Abstract
Barclays Bank is one of the public limited companies in the world and is headquartered in London. Despite the stiff competition in the financial market, the company’s performance is pretty good, with relatively good financial ratios. Besides, the company’s diversification and the use of online apps was an ideal move that enabled the company to sail on during the Covid-19 pandemic. Most people adopted cashless transactions and embraced transactions through mobile apps. The company’s resilience indicates that it can extend its investment into new markets. An analysis of Barclays Bank alongside BNP Paribas, one of its competitors, shows that there is stiff competition between the two firms. The ratio method of financial analysis has several limitations. Apart from the historical presentation approach, the ratios do not factor in external factors and forces like a recession. Besides, the method does not measure the human element of the company; hence, they give a false illusion.
Summary of Basic Company Information
Brief History and Industry
Barclays PLC was founded in 1690 in London, and the city remains its headquarters even today (Barclays Bank PLC, 2011). The company operates in the financial niche and was established as a goldsmith lender (Barnes and Newton, 2022). This company operates in two different divisions to enhance its efficiency-Barclays UK and Barclays International. Critical company services include managing wealth, investments, retailing, and commercial banking. According to findings by Haralayya and Aithal (2021), the bank is proud to have more than 83,500 employees who enhance service delivery. Despite forming a partnership between James Barclays and other goldsmiths, it has changed ownership over the years to remain in line with customers’ needs. For instance, the company changed entity in 1981 and became a public limited firm (Vakhrusheva et al., 2021). The ownership type allows members of the public domain to buy shares from the company. Examples of shareholders include Raymond, Cambier Investors LLC, and many others. Barclays PLC generated 5.75 billion sterling pounds as a profit in 2021 (Barnes and Newton (2022), this firm).
Barclays PLC started on a meager scale but gradually grew to become a significant firm in the banking industry. The company has continuously extended branches into many countries while diversifying services into investment, corporate, retail banking, and other financial operations. Today, many countries consider Barclays Bank a firm with a universally acclaimed reputation due to its broad customer base (Mazikana, 2023). This company uses closed-loop feedback in its leadership structure, as illustrated below.
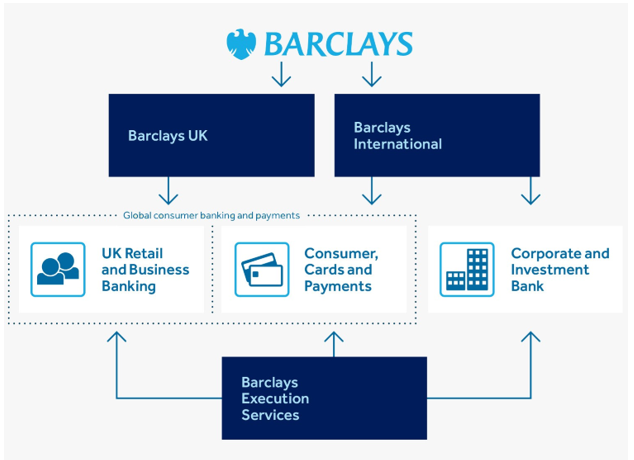
Figure 1: Barclays Business Structure (Ozili, 2022).
The chief operations officer’s and the execution services’ offices virtually coordinate all work. The operations officer receives all information from the management committee. The committee comprises the company CEO, the board chairperson, and the directors. Each level encourages specialization and division of labor. Better services result from the coordination between directors and the executive committee (Bari and Syazwani, 2018). Using closed-loop reporting and a feedback mechanism allows the bank to excel even though it operates in turbulence within the industry. Other companies can achieve effective communication, feedback, and decision-making processes if they adopt the closed-loop organizational structure.
An Exceptional Event
Recently, the worldwide Covid-19 pandemic that struck the world impacted the company’s activities somewhat. When the pandemic hit, governments, through the Ministry of Health, developed mitigation measures to curb the spread of the disease. Among them, social gatherings were banned, and people were to maintain social distancing. Many businesses closed, while others experienced fewer customers on their premises. The banking industry did not have a massive impact because people didn’t need to physically transact in banking halls. Ideally, people changed their lifestyles and particularly how they transacted. Most of them used paperless money because of the Covid-19 protocols. According to the information in the 2020 Barclays financial reports, customers who downloaded mobile apps increased during this period. Besides, there was an increase in customers’ appetite for financial advice. Ideally, the pandemic resulted in significant disruptions in the economy. Barclays Bank’s net profit dropped during the second quarter of 2020 because of the Covid-19 pandemic (Darwish and Bayyoud, 2023). Other financial institutions also faced similar impacts due to changes in lifestyle and business structures.
Barclay’s Competitive Environment and the Main Competitor
The company has several competitors working in the same industry, including the Bank of America, Citigroup, Wells Fargo and Company, and Morgan Stanley (Zaring, 2021). These competitors operate in the same financial market; hence their effect is felt within the same industry. Barclays Bank has the challenge of retaining its dominance over its traditional markets. Despite its ability to meet the present world financial crisis, the firm’s potential to service the market has gone down because of the economic conditions in the market. Barclays’ competitor BNP Paribas, headquartered in San Francisco, is doing better than Barclays Bank (Gruber and Žilinskaite, 2020). Its revenue is $47.4B, and it has employed 193,000 people, much higher than Barclays Bank employees (CADTM, 2016). Barclays PLC must review its internal control systems to enable it to successfully withstand external risks. Besides, Barclays PLC must seek to find new markets since it is only concentrated in the UK, a case limiting its capacity.
Barclays’ interest rates are declining and the firm is experiencing high costs. These are significant strategic challenges facing the company. One strategy to cope with this situation has been the lowering of interest rates while maintaining the net cost structure of the firm. Bank of England has implemented this strategy and experienced a decline in profits. The move shows that most UK financial institutions have challenges balancing risks and corporate governance strategies.
Financial Information
Although the Covid-19 pandemic destroyed the better part of the economy, Barclays PLC was profitable in all quarters in 2020. The company’s CET1 capital ratio rose 50bps within the quarter and 130bps in the entire year hitting 15.1% slightly above the company’s lowest target (Full Year 2020 Results | Barclays). The firm used a diversified business model that delivered a resilient operating model which allowed capital distribution to shareholders to the tune of 5.0p per share. Barclay’s assets in 2020 were $1732.776B, and this value was a 19% increase from the 2019 value (Full Year 2020 Results | Barclays, no date). The assets increased by 9.85% in 2021 and decreased by 1.64% in 2022. The company’s annual revenue was $27 948 but rose to $30.17B in 2021. The annual revenue has been growing since 2020. By 2020, Barclays PLC had about 89,141 employees.
Evaluation of Financial Statements: A Comparative Analysis
Financial ratios
The following table summarizes key financial ratios for Barclays Bank and BNP Pabaris, one of Barclays’ competitors.
| Ratio | Barclays PLC | BNP Paribas |
| Liquidity Ratio | 1.59 | 1.32 |
| Return on Equity | 8.624 | 0.064 |
| Debt Ratio | 7.169 | 21.57 |
| Current Ratio | 0.8511 | 0.77 |
Both companies have very high debt ratios. The ratios are more than 100%, implying that the firms’ debts are much more than their respective assets. The trend is risky for the firms, yet they must work on strategies to reduce their debt ratios. The Return on Equity encompasses the net income divided by shareholders’ equity. It is usually expressed as a percentage. According to Dao and Nguyen (2020), a good ROE must fall between 15% and 20%, yet the ROE values in the table above are lower than the suitable ones. The common ROE values for BNP Pabaris imply that the company is less efficient in generating profit and shareholder returns. The ROE value is higher for Barclays Bank, meaning it is doing reasonably well in profit generation though it is far below the excellent range. The low ROE values could be an indication of poor resource utilization. Resources include human labor. It is worth noting that ROE is a crucial measurement scale that informs how a financial institution is performing. Most banks use the measure to gauge returns the firm makes on the initial capital plowed into the venture. Lower ROE may indicate that the company is not using its resources effectively.
The liquidity ratio for Barclays Bank is 1.59, while that for BNP Paribas is 1.32 (Biondi and Graeff, 2020). Both percentages are more than one implying that both firms can successfully satisfy their current liabilities. The value for Barclays PLC is slightly higher than the corresponding value for BNP Pabaris, and its implication is that Barclays PLC stands a better chance than BNP Pabaris when it comes to the satisfaction of current liabilities. On the other hand, the current ratio depicts the relationship between a firm’s assets and liabilities. Findings have shown Barclay’s PLC to have a current ratio of 0.8511 compared to 0.77 for BNP Pabaris. These ratios imply that Barclays PLC can pay off its liabilities more easily than BNP Pabaris.
Conclusions
Barclays PLC is doing reasonably well as far as the financial market is concerned. It has established itself in many international markets yet placed itself in a position to get better profits than if it remained in the United Kingdom. The company’s financial performance has not been adversely affected despite the environmental challenges and risks, such as the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020. Most financial ratios indicate that Barclays PLC operates averagely because it can pay its liabilities. The findings inform the high potential that Barclays PLC has to invest in new markets. Moreover, the company must harness the technological trends in the present society to reach more customers. For instance, it could modify its online apps to include more customer-friendly functions and experiences. This analysis has several limitations. The ratios are, in most cases, historic. Consequently, it is hard to get current information. Secondly, the investigation did not consider external factors and forces such as a recession. Finally, the approach does not measure the human element of the company; hence, they give a false illusion.
References
All Banks. (2011). Top Ten Banks in the US.
Barnes, V. and Newton, L. (2020) “Women, uniforms and brand identity in Barclays Bank,” Business History, 64(4), pp. 801–830. Available at:
Bari, A. and Syazwani, N.A., 2018. Bank Specific and Macroeconomics Determinants of Profitability in Barclays Bank PLC, United Kingdom.
Biondi, Y. and Graeff, I. (2020) “Between Prudential Regulation and Shareholder Value: An Empirical Perspective on Bank Shareholder Equity (2001-2017),” Accounting, Economics, and Law, 0(0).
CADTM (2016) A journey into the vice-ridden banking world – CADTM.
Darwish, N.A. and Bayyoud, M., 2023. Impact of COVID-19 on UK Banks; How Banks Reshape Consumer Banking Behaviour during Pandemic. COVID, 3(2), pp.131-143.
Dao, B.T. and Nguyen, K.L.P. (2020) “Bank Capital Adequacy Ratio and Bank Performance in Vietnam: A Simultaneous Equations Framework,” Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business, 7(6), pp. 39–46.
Full Year 2020 Results | Barclays (no date). Available at: https://home.barclays/investor-relations/reports-and-events/results/barclays-full-year-2020-results/.
Gruber, M. and Žilinskaite, M. (2020) “The Long and Winding Road to Responsible Global Leadership in the Banking Industry,” Responsible Global Leadership [Preprint].
Haralayya, B. and Aithal, P.S., 2021. Inter-bank analysis of cost efficiency using mean. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering, and Technology (IJIRSET), 10(6), pp.6391-6397.
Mazikana, A.T., 2023. Application of Pestel Factors: A Case of Financial Institutions. Available at SSRN 4380768.
Ozili, P.K., 2022. Bank income smoothing during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from UK Banks. In The New Digital Era: Other Emerging Risks and Opportunities (Vol. 109, pp. 127-139). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Vakhrusheva, M.Y., Khaliev, M.S. and Pokhomchikova, E.O., 2021, October. Barclays’ application of information systems in the manufacturing process. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 2032, No. 1, p. 012129). IOP Publishing.
Zaring, D. (2021) “Enforcement against the Biggest Banks,” Journal of Financial Regulation, 7(1), pp. 1–47.
 write
write