1.0 Part A
Module Title: Identification and Management of Tuberculosis
Module Duration: 4 Months
Module Level: Undergraduate Students in Bachelor of Science and Nursing
Module Objectives.
- To learn and create awareness of causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with Tuberculosis
- To learn about the global impact and Epidemiology of Tuberculosis
- To design skills for diagnosis of Tuberculosis, inclusive of laboratory tests and imaging
- To understand the treatment methods, that is, drug regimens and management of patients.
- To explore prevention strategies and public health care strategies.
| Months/ Weeks | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 |
| 1st Month | Global Impact and Epidemiology of Tuberculosis | Risk Factors and Transmission of Tuberculosis | Signs and symptoms of Tuberculosis | Tuberculosis in distinct populations, for example, the elderly and pediatric |
| 2nd Month | Diagnostic Methods and Tools | Imaging and Radiological Assessment | Sputum and Laboratory Tests | Test result Interpretation and Case Detection. |
| 3rd Month | Analysis of Tuberculosis Therapy | Drug Regimens and Patient Compliance | Drug resistance and resistance management of TB | Monitoring and Evaluation of treatment of TB |
| 4th Month | Control and prevention measures for the infection. | Co-infection between Tuberculosis and HIV | Patient support and counseling techniques | Case Studies and Evaluation of the Program. |
Assessment and Evaluation
The assessment process will entail various methodologies to be integrated within the school timetabling department. Some of the techniques to be used include;
- Oral regular quizzes and assignments.
- Weekly Continuous Assessment Tests (CATs)
- Case Studies and Projects
- Proactive Monitored Peer Discussion
- Practical demonstrations through diagnosis and treatment
Resources
- Textbooks and Research Articles
- Guest Medic and Expert on Tuberculosis
- Online Database and Research Resources
- Practical Internships in Medical and Public Health Institutes and Hospitals
Additional Requirements
- Safety equipment: Gloves, Lab coat, Safety glasses, and Mask for practical sessions
- Adherence to laboratory protocols through Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Observation of Patient Simulation Techniques through Practicing Clinical Skills
- Enhanced safety audits and diagnostic tool standard enhancement.
Part B
Critical Issue to Anticipate in the Curriculum Development
- Ethical content development: through the comprehensive curriculum for ethical healthcare services relevant to recent content. This will help in solving ethical dilemmas in the healthcare sector.
- Interdisciplinary approach: This will be enhanced through correlation between different healthcare disciplines and integration to provide holistic education.
- Assessment and Evaluation: Enhanced by developing appropriate and standardized marking rubric and grading system. This would enhance the prompt Evaluation of the learners.
- Ethical dilemmas and Simulation: Resonate in providing learners with ethical dilemmas to enhance content sensitivity, thus enhancing the educational process.
- Availability of Resources: Affirmation that all the required resources are available, for example, Textbooks, lab resources, and guest speakers.
Challenges in Implementation with Consideration of Technology and Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
The usage of artificial intelligence in enhancing ethical healthcare education would provide more efficient personalized feedback information. However, ensuring the ethical use of AI and minimizing biasness in AI algorithms might be a significant concern.
Integration with Clinical Practices
Integrating and connecting the module to clinical experience is challenging as learners find it complex to apply knowledge in real-life experience. Thus, it requires simplification.
Faculty Training
The members of the faculty will require training on how to integrate technology and AI into the curriculum. However, addressing comfort and concern and enhancing the easy operation of technological tools might be costly to some extent.
Data Security and Privacy
The process of safeguarding student’s data through AI might be complicated, and the information might be subjected to breach. However, with clear, enhanced cybersecurity, the data can be safeguarded through encryption.
Online Learning
Implementing the information in the module may be necessary due to the drastically growing use of technology and advancement. However, engaging learners in the online learning process might face partial student resistance and a breakdown of some equipment.
Bibliography
Boulet, L. P., Reddel, H. K., Bateman, E., Pedersen, S., FitzGerald, J. M., & O’Byrne, P. M. (2019). The global initiative for asthma (GINA): 25 years later. European Respiratory Journal, 54(2). https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/54/2/1900598.short
Cameron, L. H., & Cruz, A. T. (2022). Childhood tuberculosis. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases, 35(5), 477-483. https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/wk/coidi/2022/00000035/00000005/art00016
Turecki, G., Brent, D. A., Gunnell, D., O’Connor, R. C., Oquendo, M. A., Pirkis, J., & Stanley, B. H. (2019). Suicide and suicide risk. Nature reviews Disease primers, 5(1), 74. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41572-019-0121-0
Appendices
Appendix 1: Signs and Symptoms of Tuberculosis
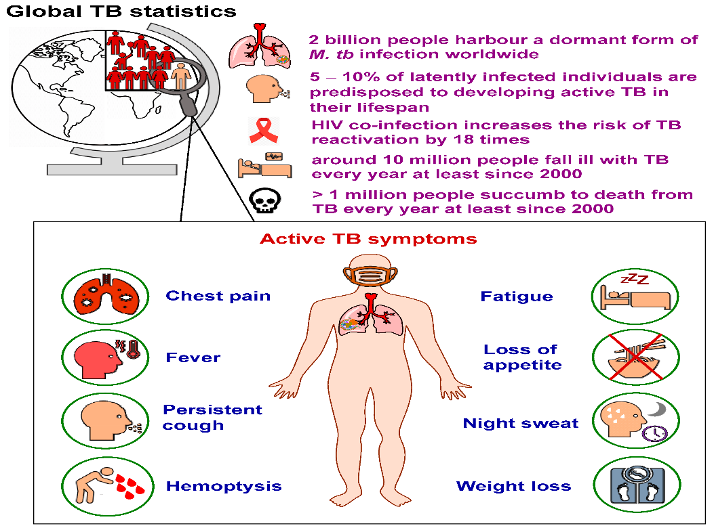
Source: MDPI
Appendix 2: Case Study Statistics of Tuberculosis Infection
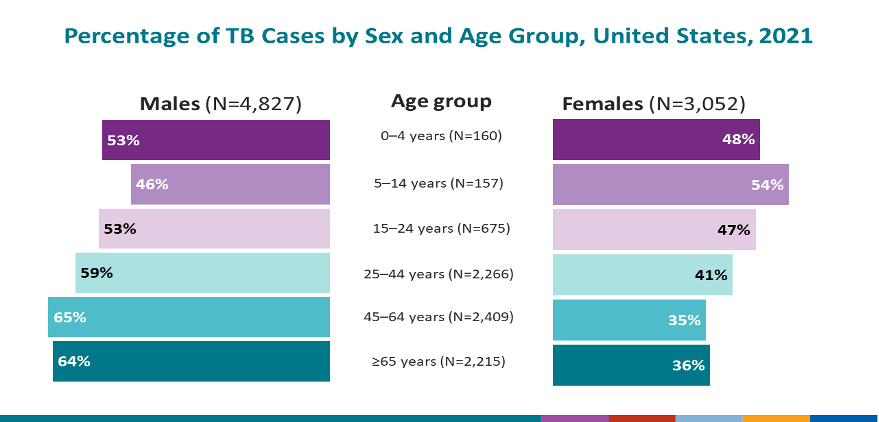
Source: CDC
 write
write