Executive Summary
Good quality and reliability in engineering systems are necessary for improving the quality of performance in a workplace. An overall system of this nature employs standard procedures and practices that improve quality, reliability, and safety efficiency. The comprehensive analysis includes identifying the main elements of the system, its implementation procedure, and what advantages it might yield in the workplace. Our organization is known to be an expert in project management and electrical engineering. However, there is a need to establish and use a quality and reliability system that will guarantee improved service delivery, thus reducing project delays and increasing customer satisfaction by narrowing down uncertainties in meeting firm expectations.
Introduction
Quality and reliability systems are defined as policies and procedures that are implemented to ensure that the products meet customers’ performance, safety, or efficiency expectations. It involves implementing a comprehensive system that integrates various components to achieve desired outcomes in the workplace. Quality is about meeting the specifications and requirements of a product or service, while reliability is the ability of a system to perform its functions under specific conditions for a specified period. These aspects are crucial for ensuring customer satisfaction, reducing defects, and enhancing overall organizational performance, which will be attained through formulating, developing, and implementing a quality and reliability system to oversee all these required changes because our firm is renowned for its expertise in project management, electrical engineering, and mechanical engineering and is facing challenges related to the efficiency of service delivery. Therefore, the organization needs to develop and implement a quality and reliability system that will assist the organization in achieving maximum operations that lead to customer satisfaction and enhance defect reduction.
Proposed Solution
The adequate technical infrastructure necessary for establishing optimal performance must begin in the conceptualization phase and persist throughout construction and ongoing operations. The strategic approach will ensure programs are aligned with industry standards and organizational objectives, dynamic change, and continuous improvement. Therefore, building a consistent system in the form of a robust system aligns the industry rules with the company strategies and addresses potential barriers. By adhering to these principles and prioritizing customer satisfaction, the organization will create a winning strategy in its technology initiatives, marked by continuous improvement and adaptability.
Problem Statement
The company faces operational challenges in integrating infrastructure and technology services, resulting in delays, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction. The most critical factors contributing to these problems are scheduling, irregular quality checks and controls, and reliability. Thus, interventions to address these issues are needed to improve management and service quality because our organization must ensure a standardized approach to quality and reliability to minimize delays and overcome increased costs, resulting in a more satisfying customer experience. Therefore, the organization should establish a solid quality and reliability system to run smoothly, reduce these problems, and increase customer satisfaction.
Analysis
Objectives and Benefits of Quality and Reliable System Implementation
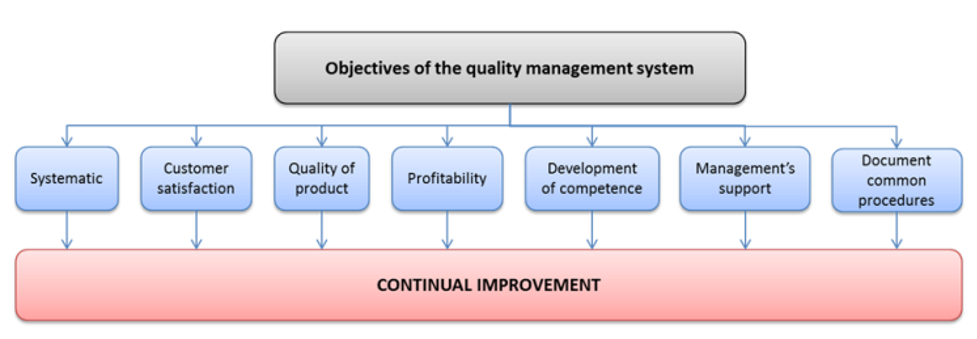
Figure 01 shows the objectives of implementing a quality and reliability management system in an organization.
Implementing quality and absolute reliability systems in engineering can provide our organization with a wide range of benefits. Key benefits include;
Increased Product Quality
An effective quality system guarantees that products match or surpass customer expectations, translating into improved customer satisfaction, enhanced brand image, and return business.
Enhanced Reliability
By aiding in identifying and acting against potential failure modes, reliability engineering practices produce reliable products and systems, which leads to a decrease in failures, shortened downtime, and increased consumer trust.
Improved Safety Culture
Compliance with safety procedures and standards creates a “safety culture” within the organization, preventing accidents among the employees and ensuring that morale and productivity increase.
Efficient Resource Utilization
Utilizing efficiency measures such as lean manufacturing and Six Sigma optimizes processes, minimizes wastes, and increases resource utilization, causing a reduction of costs and an increase in market competitiveness.
Higher Productivity Levels
Productivity improvement strategies, employee training, and engagement result from high-level proof activity. The well-trained and motivated employees contribute sufficiently to achieving objectives determined by an organization.
Key Components of the Quality and Reliability in Engineering Systems
Establish Quality Management System (QMS)
A Quality Management System is the foundation for consistently meeting customer expectations of the products and services. One widely recognized standard is the ISO 9001: 2015 standard, which helps to develop a quality system that accomplishes the goals of establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an effective quality management system. Quality Management System refers to an international standard, ISO 9001, with a systematic implementation approach (Purwanto, Asbari, and Santoso, 2020). It involves customer satisfaction, process improvement, and constantly updating the Quality Management System. The standard includes leadership, resource management, product realization, measurement, and analysis. Furthermore, implementing ISO 9001 requires establishing processes and goals for monitoring performance and encouraging a systemic mindset.
Therefore, define organizational goals and objectives according to quality standards to develop a quality system. First, identify the critical paths and then conduct a comprehensive introductory analysis. Second, choose an established framework, such as ISO 9001, that is consistent with engineering practices and document specific standard operating procedures for engineering management, including risk or quality management. Additionally, ensure employees are qualified through specific training programs and encourage adherence to established policies that foster a culture of continuous improvement by asking employees for feedback (Zonnenshain and Kenett, 2020). Moreover, establish an effective documentation system for record-keeping and monitoring performance indicators without neglecting to monitor or conduct internal audits to identify control areas. Also, establish communication channels that customers and suppliers can respond to; and finally, gain leadership commitment and seek daily reviews to ensure the relevance and effectiveness of the ongoing Quality Management System quality program that adheres to all its standards within the organization.
Develop Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
The FMEA will assess failure modes in the process, product, or system concerning their effects. It will provide information on failure modes, determine their likelihood and severity, as well as existing controls, assigning a risk priority number (RPN) for prioritizing mitigation actions. The FMEA will play a vital role in preemptively dealing with vulnerabilities, increasing dependability, and avoiding all future (Fakhravar, 2021). The second approach requires the identification of RCM that will help identify maintenance strategies to ensure system reliability.
Establish Safety Protocols
Safety is critical to quality and reliability. Thus, implementing safety measures and compliance with occupational health and safety (OHS) standards ensures employee well-being and prevents workplace accidents. Safety protocols will include regular safety training, hazard identification, and use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) by employees to improve the quality and reliability of systems.
Establish Efficiency Measures
Efficiency metrics are geared towards improving processes to eliminate waste, minimize errors, and increase overall effectiveness. Thus, adopt a lean manufacturing approach that eliminates non-value-added activities and ensures implementation of Six Sigma methodologies to reduce variations and defects from processes for better support towards a quality and reliable system.
Develop Productivity Enhancement Strategies
A well-implemented Quality and Reliability in an engineering system leads to achieving productivity as one of its outcomes. Embraced strategies that should be encouraged include continuous improvement initiatives, employee engagement programs, and adopting technology to automatize procedures and processes in the organization.
Quality and Reliability System Development Process
Creating quality and reliability in engineering systems needs to be a holistic plan. The process of development is outlined in the following steps;
Initial Assessment and Planning
The first step is an in-depth evaluation of the current quality and reliability situation at work. The evaluation will consist of analyzing current processes, pinpointing possible improvement zones, and setting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound (SMART) goals. A strategy should be formulated to facilitate the implementation process. The following steps will then initiate the planning process.
Establish a Quality and Reliability Team
Establish a separate cross-functional team of representatives from the production, engineering, quality assurance, and customer services departments. Ensure inclusion at various levels of the organization to encourage teamwork and ownership.
Conduct a Current State Assessment of the Existing System
Assess current processes, systems, and culture related to quality and reliability. Find the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Collect feedback from employees at all levels to understand the state of operation in the organization entirely.
Define Quality and Reliability Objectives
Define specific and measurable goals consistent with the organization’s broader objectives. These goals should meet the SMART criteria. Examples are decreasing defects by a given percentage or increasing the reliability of products through improvement in KPIs.
Develop a Quality Policy
Draft a quality policy that suits the mission and values of the institution. Inform all employees of this policy and their role in achieving quality and reliability goals. The policy should be a reference document for the business’s decisions and actions.
Design and Document the Development and Implementation Processes
Map out end-to-end product development, manufacturing, testing, and customer support processes. Document these processes, including critical inputs, outputs, responsibilities, and checkpoints. Implement process controls to ensure consistency and traceability.
Stakeholder Involvement in the Development and Implementation Process
The success of any quality initiative depends on the commitment and involvement of all stakeholders. Therefore, developing and implementing a quality and reliability system in engineering requires collaboration and participation from various stakeholders, including top management, employees, suppliers, and customers. Each group plays a crucial role in ensuring the system’s success since clear communication and involvement in decision-making processes create a sense of ownership and accountability. Each group plays a crucial role in ensuring the system’s success.
The Top Management
The top management is responsible for setting the organization’s overall strategic direction, including its commitment to quality and reliability. They establish policies, allocate resources, and define objectives related to quality and reliability (Silva et al., 2021). Therefore, they should be at the forefront of formulating the required policies to enhance quality and reliability in developing and implementing the required system to optimize operations.
Additionally, the top management provides organizational leadership and culture where the leaders at the top management level of the organization shape the organizational culture by promoting a commitment to quality and reliability. Their support and active involvement create an environment where employees understand the importance of these principles (Silva et al., 2021). Therefore, much emphasis should be considered to include the top management in the development and implementation process of the quality and reliability system
Employees
During the designing and implementation process of the new quality and reliability system, there should be a critical focus on training and skills development for the existing employees since they need to be adequately trained to understand and implement quality and reliability standards. The training includes training on processes, procedures, and tools that will be used upon implementing the new system to ensure that they can contribute effectively to the system and enhance productivity once it comes into play (Abbas 2020). Additionally, the training will ensure continuous improvement because the employees are directly involved in the day-to-day operations, and their commitment to continuous improvement and adherence to established quality and reliability standards are essential for the system’s success.
Suppliers
Suppliers play a critical role in the overall quality of the final product through the supply of quality materials for the final product. Therefore, an incredibly reliable and effective system development involves close collaboration with suppliers to ensure that the supply chain process meets the organization’s specified quality standards and delivers high-quality raw materials (Saragih et al., 2020). These quality materials and components are essential in developing the best quality and reliable system for implementation.
Customers
Since customers form the backbone of any business, they should be involved by providing feedback and desired expectations from the new quality and reliability system. Additionally, understanding client expectations and requirements is vital in designing products and services that align with high quality and reliability standards (Salimova et al., 2020). Therefore, ensure consumer involvement in the new system’s development, improvement, and implementation procedure because regular comments and feedback from clients can highlight regions for improvement and manual enhancements to the prevailing system.
Moreover, these customers are often those who apprehend the market dynamics and needs, which may assist within the method of a systems development and implementation cable of producing the best and desired products that yield a significant marketplace share. Thus, because client needs and marketplace developments can have an impact on the improvement of new functions or enhancements in the existing system, the prevailing customers, together with a nicely-wishing consumer community, need to be entrenched in the improvement and implementation of the brand-new system due to the fact a first-class and reliability system that is aware of marketplace demands can give the company an aggressive market aspect.
Thus, effective communication and collaboration amongst those stakeholders are essential for designing, growing, and enforcing an excellent and reliable system in engineering. Moreover, the developed and implemented system should be designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing for continuous improvement and responsiveness to changing circumstances and providing room for regular audits, assessments, and reviews, which can help ensure that the system is functioning as intended and delivers the desired level of quality and reliability.
Implementation
Quality and Reliability System Implementation Process
Implementing the Quality and Reliability System will involve establishing a framework encompassing the entire product or service lifecycle. The framework will ensure that quality is ingrained in every organization’s operations, from design and production to delivery and customer support. The process for implementation of the new system will involve the following steps;
Step 1: Define and Develop Quality Objectives
It is necessary to first identify clear and measurable quality objectives as the initial step of a Quality and Reliability System. The goals should correspond to the overall organizational direction and reflect customer expectations. For instance, this organization is facing operational challenges in infrastructure and technology services integration that cause delays and higher costs, while the main factors leading to these issues are scheduling, inconsistency, poor quality, and reliability. Therefore, the new system aims to implement interventions that address these problems for better quality management and service delivery. Then, the organization should develop objectives that lead to a normal method of quality and certainty, minimize delays, reduce costs, and increase satisfaction with customer service.
Step 2: Establish a Cross-functional Team
Quality and Reliability System is implemented with coordinated efforts for different departments in the organization. Thus, a cross-functional team that includes representatives from design, production quality control, and other related areas is needed because this team will be responsible for making important decisions concerning the implementation process, wherein every issue within the system is considered.
Step 3: Conduct a Gap Analysis
Before using the Quality and Reliability System, a gap analysis should be conducted where the organization conducts an in-depth evaluation of their quality and reliability status against identifying areas that require improvement. A comprehensive gap analysis will serve as a roadmap for identifying areas to be addressed and the development of an actionable implementation plan.
Step 4: Develop Quality Policies and Procedures
Based on noted or identified gaps, the organization should create quality policies and procedures within a comprehensive format. These policy documents are detailed with standards and guidelines that the employees should meet to guarantee production or service quality. Further, the policies and procedures should encompass all associated processes, from product design to development and production testing support, among other required processes. It incorporates putting together the Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), which are essential for preserving consistency within processes as these procedures state what, how, and quality one should do. Moreover, ongoing reviews and upgrades from the Standard Operating Procedures guarantee that organizational processes and practices are aligned with changing industry standards.
Step 5: Provide Training and Awareness
A change in the organization’s culture is necessary to implement a Quality and Reliability System. The staff members must be familiarized with these new policies and procedures. Thus, they need to be trained, and the kind of training should reach out to all organizational levels, creating a climate for betterment and accountability.
Step 6: Implement Quality Control Measures
Quality control mechanisms are essential in tracking and ensuring that the organization’s products or services meet the desired quality. Quality control procedures include applying tools and techniques like statistical process controls, Six Sigma methods, and routine audits. On the other hand, quality control procedures, including ISO 900 Standard adoption, pinpoint deviations from specified standards and allow for immediate corrective actions.
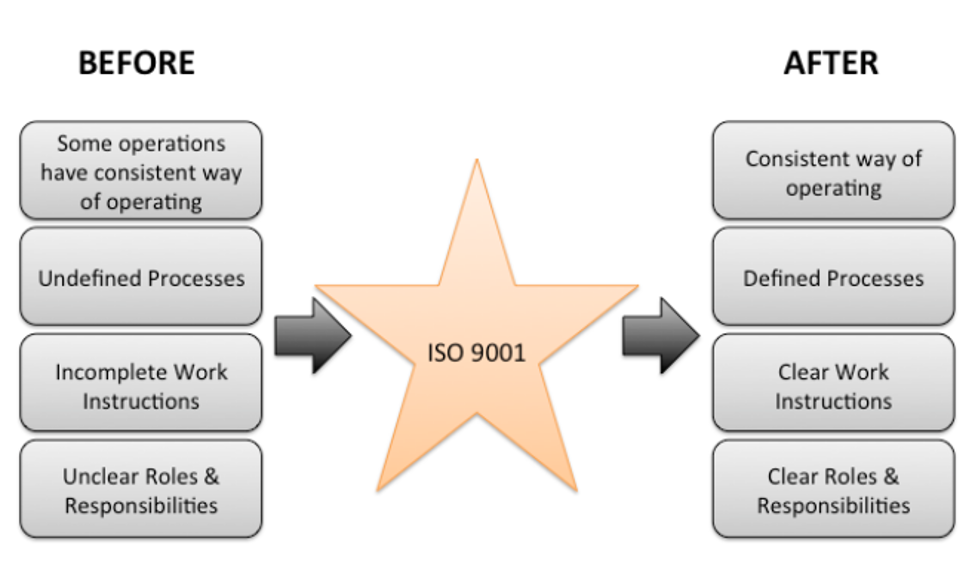
See Figure 02: It shows how establishing an ISO Standard helps solve operational problems in an organization.
Step 7: Integrate Reliability Engineering
Reliability engineering aims to predict failure in products or services, and implementing reliability engineering within the Quality and Reliability System improves the capability for the delivery of quality products or commodities. A step like this involves reliability testing, failure mode analysis, and design changes to increase product reliability.
Step 8: Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The KPIs need to be determined to evaluate the efficiency of the Quality and Reliability System. The selected KPIs should align with the identified quality objectives and measures for determining if a successful implementation has occurred. To mention some of the KPIs, defect rates, customer satisfaction scores, and compliance with production timelines may be given.
Step 9: Implement Continuous Improvement Processes
Continuous improvement is the core concept of a viable Quality and Reliability System. The system must incorporate an iterative process of performance review, problem identification, and elimination that ensures change due to altering customer expectations or industry standards.
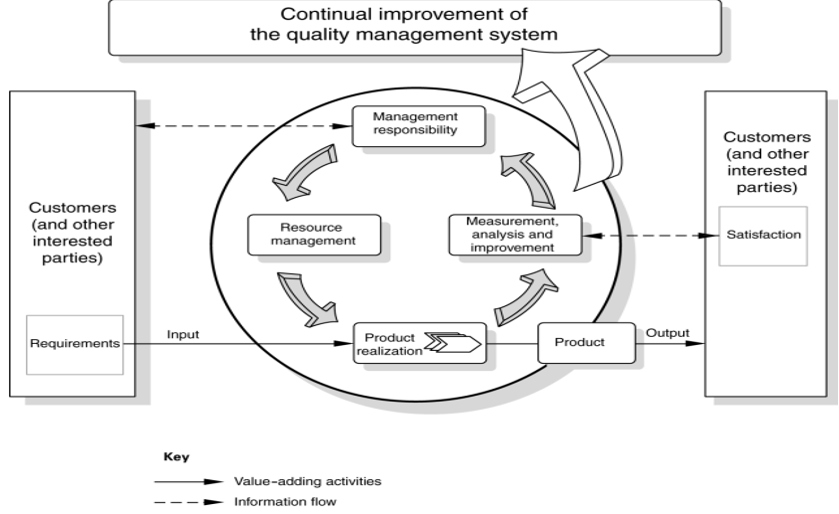
See Figure 03: It shows the continual improvement cycle of a quality management system.
Step 10: Conduct Regular Audits and Assessments
Carry out periodic audits and reviews, which are essential for ensuring continuous compliance with the quality policies and practices that have been put in place. Further, internal and external audits contribute to detecting nonconformities and areas for improvement risks. As such, the prompt response to audit findings reflects an organization’s intention of following a solid Quality and Reliability System.
Step 11: Foster a Quality Culture
A quality culture that will sustain the Quality and Reliability System has to be developed in any organization for a long time. It entails inculcating a culture of high quality and dependability in all employees, from the management level to those on the shop floor (Sony, Antony, and Douglas, 2020). Given the facts, quality-centric organizational culture is influenced by recognition and rewards for contributions to quality, open communication channels, and continuous learning.
Step 12: Document and Communicate Achievements
In implementing the quality and reliability system, the move requires identifying the improvements in the quality of products, customer satisfaction, and compliance with regulations that result from transparency created through communication, which makes successes to be shared in creating value for the system, hence commitment.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing a Quality and Reliability System is challenging. The implementation process may face challenges, which are expected in any organization and may include employee resistance to change, resource constraints for development and implementation purposes, and the need for ongoing commitment from leadership. Therefore, addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach, clear communication, and a willingness to adapt the implementation plan based on feedback and the lessons learned.
Testing
A rigorous testing technique is crucial for a quality and reliability system after its deployment to ensure the attained outcomes match the goal of achieving organizational success. The test approach includes several essential steps to evaluate the performance, reliability, and general functionality of an integrated system through such tests as;
Performance Testing
Start the testing process through extensive performance tests on quality and reliability systems to assess how effectively they would cope with expected workload and stress. Second, review and analyze the response times, throughput capacity, and resource utilization to ensure the system can smoothly manage organization processes without bottlenecks.
Functional Testing
Ensure the performance of all individual elements in a quality and reliability system, such as testing different functionality aspects, modules, or interfaces to ensure they operate correctly. Functional tests identify any deviations from the desired behavior, assuring that the capabilities provided by this system match stated requirements.
Regression Testing
Apply regression testing to validate that recent changes, updates, or improvements made in the quality and reliability system do not negatively impact existing functionalities and that processes done during the implementation process do not introduce unwanted consequences or break previously functioning components.
Perform Scalability Testing
Assess the system scalability by checking its ability to receive more data, users, or transactions for procedural purposes because scalability testing determines that increased user numbers and use do not necessarily mean degradation of service quality.
Integration Testing
Validate that there are good connection points between the quality and reliability system and other systems within the organization to ensure proper data flow movement from one component to another. Integration testing is also critical as it helps detect and address compatibility issues that may arise when the system works with other organizational tools and platforms.
Data Integrity Testing
Ensure that the system’s data is accurate, consistent, and reliable by undertaking tests to identify errors in entering, storing, or retrieving information. Therefore, ensure data integrity by introducing checks and validations that avoid the said scenario to preserve the reliability of information represented in the application.
Documentation Review
Inspect all the documentation on quality and reliability systems to ensure that process manuals, user guides, and system documents are in consonance with features applied and functionality developed. Moreover, update documentation regularly to maintain compliance with any changes made during the implementation or post-implementation testing stages.
The testing phase for quality and reliability systems is a critical stage that guarantees the effective running of the system, achievement of organizational standards, and contribution to business success. Therefore, through the systematic performance of functional tests, security testing and usability are implemented to help detect possible issues that can be corrected promptly, thereby creating a culture of continuous improvement by strengthening quality-reliability initiatives. Thus, revisit and continuously update the testing process to accommodate the changing demands of the organization or leading practices in this industry.
Conclusion
Therefore, the Quality and Reliability System ensures an intricate process that requires thorough preparation, teamwork, and continuous dedication. From setting quality objectives to promoting a quality culture, every phase is essential to consistently ensuring an organization produces high-quality products or services. By adhering to this systematic approach and persistently looking for opportunities, the organization will satisfy customers and succeed in a competitive market.
Additionally, adopting Quality and Reliability in engineering systems requires the combination of different elements, standards, and approaches. As such, the organization can ensure improved quality, reliability, safety, efficiency, and productivity through a critical approach and using global standards. Significantly, the advantages of such a rollout extend from internal processes to improving customer satisfaction levels, competitive advantage in the market, and organizational performance. Therefore, ongoing observation and assessment while maintaining a solid commitment to constant improvement are vital for achieving the longevity of the system’s effectiveness over time, and in this holistic approach, the organization is forming an environment that deeply believes in high quality.
References
Abbas, J., 2020. Impact of total quality management on corporate sustainability through the mediating effect of knowledge management—Journal of Cleaner Production, 244, p.118806.
Fakhravar, H., 2021. Application of Failure Modes and Effects Analysis in the Engineering Design Process. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.05444.
Purwanto, A., Asbari, M. and Santoso, P.B., 2020. Effect of the integrated management system of ISO 9001: 2015 and ISO 22000: 2018 implementation to packaging industries quality performance at Banten Indonesia. Jurnal Ilmiah Manajemen, Ekonomi, & Akuntansi (MEA), 4(1), pp.17-29.
Salimova, T., Vatolkina, N., Makolov, V. and Anikina, N., 2020. The perspective of quality management system development in the era of Industry 4.0. Humanities & Social Sciences Reviews, 8(4), pp.483-495.
Saragih, J., Tarigan, A., Pratama, I., Wardati, J. and Silalahi, E.F., 2020. Total quality management, supply chain management practices, and operations capability impact firm performance. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 21(2), pp.384-397.
Silva, C.S., Magano, J., Matos, A. and Nogueira, T., 2021. Sustainable quality management systems in the current paradigm: The role of leadership. Sustainability, 13(4), p.2056.
Sony, M., Antony, J. and Douglas, J.A., 2020. Essential ingredients for implementing Quality 4.0: a narrative review of the literature and future directions for research. The TQM Journal, 32(4), pp.779-793.
Zonnenshain, A. and Kenett, R.S., 2020. Quality 4.0—the challenging future of quality engineering. Quality Engineering, 32(4), pp.614-626.
 write
write