Introduction
Drastic changes have occurred in the sports industry in recent years, with numerous aspects fuelling changes to consumer behaviour and resulting in changes in fan and participant engagement. One significant change facilitator in the sports industry has been digitisation. The increase in the use and popularity of digital technologies has enabled fans to watch matches and recaps on their computers, phone, and tablets, enhancing the accessibility and reach of sports (Crawford, 2004). It has led to the growth of fans connecting through online communities and social media platforms. Social media has become a vital tool for sports firms, offering a direct channel to enhance brand loyalty and fan engagement (Crawford, 2004). Sports organisations can now connect with fans directly, share exclusive content, create engaging conversations, and formulate relationships beyond match attendance. Fan experience has also significantly influenced the sports industry, emphasising the need to offer fans memorable experiences crucial to formulating brand loyalty and increasing revenues (Crawford, 2004). Sports firms constantly seek unique ways to create engaging experiences that supersede traditional sports events, focusing on formulating experiences that can be shared on social media to attract digitally savvy and younger fans. The growth of health and wellness activities has impacted sports because people understand their benefits in improving health (Crawford, 2004). It has resulted in the growth of sports activities, such as fitness classes, that have become popular with younger generations. Sports firms are seeking methods to exploit these trends with numerous initiatives and programs that aim to enhance healthy living and physical activities. All these aspects have facilitated fan and participant engagement change in sports. Fans are currently more extensively connected than ever, facilitated by vast information availability. Coincidentally, sports firms have been forced to adapt to these changes by creating unique strategies for fan engagement, resulting in enhanced innovation and creating in areas including fan engagement, fan loyalty initiatives, and content creation.
FPE theories and related consumer behaviour and marketing concepts
Fan participation and engagement (FPE) is an essential marketing and consumer research area, especially for sports organisations and marketers. FPE theories reveal how fans engage and build allegiance to a specific sports brand and how marketers can impact these tendencies through different marketing strategies. The self-determination theory suggests that people have personal preferences for competence, autonomy, and relatedness, which influence their actions (Funk et al., 2016). FPE fans have an excellent relationship with their favourite sports brands because it satisfies their preferences. Marketers can utilise this theory by developing experiences and content that allows fans to have more information about the brand, connect with other supporters, and express themselves.
The theory of planned behaviour also influences FPE because it seeks to explain how supporters create intentions to engage with their preferred sports brand and aspects that impact their actions. Attitudes can impact fans’ intentions to relate to a specific sports brand (Yoshida et al., 2014). For instance, when a fan has a positive attitude towards a sports organisation, the chances of purchasing merchandise and attending matches are high. Cultural norms refer to social pressure to act in a certain way and can influence fan behaviour (Yoshida et al., 2014). For instance, individuals are like to support a certain team if their peers support them. Perceived behavioural control is the ability of an individual to engage in behaviour (Yoshida et al., 2014). In FPE, it is influenced by personal interest, accessibility, and affordability. For instance, if a fan views a team’s merchandise as affordable, the chance of engaging with the brand heightens. Marketers can utilise this behaviour by enhancing the accessibility of their brands through different pricing initiatives and channels.
The psychological continuum model (PMC) is used in FPE to explain how fan and participants can examine their interactions with sports brands based on utilitarian and hedonic motivations. A fan’s affinity to seek pleasure is referred to as hedonic motivation (Funk et al., 2016). For instance, supporters can attend live matches because they enjoy the experience or feel connected to a brand. PCM reveals that hedonic motivations are impacted by sensory stimuli such as the venue’s atmosphere, quality of team performance, and interactions with other supporters. The ethical perception of sports brand fans is called utilitarian motivation (Da Silva & Las Casas, 2017). For instance, supporters may interact with a sports brand because they view it as trustworthy or because they align with personal preferences and values. PCM reveals that these utilitarian motivations are impacted by non-sensory stimuli such as perceived engagement benefits, brand reputation, and marketing messages.
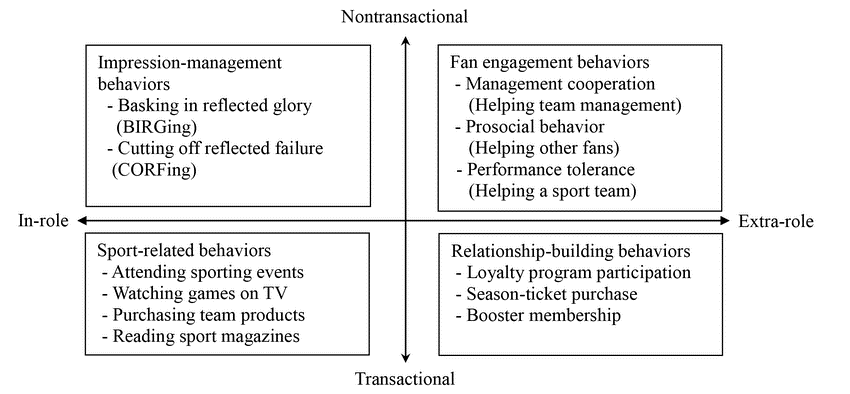
Fig 1: A decision-making process model
These concepts and approaches can boost consumer decision-making if marketers effectively leverage them. (Fig, 1), reveals the consumer decision-making process and the levels consumers pass to make purchasing decisions. The theories can enhance the process because they reveal how customer engagement can be boosted, which is a factor that boosts the sale of merchandise and tickets. It can reveal all purchase problems and allow organisations to make strategies to enhance the process.
Typology of modern sporting organisations and the focus of their engagement activities
In the contemporary world, sports organisations have developed into complex entities whose primary focus is to make the experience of different stakeholders, such as sponsors, fans, and athletes, exceptional. Fan focus is a strategy that prioritises fan engagement to build allegiance (Schmidt & Flegr, 2023). It involves developing an emotional connection with supporters through fan engagement programs, branding, and marketing. Organisations that embrace this strategy prioritise loyalty, retention, and satisfaction over aspects such as revenue generation. Participant focus is a strategy that prioritises athletes engaging and offering them all they require to succeed (Schmidt & Flegr, 2023). It involves creating effective environments to facilitate athlete success and promoting training and development. Organisations that have adopted this strategy prioritise athlete development and performance over other aspects, such as revenue generation and fan engagement. Combined focus is a strategy that combines fan engagement and athlete development and performance (Schmidt & Flegr, 2023). It strives to create mutual relationships between fans and athletes, where fans can have excellent experiences while athletes have adequate resources to enhance their performances. The choice of these strategies depends on an organisation’s values and goals and the sports industry’s structure. An effective strategy can give an organisation positive outcomes because they understand appropriate methods to deal with fans and athletes, leading to increased loyalty, revenue, and engagement.
Football organisations should adopt the fan-focus strategy because it guarantees growth and success. Fan engagement would allow sports organisations to have a loyal fan base to support the team regardless of the situation (Biscaia, 2021). It leads to enhanced revenue generation through sponsorship deals, ticket sales, and merchandise. The International Olympic Committee should adopt a participant focus strategy to promote athlete development can assist athletes in fulfilling their potential. It can result in improved performances, creating more competitive and exciting events for spectators to enjoy (Schmidt & Flegr, 2023). The NBA should adopt a combined focus to enhance performance and build a strong fan base. The NBA does not have numerous compared to other popular sports such as football and athletics, meaning a combined focus can increase interest in the sport (Schmidt & Flegr, 2023). The organisations will benefit from the strategies because they will allow them to thrive in areas they have failed.
The theory of planned behaviour can be effective in the fan focus segment because it will focus on fan satisfaction. The theory will allow organisations to study fan behaviour and understand effective methods that can make them engage with the brand (Biscaia, 2021). They can enhance venue experiences and place the merchandise where it can be easily accessible. The personal investment theory (PIT) is an approach that reveals how individuals invest and are committed to certain groups or activities. It will allow the organisation to boost athlete performance because they will have invested time, effort, and resources into the process (Da Silva & Las Casas, 2017). Continued investment can allow sports organisations to be engrossed in development and performance, motivating them to enhance their involvement. The psychological continuum model can support the combined focus strategy because it showcases how fans and participants examine their experiences with sports brands. It can allow organisations to understand the motivations that make fans and participants engaged in a sport (Funk et al., 2016). Organisations can then create effective strategies that can allow them to boost fan and participant engagement, increasing revenues and fan loyalty.
Sports organisation for Fan, Participant, and Combined Segments and FPE Strategy the use
National Football League (NFL)
The development of American football is based on a fan-focused strategy because they constantly aim to boost stadium attendance and game viewership. The organisation uses the theory of planned behaviour to understand how fans initiate decisions about interacting with the league and its sports organisations. The NFL has used the theory to identify aspects that can promote fan engagement. For instance, by understanding how fans perception of the leagues through perceived behavioural control and subjective norms, which are important aspects of fan engagement, the organisation has created strategies to increase them. The firm has utilised marketing campaigns such as “Football is Family” to showcase the positive impact of football on communities and change attitudes about the sport (Vincent & Kian, 2014). They have used subjective norms by promoting football as a social activity by stressing the importance of supporting a team and being part of a community. The NFL has also used the theory to enhance perceived behavioural control by enhancing fans’ experiences.
Amateur Athletic Union (AAU)
The Amateur Athletic Union (AAU) is a non-profit sports organisation in the US whose primary goal is developing and promoting amateur sports initiatives. The AAU uses the participant focus strategy to provide young and amateur athletes with opportunities to participate in different sports. The organisation utilised the self-determination theory by offering athletes opportunities for autonomy. The firm enables athletes to select their preferred sports and encourages them to decide about competition schedules and training (Calvin, Abiodun & Marvin, 2019). AAU also focuses on enhancing athletes’ competence by offering exceptional training facilities and coaching. Offering expert support to athletes enables them to develop their skills and confidence. AAU enhances a sense of relatedness among athletes by enhancing social connections and teamwork. The organisation encourages athletes to collaborate and form relationships, creating a community that allows athletes to feel more connected and motivated to perform at top levels.
Major League Baseball (MLB)
Major League Baseball (MLB) is among the US’s most popular and competitive professional sports leagues. The organisation uses the combined strategy because it aims to attract both fans and participants to the game. Although the sport is popular in the US, it has failed to make inroads internationally (Mathew, 2016). MLB utilises the psychological continuum model to build allegiance to the sport. The organisation ensures that people know their teams and games through marketing activities such as online and television advertisements. MLB strives to understand where fans and participants fall in the continuum to allow them to formulate communication initiatives that satisfy their needs. It allows them to build allegiance where they can be sure that fans and participants are engaged and create strategies that boost revenue generation.
FPE strategy to help the commercial organisation grow
The commercial organisation utilised a combined focus to boost fan and participant engagement to boost the sport’s popularity and increase revenues. The MLB can have more active participants if they focus on enhancing their fan base in other areas globally. The sport is only popular in the US, meaning they only depend on fans from the country. It means the teams may have supporters but not the amount to boost their profitability. To ensure that the organisation boosts its popularity, they can use the theory of planned behaviour to understand how fans make decisions about engaging with teams. The organisation should use interactive social media campaigns to enhance the popularity of sports by changing consumer attitudes about the sport (Yoshida et al., 2015). The campaign will target citizens from other countries, especially in Asia and Africa, where sports knowledge is deficient. The campaign’s focus will be to showcase memorable moments in the game and showcase the venue to capture audiences’ attention. It will also provide them with avenues where they can watch live matches, provide information about stadium visits, and organise events to promote the sport in the locations of target audiences (Su et al., 2021). Evaluation of fans and participants will be conducted by identifying foreign players in the league, merchandise sales, and viewership of live games. An increase in these elements will reveal increased active participants, which means the combined focus strategy is enhanced.
Conclusion
The outcomes of FPE in modern sports reveal that it is a crucial element of the sports industry that can influence revenue generation, fan loyalty, and team performance. The analysis reveals that FPE can be elevated through various strategies such as marketing campaigns, digital events, and fan events. FPE is vital for the success of modern sports organisations. Fan engagement makes people more likely to purchase merchandise, attend matches, and support teams regardless of performance. Conversely, the lack of fan engagement results in reduced revenue, decreased game attendance, and lost fan allegiance.
Additionally, FPE can enhance the performance of a team. The team engaged with fans can have advantages when playing at home because the support of home fans will be immense. Fan support creates an environment that can motivate players to register excellent performances. According to the findings, sports organisations should invest in strategies that enhance FPE. It includes formulating engaging stadium experiences, investing in digital media, and promoting events that could enhance fan participation in the sport. Sports organisations should also create fan engagement and feedback opportunities such as interactive fan experiences or fan surveys. Generally, FPE is an essential element of modern sports that sports organisations should adopt. By investing in techniques that enhance fan engagement, sports firms can formulate positive fan experiences and enhance fan loyalty, impacting team performance and revenue generation.
References
Biscaia, R. (2021). Fan engagement: Can fans influence the strategy of sports organisations? – Johan Cruyff Institute. Johan Cruyff Institute. https://johancruyffinstitute.com/en/blog-en/sport-marketing/fan-engagement-fans-influence-sports-organizations/
Calvin, N., Abiodun, I., & Marvin, W. (2019). The evolving institutional work of the National Collegiate Athletic Association to maintain dominance in a fragmented field. Sport Management Review, 22(3), 379–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smr.2018.05.002
Crawford, G. (2004). Consuming Sport: Fans, Sport and Culture. In Google Books. Routledge.
Da Silva, E. C., & Las Casas, A. L. (2017). Sports Fans as Consumers: An Approach To Sports Marketing. British Journal of Marketing Studies, 5(4), 36–48.
Mathew, R. (2016). Customer Relationship Management and Fan Engagement Analytics. In Sports Business Analytics. Auerbach Publications.
Schmidt, S. L., & Flegr, S. (2023). Lessons on Customer Engagement from Fan Controlled Football. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2023/03/lessons-on-customer-engagement-from-fan-controlled-football
Su, Y., Du, J., Biscaia, R., & Inoue, Y. (2021). We are in this together: sports brand involvement and fans’ well-being. European Sport Management Quarterly, 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/16184742.2021.1978519
Vincent, J., & Kian, E. M. (2014). Sport, New Media, and National Identity. Routledge Handbook of Sport and New Media, 225–236. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Vince-Benigni/publication/327285064_The_New_Game_Day_Fan_Engagement_and_the_Marriage_of_Mediated_and_Mobile_Benigni_VL_Porter_LV_Wood_JC_Handbook_of_Sport_and_New_Media_2nd_ed_Billings_A_Hardin_M_eds_Routledge_2014_2016/links/5bb2a05045851574f7f43184/The-New-Game-Day-Fan-Engagement-and-the-Marriage-of-Mediated-and-Mobile-Benigni-VL-Porter-LV-Wood-JC-Handbook-of-Sport-and-New-Media-2nd-ed-Billings-A-Hardin-M-eds-Routledge-2014-2016.pdf
Yoshida, M., Gordon, B. S., Heere, B., & James, J. D. (2015). Fan Community Identification: An Empirical Examination of Its Outcomes in Japanese Professional Sport. Kuscholarworks.ku.edu. https://kuscholarworks.ku.edu/handle/1808/22131
Yoshida, M., Gordon, B., Nakazawa, M., & Biscaia, R. (2014). Conceptualisation and Measurement of Fan Engagement: Empirical Evidence From a Professional Sport Context. Journal of Sport Management, 28(4), 399–417. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsm.2013-0199
 write
write