic opportunities for new ventures (Van Aube and Poll, 2022). However, the regulations are still not enough as data privacy concerns, especially with EVs, continue to hit a record high. With international businesses continuously suffering due to violations of privacy laws, it is increasingly becoming important to globally harmonise cybersecurity and privacy regulations.
Relevance of the Privacy Issues Linked EV Charging Systems to Jarrad Morris, Fleet-e & PLUG Charging and their Future Internationalisation aims or Potential.
The data privacy issues associated with EV charging systems directly affect Jarrad Morris and Fleet-e & PLUG Charging’s operations. As consumers continue to increasingly adopt EVs, more awareness will be raised regarding the unauthorised collection of consumer data. While currently based in England, the company needs to adopt appropriate strategies that safeguard it from violating privacy laws across borders and regions (Broadbent et al., 2018). One of these strategies that it needs to consider adopting is Cyber Risk Institute’s Financial Services Cybersecurity diagnostic statements. While these statements are not internationally recognised, they help businesses stay in line with data privacy regulations across borders. The diagnostic statements are derived from various regulations and consolidated into one.
In addition, in countries where regulations have been imposed, companies such as Fleet-e & PLUG are required to provide detailed record-keeping documentation. Therefore, Jarrad Morris should ensure that the company regularly updates information on customer data collected to avoid violation of privacy laws. EV companies have been victims of privacy lawsuits due to data breaches. According to Nuhu et al. (2021), the most recent case has been that of Tesla when a customer sued the company at the US District Cout for sharing their private information. These lawsuits present significant financial implications to EV companies as they have to incur huge expenses on a legal team, as well as compensation when found guilty. Embracing consolidated regulations reduces the likelihood of being sued for data breaches, as these policies aim to ensure that companies stay in line with the policies and regulations of different countries and regions.
Recognising that the compliance of policies in one region does not apply in another region is also important for the future internationalisation aims of Fleet-e & PLUG. As earlier mentioned, some data privacy regulations apply in one region while they do not apply in others. Vadana et al. (2020) state that it is crucial to understand the various regulations that apply differently across regions as they may reduce the likelihood of the company violating privacy laws. For instance, there have been data privacy laws that have been found to apply in the UK while they are not applicable in North American countries such as Canada.
Jarrad Morriss should also be informed of the various changes made to policies and regulations across the international market. With the unprecedented changes in the current business world, policies are likely to change rapidly. Technological innovations have played a pivotal role in the rapid changes in data privacy regulations as they constantly highlight existing loopholes (Raats and Krakauer, pg. 57). As a result, it is important that the company is updated with the changes in technological innovations as well as policies that may impact its future.
Conclusion.
In summary, data privacy issues are likely to intensify even more in the coming years. As organisations such as Fleet-e & Charging look to get into the international market, it is important that they have appropriate strategies for future success. Incorporating strategies recommended by Cyber Risk Institute’s Financial Services Cybersecurity diagnostic statements can be vital for ensuring compliance with various regions. These strategies are derived from a range of regulations around the world in order to help businesses comply with the varying policies across borders. In addition, being constantly informed on the changes made in cybersecurity policies across countries is important for international success. As rapid technological advancements continue to take place, data privacy regulations are likely to be amended regularly. It is, therefore, important that the business remains constantly updated on these changes.
References.
Babu, P.R., Palaniswamy, B., Reddy, A.G., Odelu, V. and Kim, H.S., 2022. A survey on security challenges and protocols of electric vehicle dynamic charging system. Security and Privacy, 5(3), p.e210. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/spy2.210 (Accessed 30 January 2024).
Broadbent, G.H., Drozdzewski, D. and Metternicht, G., 2018. Electric vehicle adoption: An analysis of best practice and pitfalls for policy making from experiences of Europe and the US. Geography compass, 12(2), p.e12358. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/gec3.12358 (Accessed 31 January 2024).
Featherman, M., Jia, S.J., Califf, C.B. and Hajli, N., 2021. The impact of new technologies on consumers beliefs: Reducing the perceived risks of electric vehicle adoption. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 169, p.120847. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120847 (Accessed 30 January 2024).
Flammini, M.G., Prettico, G., Julea, A., Fulli, G., Mazza, A. and Chicco, G., 2019. Statistical characterisation of the real transaction data gathered from electric vehicle charging stations. Electric Power Systems Research, 166, pp.136-150. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2018.09.022 (Accessed 30 January 2024).
Jiang, H., Xu, H., Liu, Q., Ma, L. and Song, J., 2024. An urban planning perspective on enhancing electric vehicle (EV) adoption: Evidence from Beijing. Travel Behaviour and Society, 34, p.100712. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tbs.2023.100712 (Accessed 30 January 2024).
Metere, R., Pourmirza, Z., Walker, S. and Neaimeh, M., 2022. An Overview of Cyber Security and Privacy on the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.07842. Available at:
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2209.07842 (Accessed 29 January 2024).
Nuhu, N.S., Owens, M. and McQuillan, D., 2021. International entrepreneurship from emerging to developed markets: an institutional perspective. International Marketing Review, 38(3), pp.453-486. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-02-2020-0028 (Accessed 29 January 2024).
Raats, R. and Krakauer, P.V.D.C., 2020. International entrepreneurial orientation: Exploring the Brazilian context. Raats, R., & Krakauer, P., International Entrepreneurial Orientation: Exploring the Brazilian Context. Entrepreneurial Business and Economics Review, 8(1), pp.51-69. Available at: https://doi.org/10.15678/eber.2020.080103 (Accessed 28 January 2024).
Unterweger, A., Knirsch, F., Engel, D., Musikhina, D., Alyousef, A. and de Meer, H., 2022. An analysis of privacy preservation in electric vehicle charging. Energy Informatics, 5(1), pp.1-27. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42162-022-00190-y (Accessed 29 January 2024).
Vadana, I.I., Torkkeli, L., Kuivalainen, O. and Saarenketo, S., 2020. Digitalisation of companies in international entrepreneurship and marketing. International Marketing Review, 37(3), pp.471-492. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-04-2018-0129 (Accessed 30 January 2024).
Van Aubel, P. and Poll, E., 2022. Security of EV-charging protocols. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.04631. Available at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2202.04631 (Accessed 28 January 2024).
 write
write