Introduction
More often than not, a skilled and competent dribbler draws the spectators’ attention in soccer. As a result, such players win the hearts of their fans, as illustrated by legends such as Lionel Messi, who is widely regarded as the king of dribbling in football (Brach, p. 415). On the same note, Messi also contends for the greatest football players. Messi is scientifically destined to dominate the dribbling aspect of football. The popularity of dribblers arises from their willingness to engage in risks that lead to goal-scoring opportunities (Anderson et al., p. 92). Dribbling refers to the players’ ability to maneuver the ball through the defending opponents and goalkeeper, as demonstrated by strikers during football matches. It entails the players’ control of the ball to ensure it does not land in the hands of the opposing team.
Soccer is considered open for smaller players, as illustrated by the previous World Cup, which earned the title “Little guys enjoying the last laugh” (Khazan ). Notably, the small-statured players would not experience similar favorable outcomes in other sports, such as basketball and American football. FC Barcelona, one of the best clubs, registered the shortest players since the team’s average height is five foot nine. Moreover, even the most picked players were shorter than their teammates. The celebrated football players are quite compact, for example, Xavi Hernandez, the Spaniard player who has won the most trophies in the sport. Moreover, the celebrated Brazilian Pele was only five foot eight tall, while Diego Maradona was five foot five (Brach, p. 417). The rise of the little stars in soccer is due to their closeness to the ground, which poses a major advantage for the forwards and midfielders.
On the same note, shorter people have quicker stepping patterns, can change directions at a much faster rate, and are more effective in controlling their limbs. This makes them elusive for the defenders, as illustrated by Maradona’s famous goal in 1986 (Khazan ). Moreover, Messi was awarded the four Golden Ball player of the year. Just like Maradona, Messi cruises through the tiny creases of defenders while his low center of gravity facilitates lightning quick pivots, transforming him into the globe’s fastest dribbler. Thus, this study seeks to determine how a player’s height and weight influences their dribbling ability. Notably, short people have a lesser weight since they have a lower body mass.
What does research indicate?
In determining the role of a player’s weight and height in football, it is essential to factor in the nature vs. nurture debate since some players are naturally talented, for example Messi, while others have been nurtured to become elite footballers, for instance Christiane Ronaldo (Mooney, p. 15). Research performed by the School of Human Sciences at Liverpool John Moores University reports that unorthodox motion strategies, for example, running sideways and backward, decelerating, accelerating, and changing direction, heighten metabolic loading, hence impacting the player’s dribbling capacity.
Studies indicate that weight and height play a crucial role in a player’s dribbling ability since they impact the player’s agility in the field. FIFA 23 computes and assigns the Accelerate archetypes, which are dependent on a player’s height, strength and agility. Notably, a player’s strength and speed is dependent on their weight and height. These attributes determine a player’s strength and speed on the field. The fifa gamers reports that best players weigh between 68.03 and 86 kilogram and fall in the height category of 1.68 meters to 1.83 meters (Shoup). For this reason, the gaming application recommends these attributes in building a competent striker in the games.
A shorter person is likely to have a higher leg velocity when investing similar energy in moving a ball small leg in comparison to a big leg resulting in high leg velocity for the short person (Shan). Notably, footballers that have a shorter running stride and whose center of gravity is lower have the capacity of decelerating quickie while expecting changes in motion. On the same note, they have high accelerating capacity, hence, their impeccable dribbling skill. While Ronaldo is a gifted sprinter, he has had to lower his center of gravity and adopts shorter running stride to enable faster deceleration accompanied by effective anticipation of changes in motion. Ronaldo has a height of 1.87 meters and weighs 83 kilogram, hence his height forces him to adopt his running stride. on the same note, Ronaldo has favorable weight compared to his height hence his outstanding sprinting peed in the field. On the other hand, Messi is blessed with natural agility and lower center of gravity, hence his remarkable dribbling skill.
Research question
In the age of advanced sports science, players have the opportunity to transform into more agile versions of themselves in enhancing their efficacy in the field. Football is a highly competitive sport, hence the need for identifying areas of improvement in enhancing the players’ performance in the field. For instance, this development is illustrated by players such as Gareth Bale’s and David De Gea’s physical transformation by enhancing their muscular mass, which resulted in improved performance in the field. Moreover, the talent managers and football academy can use height and weight information to leverage the players’ talents. Besides, dribbling ability is considered a lethal aspect in creating goal scoring opportunities. For this reason, I seek to determine the effect of a player’s height and weight on their dribbling ability.
The primary research question of this study is to determine if the height and weight of a professional football player jointly and individually influence their dribbling ability. The variables under study will be the height, weight, and dribbling ability of a professional football player
Hypothesis
Developing a hypothesis underlies reliable research through issuing clear focus and direction of the research while facilitating clear communication of the assumptions and expectations to the audience. Since this study analyzes the variables under study both individually and jointly, there will be three hypotheses as follows:
Hypothesis one
H0: The height of a football player is insignificantly related to their dribbling ability
H1: The height of a football player is significantly related to their dribbling ability
Hypothesis two
H0: The weight of a football player is insignificantly related to their dribbling ability
H1: The weight of a football player is significantly related to their dribbling ability
Hypothesis three
H0: The height and weight of a football player joint has an insignificant effect to their dribbling ability.
H1: The height and weight of a football player joint has a significant effect to their dribbling ability.
Data Collection
This research utilizes secondary data, whereby the dribbling rating was collected from FIFA.com. The launch of every FIFA game is accompanied by EA Sports’ release of the top 100 ratings for best professional football players and a complete database of ratings for each player from the licensed leagues. The EA Sports deploys a team comprising 25 EA producers and 400 data contributor led by Muller-Moehring that ensures that players’ database is updated. Also, EA collects data from 6000 FIFA Data reviewers across the globe, hence illustrating the precision of data utilized for this study. The players’ height and weight data was collected from Stars unfolded website that lists the physical attributes of the professional players. This study employed secondary data because collecting primary data is unfeasible due to the hefty demand for time and financial resources required in the process. On the same note, the data collected from the sites mentioned above is the most precise that would be obtained in sports statistics. The data collected was based on the three variables, whereby the height and weight comprised the independent variables while the dribbling ability is the dependent variable. Whereby the dribbling ability corresponds with the players’ height and weight. The sample, was relatively large, thus it was considered representative. Important to note, multiple factors impact a player’s dribbling ability, specifically, their age, fitness, and skill level. Footballers’ competency in the field declines with their age. In controlling these factors, this study selected professional players in their prime, whereby they were within the eligible age and at their peak in terms of physical fitness and skill level in the sport.
(https://www.fifacm.com/players)
(https://starsunfolded.com/category/sports/)
Raw Data: FIFA dribbling ability rating, height and weight.
| Players | FIFA Rating | Height(M) | Weight(kg) |
| Lionel Messi | 94 | 1.7 | 72 |
| Neymar | 93 | 1.75 | 68 |
| Eden Hazard | 92 | 1.75 | 74 |
| Luis Diaz | 89 | 1.78 | 65 |
| Allan Saint-Maximin | 92 | 1.73 | 67 |
| Kylian Mbappe | 91 | 1.78 | 75 |
| Sergio Aguero | 86 | 1.73 | 77 |
| Leroy Sane | 87 | 1.83 | 80 |
| Paulo Dybala | 90 | 1.77 | 75 |
| Jadon Sancho | 91 | 1.8 | 76 |
| Ousmane Dembele | 89 | 1.78 | 67 |
| Luis Muriel | 88 | 1.8 | 79 |
| David Silva | 85 | 1.7 | 67 |
| Philippe Coutinho | 80 | 1.72 | 68 |
| Josip Ilicic | 86 | 1.9 | 79 |
| Jesus Corona | 85 | 1.73 | 62 |
| Felipe Anderson | 85 | 1.75 | 70 |
| Adama Traore | 76 | 1.78 | 86 |
| Yacine Brahimi | 93 | 1.75 | 66 |
| Jeremie Boga | 84 | 1.72 | 68 |
| Franck Ribery | 76 | 1.75 | 66 |
| Franco Vazquez | 81 | 1.87 | 80 |
| Moussa Dembele | 73 | 1.85 | 88 |
| Ricardo Quaresma | 85 | 1.75 | 74 |
| Marcos Lliuya | 73 | 1.68 | 73 |
| Phakamani Mahlambi | 74 | 1.73 | 67 |
| Mark Mayambela | 75 | 1.87 | 83 |
| Mohamed Salah | 88 | 1.75 | 73 |
| Luka Modric | 84 | 1.72 | 66 |
| Bernardo Silva | 92 | 1.73 | 64 |
| Jack Grealish | 89 | 1.75 | 76 |
| Thiago | 90 | 1.74 | 71 |
| Yannick Carrasco | 86 | 1.81 | 71 |
| Juan Cuadrado | 90 | 1.76 | 72 |
| Joao Felix | 86 | 1.81 | 70 |
| Riyad Mahrez | 91 | 1.79 | 67 |
| Alejandro Gomez | 85 | 1.67 | 68 |
| Vinicius Junior | 92 | 1.76 | 73 |
| Kingsley Coman | 88 | 1.81 | 76 |
| Pedri | 87 | 1.74 | 60 |
| Rodrigo De Paul | 82 | 1.8 | 70 |
| Mateo Kovacic | 89 | 1.77 | 77 |
| Joaquin Correa | 88 | 1.89 | 77 |
| Dani Olmo | 87 | 1.79 | 72 |
| Rafael Leao | 89 | 1.89 | 81 |
| Andre-Frank Zambo Anguissa | 84 | 1.84 | 78 |
| Adam Lallana | 77 | 1.72 | 73 |
| Jamal Musiala | 94 | 1.84 | 72 |
| David Neres | 86 | 1.75 | 66 |
| Nicolas Pepe | 85 | 1.83 | 73 |
Mathematical Computations
This section entails the mathematical processes, specifically, descriptive statistical measures, correlation analysis and regression analysis
Descriptive Statistics
In this section, I created a statistics table based on the variables computed from measures of central tendency, dispersion and variation as displayed below. I computed measures of central tendency, dispersion and variation as displayed below. I computed the average for the dribbling rating, height, and weight which I fund to be 86.04 attribute, 1.7742 meters and 72.36 kilograms. The standard error was 0.791774035, 0.007783237 and 0.84937432 for the dribbling rating m, height and weight respectively. The median for the dribbling rating, height and weight were 87, 1.76 and 72 kilogram respectively. The mode for the dribbling rating, height and weight were 85, 1.75 meters and 67 kilogram respectively. This implies that most of the competent dribblers are 1.75 meters tall and weigh 67 kilogram. The standard deviation illustrates the deviation of each observation from the mean value. The standard deviations for the player’s dribbling ability, height and weight were 5.598687893, 0.055035795 and 6.005983411 respectively. Skewness illustrates the distribution of observations around the mean. The skewness for the player’s dribbling ability, height and weight were -0.907348059, 0.553362207 and 0.412395012 respectively. I also computed the range, which is the difference between the maximum and minimum value in a data set. The range for three variables was 21, 0.23 and 28 respectively
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics
| FIFA Dribbling Rating | Height(M) | Weight(kg) | |||
| Mean | 86.04 | Mean | 1.7742 | Mean | 72.36 |
| Standard Error | 0.791774 | Standard Error | 0.007783 | Standard Error | 0.849374 |
| Median | 87 | Median | 1.76 | Median | 72 |
| Mode | 85 | Mode | 1.75 | Mode | 67 |
| Standard Deviation | 5.598688 | Standard Deviation | 0.055036 | Standard Deviation | 6.005983 |
| Sample Variance | 31.34531 | Sample Variance | 0.003029 | Sample Variance | 36.07184 |
| Kurtosis | 0.18255 | Kurtosis | -0.19676 | Kurtosis | 0.024431 |
| Skewness | -0.90735 | Skewness | 0.553362 | Skewness | 0.412395 |
| Range | 21 | Range | 0.23 | Range | 28 |
| Minimum | 73 | Minimum | 1.67 | Minimum | 60 |
| Maximum | 94 | Maximum | 1.9 | Maximum | 88 |
| Sum | 4302 | Sum | 88.71 | Sum | 3618 |
| Count | 50 | Count | 50 | Count | 50 |
Histograms
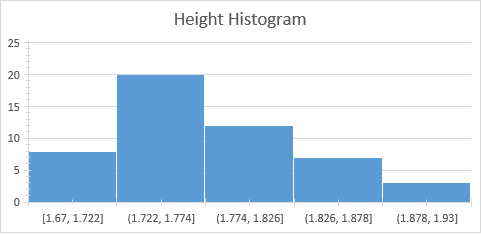
The histogram above depicts the median height and mode, which are 1.76 and 1.75, respectively. Thus, most of the professional dribbler’s height is between 1.722 and 1.826, as is the concentration of players in this height category. Players with the height 1.86 -1, 93 meters may be considered outliers (Nikolaidis, p. 42).
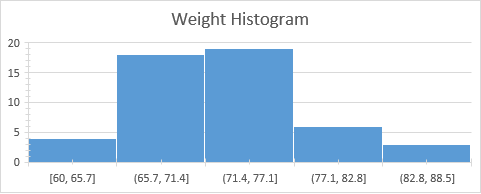
The histogram shows that most players are concentrated on the mean weight, which is 72.36 kg. Most of the players weigh between 65.7 kg and 82.8 kg, which corresponds with the mode that was computed to be 67 kg and the median, 72 kg
Inferential Statistics
This study also involves inferential statistics, which encompasses the correlation analysis in ensuring the research question is sufficiently addressed. The inferential statistics plotted two scatter plots to determine how a player’s height and weight impact their dribbling ability. I also incorporated the equation in the scatter plot in indicating the relationship between the variables under study. I also computed the Pearson’s correlation coefficient, which facilitated the validation of the hypothesis developed for the study.
Scatter plot
Figure 1: Scatter plot of Height and Dribbling
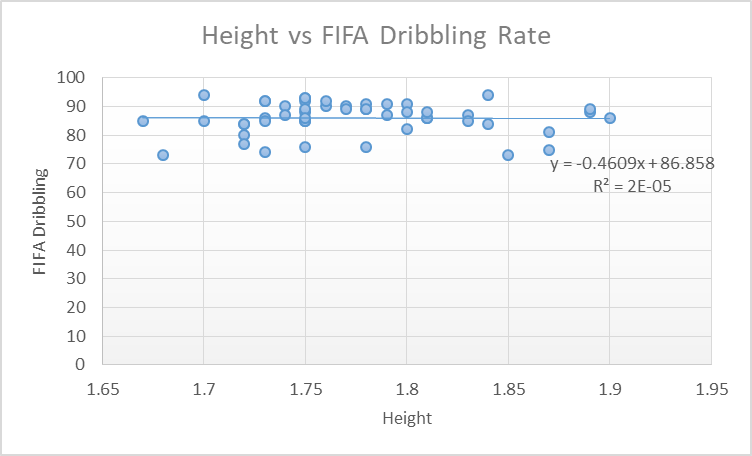
The scatter plot depicts a linear relationship between the player’s height and their FIFA dribbling ability. The nature of the relationship is negative, hence indicating that if the height of a player increases, their dribbling ability reduces. Thus, the player’s dribbling ability is dependent on their height (Chambers, p. 97). The equation of the regression line is as follows:
y= -0.4609x + 86.858
Y (FIFA dribbling ability) = -0.4609(height) + 86.858
The equation depicts a negative linear relationship between a player’s height and their dribbling ability. If the player’s height is zero, their dribbling ability is 86.858. Moreover, if the player’s height increases by one unit, their dribbling ability reduces by 0.4609. Thus, a player’s height negatively impacts their dribbling ability, hence a negative relationship between the two variables (Chambers, p. 98).
Figure 2: Scatter plot of Weight and Dribbling
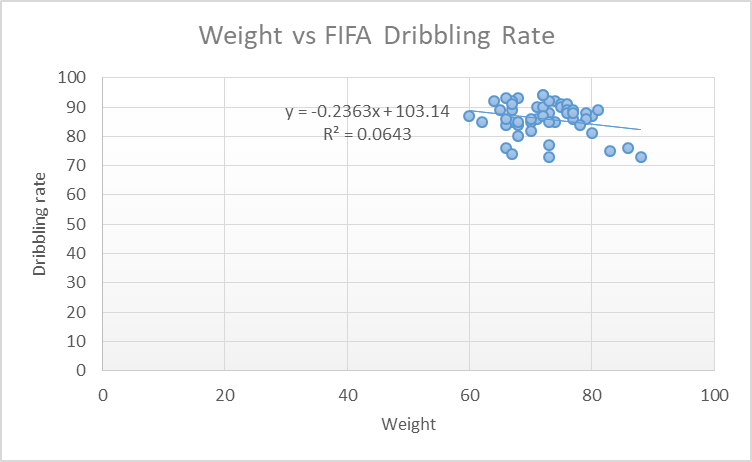
The scatter plot depicts a linear relationship between the player’s weight and dribbling ability. Thus, the footballer’s weight is linearly related to their dribbling ability. Besides, the equation depicts a negative relationship; thus, an increase in the player’s weight negatively affects their dribbling ability. Therefore, if the footballer’s weight increases, their dribbling ability reduces. The line of best fit is captured in the following equation
y = -0.2362x +103.4
Y (dribbling ability) = -0.2362 (weight) +103.4
The equation above implies that when a player’s weight is zero, their dribbling ability decreases by 0.2362. Also, if the player’s weight increase by one unit, the player’s dribbling ability reduces by 0.2362. From the equation, the player’s weight negatively impacts their dribbling ability. From the equation, the player’s weight is negatively linearly related to their dribbling ability
Correlation Coefficient and Hypothesis Validation
I computed the correlation coefficient in evaluating the hypothesis developed for the study.
Table 2: Correlation between Height and Dribbling
| Correlations | |||
| FIFA Dribbling Rating | Height(M) | ||
| FIFA Dribbling Rating | Pearson Correlation | 1 | -0.005 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.975 | ||
| N | 50 | 50 | |
| Height(M) | Pearson Correlation | -0.005 | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.975 | ||
| N | 50 | 50 | |
The correlation coefficient is -0.005, which is close to zero. This means that there is no effect of a player’s height on their dribbling ability. Thus, a player’s dribbling attribute is not related to their height. Thus, a short player is likely to almost similar dribbling skills compared to a taller player. Thus, a shorter player has not advantage over a tall player in terms of dribbling competently in a match. Nonetheless, based on the p-values, we can observe that is 0.975, which is bigger than the stated significance level, which is 5% i.e., 0.05 (Kanchan, p. 241). In comparing the two values, the p-value is greater than the significance level, i.e., 0.975> 0.05. Thus, we can conclude that there is no sufficient evidence to support the null hypothesis. Thus, we deduce that a player’s height is insignificantly related to their dribbling ability. Despite the slight negative association shown in the scatter plot between a player’s height and their dribbling ability, the relationship is insignificant at a 5% significance level. Thus, a player’s dribbling attribute is not dependent on their height.
Weight
Table 3: Correlation between Weight and Dribbling
| Correlations | |||
| FIFA Dribbling Rating | Weight(kg) | ||
| FIFA Dribbling Rating | Pearson Correlation | 1 | -0.254 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.016 | ||
| N | 50 | 50 | |
| Weight(kg) | Pearson Correlation | -0.254 | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.016 | ||
| N | 50 | 50 | |
The correlation coefficient is -0.254, implying a weak negative relationship between a player’s weight and dribbling ability. This means that a player’s dribbling ability is negatively affected by a player’s weight. Hence, a lighter player will likely depict better dribbling ability than a heavier player. Thus, a shorter player has more advantage in dribbling in a football match. There is a need to determine if the correlation coefficient is as significant as the stated significance level. From the table below, the p-value of the correlation coefficient is 0.016, while the indicated significance level is 5%, 0.05 (Kanchan, p. 241). In comparing the two, the p-value is lower than the significance level, i.e., 0,016<0.05. Hence, at α=5%, we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis and deduce that the football player’s weight is significantly related to their weight. Thus, the relationship between a player’s weight and dribbling attribute is valid. We hence deduce that a player’s dribbling attribute is dependent on a player’s weight
Regression Analysis
The regression analysis was done to determine if weight and height affects the dribbling ability jointly
Table 4: Regression Analysis
| Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | P-value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | Lower 95.0% | Upper 95.0% | ||
| Intercept | 70.1844 | 26.0430 | 2.6949 | 0.0097 | 17.7927 | 122.5761 | 17.7927 | 122.5761 | |
| Height(M) | 24.0207 | 17.7111 | 1.3563 | 0.1815 | -11.6095 | 59.6509 | -11.6095 | 59.6509 | |
| Weight(kg) | -0.3698 | 0.1623 | -2.2788 | 0.0273 | -0.6963 | -0.0433 | -0.6963 | -0.0433 | |
Based on the regression table above, we can see that the p-value of height is 0.1815, which is greater than 0.05 (5% significance level), meaning that it has no significant effect on the dribbling ability even when considered jointly with weight. On the other hand, we observe that the p-value of weight is 0.0273, which is less than 0.05, meaning that it has a significant effect on the dribbling ability.
The regression equation is y (dribbling ability) = 24.0207 (height) – 0.3698 (weight) +70.1844
According to the regression equation, when all the factors are held constant, that is, weight and height, the dribbling ability of a player is 70.1844. In terms of height, and holding weight constant, the dribbling ability of a player increases by 24.0207 for every unit increase of height. Conversely, regarding weight and holding height constant, the dribbling ability reduces by 0.3698 for every unit increase.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the average height and weight of the best dribblers are 1.7742 and 72.36 kg, respectively, while their average FIFA dribbling rating is 86.044. I performed statistical processes that revealed that the height of a football player is not significantly related to their dribbling ability. Although the study found a weak negative line r relation between height and dribbling ability, it is insignificant in impacting a player’s dribbling performance in the field. Thus, a player may display outstanding dribbling ability despite their height even though the football world has been dominated by short players winning numerous categories, as discussed in the paper. On the other hand, their weight is significantly related to their dribbling capability since it impacts their speed in maneuvering the ball. For example, Cristiano Ronaldo exhibits outstanding dribbling ability in the field due to maintaining a healthy weight. Thus a player’s dribbling ability is dependent on their weight, hence the need to maintain the ideal bodyweight in ensuring outstanding performance in the field.
Works Cited
Anderson, Christopher J., et al. “Messi, Ronaldo, and the politics of celebrity elections: voting for the best soccer player in the world.” Perspectives on Politics 18.1 (2020): 91-110.
Brach, Bartlomiej. “Who is Lionel Messi? A comparative study of Diego Maradona and Lionel Messi.” International Journal of Cultural Studies 15.4 (2012): 415-428.
Chambers, John M. “Linear models.” Statistical models in S. Routledge, 2017. 95-144.
Kanchan, Tanuj, et al. “Stature estimation from foot dimensions.” Forensic Science International 179.2-3 (2008): 241-e1.
Khazan Olga. “ Why Being Short Can Help in Soccer, 2014. The Atlantic. https://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2014/06/in-soccer-being-short-can-help/372617/. Accesed 29th September 2023.
Mooney, Carla. Ronaldo Vs. Messi Vs. Beckham Vs. Pelé. The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc, 2019.
Nikolaidis, P. T. “Weight status and physical fitness in female soccer players: is there an optimal BMI?.” Sport Sciences for Health 10.1 (2014): 41-48.
Shan, Gongbing. “The Practicality and Effectiveness of Soccer Scoring Techniques Revealed by Top Elite Soccer Scorers.” Physical Activity Review 11.1 (2023).
Shoup, Kate. Lionel Messi: Legendary Soccer Player. Cavendish Square Publishing, LLC, 2019.
 write
write