The international sports governing bodies are diversified depending on the specific sporting activities they control nationally, internationally or globally. The Basic Indicators for Better Governance (BIBGIS) framework is applied to ensure proper governance of these organizations. This framework directly relates to the International Basketball Federation’s performance and governance. The score of every indicator significantly indicates the state of governance in every governing body. These indicators include organizational transparency, sports integrity, reporting transparency, stakeholders’ representation, solidarity, control mechanisms, and democratic process. All these indicators are used to rank the governance performance of the FIBA. This report emphasizes vital indicators, i.e., the control mechanisms and their effects on the International Basketball Federation’s governance. In control mechanisms, aspects of behaviours, social mechanisms, and organizational output in terms of the progress in its operations are essential. Social factors manage the relationship between the key stakeholders and the managers of the International Basketball Federation. They are focusing more on the solutions to challenges hindering the application of various control mechanisms as a tool for governance.
This report emphasizes the dimension of studying control mechanisms as a primary indicator of the BIBGIS framework. Control mechanisms, management strategies, and critical programs are set by the executives internally and outside the governing body to achieve the objectives through proper governance. The mechanisms include management composition, executive election procedures, financial budgeting and planning control, compliance with the laws and other control mechanisms for resources. All these mechanisms must be implemented to ensure good decision-making in the governance of basketball sporting activities. To ensure the successful implementation of the control mechanisms, the International Basketball Federation experiences various challenges in the process. According to Stephanos et al. (2021, p.6), Inadequate financing base and limitations of activities, legal and political barriers between member nations, and cultural differences are serious challenges affecting governance as far as control mechanisms are concerned. Management requires skilled personnel, and the acquisition of human resources from international teams becomes challenging as the body’s purpose is to achieve proper governance. The human resources needed to control the activities and the plans include all main stakeholders of the International Basketball Federation.
Gulak (2020, p.3592) states in his study that despite the challenges hindering the implementation of control mechanisms as an indicator for better governance of the International Basketball Federation, there are various mitigations and solutions. To solve the funding control measures, the federation can collect funds from sporting activities in foreign countries and, for example, get international sponsorship and company engagements through sports promotions. In ensuring a favourable political, social and cultural environment for easy management and controlling governance, the International Basketball Federation uses basketball-organized championships to develop reasonable measures. Gulak (2020, p.3592) emphasizes the use of technology and social media platforms to popularize changes and the management criteria the FIBA sets to minimize opposition from member countries when implementing control mechanisms like policies. This also makes it easy for critical stakeholders, managers, and players to collaborate and contribute to the management.
To ensure it efficiently recruits skilled human resources internationally, the federation engages member countries in developing uniform laws governing hiring qualified personnel across the board. This will ensure the team gets experts in the governance of its activities and achieving its objective. The inclusion of stakeholders in decision-making, making laws and planning enhances accountability and transparency for easy control of basketball activities (Rusell et al., 2021, p.81). There is a significant need for the International Basketball Federation to set up an integrity team that ensures cases of bribery within the management are dealt with and charges made to the individuals held accountable. It is important to note that every control mechanism significantly impacts the general governance level, and therefore, ethical values help in achieving these management goals. These measures are vital in ensuring the progress of any sports governing body, not only the International Basketball Federation. (Husari et, al.2021, p.)
Having done the assessment touching on the challenges and solutions to control mechanisms application for the FIBA, the following are the key recommendations to consider: The statutes and governing principles should be made clear and accessible to all key stakeholders of the FIBA by distributing a well-documented set of laws in articles and other accessible soft books. All stakeholders, managers, and the public should be engaged before making sensitive decisions governing FIBA. This will be easy to execute by giving prior public notifications to member nations for proper participation. Executive members should be appointed with clear procedures that consider the interests of the whole organization regardless of nationality. Through delegate election systems composed of all stakeholders of the FIBA, they are ensuring inclusion.
In conclusion, this report supports with evidence from research done by other authors that international sports governing bodies require proper control mechanisms discussed above to ensure easy management. Governance is achieved when all management aspects are applied successfully, and the control measures are well implemented.
References
Durán, G., Guajardo, M. and Gutiérrez, F., 2021. Efficient referee assignment in Argentinean professional basketball leagues using operations research methods. Annals of Operations Research, pp.1-19.
Gulak-Lipka, P., 2020. Internationalization and managing diversity based on professional basketball clubs. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 20(6), pp.3591-3598.
Muniz, M. and Flamand, T., 2023. Sports analytics for balanced team-building decisions. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 74(8), pp.1892-1909.
Russell, J.L., McLean, B.D., Impellizzeri, F.M., Strack, D.S. and Coutts, A.J., 2021. Measuring physical demands in basketball: an explorative systematic review of practices. Sports Medicine, 51, pp.81-112
Stephanos, D.K., Husari, G., Bennett, B.T. and Stephanos, E., 2021, April. Machine learning predictive analytics for player movement prediction in NBA: applications, opportunities, and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Southeast Conference (pp. 2-8).
Appendix.
Appendix A. The BIBGIS framework diagram showing the scores of each indicator comparing two different years……………………………………….5
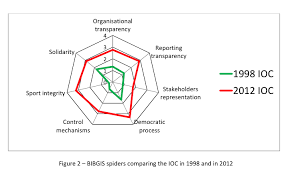
Appendix B. The table showing a summary of the score results for the seven dimensions of governance for the IOC (illustration using the year 2012 scores) …………………………………….5
| SCORES | DESCRIPTION | DIMENSION/ INDICATOR |
| 0 | The indicator is not fulfilled at all | None |
| 1 | Indicator partially fulfilled | None |
| 2 | Indicator fulfilled | Stakeholders’ representation |
| 3 | Indicator well fulfilled | Sports integrity, reporting and organizational transparency, control mechanisms, solidarity |
| 4 | The indicator is fulfilled in a state-of-the-art way | Democratic process |
 write
write