Introduction
The music performance industry has long provided fans with amazing performances and experiences. On the other hand, many kinds of activities pertaining to consumer welfare, competitiveness, and market dynamics are occurring behind the scenes. Talks concerning government interference and market power often revolve around Ticketmaster, the industry leader in the ticketing sector. This essay examines the degree to which US and UK competition authorities should step in to limit the market dominance of firms like Ticketmaster or to let the free market function with the least amount of interference.
The monopolistic powers
Before delving deeper into this research, it’s important to comprehend the concept of monopoly, a fundamental phrase in economics. In the language of economics, a monopoly is a unique market structure defined by the unrivalled domination of one business over another in the manufacturing or marketing of a specific good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a number of distinctive features that set it apart from other forces in the economy (Albrecht et al., 2023, np). Monopolies are distinguished by the absence of close substitutes for their products or services. Essentially, when looking for a certain good or service that is under monopolist control, consumers have very few, if any, options. Due to the absence of alternatives, the monopolistic firm has substantial control over market dynamics and prices. Additionally, the presence of formidable entry obstacles is another attribute of monopolistic power. These barriers can take many different forms, including as high initial capital needs, incumbents’ technological superiority, and exclusive access to vital resources. Because of this, prospective rivals encounter formidable barriers when attempting to join the market, hence strengthening their monopolistic advantage (Heller and Salzman, 2021, np).
Ticketmaster, a significant provider of ticketing services for live music events, exemplifies the importance of exclusivity. Due to its dominant market position, the corporation has extensive control over important factors like ticket costs, distribution routes, and entry to well-attended events. The absence of direct rivals with a similar market share highlights Ticketmaster’s extensive influence even further. Because of this, customers frequently have few options when trying to find tickets for their preferred performances.
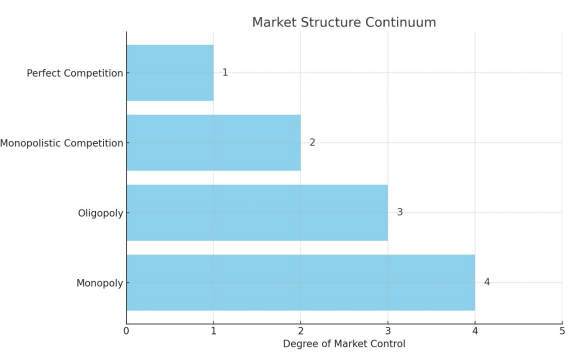
Figure 1: Continuum of Market Structure (Monopoly – Perfect Competition)
This figure illustrates a range of market structures that are cross-monopolies to ideal competition. Every market structure has a specific degree of control that is used by four companies operating in that market. The market structure becomes less competitive as control levels rise.
Monopoly (Level 4): A monopoly, in which a single business has complete control over the market, is seen on the far left. The entry barrier is high, and there are no close equivalents.
Oligopoly (level 3): As we proceed to the right, we come across an oligopoly, which is defined by a limited number of powerful enterprises that have a substantial amount of control. Oligopolies confront modest entry hurdles and the ability to affect prices.
Monopolistic competition (level 2): This type of competition involves multiple businesses competing with unique items. Although there are fewer barriers to entry and some product differentiation, companies still have some control over pricing.
Lastly, we have ideal competition (level l), where a large number of tiny firms are present. Easy entry and leave, identical products, and a lack of market power are the defining characteristics of this market structure.
The Perspective of the Free Market
According to the theory behind free markets, prices can be set, and resources may be distributed effectively with little interference from the government and a laissez-faire economy. Free market advocates contend that a hands-off policy promotes competition, innovation, and economic efficiency in the live music ticketing sector (Hunt, 2022, p.269).
In a competitive market, corporations prioritize providing high-quality services and products at reasonable costs to level up consumer welfare. Fair prices and customer access are encouraged when monopolistic power is absent. Supporters of this viewpoint think that regulatory action is not always necessary as a result of Ticketmaster’s market dominance. Instead, they contend that the business will naturally develop as a result of market forces, consumer demand, rivalry from smaller ticket sellers, and new technologies. Nonetheless, some significant issues come up when we apply free market theory to the live music ticketing industry. Does Ticketmaster’s hegemony restrict consumer choice and impede competition? A system where a single corporation has substantial control over distribution and price benefits consumers. Is it?
Customers have voiced concerns about expensive tickets, ambiguous pricing, and transactions that they have concealed from the secondary market. These problems necessitate research and action. Although a free market viewpoint places a premium on economic efficiency, some contend that the distinction between market exploitation and economic efficiency can become hazy when it comes to live music events.
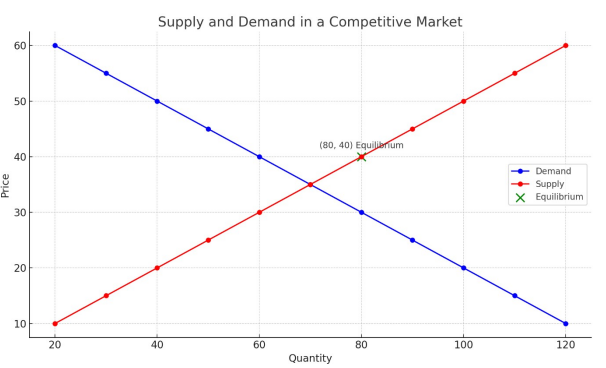
Figure 2: Demand and Supply in a Competitive Market
The relationship between demand and supply in a competitive market is depicted in this figure. The demand curve is represented by the blue line, which indicates that the amount required rises as the price falls. On the other hand, the supply curve, represented by the red line, demonstrates that when the price rises, so does the quantity delivered. The equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the point at which the quantity supplied and the quantity required are equal, as indicated by the green “x”. It demonstrates how a market with competition brings supply and demand into balance, with a certain price and quantity at that point.
The Viewpoint of the Intervention
In contrast to the faire-laissez-faire strategy, there are strong justifications for government involvement in monopolistic markets. Competition regulators in the US and the UK have acknowledged the need to preserve the values of fair competition and safeguard consumer interests. Consequently, a wide range of interventions have been employed sparingly to address the threat of monopoly power in some industries, ranging from regulatory oversight to strict antitrust laws (Heller and Salzman, 2021, np).
Given Ticketmaster’s unwavering dominance in the market, initiatives are needed. The goal of these intervention methods is to create fair competition for companies in the concert ticketing market and enhance the welfare of consumers. Opponents of intervention contend that in the absence of robust regulatory mechanisms, consumers could become entangled in a web of detrimental outcomes (Weglarz, 2020, np). These could include the spectre of ever-increasing ticket prices, limitations on how affordable tickets can be, and a chronic lack of transparency in ticket pricing schemes.
Taylor Swift’s high-profile occurrences and ticket sales scandal raise worries about market power and its impact on consumers. The need for competition authorities to reconsider their powers and responsibilities in opposing monopolistic tactics is increased by such events. In this situation, government action plays a crucial role in defending the rights of the customers who fuel the vibrancy of the live music scene.
Intervention measures try to balance consumer competition and protection despite potential legislative limits. By doing this, they want to prevent monopolistic distortions and guarantee that market dynamics evolve naturally. We may more accurately evaluate these intervention methods’ capacity to lessen the detrimental impacts of monopolistic power and support equitable markets for all players by evaluating their viability.
Assessment of the Two Perspectives’ Positions
To determine whether competition authorities should intervene in Ticketmaster’s market strength, two opposing viewpoints must be carefully considered. One view of the free market respects the benefits of innovation and competition as the cornerstones of advancing economic efficiency. The intervention approach, on the other hand, highlights how crucial it is to uphold the concepts of consumer protection and market justice. When navigating this complicated terrain, one must carefully weigh the possible outcomes of each strategy. In the long run, the free-market viewpoint, which prioritizes less government involvement, is expected to promote innovation and intense competition. Laissez-faire policies let market forces spontaneously mould the sector, which ought to improve efficiency and allocate resources optimally. There is a risk associated with this possibility, though: in the near run, customers may be subjected to monopolistic activities. There could be a rise in ticket costs, restrictions on who can attend events, and ongoing questions about pricing structures’ transparency (Khan, 2019, np).
The pro-intervention viewpoint, on the other hand, promises instantaneous consumer protection. The negative impacts of monopolistic power can be reduced, and market distortions can be promptly corrected with the use of regulatory tools like supervision and antitrust laws (Lorsch, 2023, p123). Nonetheless, thoughtful policy formulation and execution are necessary for the intervention to be effective. Finding a careful balance between consumer protection, competition, and innovation is crucial. Excessive involvement may inadvertently hinder innovation and competition, undermining the same goals it seeks to achieve.
The ability and diligence of the competition authorities tasked with carrying out the intervention also have a significant impact on its efficacy. These organizations are essential in putting regulations into action and making sure market players follow the rules as set forth. Their efforts serve as a deterrent against future monopolistic behaviour in addition to mitigating the current issues caused by Ticketmaster’s dominant market position (Hunt, 2022).
Therefore, evaluating the two viewpoints of interventionism and the free market paints a nuanced picture. Every strategy has advantages and disadvantages, and the relative efficacy of each rests on the meticulous creation of policies and the strict application of those policies. Competition regulators have delicate decisions ahead of them as they must weigh the advantages of protecting consumers against the necessity of promoting competition and innovation in the live music ticketing sector. Competition regulators can steer the market in a way that best serves the interests of consumers by carefully navigating this complex issue.
Conclusion
It is a complicated matter that necessitates careful consideration of whether or not US and UK competition authorities should become involved with Ticketmaster’s dominant market position. The notion of monopoly power in the live music ticketing sector has significant effects on customers and the competitiveness of the market. A free-market viewpoint encourages economic efficiency and inventiveness, but it may also expose customers to monopolistic behaviour. On the other hand, from the standpoint of intervention, consumer protection comes first, but careful consideration is necessary to make sure it doesn’t impede competitiveness.
The challenging task of balancing different viewpoints falls to competition authorities. Legislators and regulators need to be on the lookout for new issues as the concert ticketing sector develops in order to guarantee a fair and competitive market. In the end, the degree of involvement necessary may vary over time in light of the market’s volatility and shifting demands from consumers. There’s still a major question in this continuing discussion. Should competition authorities take the lead in limiting Ticketmaster’s market dominance, or should they let the market’s drama unfold in the live music ticketing space? A close examination of the dynamically shifting relationship between consumer welfare and competition in contemporary economies holds the key to the solution.
Reference list
Albrecht, B.C., Auer, D., Fruits, E. and Manne, G.A. (2023). Doomsday Mergers: A Retrospective Study of False Alarms. [online] Social Science Research Network. Doi:https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4407779.
Heller, M.A. and Salzman, J. (2021). Mine: How the Hidden Rules of Ownership Control Our Lives. [online] Amazon. New York: Doubleday. Available at: https://www.amazon.com/Mine-Hidden-Rules-Ownership-Control/dp/0385544723#:~:text=In%20Mine [Accessed 16 Mar. 2024].
Hunt, T. (2022). Increasing Competition in Live Music: The Case for Better Enforcement of the Live Nation Entertainment Consent Decree. Cleveland State Law Review, [online] 71(1), p.269. Available at: https://engagedscholarship.csuohio.edu/clevstlrev/vol71/iss1/12/.
Khan, L. (2019). Amazon’s Antitrust Paradox. [online] Yale Law Journal. Available at: https://www.yalelawjournal.org/pdf/e.710.Khan.805_zuvfyyeh.pdf.
Lorsch, E. (2023). Why Live Nation and Ticketmaster dominate the live entertainment industry. [online] CNBC. Available at: https://www.cnbc.com/2023/01/25/the-live-nation-and-ticketmaster-monopoly-of-live-entertainment.html.
Weglarz (2020). Rock Brand: The Political and Cultural Economy of Live Rock. [online] Available at: https://conservancy.umn.edu/bitstream/handle/11299/144065/Weglarz_umn_0130E_12375.pdf;jsessionid=731252A5BB2A900D155FAE75C3254E2A?sequence=1.
 write
write