Introduction
The effective distribution of Berry Smartwatches and their success in the European market is highly dependent on the success of the company’s freight arrangements. Freight transportation involves the movement of goods from one location to another through the different modes of transportation available for freight, such as trains, trucks, aeroplanes and ships. Freight transportation is a central part of the global economy and a defining feature of successful supply chain management across many industries. Freight transportation is one of the decisive necessities for a business to grow internationally. Given the importance of freight forwarding, it is important to discover valuable insights and practical tips that can help Berry optimize the company’s freight transportation strategy. By evaluating the costs and different advantages and disadvantages associated with each mode of transportation, the current report offers Berry guidance on the best mode for the business based on factors such as cost, speed of door-to-door delivery and the environmental impact of each mode. Understanding these attributes of each mode of transportation can help Berry make informed decisions concerning the company’s transportation needs and ensure the optimization of the company’s supply chain management.
Berry Smartwatches Company Background
This proposal is developed with the understanding of specific details and assumptions about Berry company, as well as its growth strategy and needs. First, Berry is a smartwatch company based in Canada. The company sells high-end smartwatches distributed across the Asian and North American markets. The company’s rapid growth has promoted the development of the desire to expand to the European market. The move to Europe is motivated by the existence of a strong demand for smartwatches in Europe. According to the company’s forecasts, the monthly demand in Europe could reach 80,000 pieces of smartwatches across the initial years. To effectively expand to Europe, there is a need to develop a distribution centre close to the market and ensure effective freight transportation to the distribution centre from the manufacturing point in China (Browne, Dubois & Hulthén, 2023). over the next three months and to kickstart their operations in Europe, the company plans to have a Distribution Centre in Ossendorf, Cologne, Germany. The distribution centre can hold approximately 6,000 cubic feet (ft3).
Effective freight transportation would allow the watches to be efficiently moved from the manufacturer to the distribution centre to facilitate door-to-door distribution. The Berry-branded smartwatches are manufactured by MTT based in Baiyun, Guangzhou, China. To facilitate the European expansion project, Berry needs to move the finished smartwatches to the Germany distribution centre, which is developed to create ease in serving the European market. Only effective freight forwarding would guarantee suitable transportation of the smartwatches from Guangzhou, China, to the distribution centre in Cologne, Germany.
Theoretical Framework: Freight Transport
The case of Berry Smartwatches involves a Freight transport problem, as the company seeks the most appropriate and feasible approach to meeting its European growth plans. Freight Transport involves the movement of goods from one place, usually the supplier, to another place, usually to the customer. In the market today, common freight includes moving raw materials, commercial goods, commodities, and merchandise, often moved in bulk across the world. According to Crainic & Laporte (1997), suitable freight transport involves a company’s decisions to move goods over long distances, usually between countries or continents, in the most cost-effective ways. Modern researchers have added a further need for environmental concern in freight transportation decisions. Fulzele & Shankar (2022) emphasize that shipping, or the use of sea transports, has impacted costs and the environment globally and is the main mode of freight used to move around 90% of traded goods. However, improving freight transportation performance also involves looking at the opportunities and challenges associated with other modes of freight transport.
Since freight transport is primarily concerned with the movement of goods from the suppliers to the customers, Berry company must identify several essential features of each mode of transport. These features are then used to decide the most appropriate mode of transportation to adopt. The different features to consider in making the freight transport decision include the following:
- Distance – measured in kilometres or miles, the distance through which goods are to be moved can involve long or short distances. These define that in planning for freight transportation, it is important to understand that the movement of goods planned is local, regional and global, and the company must meet the needs at each level (Browne, Dubois & Hulthén, 2023).
- Cost – the second attribute is transportation cost, which directly affects the cost of the goods transported. The cost of freight transportation depends on the selected transportation mode, the distance to be covered, and services, among others (Browne, Dubois & Hulthén, 2023). An important feature is that freight transportation costs decrease as the number of units to be carried increases.
- Speed – freight transportation also includes concerns about speed, which is also an important characteristic of the quality of service. The speed of freight is also affected by the type of goods and their perishability. Speed desired thus directly influences the decision about the mode or modes used.
- Accessibility – Effective freight transport also covers accessibility and ensures that goods are loaded and offloaded in reasonable timelines and that decisions are targeted to enhance overall transport productivity.
- Safety and Reliability – Decisions about freight transport also demand reliability, which involves the ability to perform all the intended or desired functions to acceptable performance standards within a defined period (Browne, Dubois & Hulthén, 2023). Decisions must ensure goods are securely protected, and there is a predictability of the freight transport arrangements. Involves repeatedly delivering products (smartwatches) on time, in the right way and condition, at the minimum possible cost.
- Environmental Friendliness – great freight systems also consider the company’s contribution to pollutants. He et al. (2021), in their evaluation of the robustness of multimodal freight transport networks, established that transportation equipment is responsible for over 20% of black carbon emitted to the atmosphere and is a powerful climate pollutant. As a result, freight transport effectiveness must also consider the environmental impact of the modes used.
Freight transport depends on a number of factors that are specific to each company, such as the type of goods to be transported, the distance to be covered, the time sensitivity of the freight, and the budget. Different transport modes offer these attributes and ensure goods can be transported safely, accurately and consistently, without damage to the Cargo and with the least damage to the environment. The following section describes the different Freight Transport modes applicable in the case of Berry Smartwatches.
Freight Transportation Options
Businesses seeking freight transport have options to choose from. These include road, rail, Air, ocean/ship, and multimodal transport arrangements. Each of these modes of transportation boasts different benefits and drawbacks, which companies use to make decisions. A detailed consideration of factors associated with each is important in objectively deciding on the most appropriate methods to use in transporting goods. For example, for Berry Smartwatches, air transportation may offer a faster way of reaching the distribution centre. However, it is more expensive compared to all the others.
Further, sea transportation may need to be faster. However, it provides companies with the most cost-effective long-distance freight transport. There are also cases where multiple transport options may be preferred. In such cases, a business could opt for multimodal transportation, which deploys multiple means of transportation to lower costs and optimize supply chain management. Ultimately, for Berry Smartwatches, the most appropriate mode is to meet the company’s specific needs, such as the perishability of the products to be transported and the environmental sustainability of the freight transport solution. The different factors influencing the choice of a mode are effectively considered in evaluating the different modes of transport below.
Option 1: Road Transport
The first option in Freight transport is moving goods by road using trucks from Guangzhou, China, to Cologne, Germany. According to Centobelli et al. (2020), road transport is the most used mode of freight transportation. Trucks and other vehicles transport goods from one location to another overland. Businesses prefer road transport for various reasons. A primary advantage is that the road is the most flexible mode of freight transportation. Its flexibility allows effective door-to-door delivery and ensures products can reach every destination locally, regionally and globally (Cargo Router 2023). Also, the vehicles businesses use are of different types and offer flexibility on the quantity, size, and weight of products to be transported. For example, Berry Smartwatches can use trucks to distribute to the company’s distribution centre and use vans and pickups for different sizes of deliveries in the door-to-door distribution.
Important to mention is the disadvantage that road transport is also exposed to traffic congestion, adverse weather conditions, and local conditions that can result in delays and unexpectedly increase the cost of transportation. Shipping by truck will also demand trips (over 20) to achieve the quantities demanded in Europe (Cargo Router 2023). There are also other notable factors, such as regulations on weight limits and safety measures, such as speed limits and driver requirements, that apply for all road freight transport that may cause delays and increase the cost of transporting goods (Kiani Mavi et al. 2022). Nonetheless, road transport offers the most flexible option for the company to meet all its door-to-door delivery needs.
Another factor to consider in choosing the freight transportation option is the transport cost per unit, time and security of the products transported. The distance from Guangzhou to Cologne is 11051 km, and the cost to transport freight is 0.93$/unit for the smartwatches (Cargo Router 2023). Road takes longer, and it will take an average of 25.5 days for the goods to arrive at the distribution centre (figure 1). Thus, the door-to-door transit time is approximately 25.5 days (Kiani Mavi et al., 2022). The service reliability is relatively low, given the uncertainties associated with road transport. In terms of security, road transport is the most insecure of the freight transport options; thus, there needs to be more cargo security. However, it promises a more flexible way of transporting the watches from China to Germany.
Cost: $0.93/unit
Freight rate index: 22585
Transit time estimate: 25.5 days
CO2 emission index: 20605
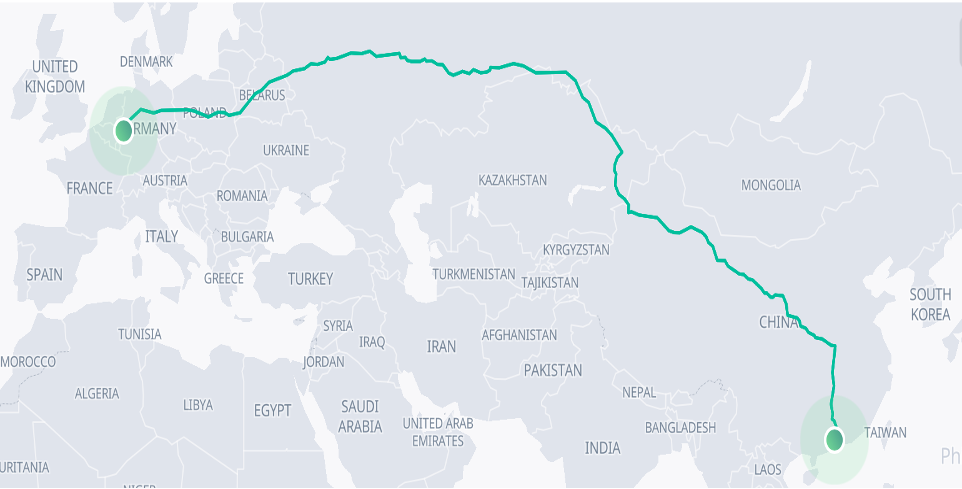
Figure 1: Freight transportation by Road (Guangzhou, China to Cologne, Germany)
Option 2: Rail Transport
Freight transport by rail involves using trains to transport goods from Guangzhou, China, to Cologne, Germany. Rail offers several advantages. Using the railway will involve delivering the Cargo from the manufacturing facility by truck from the Guangzhou rail yard, then transferring the Cargo to wagons, which will transport them by rail to the Köln – Eifeltor rail yard before they are delivered by road to the Cologne distribution centre. The route’s total transit time is about 30.8 days, which includes terminal, loading and unloading operations (Schlumberger, 2023). Using the railway option is slower compared to the road. It would take approximately 30.8 days, which includes supplementary operations such as loading at the source and unloading operations at the destination and all the terminal handling operations. Meaning. Using railways will also involve using roads at the origin and the destination.
A major advantage associated with the road-rail-road arrangement is that it offers the ability of rail to transport large quantities of goods efficiently. It is also more cost-effective than the road as it costs about $0.27/unit to transport Cargo over a distance (Cargo Router 2023). Second, rail transport is also environmentally friendly compared to road transport as rail transport is associated with lower emission levels per unit of goods transported. The schedule also has greater reliability as rail transport is not hampered by traffic congestion or local travel conditions.
However, rail transport is less flexible than road transport, which demands access to rail lines and terminals. It will demand at least three shipments to meet the company’s targets. Rail transport also has several regulations and safety measures, such as safety measures, transportation of hazardous materials and regulations for holding and loading Cargo, which may increase costs and delay times (Schlumberger, 2023). Regulations and safety measures apply to rail transport, such as regulations for transporting hazardous materials and safety measures for loading and unloading Cargo.
Cost: $0.27/unit
Freight rate index: 9167
Transit time estimate: 30.8 days
CO2 emission index: 1904
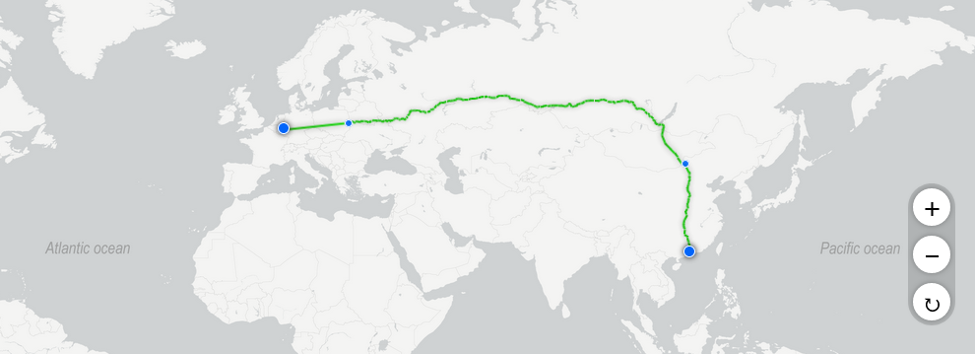
Figure 2: Railway line from Guangzhou, China to Germany
Option 3: Air Transport
Another option for the Berry Smartwatches freight transportation problem is using Air, which will also demand a combination with road. Macharis & Bontekoning (2004) state that air transportation was the fastest cargo transportation from its very early days. It involves using aeroplanes to transport goods over long distances and is often ideal for urgent and time-sensitive products. In the case of Berry, air cargo would meet the company’s needs. Air cargo involves the use of specialized cargo planes for freight transport. For the current freight problem, shipping from Guangzhou, China, to Cologne, Germany, would involve first delivering the products from the manufacturing facility to Baoan International Airport, loading them into a Cargo plane, delivering them to Koln Bonn Airport, and then finally delivering the Cargo through trucks to the distribution centre by road (Figure 3).
Using the aeroplane arrangement would ensure a total transit time of about 6.8 days, including the time spent in loading and unloading operations at the origin and destination. The time also includes all operations at terminal handling. However, this is the most expensive way of transporting Cargo among the options available. While it offers a great time, it costs, on average, $2.00/unit to transport the watches by Air (Tommy, 2023). Also, it is established as being very high on pollution, which Berry company seeks to help circumvent. Further, air transport is also impacted by weather conditions, regulations and safety measures, and flight cancellations that affect reliability and may cause delays and disruptions in the company’s supply chain. However, these problems are also present in the other modes of transport and must be mitigated effectively.
Cost: $2.00/unit
Freight rate index: 97181
Transit time estimate: 6.8 days
CO2 emission index: 85881
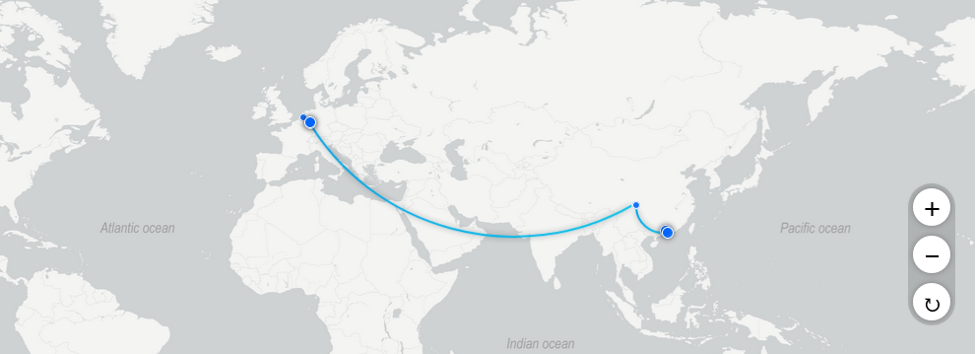
Figure 3: Air Route from Guangzhou, China to Germany
Option 4: Ocean/Ship Transport
Ocean/ship transport would involve the transportation of the Berry Smartwatches via a ship through the sea from Guangzhou, China, to Cologne, Germany. Using ships is the most popular and cost-effective means of moving products over a long distance. Ocean/ship freight transport is ideal for transporting large quantities of goods. The shipping would involve packaging the products into large containers and then moving them to their destination.
The products would be delivered by truck from the Guangzhou manufacturing facility to the Nansha port. The goods would then be transferred to a vessel and shipped to the Bremerhaven port in Germany. They would then be delivered to the distribution centre. Using ships ensures an average route total transit time of about 53 days (Hasan et al., 2022). The time includes all the time for loading and unloading operations and the terminal handling durations. Ships are also affected by sea conditions and weather patterns. They are also controlled by regulations and safety measures, often increasing costs and time delays. The shipping route from Guangzhou, China, to Germany, is also complex and involves passing through different regions that may increase costs and time.
Cost: $0.045/unit
Freight rate index: 3044
Transit time estimate: 53 days
CO2 emission index: 3680
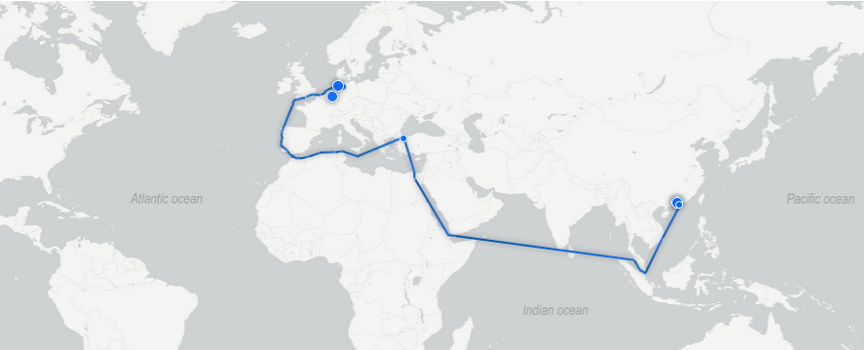
Figure 4: Ocean/ship transport route
Multimodal Transport Considerations
There are various characteristics of the Berry Smartwatches that demand the use of multiple modes of freight transportation. For example, the location of the manufacturing facility and the distribution centre away from seaports, airports and railway yards means that goods using these modes must also use road transport to achieve the flexibility desired in accessing the manufacturing facility and the distribution centre. Multimodal transportation involves using at least two different modes of transport to move goods from one location to another. For example, Berry Smartwatches could demand a combination of any two: road, rail freight, sea, or Air. The transportation would be included in a single contract, with one transport provider handling all the responsibilities of the organization of all the modes of freight transportation across the terminals.
The arrangement differs from intermodal transportation, which involves the products being transported through multiple modes. Still, each transportation segment is handled by separate providers under separate contracts. The multimodal formula would see the same company handle the products from the start to the end of the journey but utilize different transportation modes to complete the journey (Tommy, 2023). The effectiveness and efficiency of multimodal transportation would be defined by the ability of the modes to seamlessly integrate into the transportation process to ensure that the Berry Smartwatches are effectively and efficiently delivered through the lowest possible cost and using an environmentally friendly mode.
Decision and Conclusion: The Optimal Freight Transport Mode for Berry Smartwatches
The Multimodal Freight Transport Exercise (Berry Case Study – Day 2) presents a special freight transportation problem with specific demands that would be best met using a multimodal configuration, including road and railway or a road-rail-road freight transport configuration. Among the considerations is that the products to be transported are perishable goods and that the company emphasizes an environmentally sustainable freight transport solution. The distribution centre is also in Cologne, Germany, while the manufacturing facility is in Guangzhou, China.
In every circumstance, the optimal mode for transporting goods is defined by several factors. These include the type of goods to be transported, the distance to be covered, the time sensitivity of the goods, the environmental friendliness of the mode of transportation and the cost of transportation. As evaluated above, the different transportation modes offer different advantages and disadvantages. It is important to consider what each mode offers and its drawbacks before deciding the mode to use. The table below summarizes some important aspects of the modes discussed above:
Table 1: Mode Comparison Table
| Mode | Cost($/unit) | Time(days) | Service reliability | Security of Cargo | Environmental Impact (CO2 emission index) | |
| 1 | Road | 0.93 | 25.5 | 3 | 2 | 20605 |
| 2 | Road-railway-road | 0.27 | 30.8 | 4 | 3 | 1904 |
| 3 | Road-air-road | 2.00 | 6.8 | 4 | 4 | 85881 |
| 4 | Road-waterway-road | 0.045 | 53 | 3 | 3 | 3680 |
Evaluating the different modes, the most suitable would be to use the road-railway-road configuration as it offers all the targeted advantages. Using this option will involve delivering the Cargo from the manufacturing facility by truck from the Guangzhou rail yard, then transferring the Cargo to wagons, which then transport the watches by rail to the Köln – Eifeltor rail yard in Germany before they are delivered by road to Cologne distribution centre. The option would cost $0.27/unit and a delivery time of 30.8 days. Additionally, this is the most environmentally friendly way of transporting goods as it has the lowest CO2 emission index (1904). Thus, It is the shipping alternative between Guangzhou, China and Cologne, Germany, with the lowest estimated emissions and a realistic door-to-door delivery time for smartwatches. While air transport would have offered the fastest freight transport, it is not suitable for Berry Smartwatches, given its being the greatest polluter and its expensive nature, which could increase the cost of the watches from the intended $250 price. As a result, the use of road-railway-road is the optimal freight transportation solution for Berry Smartwatches and serves the company’s best interests. Under a Multimodal transport agreement, all the transport needs across each terminal will be provided under a single contract despite using both road and rail at different stages of the journey.
References
Browne, M., Dubois, A., & Hulthén, K. (2023). Transportation as a loosely coupled system: A fundamental challenge for sustainable freight transportation. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 17(7), 804-814.
Cargo Router. (2023). Shipping from China to Germany (from Guangzhou to Köln) by sea, road, rail and air freight. Www.cargorouter.com. https://www.cargorouter.com/freight-shipping/China/Guangzhou/Germany/Cologne/
Centobelli, P., Cerchione, R., Esposito, E., & Shashi. (2020). Evaluating environmental sustainability strategies in freight transport and logistics industry. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(3), 1563-1574.
Crainic, T. G., & Laporte, G. (1997). Planning models for freight transportation. European journal of operational research, 97(3), 409-438.
Fulzele, V., & Shankar, R. (2022). Improving freight transportation performance through sustainability best practices. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 165, 285-299.
Hasan, R. A., Irshaid, H., Alhomaidat, F., Lee, S., & Oh, J.-S. (2022). Transportation Mode Detection by Using Smartphones and Smartwatches with Machine Learning. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 26(8), 3578–3589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-1281-0
He, Z., Navneet, K., van Dam, W., & Van Mieghem, P. (2021). Robustness assessment of multimodal freight transport networks. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 207, 107315.
Kiani Mavi, R., Kiani Mavi, N., Olaru, D., Biermann, S., & Chi, S. (2022). Innovations in freight transport: A systematic literature evaluation and COVID implications. The International Journal of Logistics Management, 33(4), 1157-1195.
Macharis, C., & Bontekoning, Y. M. (2004). Opportunities for OR in intermodal freight transport research: A review. European Journal of Operational Research, 153(2), 400-416.
Schlumberger, C. (2023). Air Freight: A Market Study with Implications for Landlocked Countries. World Bank. https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/transport/publication/air-freight-study
Tommy. (2023, March 17). Air Freight Cost Calculator: Step Guide and Example. Air supply. https://www.airsupplycn.com/air-freight-cost-calculator/
 write
write